Unit 4 Study Guide: Water Cycle & Location of Water
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Water Cycle & Location of Water
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Which of the water features shown on the diagram would MOST LIKELY contain salt
water
Sea
What is the main difference between a lake and a pond?
A lake is larger in size than a pond.
This table shows sizes of Earth's oceans:
Ocean Square Kilometers % of Earth’s Water
Pacific 168,723,000 46.6%
Atlantic 85,133,000 23.5%
Indian 70,560,000 19.5%
Southern 21,960,000 6.1%
Arctic 15,558,000 1.4%
Based on this table and the makeup of Earth’s total water, which reasonable
conclusion can be made?
Earth’s largest source of salt water is the Pacific Ocean
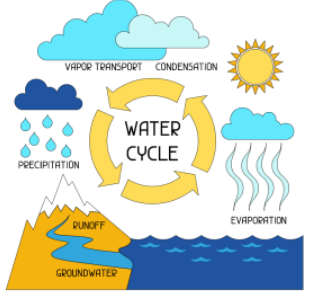
Which part of the diagram represents the largest amount of water on Earth?
Oceans
The Ogallala Aquifer is shrinking in size. Which describes why this is happening?
Overuse for agriculture
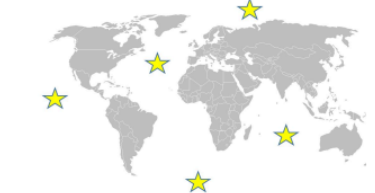
Which is a shared characteristic of all the locations marked by stars on the map?
Saltwater sources
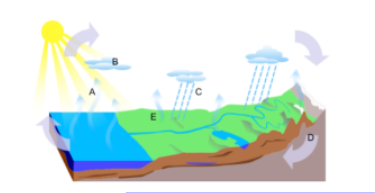
Correctly label the unlabeled water cycle model
A = Evaporation, B= condensation, C= precipitation, D = Infiltration,
E = Transpiration
The Great Salt Lake in Utah has a saline content that can be up to ten times greater
than the ocean. It is fed by 3 freshwater tributaries. What causes the Great Salt Lake
to have such a high concentration of salt?
Salt becomes concentrated as water evaporates.
Where did the salt in Earth’s oceans originally come from?
Elements from Earth’s crust dissolve in water and return to the
oceans.
Usable freshwater comes from many places on Earth. Match the source of water
with its description
Snow fields- Natural reservoirs for many western, mountainous states;
responsible for almost all of the streamflow in a river.
- Oceans- 96.5% of water on Earth; supplies about 90% of the evaporated
water that goes into the water cycle.
- Precipitation- The primary delivery of atmospheric water to the Earth.
- Aquifer- This is is an underground layer of waterbearing permeable rock
from which groundwater can be easily extracted using a well.
- Surface freshwater- Streams (of all sizes, from large rivers to small
creeks), ponds, lakes, reservoirs, canals, and freshwater wetlands.