A&P - Membranes, Muscle Tissue, & Nervous Tissue
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Types of membranes
Epithelial membranes
Synovial membranes
Epithelial membranes
Thin, sheet-like structures composed of epithelium and underlying connective tissue, covering surfaces and lining body cavities
Types of epithelial membranes
Serous
Mucous
Cutaneous
Serous membranes - Function(s)
Lines body cavities that lack openings to the outside of the body
Cells secrete watery, serous fluid to lubricate surfaces
Consists of simple squamous epithelium and a single layer of areolar connective tissue
Type of epithelial membrane
Serous membranes - Location(s)
Forms inner linings of the thorax and abdominal cavities, and covers organs in those cavities
Type of epithelial membrane
Mucous membranes - Function(s)
Lines body cavities and tubes that open to the outside of the body
Consists of simple columnar epithelium overlying a layer of areolar connective tissue
Goblet cells contained within the membrane that secretes mucus
Type of epithelial membrane
Mucous membranes - Location(s)
Lines:
Oral and nasal cavities
Tubes of digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive
Type of epithelial membrane
Cutaneous membranes - Function(s)
Epidermis → Stratified squamous epithelium
Dermis → Areolar connective tissue and mainly dense irregular epithelium
Hypodermis → Adipose connective tissue
Consists of stratified squamous epithelium and dense irregular connective tissue
Type of epithelial membrane
Cutaneous membranes - Location(s)
AKA skin (found only on skin)
Type of epithelial membrane
Synovial membranes - Function(s)
Lines, surrounds, and lubricates joints by secreting synovial fluid
Composed mainly of connective tissue
Synovial membranes - Location(s)
Joints of limbs (shoulder, elbow, wrist, knee, ankle, hip)
Joints of the spine (cervical vertebrae and lumbar vertebrae)
Muscle fibers
Elongated cells in muscle tissue
May contain multiple nuclei
Muscle tissue - Function(s)
Movement, ability to contract, maintains posture, produces heat, pumps blood, peristalsis (movement of intestines)
Types of muscle tissue
Skeletal
Smooth
Cardiac
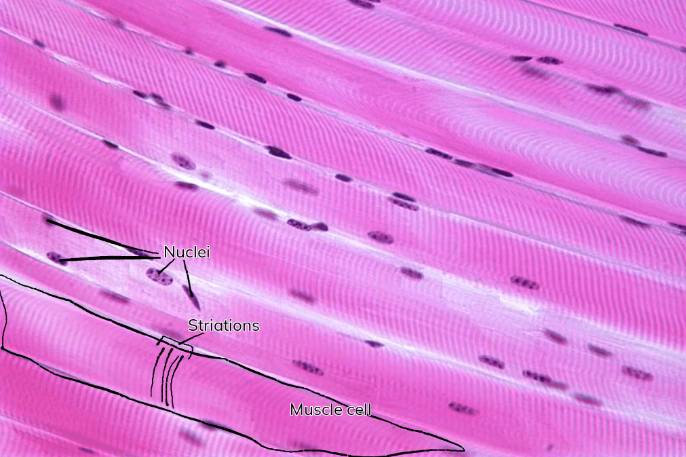
Skeletal muscle tissue - Function(s)
Attached to bone and can be controlled by conscious (voluntary) effort
The cells are long and cylindrical, striated, have many nuclei, and contract from nervous impulses
Skeletal muscle tissue - Location(s)
Attached to bones, skin, and to some facial muscles
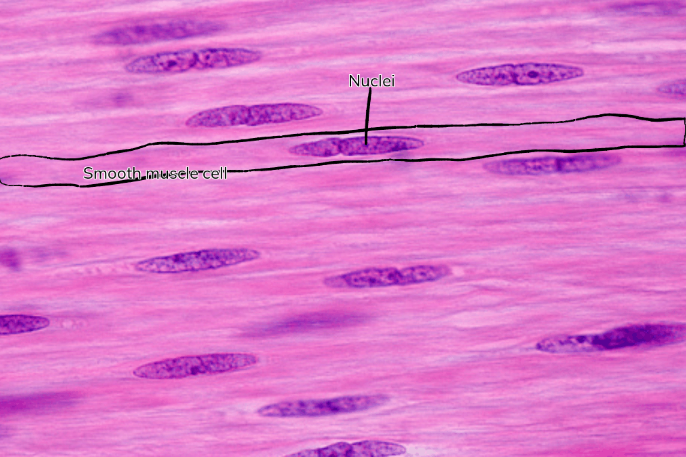
Smooth muscle tissue - Function(s)
Involuntary (unconscious) muscle movement
Lacks striations, is uninucleate, and consists of spindle-shaped cells
Smooth muscle tissue - Location(s)
Walls of internal organs, digestive tract, blood vessels, and urinary bladder
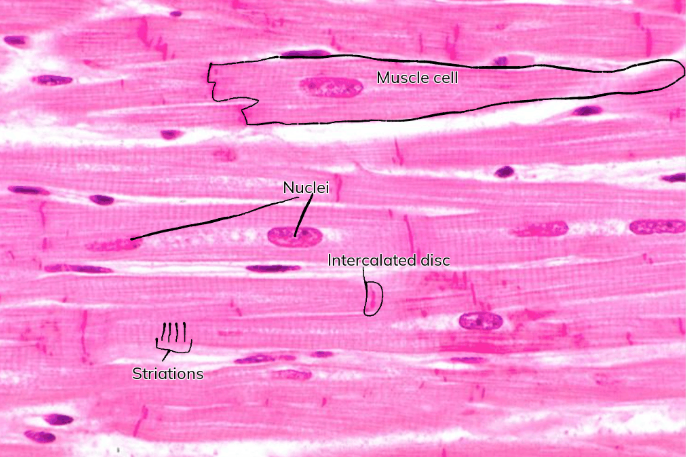
Cardiac muscle tissue - Function(s)
Involuntary muscle movement
Consists of branching muscle fibers/cells that are connected to each other with intercalated discs
Each muscle fiber has a single nucleus in each cell but appears to be striated
Cardiac muscle tissue - Location(s)
Only found in the heart
Nervous tissue - Function(s)
Regulates and controls body functions
Generates and transmits nerve impulses
Supports, insulates, and protects impulse-generating neurons
Main component of the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, nerves)
Nervous tissue - Location(s)
Central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
Peripheral nervous system
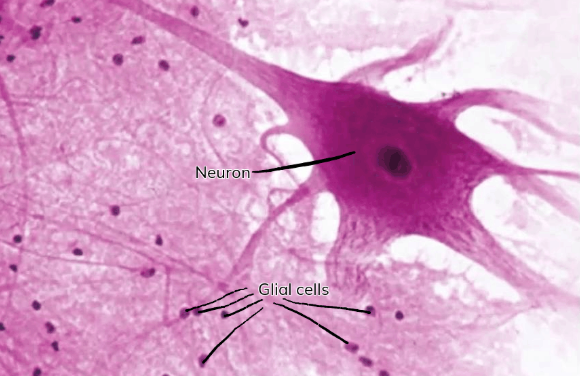
Neurons
Largest cells of the neurons, transmits neural impulses
Glial cells
Smaller, more abundant cells of the neurons
Acts as support for neurons
Myelin sheaths of glial cells provide insulation for neurons
Regulates neurotransmitter levels
Maintains the environment
Striations
The visible bands/stripes on muscle fibers/cells that allow for powerful and efficient contractions essential for muscle functions
Intercalated discs
Specialized junctions unique to cardiac muscle tissue that connect adjacent heart cells to enable synchronized contraction (heartbeats)
% of muscle tissue in the body
40% of the body is skeletal muscle tissue
~10% of the body is smooth or cardiac muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle tissue
Smooth muscle tissue
Cardiac muscle tissue
Nervous tissue