Simple Epithelium Cells
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
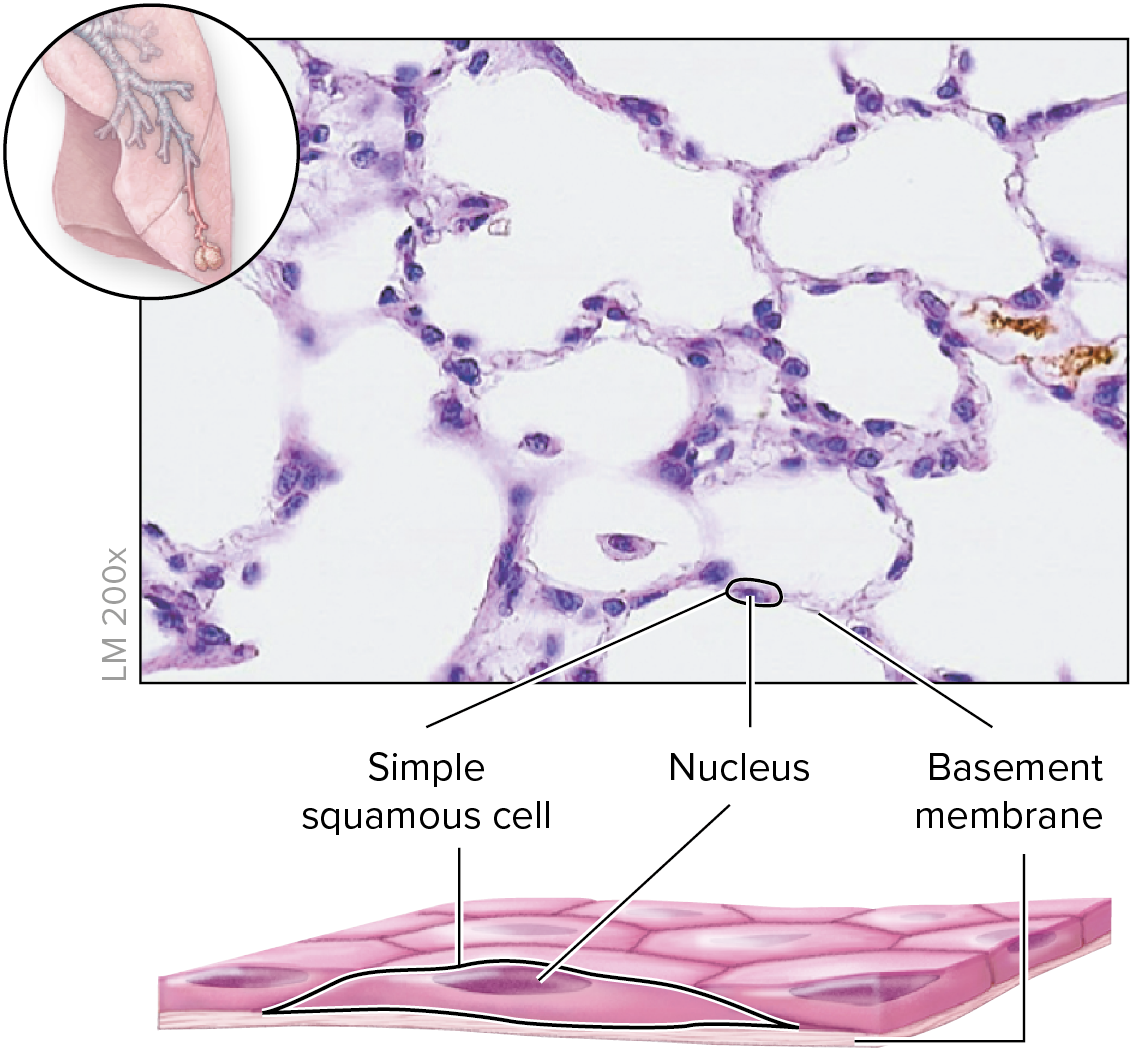
Simple squamous epithelium
Single layer of flat cells
spherical to oval nucleus
thinnest barrier
allows rapid movements of molecules across surface
lines air sacs of lungs (alveoli), vessel walls (endothelium), serous membranes (mesothelium)
Simple Squamous epithelium
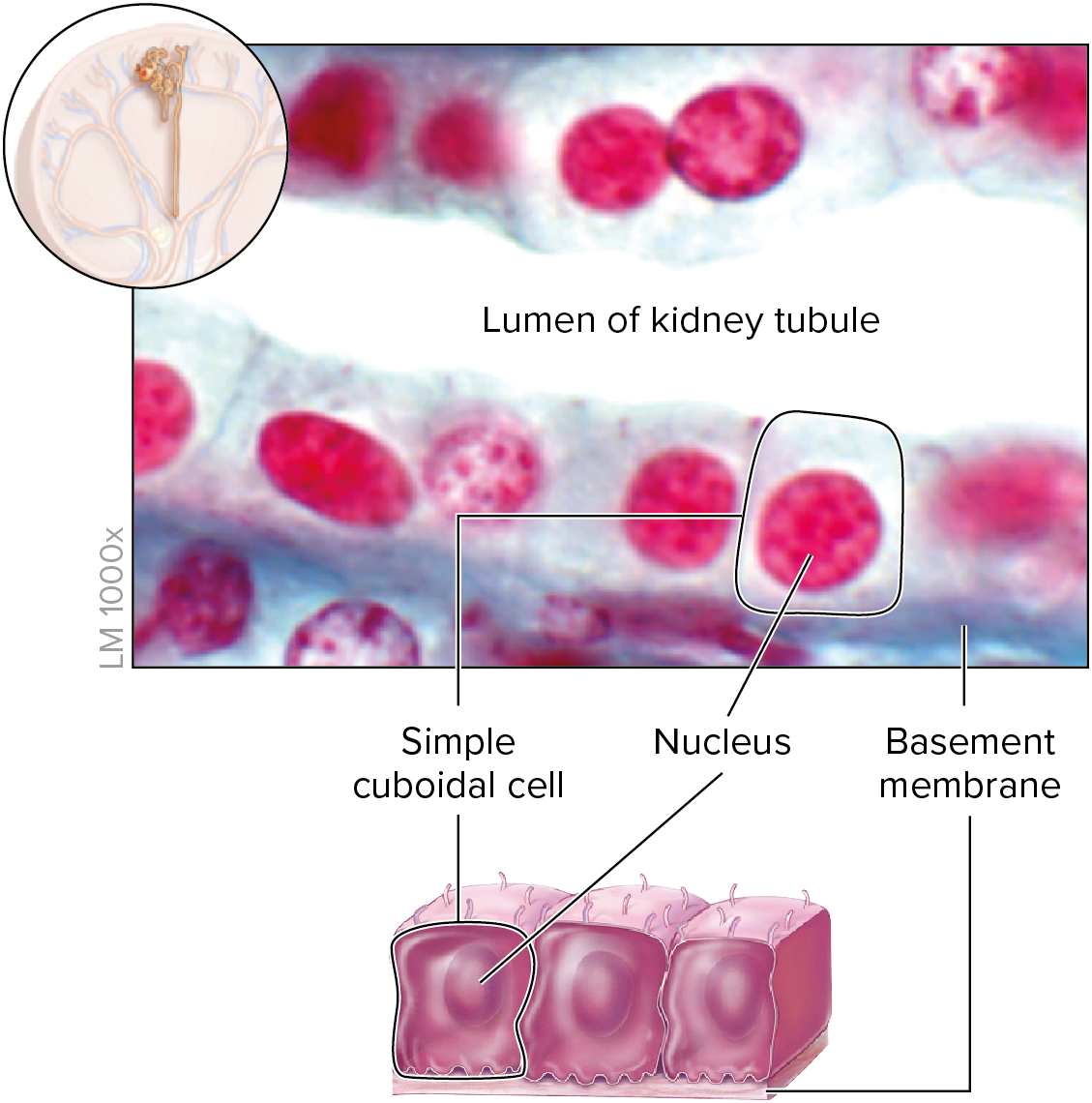
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
– Single layer of uniformly shaped cells
– About as tall as they are wide
– Centrally located spherical nucleus
– Designed for absorption and secretion
– Ideal for structural components of glands
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium : fuction and location
Function
Absorption and secretion; forms secretory tissue of most glands and small ducts
Location
Lining of kidney tubules; thyroid gland follicles; surface of ovary; secretory regions and ducts of most exocrine glands
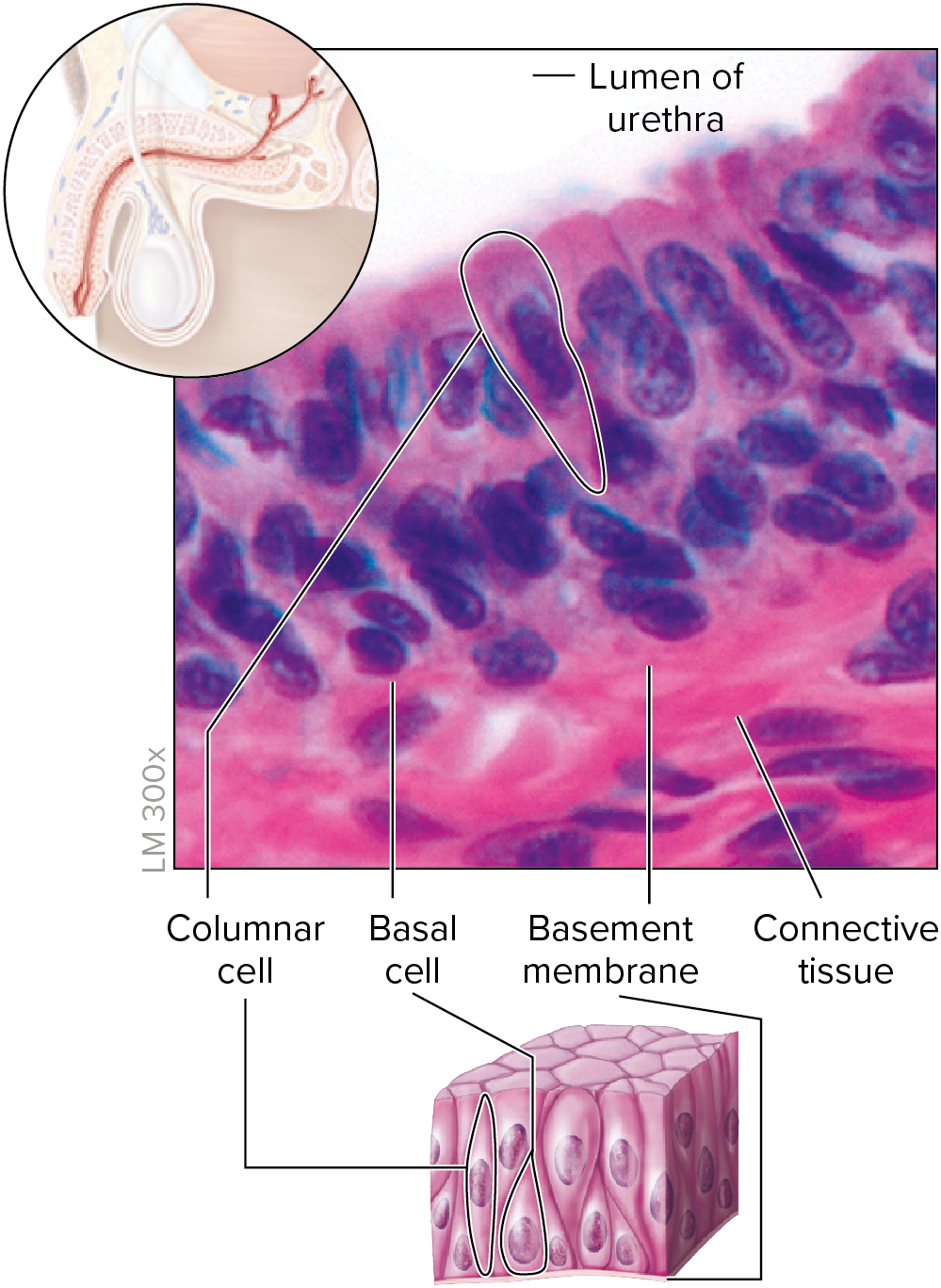
Simple columnar epithelium
• Single layer of cells
• Taller than they are wide
• Oval nucleus, lengthwise in basal region
• Ideal for secretory and absorptive functions
• Two forms: Nonciliated and Ciliated
Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Contains microvilli
Fuzzy structure—brush border
Unicellular glands—goblet cells
Secrete glycoprotein—mucin
Forms mucus when mixed with water
Lines most of digestive tract from stomach to anal canal (stomach, small and large intestine)
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium - structure
Structure
Single layer of ciliated cells taller than they are wide; oval-shaped nucleus oriented lengthwise in basal region of cell; may contain goblet cells
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium - function
Function
Secretion of mucin and movement of mucus along apical surface of epithelium by cilia; oocyte movement through uterine tube
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium - location
Location
Lining of the larger bronchioles (air passageways) of the lung and the uterine tubes
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium