Soil Science and the concept of soil
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Soil
Derived from the latin word “SOLUM” means floor/ground
Soil
True soil
Soil
Non-renewable
Inorganic matter
Sand, Silt & clay
Organic matter
5% is the ideal OM
Decomposition
Releases Oxygen and carbon dioxide
VV Dokuchaiev (1900)
Father of Soil Science
Whitney, 1892
Says that Soil a nutrient bin which supplies the nutrients necessary for plant growth.
VV Dokuchaiev
Soil is natural body composed of mineral and organic matter
Joffe, 1936
Soil is a dynamic natural body of mineral and organic matter that is spatially differentiated into different unconsolidated horizons of varialble depths
Brady, 1969
Says that it is a natural body that is a varialble mixture of inorganic matter derived from the weatherin and disintregation of rocks and minerals and organic matter derived from the actively and fully decomposed organic matter.
Jenny, 1941
Soil is equal to a combined influence of Climate and Organisms, modified by Relief/Topography, acting upon the Parent Material ove Significat period of Time (S=CL,O,R,PT)
Soil
A natural body with thickness and width with distinct and indistict horizontal boundaries
Components of Soil
Soil Solids 50%
Pores Spaces 50%
Soil Solids
Mineral Water (45%)
Organic Matter (5%)
Pore Spaces
Air (20-30%)
Water (20-30%)
Mineral Matter
Derived from the decomposition and disintegration of rocks and minerals; “Soil Particles”; source of most nutrients present in the soil except nitrogen, oxygen and carbon
Organic Matter
Derived from the decomposed living organisms; major source of nitrogen in the soil, thus, an indicative of N level in the soil
Air 20-30%
Primarily composed of nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide; soil air is the major source of oxygen for plants; has a humdity of 100%
Carbon dioxide in soil air
Higher than atmospheric carbon dioxide with 78% N, 20% O, 0.5% CO2
Water 20-30%
Transport nutrients to the roots; causes weathering of rocks and minerals Resulting to nutrient supply; also known as the soil solution; carries and moves dissolved nutrients
Ped
A natural aggregates which continue persist when wetted and dried
Pedon
A hexagonal column
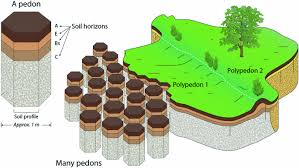
Basic unit of soil
Ped
Clod
Pedon
Polypedon
Pedosphere
Clod
An artificial structural unit formed by cultivation
Pedon
Basic sampling unit in soil survey
Pedon
Typically used to classify soil
Polypedon
Typically used to map soil
Polypedon
Multiple pedons that has distinct characteristics that differentiate it from surrounding polypedons or within a defined limit of single soil series
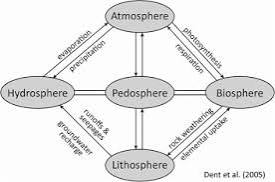
Pedosphere
the soil mantle of the Earth
A zone of activity in which mineral, water, air and biological components come together to form soils
Air and Water content
Is depending in the moisture condition of the soil 20-30% is the ideal level
A saturated soil
Means that the pore spaces are fully occupied by water
Field of soil science
Pedalogical
Edaphology
Soil Science
The science that deals with soil as a natural body/resource, its pedology (classification and genesis), physical, chemical, biological and fertility characteristics in ultimate relation to crop management and production
Pedological
Deals with the genesis, survey, classification and study of soils as a natural body. “Pedon”= Soil earth
Science concerned with the formation, nature, ecology, classification of soil
Study of soil's characteristics and its variations and does not focus on its immediate practical use or application
Edaphology
Deals with the study of soils in relation to higher plants. “Edaphos”= Soil or ground
Science concerned with the study of how soil influences human's overall use of the land and also the effect of the soil to plants
Difference of Pedalogical and Edaphology
Pedology is the study of nature or classification of soil while the edaphology is the study of soil influences human and plants
Branches of Soil Science
Soil fertility
Soil physics
Soil Chemistry
Soil Biology and ecology
Soil Conservation and management
Soil Survey
Soil Genesis, Morphology and classification
Land-Use Plannin and Classification
Soil Mineralogy
Essential Functions of Soil
Soil support plant growth
Soils regulate water supply
Soil functions as nature's recycling system
Soils are alive and home to various and diverse organisms
Soils influence the composition and physical condition of the atmosphere
Foundation and structural support of engineering structure
Preservation of earth's ecosystem
Soils serve sas an engineering medium
Soil Fertility
Deals with the study of the properties of the soil which enables it to provide essential chemical elements in quantities and proportions for the growth of specific plants
Quality of sioils to provide optimum level of nutrients for plant growth
Sol physics
Deals characteristics, properties, or interaction of soil which is caused by physical forces
Deals with the properties and interactionof the three soil phases (soild, liquid &gas)
Soil Chemistry
Study the various chemical reactions in the soil solution, considering that the soil is an open system
Interaction between solid, liquid and gaseous phases of the soil
Soil Biology & Ecology
Living organisms in the soil (bacteria, fungi, earthworms, nematodes).
Nutrient cycling, decomposition, soil health, and ecosystem services.
Soil Conservation & Management
Protecting soil from erosion, degradation, and pollution.
Sustainable agriculture, watershed management, and climate adaptation.
Soil Survey
Systematic study, description, and mapping of soils.
Provides data for agriculture, engineering, land-use planning.
Soil Genesis, Morphology & Classification
Genesis: Soil formation processes.
Morphology: Physical appearance and profile properties.
Classification: Grouping soils based on characteristics (like USDA Soil Taxonomy, FAO, WRB).
Land-Use Planning & Classification
Evaluating soil suitability for agriculture, forestry, urbanization, and engineering projects.
Guides proper land utilization while preventing degradation.
Soil Mineralogy
Minerals in soils (clays, silicates, oxides).
Controls soil fertility, nutrient availability, and engineering properties.
two main umbrellas
Pedology-Soil Survey, Genesis, Morphology, Classification, Mineralogy.
Edaphology-Soil Biology & Ecology, Soil Conservation & Management, Land-use planning.