Measurement of Motor Performance
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What are types of skills?
discrete
continuous
serial
open
closed
Why is performance measurement important?
It is essential for performance asessment
tracks patient progress ot ensure goals are met
identifies strengths and weaknesses
informs clinical decisions
promotes motivation and reinforce positive performance behaviors
enhances accountability for actions and results
What are the two general categories of measurements?
performance outcome measures
performance production measures
What is a Performance Outcome Measure?
This provides us with information about what happened at the level of actions, where the major concern is, whether or not the goal of the task was accomplished.
Indicates the outcome or result of performing a motor skill.
Ex.
Reaction Time - speed of response
Error Measures - accuracy of performance
Functional Outcome Measures - effectiveness in real-world tasks (Berg Balance Scale, TUG, 10 Meter Walk Test)
Do performance outcome measures tell us about the movements that led to the outcome?
no
Do performance outcome measures tell us about the information about the activity of various muscles involved?
no
What is Performance Production Measure?
It provides us information about HOW the brain and body produced the outcome, how the nervous-musculoskeltal system functions, how the limbs and joints are acting during a particular task or skill, info relevant to the analysis of movement and neuromotor processes.
Indicates the activity of specific aspects of the motor control system during the performance.
Ex.
kinematic measures (joint angles, velocity)
kinetic measures (torque, GRF)
neural activity - electrodes and brain imaging
high computational methods - movement coordination and computer simulation models
Reaction Time (RT)
Time between the stimulus (signal) and the initiation of the movement.
Movement Time (MT)
Interval of time between the initiation of a movement and the completion of the movement.
Response Time (RT+MT)
Time interval involving both reaction time and movement time, from the onset of a signal (stimulus) to the completion of a movement
T or F RT includes any movement related to the specific action.
FALSE
Does the measurement of RT include a “go” signal?
yes
T or F Reaction Time and Movement Time are independent of each other and do NOT predict the other.
TRUE
Can you have a slow reaction time but a fast movement time?
YES
Simple RT
Involves only one signal and requires only one movement in response.
Ex.
press the button —> light turns on.
Choice RT
Involves more than one signal, and each signal has a specified response.
Ex.
Press the button on the left—> blue light turns on.
Press the button on the right —> red light turns on.
Discrimination RT
Involves more than one signal, but only one response.
Ex.
Press the button on the left —> blue light turns on.
If you don’t press the button a red, yellow, or green light turns on.
Blazepods
When performing agility training with a series of simple reaction time laterally direction agility movements.


Visual Motor Training
Improves reaction time, scanning, hand-eye coordination, and scanning for saccadic eye movement.
What is the Stroop Stepping Test?
Participants step according to the word and not the arrow of orientation.
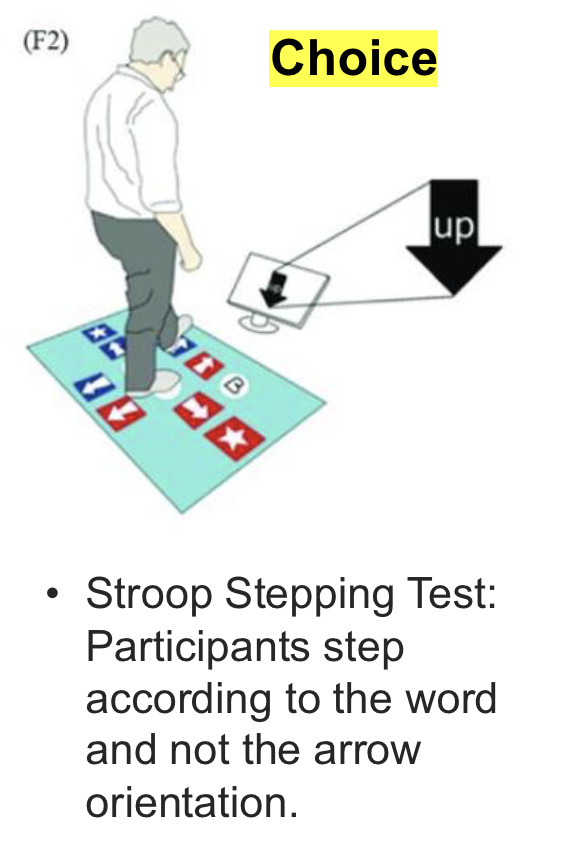

What kind of Reaction Time?
Choice Reaction Time

What kind of Reaction Time?
Choice Reaction Time

What kind of Reaction Time?
Discrimination Reaction Time

What kind of Reaction Time?
Discrimination Reaction Time
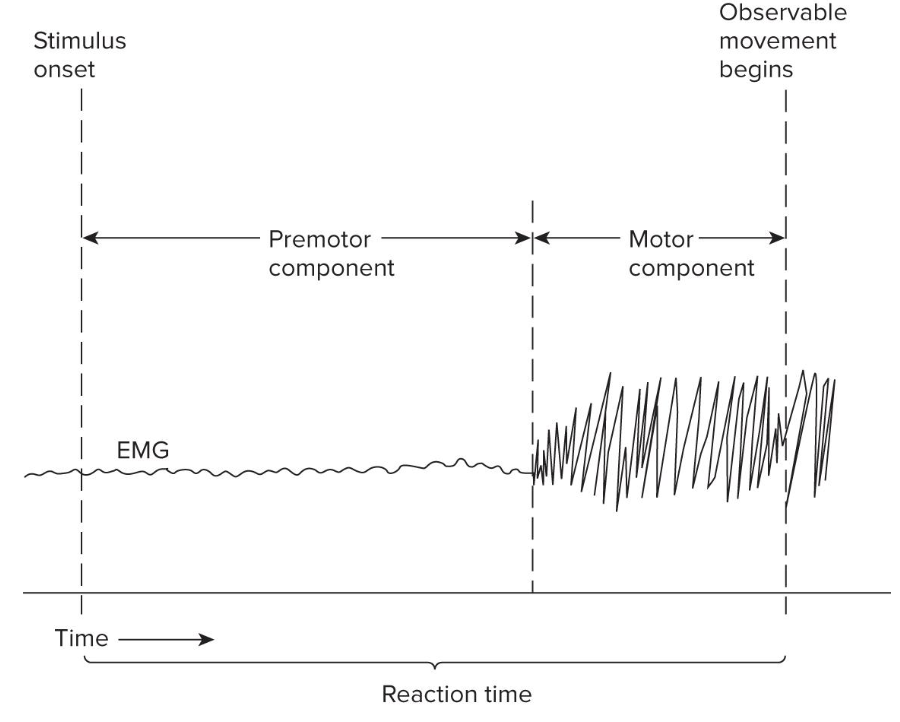
What are the two components within the Reaction Time peiod?
Premotor time (cognitive) and motor time (biomechanical)
What is Premotor Time?
Quiet interval of time between the onset of the stimulus signal and the beginning of the muscle activity.
What is Motor Time?
Period of time from increase in muscle activity until the actual beginning of observable limb movement.
Accuracy involves either _____, _____ measures or both
spatial, temporal
Inconsistency is. . .
lack in acquiring basic movement pattern, performance varies from trial to trial
Bias
Suggests that the person has acquired movement patterns but having difficulty adapting to the performance situation, performance varies in a specific direction.
What are the 3 error measures?
absolute error (AE)
constant error (CE)
variable error
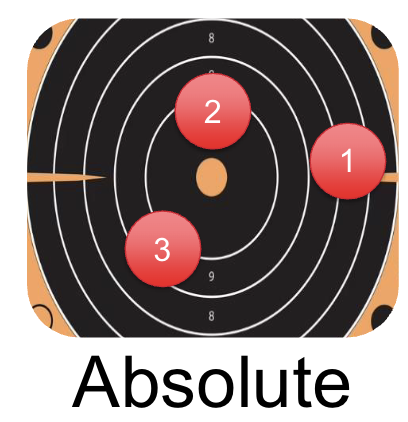

What is Absolute Error?
the absolute difference between the actual performance on each repetition and the goal
Gives a general index of accuracy and the magnitude of error (accuracy)
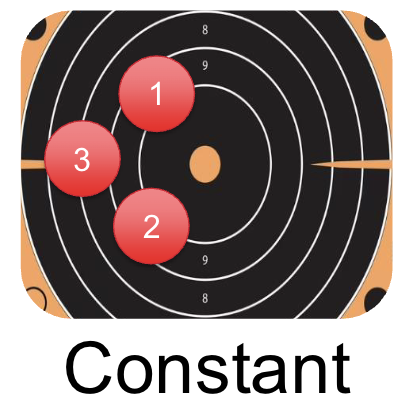
What is Constant Error?
Signed (±) deviation from the target/goal - factors in direction.
Fibers an indicate of the person’s tendency to be directionally biased.
Serves as a measure of performance bias.
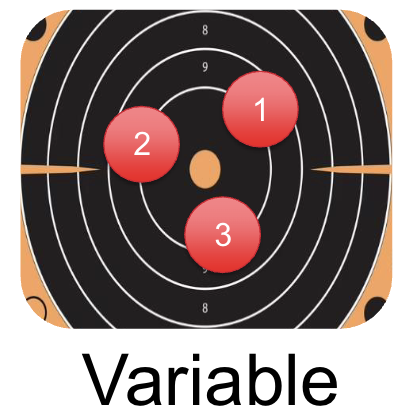
What is Variable Error?
Standard deviation of the CE scores for the series of repetitions.
Gives an index of variability or consistency of performance.

What are the two devices that we talked about the assess and train reaching accuracy?
InMotion ARM and ADLER
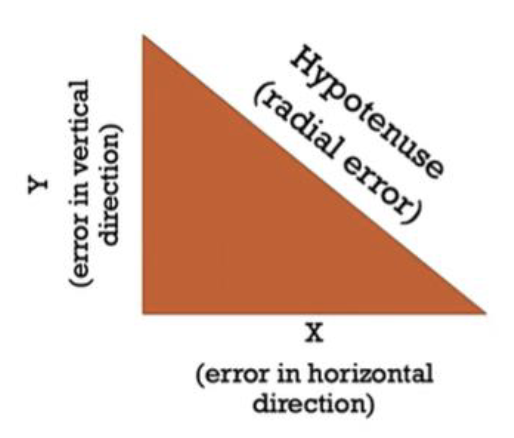
Radial Error
Has more complex movements occurring in 2 dimensions (vertical and horizontal).
Functionally similar to Absolute Error but takes into consideration 2 complex movements instead of 1.
You calculate the hypotenuse to find radial error.
Root Mean Squared Error
This is a complex calculation requiring statistical software and quantifies how far the actual performance deviates from a desired performance.
This looks at the difference between the movement and the ideal at many points in time.
This is calculated overall error, if smaller number then you are closer to the target.
What is Kinetics?
This describes forces causing movement.
Ex. GRF during running over force plates, joint torques via Biodex Isokinetic Testing, EMG to estimate quad muscle forces during stair climbing
What is Kinematics?
This describes motions without regard to forces. This is generally completed by video analysis, motion capture
Ex. joint angles during walking - how much knee flexion during swing, step or stride length, and velocity or acceleration of a limb.
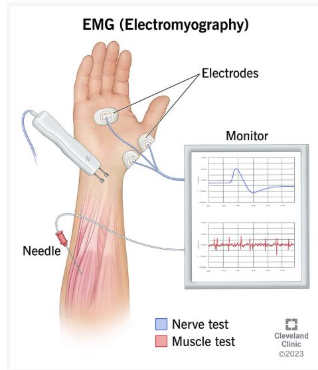
Electromyography (EMG)
This is a recording of the electrical activity of a muscle or group of muscles to detect issues with motor nerves, muscles, or communication between the two.
Whole Muscle Mechanomyography (wMMG)
Detects muscle activity, with the added benefit of estimating muscle fiber composition within the muscle
Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS)
Determines the level of oxygenation in the muscle
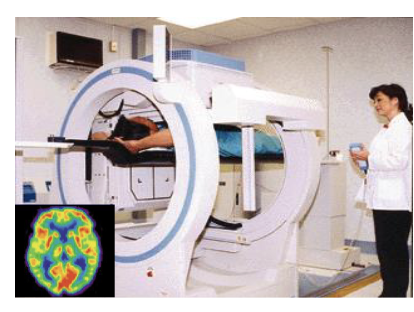
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Small amount of radioactive tracer to detect metabolic activity in the brain or other tissues (tumors, AlzD)
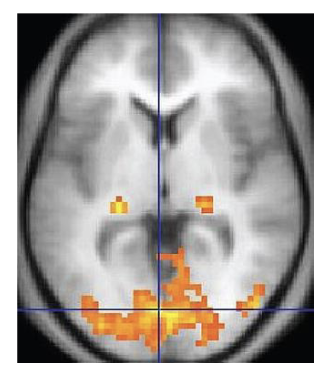
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
Is a non-invasive brain imaging that detects changes in blood flow and oxygenation in specific areas of the brain (epilepsy, tumors)
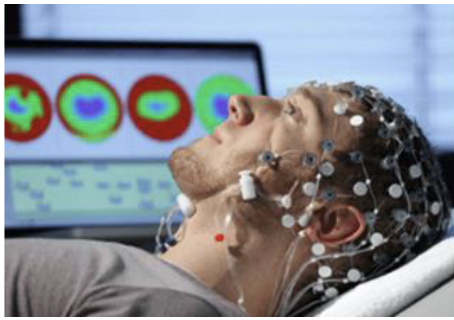
Electroencephalography
Is a non-invasive method to record electrical activity of the brain (seizures, coma, TBI)
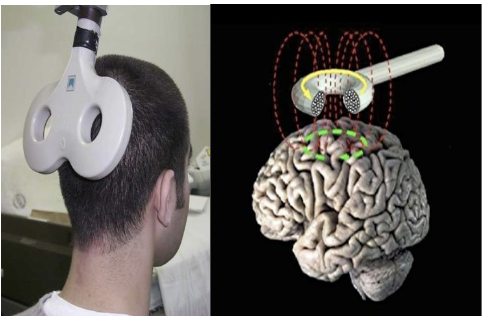
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Uses magnetic fields to stimulate neurons in the brain (PD, depression)
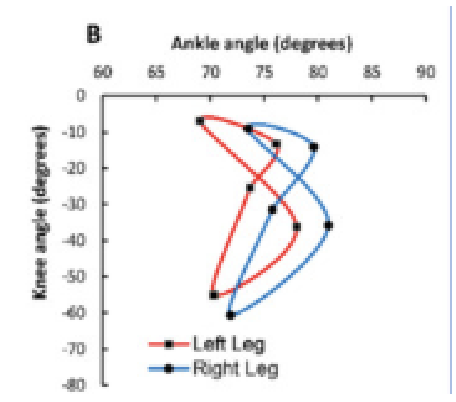
What are Angle-Angle Diagrams?
These plot the angle of one joint against the angle of another joint over time.
What is the cross correlation of angle-angle diagrams?
How the 2 segments are coordinated.
This produces the correlation coefficient.
What is the Relative Phase Relationship?
This is measure of timing relationship between 2 oscillating segments (lim or joints)