Culture 1: Introduction to Mycenae, Tiryns and Troy
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
When was the Mycenaean age?
1600-1150 BC
When was the early period of the Mycenaean civilisation?
1600-1400 BC
When was the palatial period of the Mycenaean civilisation?
1400-1250 BC
When was the later period of the Mycenaean civilisation
1250-1150 BC
When was the Minoan Age?
3500-1400 BCE
How did the Greeks believe that Mycenae was founded?
They believed that Perseus, the man who killed Medusa, founded it. They believed that cyclopses helped him, since no humans could build such huge stuctures.
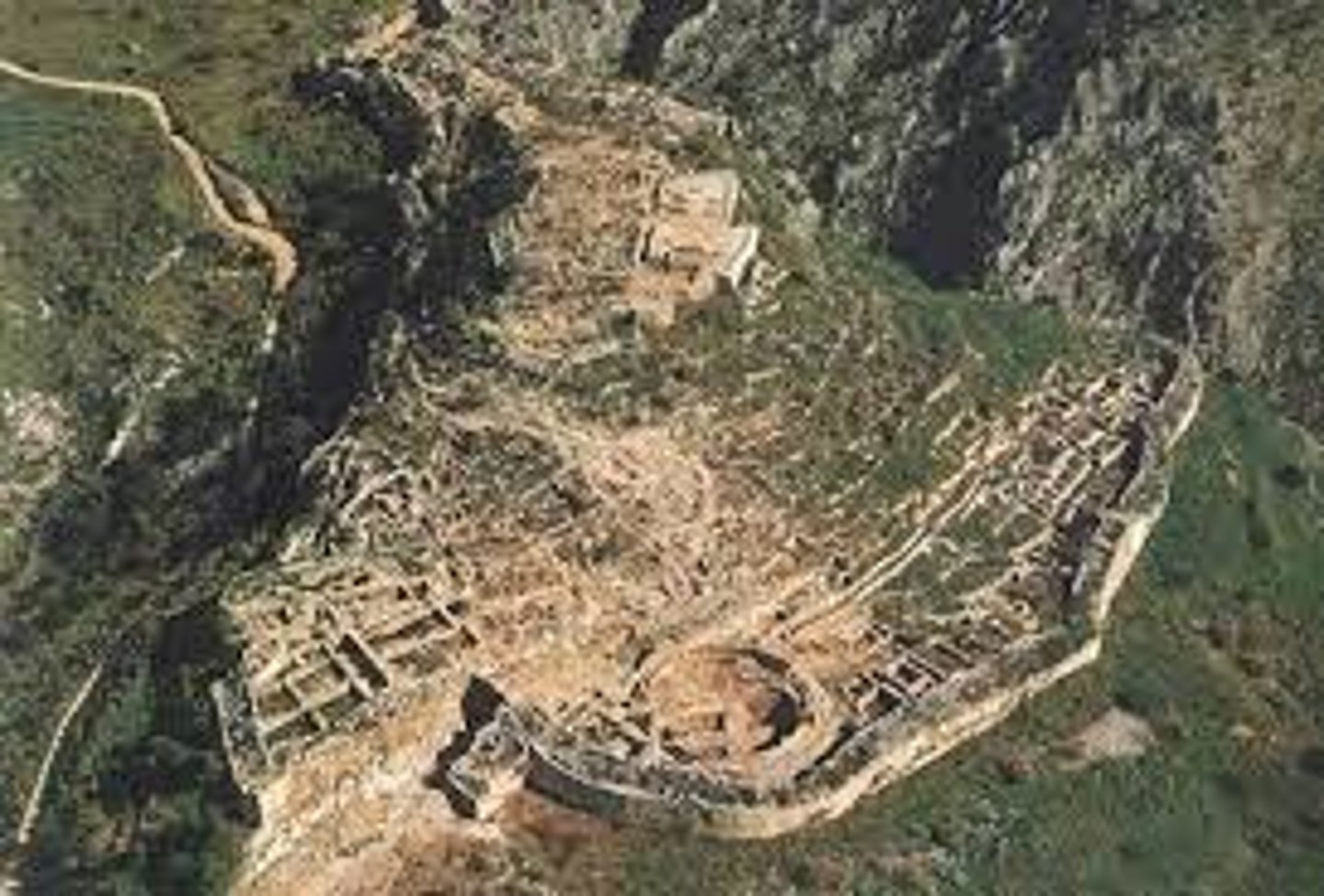
Where was Mycenae?
On a hill on the Greek mountains, in the northeast Peloponnese. The top of the hill was artificially levelled. It overlooked a fertile plane. There were two other hills on the North and South, providing natural fortifications. It was about 15km from the sea.
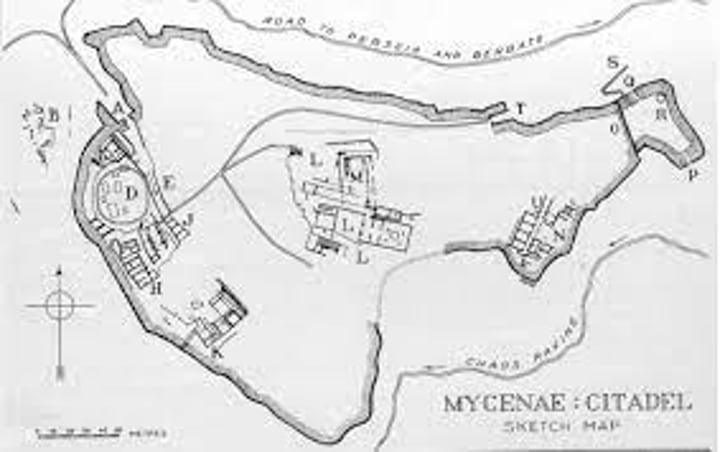
What were the cyclopean walls like?
The cyclopean walls were up to 12m high and from 3.5-7m thick. They made a 900m circuit of the city. Larger, regularly shaped bricks were put on the outside and earth and rubble was in the centre.
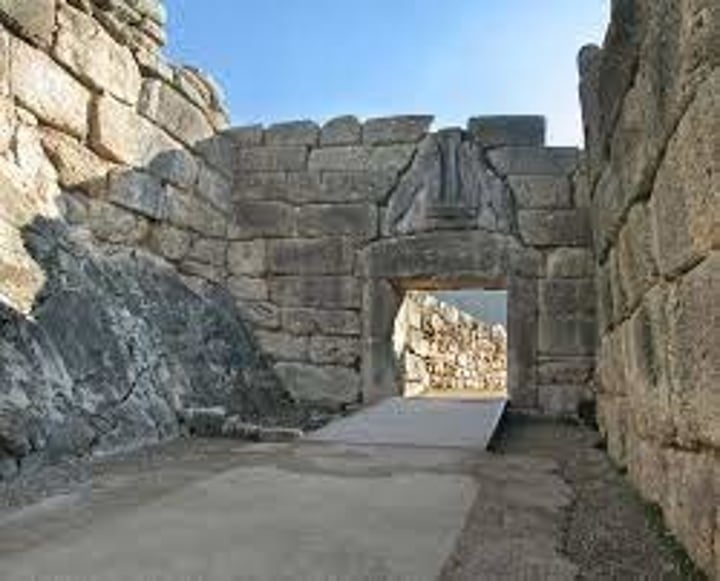
Lion gate
The main entrance to Mycenae. In the triangle created by a corbel arch two lions are carved in relief. Their heads have not survived. The gate was at the top of an uphill slope, in order to tire out attackers.

Sally ports
A gap in the outer wall through which defenders could rush out and surprise attackers.
Corbelling
technique in which each course of stone projects slightly beyond the one below, used to span a gap between two structures and create a vaulted roof.
Mycenae underground cistern
A large tank of water 18 m underground. If attackers laid siege to the city then the Mycenaeans could still have a large supply of water. It collected water through a series of pipes in the roof. The passage leading to the cistern shows an example of corbelling.

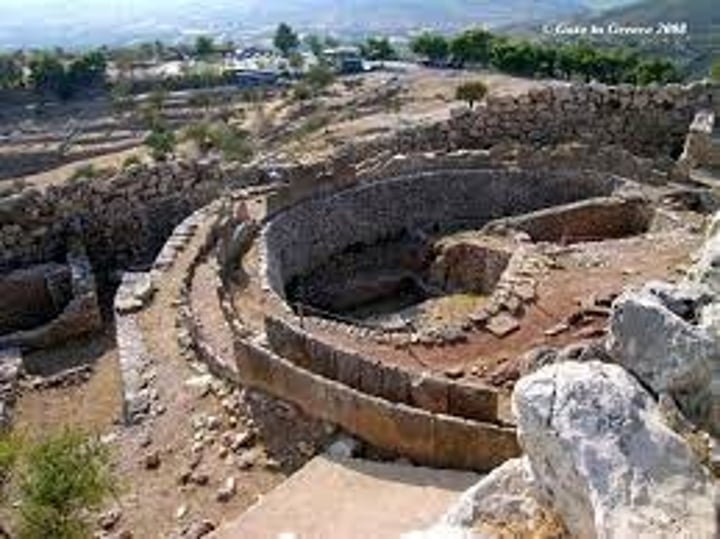
Grave circle B
The earlier grave circle, located 200m outside of Mycenae. It contains 24 graves from the 16th and 17th centuries BC. It is enclosed with a stone wall, diameter 28m. Just over half of the graves are thought to have been for members of the royal family. Around 35 bodies have been found there. Males were marked with carved stelai and females with uncarved ones.
Grave circle A
Situated in the South-West of the city. Also 28m in diameter. It contained six shaft graves and was also thought to be the graves of royalty. The bodies buried there were buried with gold, silver, glass and ivory. Later, when the lion gate was built, it was rebuilt with a new wall and the level of the ground was raised.

Stele
A carved stone slab used to mark graves or to commemorate historical events.
When was Tiryns built?
13th-15th century BC (approximately)
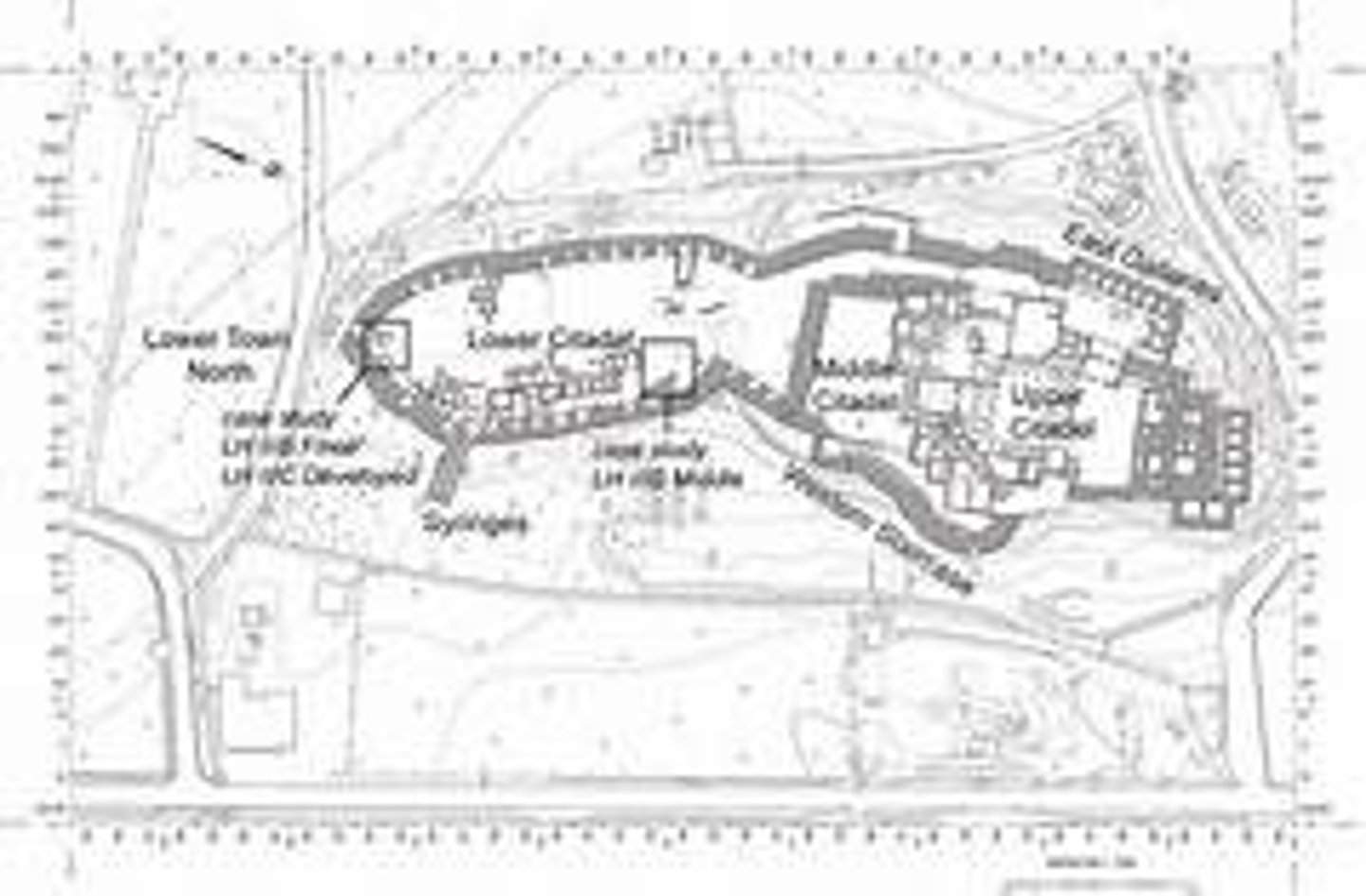
Where was Tiryns?
East Peloponnese, Greece. It was 1km away from the was built on the highest ground in the surrounding area.
When was Mycenae built?
17th-11th century BC (approximately)

Tiryns cyclopean walls
Around 10m tall
Tiryns Palace
Built on the highes part of Tiryns, in the upper city, which was protected by its own walls. A grand entranceway led to the megaron. The central hearth was surrounded bu four wooden pillars, whose bases still survive. The plastered floor had images of octopi and dolphins and the walls were also covered with frescoes.
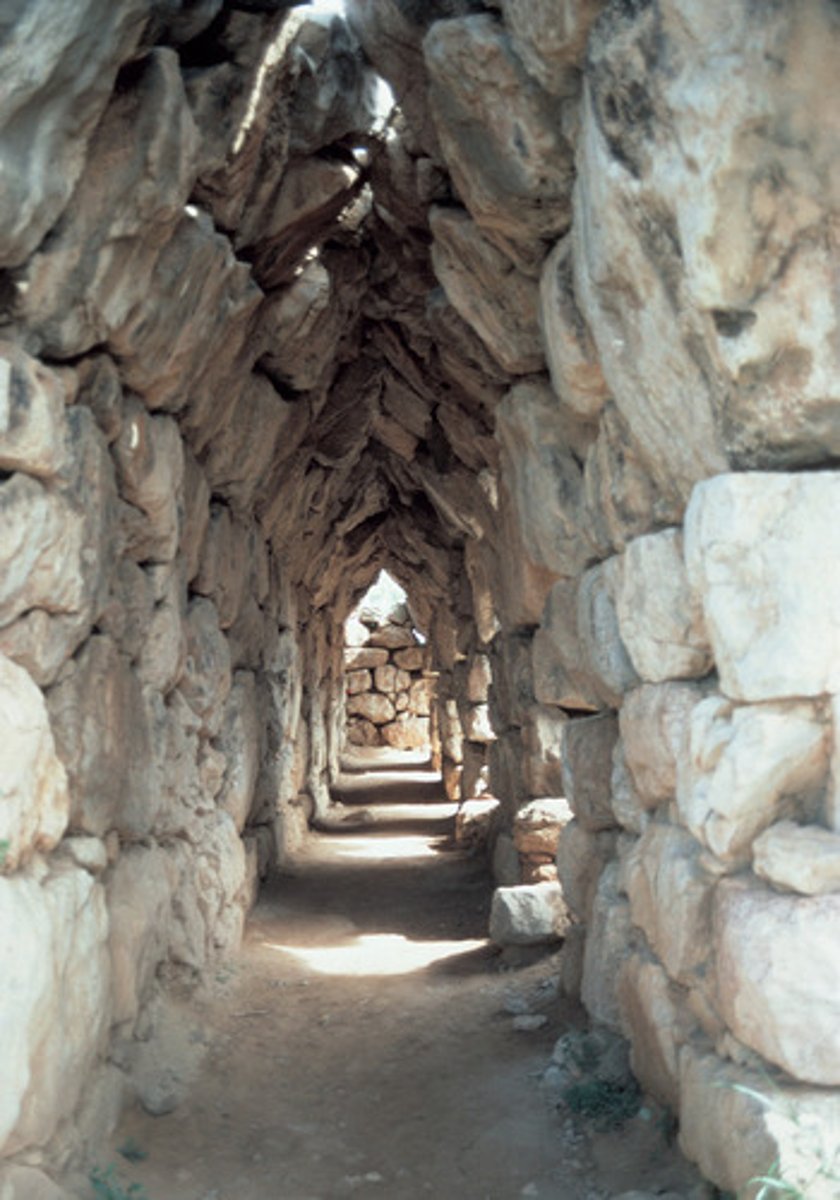
Tiryns galleries
They were built into the outer walls of the city. They used corbelling. Some were up to 30m long. Leading off of the galleries were a large number of rooms.

Reasons that troy VI was the site of the Trojan War (4)
It was destroyed around 1250 BC, similar to the dates of the Trojan War
It was a rich city with numerous wealthy houses
The walls were over 7m tall, and the Iliad refers to the high walls of Troy
The walls seem to have towers, also featured in the Iliad.
Reasons that troy VI was not the site of the Trojan War
It is believed to have been destroyed in an earthquake, not a fire like ancient literature suggests
Reasons that Troy VIIa was the site of the Trojan War (7)
It only existed for 30-40 years
Also had large towers
Crowded, single-story houses built in a hurry fits with the idea of emergency housing built for the Trojans whilst the Greeks attacked
Storage jars had been sunk deep in the ground, possibly for storing up food whilst under siege.
It was destroyed nu a fire, like in ancient literature
Partial human remains, possibly killed in a fire, have been found
Three bronze arrows have been found.
Reasons why Troy VIIa wasn't the site of the Trojan War
Crowded houses suggest a poor city, unlike the one described by Homer.
The sunken jars possibly don't indicate a siege, just a lack of space for food storage.
Tombs of Clymnestra and Aegisthus and Treasury of Atreus
Built in the 14th century BC. They were tholos tombs and not acrually the tombs of Clymenestra and Aegisthus- that was just their names given by relatively recent visitors. It is possible, but unlikely, that it was actually Aterus’ tomb. They are all a little outside of Mycenae. The tombs of Clytemnestra and Aegisthus each have a diameter of 13m. They had all been robbed of their treasure before archeologists found them.
