Hock & Distal Limb Muscles
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What type of bones compose the tarsus?
The tarsal bones
Type - short bones
Describe the three rows of bones composing the tarsus.
Proximal row:
Talus
Calcaneus - palpable
Middle row:
• Central Tarsal Bone & 4th TBs
Distal row:
• 1, 2,3 & 4 TBs
• 4th TB bridges middle and distal rows (In middle and distal row)
Describe the differences between the equine and canine species considering the tarsal bones.
Horse
• 1 & 2 fused
• 3 very large, as it articulates with the third metacarpal
Describe the 4 joints making up the tarsus and what articulating bones form these joints.
What type of joints are the intratarsal joints?
1. Tibio-tarsal joint (TT):
• Talus - tibia & fibula
• Large range of movement
• Calcaneus - not articular
2. Proximal intertarsal joint (PIT):
• Talus & calcaneus -
Central TB & 4 Tbs
Distal intertarsal joint (DIT):
• Central - 1, 2 & 3 TBs
4th articulates with this
4. Tarso-metatarsal joint (TMT):
• 1,2,3 & 4 TBs - metatarsal bones
Fibrous Joint
Describe what type of movement occurs in the tarsus and which of these joints have the most-least mobility.
• Large range of flexion:
• Most movement tibio-tarsal joint
• Little movement at other joints
What is the significance of a oblique trochlea in the talus of the equine? What angle are these trochlea in the dog?
Produces rotation as they create an oblique angle
In dogs these trochlea are vertical, so they move more cranial with their limbs, restricting to extension and flexion only
In horses: the movement is a combination of flexion/extension and a slight outward rotation.
This anatomical adaptation is a result of the horse's evolution for cursorial (adapted for running) locomotion, optimizing the hind limb for powerful propulsion and weight-bearing.
What direction are the distal hindlimbs in flexion and protraction?
• Distal hindlimb directed lateral to forelimbs
• Prevents 'over-reach' injuries
What direction are the distal hindlimbs in extension and retraction?
• Distal hindlimb directed in axial plane, midline
• Aids in propulsion!
What type of joint is the tarsus?
• Features of typical synovial joint:
Extensive joint capsule due to complexity of joint
Poor communications between compartments in ALL species, most marked in the larger species
What aspects of the tibio-tarsal joint are palpable?
What are the compartments?
Tibio-tarsal joint separate from the rest
• Dorsomedial aspect
• Plantarolateral aspect
• Plantaromedial aspect
Distal Regions
• Dorsomedial aspect
• Dorsolateral aspect
What provides the tarsal joint with the necessary stability?
• Stability:
1. Collateral ligaments (A series of them)
Long: Tibia - metatarsal bone
Short: Bridge bone - bone
Clinical significance: dressage horses
2. Fibrocartilagenous reinforcement of joint capsule
3. Retinaculum
4. Plantar ligament
'Curb' - inflammation or swelling, can cause mineralization, called curb in equines
Describe the centers of ossification found within the tarsal bones.
• Development:
• All single centre of ossification:
• Except calcaneus = 2
List the following for the cranial tibial muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
Muscle located in cranial aspect of tibial region.
1. Cranial tibial muscle
• O - proximal tibia
• I - metatarsal bones (all species)
• I - Additionally, on medial aspect hock (horse) = Cunean tendon
• Function - Hock flexion
• Nerve Supply: Peroneal / fibular Nerve (branch of Sciatic)
List the following for the peroneus muscle. For this muscle note the aspect present in the horse, and the dog and cat.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
A. Peroneus longus / long fibular muscle - (Dog & cat (not horse)
• O = Lateral tibia & fibula
• I = Plantar aspect tarsus
B. Peroneus tertius / third fibular muscle
• Horse (not dog and cat)
• O - lateral femoral condyle (with long digital extensor muscle)
• I - 3rd MT (with cranial tibial muscle)
• I - lateral aspect tarsus
• Function: Hock flexion
• Nerve supply: Peroneal / fibular Nerve (branch of Sciatic)
List the following for the long digital extensor muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
• O - extensor fossa (femur)
Tendon of origin incorporated into stifle joint capsule
Provides lateral collateral support to stifle
• I - all digits
distal phalanx - extensor process
• Function: Hock flexion, Digital extension
• Nerve supply: Peroneal / fibular Nerve (branch of Sciatic)
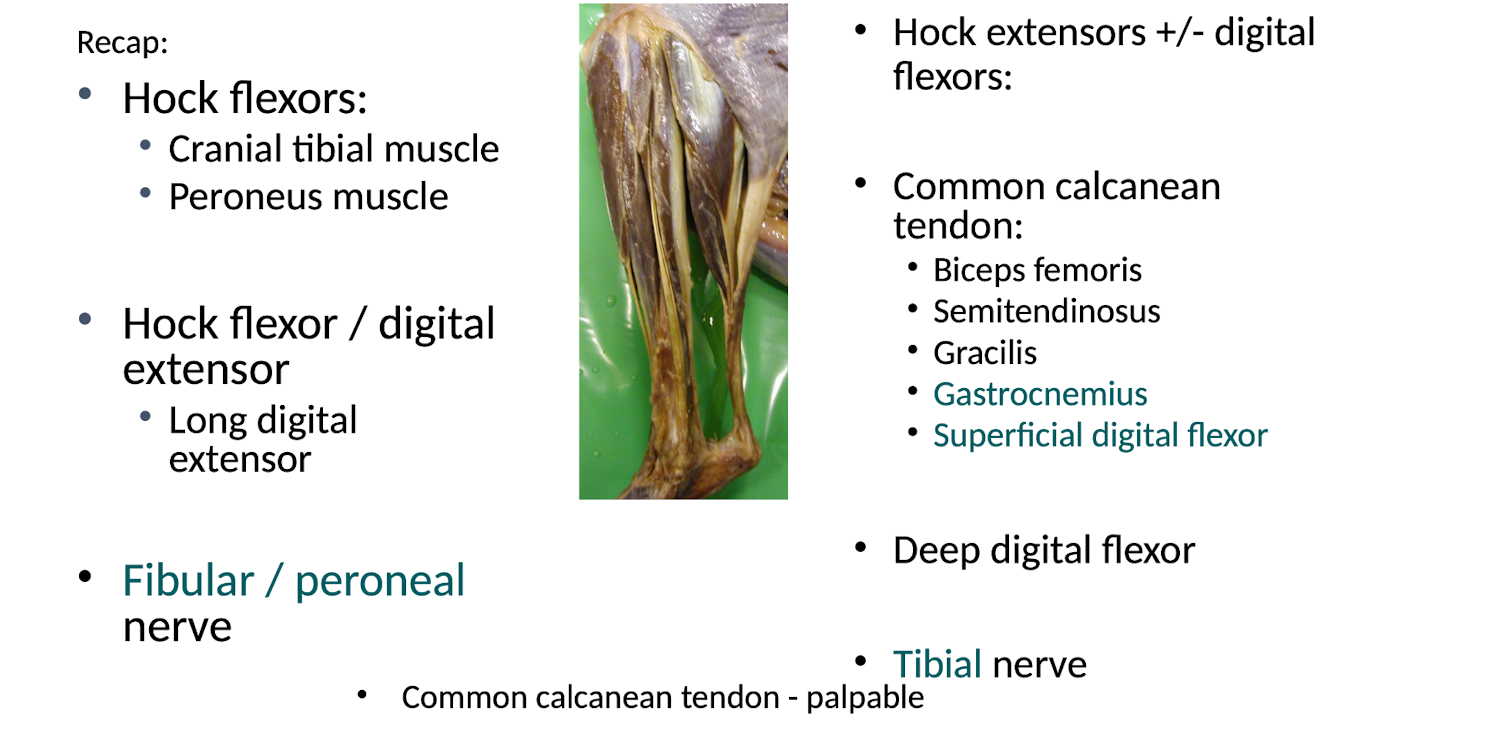
List the following muscles which are components of the common calcanean tendon. Also list the other following details:
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
Components:
1. Biceps femoris
2. Semitendinosis
3. Gracilis
4. Gastrocnemius
5. Superficial digital flexor
• I - calcaneus
Tuber calcis / calcanean tuberosity
Acts as lever for distal limb
Plantar ligament
• Function = hock extension
• Nerve supply - reflects contributors
List the following for the gastrocnemius muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
• O - femur, 2 tendons of origin (fabellae)
• I - calcaneus
Most significant component of common calcanean tendon
• Function: Hock extensor, (Stifle flexor)
• Nerve supply: Tibial Nerve (branch of Sciatic)
List the following for the superficial digital flexor muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
• O- distal femur (with gastrocnemius)
• I - calcaneus (part of common calcanean tendon)
• I - branches to all digits (middle phalanx)
• Function: Hock extension, Digital flexion
Support of distal limbs joints in extension
No accessory check ligament
• Nerve supply: Tibial Nerve (branch of sciatic)
List the following for the deep digital flexor muscle.
Origin
Insertion
Function
Nerve Supply
O- tibia (Runs over tarsus)
Not part of common calcanean tendon
Passes through slit of SDFT
• I - branches to all digits (distal phalanx)
• Function: Hock extensor, Digital flexor
Support of distal limbs joints in extension
Weak accessory check ligament
• Nerve supply: Tibial Nerve (branch of sciatic)
Summarize the distal hindlimb muscles.
What is the purpose of the hindlimb stay apparatus?
• Natural weightbearing position = extension
• Ability to lock weight bearing hindlimb in extension while other rested
• NB: Resting forelimb = lame
What systems are in place that makes the hindlimb stay apparatus possible?
Hip / stifle / hock:
Prevention of collapse into flexion, keep in natural extension
Hip - no passive system
Stifle locked into place via the: Patellar locking mechanism
Hock locked into place via the: Reciprocal apparatus
What is the reciprocal apparatus?
How does it function?
Part of the equine, hindlimb stay apparatus, part of the hock. Formed by interaction of two structures:
• Peroneus tertius
• Superficial digital flexor
• Fibrous bands - acts like a pulley system, if stifle is extended, tarsus must also extend, if flexed tarus and stifle must both be flexed
• Proximal movement of origin = proximal movement of insertion
• Stifle and hock must move together
What prevents the MTP/PIP/DIP joints from hyperextending, thus contributing to the hindlimb stay apparatus?
• MTP joint:
Suspensory apparatus:
Suspensory ligament
Proximal sesamoids
Distal sesamoidean ligaments
Long digital extensor
• MTP, PIP & DIP joints:
SDFT (no accessory check lig)
DDFT + accessory check lig
Annular ligaments
What allows the horse to produce massive power during hindlimb extension?
Combined force from huge muscle mass
Gluteal muscles → Very well developed
hip extensors / limb retractors (extra heads)
stifle extensors
hock extensors (reciprocal apparatus)
• Forces directed caudally in axial plane:
Angled trochlea on talus - limb is extended, makes limb direct caudally
Great for jumping!
Significance for you?
Horses kick straight back
Don't stand directly behind a horse!