5.1 The role of operations management
Introduction - the nature of operations
“Operations” or “operations management” is concerned with the use of resources called inputs (land, labor and capital) to provide outputs in the form of goods/services.
Essentially, operations managers are aiming to produce goods and services of the required quality, in the required quantity, at the time needed, in the most cost-effective way.
Operations management: the production process
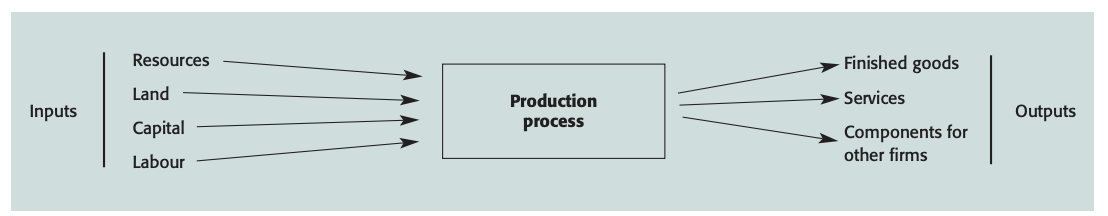
- The degree of value added to the inputs will depend on a number of factors - not all of them operations management issues:
- The design of the product or the nature of the service.
- The efficiency with which the input resources are combined and managed.
- Being able to convince consumers to pay more for the good or service than the cost of the inputs.
Resources
- Production inputs
- Land: water, oil, copper, natural gas, coal, forests, etc.
- Labor: fuel, materials, buildings, equipment, etc.
- Capital: tractor purchased for farming, desks and chairs used in an office, etc.
Ecological, social and economic sustainability - the role of operations management
Ecological sustainability: capacity of ecosystems to maintain their essential functions and processes, and retain their biodiversity in full measure over the long term.
Social sustainability: ability of a community to develop processes and structures which not only meet the needs of its current members but also support the ability of future generations to maintain a healthy community.
Economic sustainability: within a business context, economic sustainability involves using the assets of the company efficiently to allow it to continue functioning profitability over time.