E2: peds - ophtho & dental disorders
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what age do you start testing for visual acuity?
age 3 → younger than 3, test for visual behavior
what is the visual fixation test?
a colorful object/sticker on the end of a tongue depressor is moved side to side
what is the Sheridan Gardiner test?
aka visual acuity test
- letters of ↓ size are shown to child and they match the letter to one on a card
- good for children who haven't mastered reading the alphabet yet
light is focused in front of the retina
myopia
light is focused behind the retina
hyperopia
light in different meridians is brought to focus either in front or behind the retina
astigmatism
light is focused on the retina
emmetropic (aka normal)
inward convergence to the eye for a prolonged period seen in < 6 months of age
infantile esotropia
treatment for infantile esotropia?
surgery → weaken the medial rectus muscle
botox can also be used
what condition has features:
- acquired strabismus at age 2-5
- hyperopia
- eyes straight with glasses on and esotropic with glasses off
- MCC of esotropia in children
Accommodative esotropia
what condition has feature:
- esodeviation that is present with & w/o glasses
nonaccommodative esotropia
what conditions have features:
- white of the scleral is between the cornea and inner canthus is obscured (gives appearance of esotropia)
- worsens with gaze to the right or left
- prominent epicanthal folds
- closely spaced eyes
- flat nasal bridge
- asymmetry of lids or nasal bridge
pseudostrabismus
how is pseduostrabismus differentiated from true strabismus?
pseduostrabismus has symmetrical corneal light reflex & cover/uncover test is normal
what condition has features:
- form of pseduostrabismus
- appearance of exotropia
- caused by cicatricial changes of retina after retinopathy of prematurity or the eyes rotating outward to focus light on the fovea (bc fovea is displaced)
positive angle kappa → no tx required
which condition has features:
- esotropia that ↑ with gaze directed toward the side of the palsy
- esodeviation
- can be caused by pathological (trauma, tumor, ↑ ICP) or post-viral illness
6th CN palsy
if 6th CN palsy is idiopathic, what should you suspect?
pontine glioma
what causes Duane syndrome?
- failure of normal development of CN VI followed by anomalous innervation of lateral rectus muscle by CN III
- malformation of CN nuclei producing co-innervation of the medial & lateral rectus muscles
what syndrome has features:
- esotropia or exotropia
- unilateral or bilateral congenital defect
- up or down shoot of the eye & narrowing of the lid tissue on attempted adduction
Duane Syndrome
what condition has features:
- caused by vision loss in one eye or CN III paralysis
- affected eye deviates laterally
- pt squints one eye in bright light or complain of discomfort at night when tired
exodeviation
what condition has features:
- MC form of exodeviation in children
- eye "floats" or drifts when child is tired or inattentive
- child blinks repeatedly to reestablish fusion and realign their eyes
intermittent exotropia
what condition has features:
- down and outward position (inability to elevate & adduct eye)
- eyelid ptosis
- pupil enlargement
- caused by congenital defects, trauma, tumor or CN III paralysis
CN III palsy
a form of strabismus that causes the eyes to deviate upward and has features:
- diploplia
- HA
- blurred vision
- eye strain/fatigue
- head tilt or head posture
hypertropia
what condition has features:
- head is tilted to the shoulder opposite the side of the affected eye
- upward deviation of the eye and difficulty depressing the eye on adduction
- diplopia in the contralateral field of gaze
- caused by congenital defect or due to trauma
CN IV palsy
overreaction of the inferior oblique muscle, whose action is elevation and adduction
inferior oblique overaction
an uncommon form of vertical strabismus that may be congenital or acquired and caused by trauma, inflammatory disorders, or congenital abnormality of the superior oblique tendon
brown syndrome → inability to elevate eye in adduction
what are some causes of vertical deviations?
myasthenia gravis
thyroid ophthalmopathy
chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia
orbital fxs w muscle entrapment
orbital disease w intraorbital masses
what are the special tests for strabismus?
light reflex test → norm = reflex symmetrical in both eyes
cover test → norm = no mvmt of uncovered eye
cover/uncover test → norm = covered eye has no mvmt
functional reduction in VA caused by abnormal visual development in early life caused by strabismus, refractive error or deprivation
amblyopia → refer ophtho, patch unaffected eye
which type of amblyopia:
misalignment of eyes results in visual cortex suppression of the visual input of the deviating eye
strabismic
which type of amblyopia:
difference of VA between eyes leads to visual blurring of one eye and visual cortex suppression of the visual input of the blurred eye
anisometropic
which type of amblyopia:
eye misalignment and refractive error leads to visual cortex suppression of the chronically blurred image
combined strabismic and anisometropic
which type of amblyopia:
bilateral, symmetric high refractive error resulting in blurred vision in both eyes and inadequate development of the visual cortex
ametropic
which type of amblyopia:
obstruction of the visual axis results in suppression of the visual cortex
deprivation
a bluish mass below the medial canthal tendon caused by proximal obstruction of the nasolacrimal system
congenital dacryocystocele/mucocele → refer ophtho
!
swelling and inflammation of the lacrimal gland visible beneath the lateral aspect of the upper eyelid accompanied by symptoms of pain and tenderness
dacryoadenitis
neuronal dendrite seen with fluorescein staining
herpes simplex keratitis
congenital anomaly caused by genetic mutation that presents with partial or complete absence of the iris
- associated with WAGR syndrome and ↑ risk of glaucoma
aniridia
what condition has features:
- leukocoria (white reflex)
- poor vision (partial or total vision loss)
- strabismus
- photophobia
- due to congenital, disease or idiopathic causes
cataracts
what condition has features:
- iris heterchromia
- anisocoria
Horner syndrome
tooth eruption chart
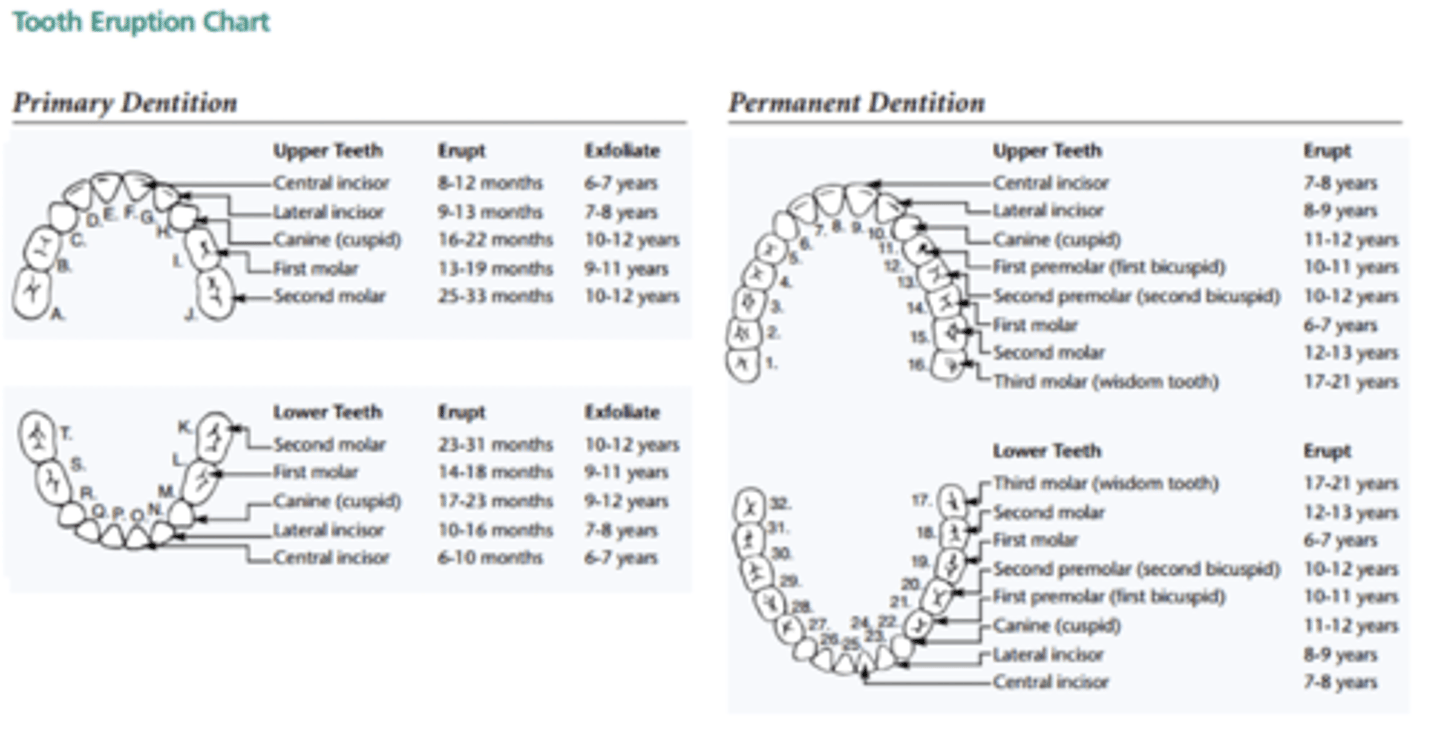
changes in the bite often occur as a result of?
prolonged thumbsucking
small, white cystic lesions seen along the midpalantine raphe
gingival cyst → epstein pearls
firm, grayish-white mucous gland cysts on the buccal aspect of the alveolar ridges
gingival cysts → bohn nodules
benign tumor in newborns that arises from the mucosa of the gingiva
congenital epulis
benign, but locally aggressive, tumor of the anterior maxilla that produces elevation of the lip and displaced primary teeth
melanotic neuroectodermal tumor
chronic and recurring condition affecting the filiform papillae of the tongue. lesions are red, slightly depressed and bordered by a whitish band
benign migratory glossitis (geographic tongue)
bluish, opalescent sheen on several teeth resulting from genetically defective dentin and is associated with osteogenesis imperfecta
dentinogenesis
white spots on the tooth which represent demineralization of the enamel are precursors to this condition
dental caries (aka cavities)
ulceration on the labial mucosa surrounded by a erythematous halo
recurrent aphthous ulcers
this condition is associated with an abscessed maxillary tooth
facial cellulitis → hospitalized w IV ABX, I&D and tooth extraction
food particles and bacteria that become trapped under the residual overlying gingiva resulting in inflammation and abscess formation, most commonly affecting partially erupted third molars (wisdom teeth)
pericoronitis
localized necrosis and hemorrhage covered with pseudomembranes
acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
bluish, fluctuant swelling in the floor of the mouth (retention cyst) associated with trauma to a salivary duct
ranula