Pharm unit 2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Shock
What are the 4 types of shock?
inadequate tissue perfusion (O2 to tissues)
-Hypovolemic = low volume of blood
-Cardiogenic = heart can’t pump blood efficiently
-Obstructive = something is blocking the vessels (example: pulm embolism)
-Distributive = fluid collects in between BV, making it hard for O2 to pass thru into the tissues
Thrombocytopenia
Low platelet count → bleeding
Intrinsic factors
Common intrinsic factors of bleeding disorders
Measured by “PTT”
-Von Wilderbrand disease, Bernard Soulier Syndrome, Glansmann Thrombosthania
Extrinsic factors
Common extrinsic factors of bleeding disorders
Measured by “PT”
-Taking warfarin, liver disease, vitamin K deficient, CF7 deficiency or AF inhibitor
K Potassium normal blood level
3.5 - 5
Na sodium normal blood level
135-145
Magnesium normal blood level
1.3-2.1
Calcium normal blood level
9.0-10.5
Phosphate normal blood level
3.0-4.5
Chloride normal blood level
98-106
Normal mOsm in the blood level
275-295 mmol/kg
Potassium food sources
Green leafy veggies, banana, avocado, salt substitues
Sodium food sources
Canned food, fast food, processed meat and cheese
Magnesium food sources
green leafy veggies, spinach, almonds, yogurt
Electrolyte food sources all together

Folic acid sources
FOOL - Fish, organ meats, oranges, leafy green veggies
Iron sources
Meat
How do electrolytes get lost from the body?
VPPS
Vomiting, Peeing, Pooping, Sweating
The role of the liver in managing bleeding disorders is to _________
create clotting factors
Which fluid is the closest in content to blood?
A. plasmalyte
B. normal saline
C. lactated ringers
D. dextrose in water
A. Plasmalyte
Long term use of normal saline can cause…?
A. respiratory acidosis
B. respiratory alkalosis
C. metabolic acidosis
D. metabolic alkalosis
C. metabolic acidosis
Hypernatremia and Hyponatremia
HypER = high Na (sodium) in blood
HypO = low Na
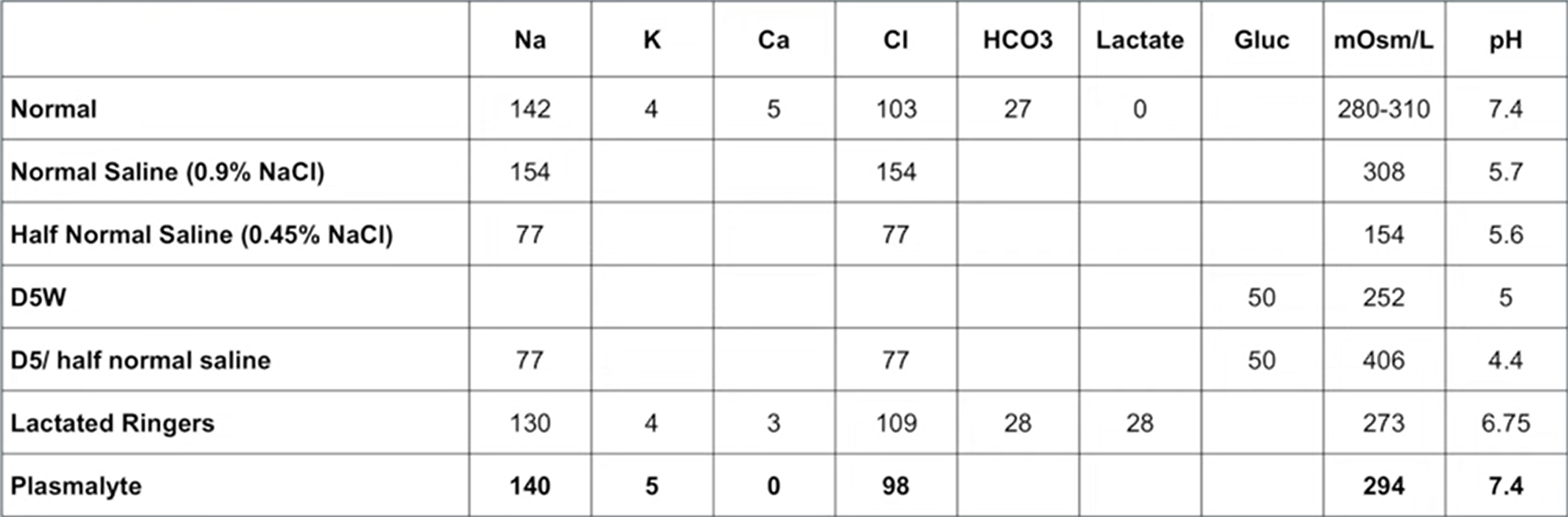
Normal Saline (NS) 0.9%
-Made of Na and Cl (154 of each)
*isotonic —> mOsm is similar to blood
-acidic pH of 5.7
-Resuscitation fluid
Half Normal Saline 0.45% (1/2 NS)
-made of Na and Cl (77 of each)
-NOT isotonic, has higher mOsm
-still acidic at 5.6 pH
-Used for hypernatremia
Hypertonic saline 3%
-made of Na and Cl, has lots of Na
-used for hypOnatremia
D5W
-made of glucose → sugar water. Has no electrolytes
-over mOsm
-acidic pH of 5
-Used for hypernatremia, maintanance fluid
D5/ half Normal Saline (D5 1/2)
-combine HNS and D5 → Na, Cl, glucose
-77 Na & Cl
-VERY high mOsm
-even more acidic pH of 4.4
Lactated Ringers (LR)
-Na, Cl, as well as HCO3, lactate, K, and Ca
-Isotonic
-pH of 6.75 which is close to 7.4 blood pH
-Used in surgery, Resuscitation fluid
Plasmalyte
-closest to real blood composition
Na 140 and Cl 98, as well as some K
-Isotonic
-7.4 pH
What fluid do you give to hypovolemic patient?
NS 0.9%
Eventually switch to LR or plasmacyte to prevent acidosis
What fluid do you give to a pre-procedure or NPO patient?
D5 ½, and possibly maintenance sugar
What fluid do you give for hypOnatremia?
Hypertonic saline 3% NaCl
Normal Saline 0.9%
What fluid do you give for hypERnatremia?
D5W
½ NS
All fluids table comparison
Microcytic anemia
Anemia caused by not enough iron available
→ treat with iron supplements
Megaloblastic anemia
anemia caused by malabsorption of B12 or folic acid
→ treat with B12, folic acid, or both
Pernicious anemia
How do we test for it?
Specifically anemia caused by lack of B12
→ low IF in stomach to absorb B12
→ tested with Shilling test - give radioactive B12 and track elimination 24h later. Less than 10% is normal, but lower = pernicious anemia
How is pernicious anemia tested?
B12 injections
Hemolytic anemia
occurs when RBC are destroyed faster than they can be produced
→ caused by drugs, immune disorders
Sickle cell anemia
How is it treated?
RBC are abnormally shaped and they can’t carry O2 efficiently
→ treated with administering O2 and fluid
Aplastic anemia
considered a type of cancer, the body stops producing RBC
What factors contribute risk to B6 deficiency?
Alcohol use, bleeding, old age, kidney failure, diseases like celiac
Hgb normal lab values
Males 14-18
Females 12-16
Hematocrit
How is it affected by dehydration, anemia, or bleeding?
Vol of RBC compared to total blood volume
→ when you are dehydrated this number goes up as there is less fluid
→ anemic pts have low Hematocrit
→ bleeding will not affect it much
Hematocrit normal lab values
Males 40-54%
Females 36-48%
What instructions to give for administering iron?
Take on empty stomach, can take with orange juice to help absorption, measure Hgb and hematocrit regularly
Are malabsorption or chronic blood loss worse risk factors for anemia?
Chronic blood loss
T or F
People with bleeding disorders are at high risk for hemorrhage or hypovolemic shock
True
DIC
Who is at risk for it? How do we test for it?
a process of abnormal over-coagulation; the pt uses all their clotting factors and then they bleed w/o ability to stop it
-more risk for ppl after trauma/injury or surgery
-risk indicated by low fibrinogen
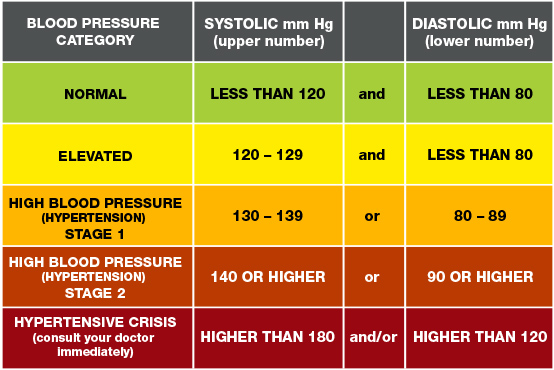
Hypertension BP values table (must memorize)
Complications of hypertension
it causes cracks in the endothelial cells in the BVs
→ lead to myocardial infarction, aneurysm, or stroke
Primary vs secondary hypertension
Primary = most common (>90%!) where there is no known cause, and BP goes up steadily
Secondary = has another cause → usually caused by altered kidney function causing more renin → more fluid stays in BV
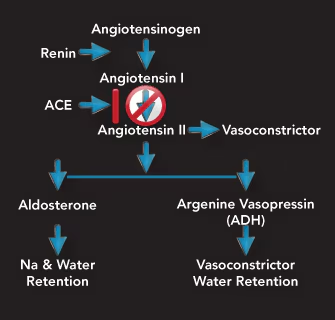
How do kidneys affect hypertension?
Kidneys release renin
Renin converts angiotensin → leads to more fluid retention
If kidneys produce too much renin, then too much fluid retention, and BP will rise
Risk factors for primary hypertension
Old age
obesity
high-salt diet
sedentary lifestyle
Hypertensive crisis
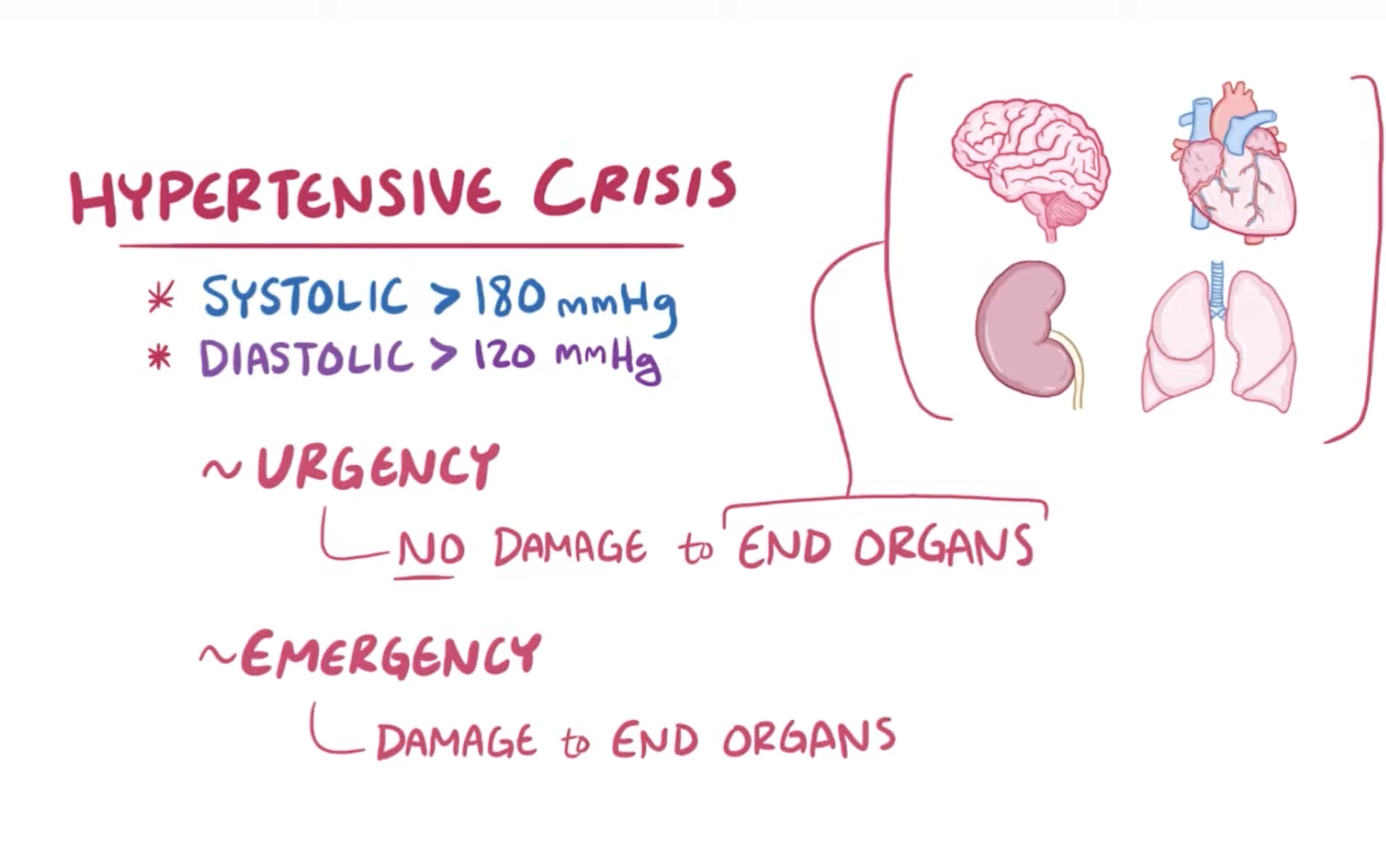
Hypertension symptoms

Hypertension treatment
Diet changes
Lifestyle/exercise changes
Stress mgmt
Antihypertensive drugs
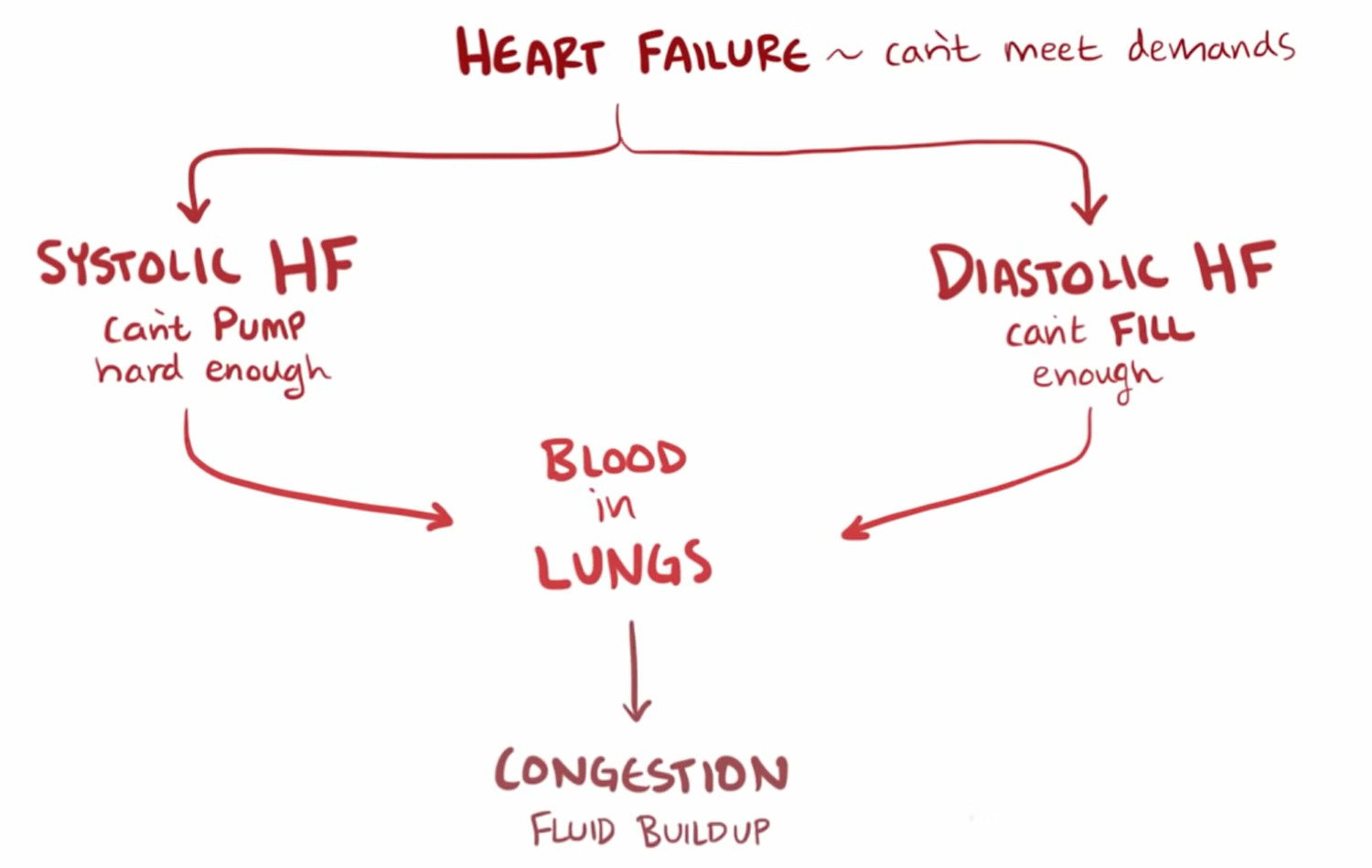
(congestive) Heart failure definition
Prior to administration of digoxin (Lanoxin), the nurse completes which assessment?
Apical pulse
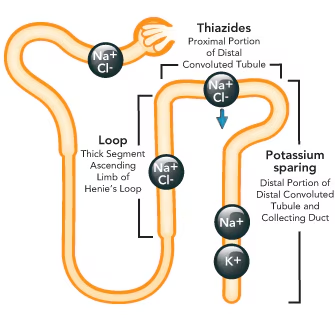
Where each diuretic (loop, thiazide, potassium sparing) acts on the kidney
Preload, afterload
Preload = blood left in ventricles after pumping
Afterload = peripheral resistance
Right vs Left-sided heart failure causes
Right = lung disease, LHR, preload problem
Left = stress of left ventricle, HTN, MI, afterload problem
Warfarin antidote
vitamin K
Heparin antidote
Protamine sulfate
Alteplase antidote
aminocaproic acid
Name the list of drugs that has bleeding as an adverse effect (6 drugs)
aspirin, alteplase, warfarin, heparin, enoxaparen, and dabigatran
What is the mechanism of action for drugs to treat dysrhythmias?
Prolongs cardiac action potential
coronary artery disease (CAD)
clogged BV’s
Atherosclerosis
cholesterol buildup in BVs
-symptom of CAD
Heart attack (MI) vs heart failure
MI = necrosis of part of heart tissue due to blockage
HF = heart can’t pump enough blood effectively
Site of origin for arrythmias for:
Sinus, Atrial, Ventricular,
Sinus = SA node
Atrial = atria
ventricular = ventricles
Major food source that increases triglycerides
Sugar
→ nonpharm low triglyceride diet includes reducing sugar in diet