AP Biology: Plants and Kingdoms
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
monocotyledons
Plants with one seed leaf.
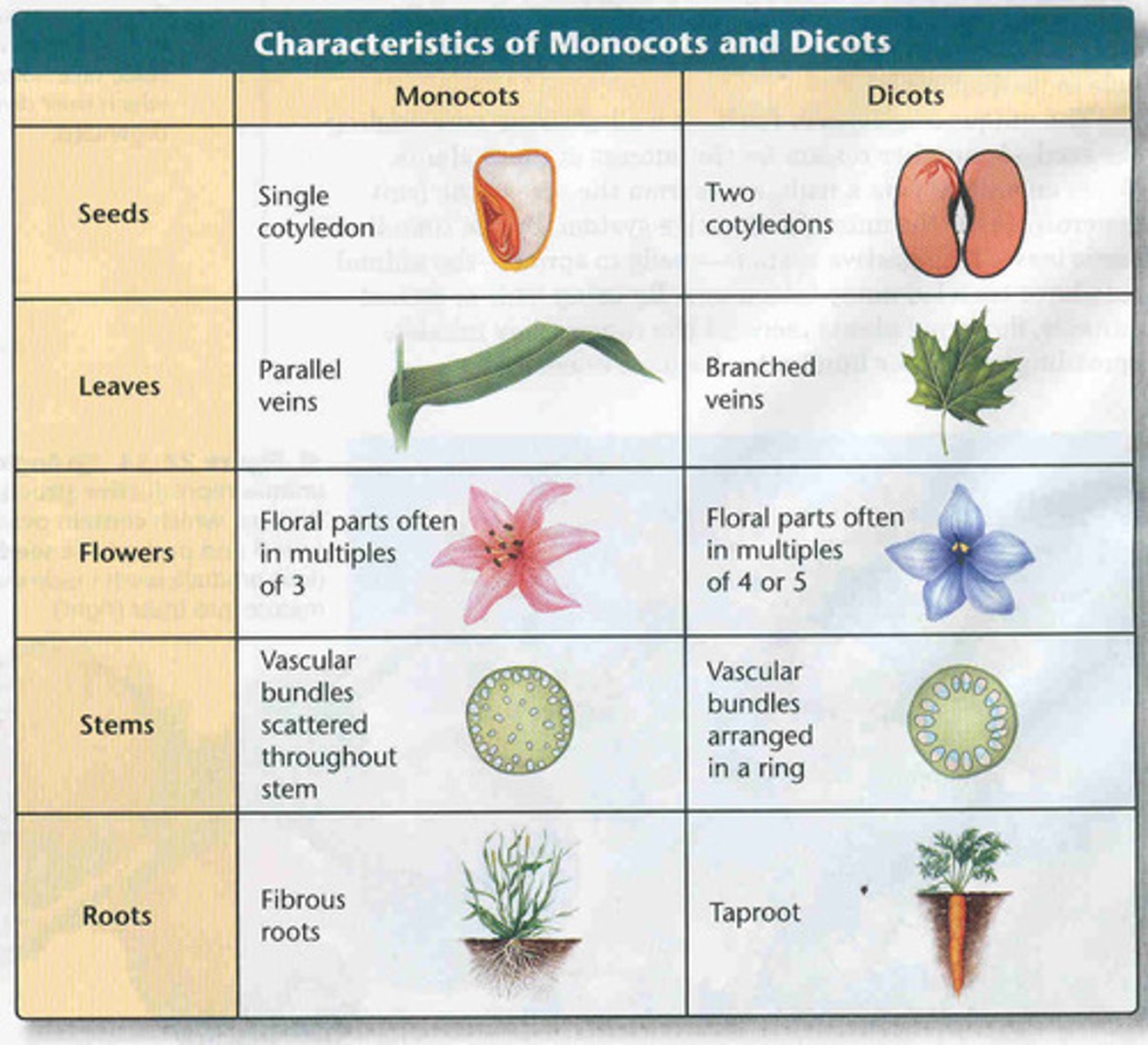
Dicotyledon
a plant that has two seed leaves or cotyledons

biofuel
Liquid fuel created from processed or refined biomass

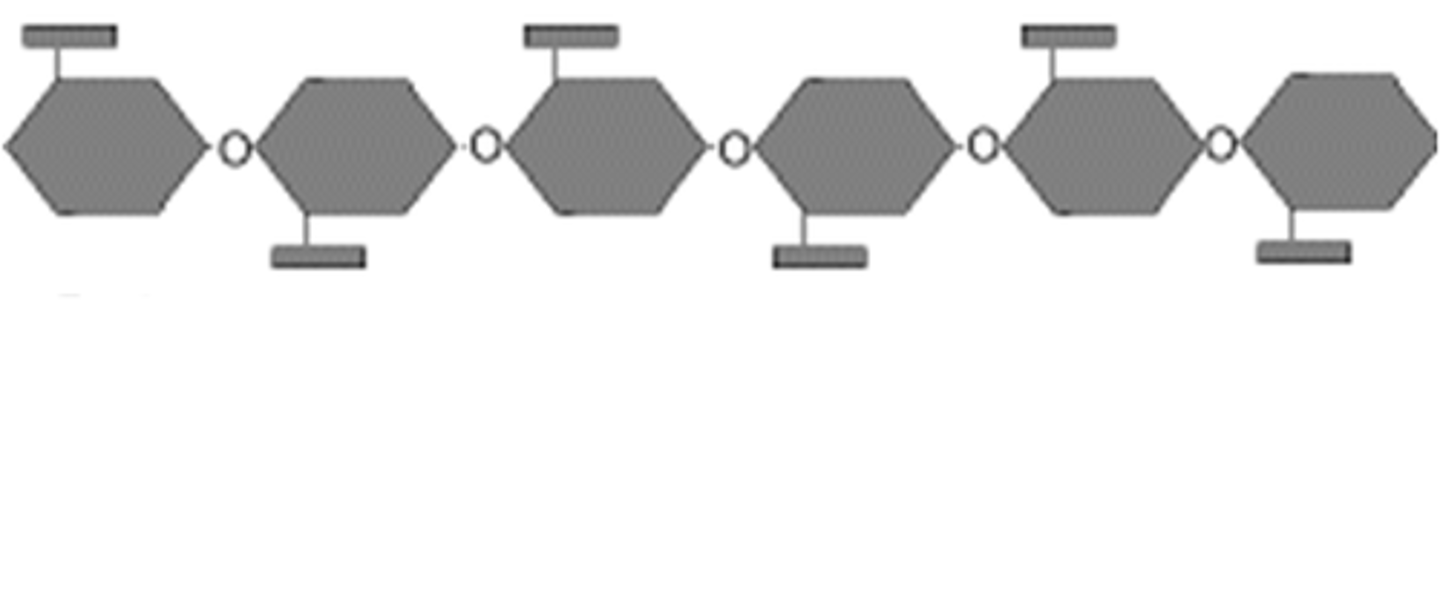
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
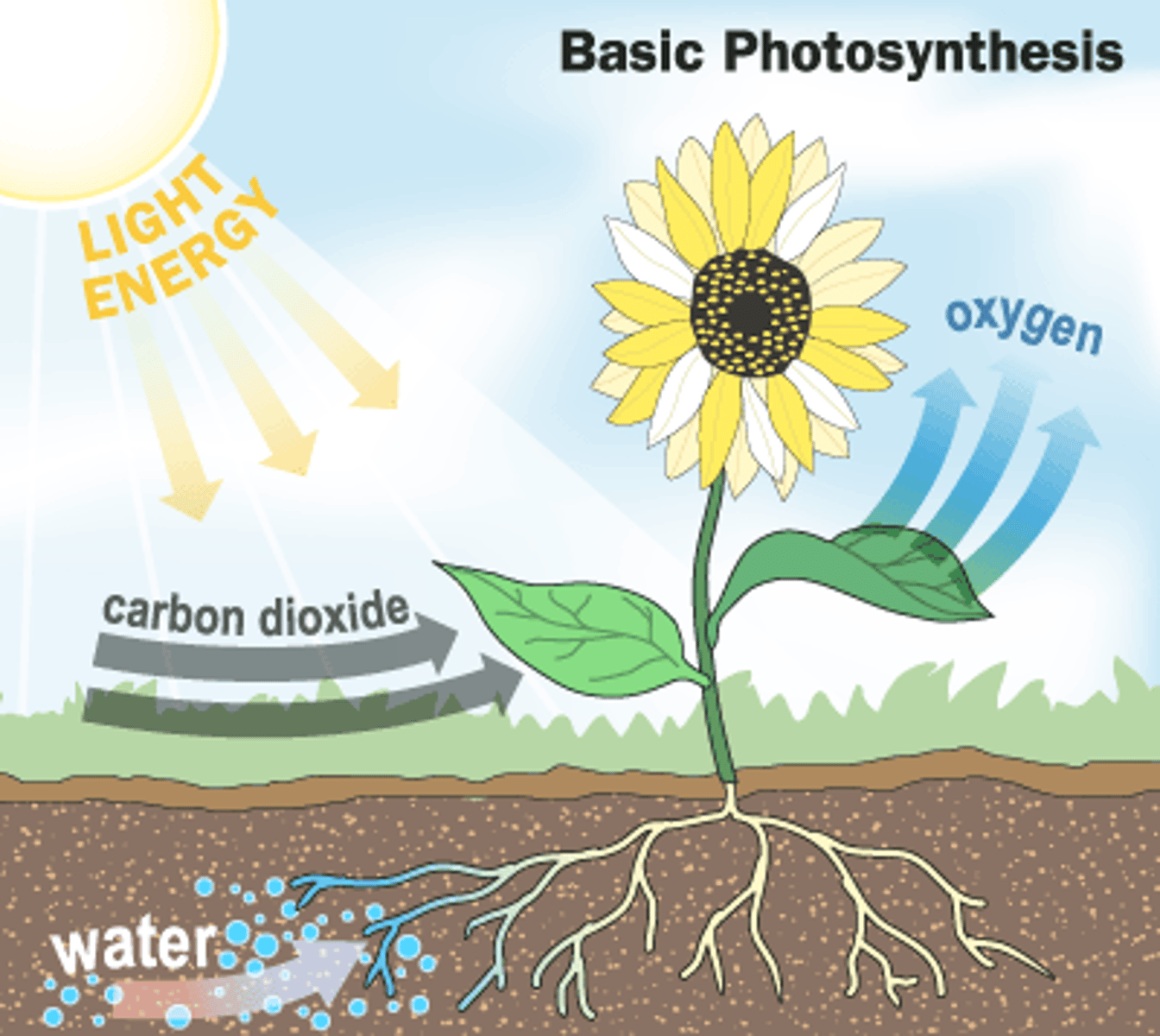
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy.
sustainable agriculture
Farming methods that preserve long-term productivity of land and minimize pollution, typically by rotating soil- restoring crops with cash crops and reducing in-puts of fertilizer and pesticides.

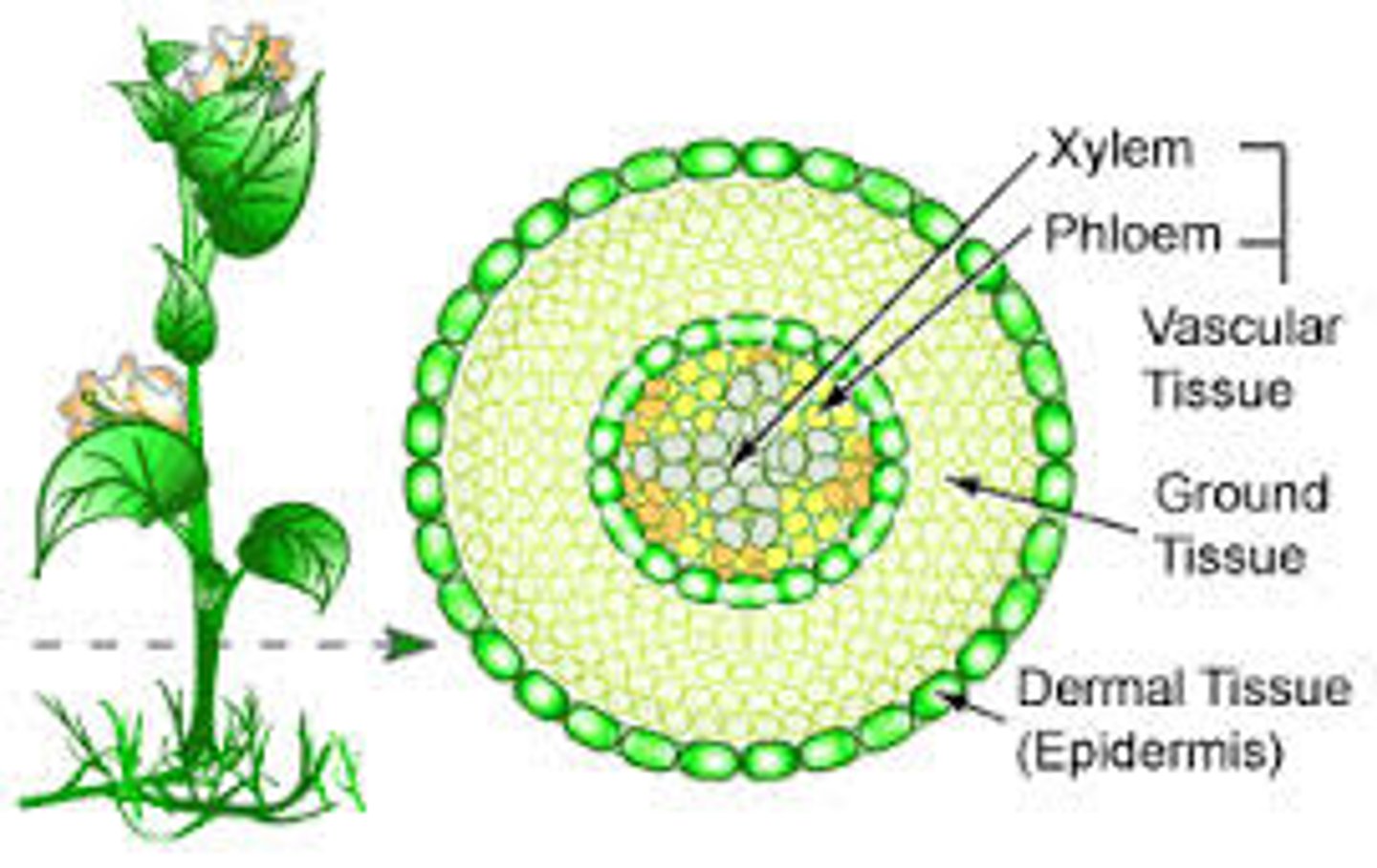
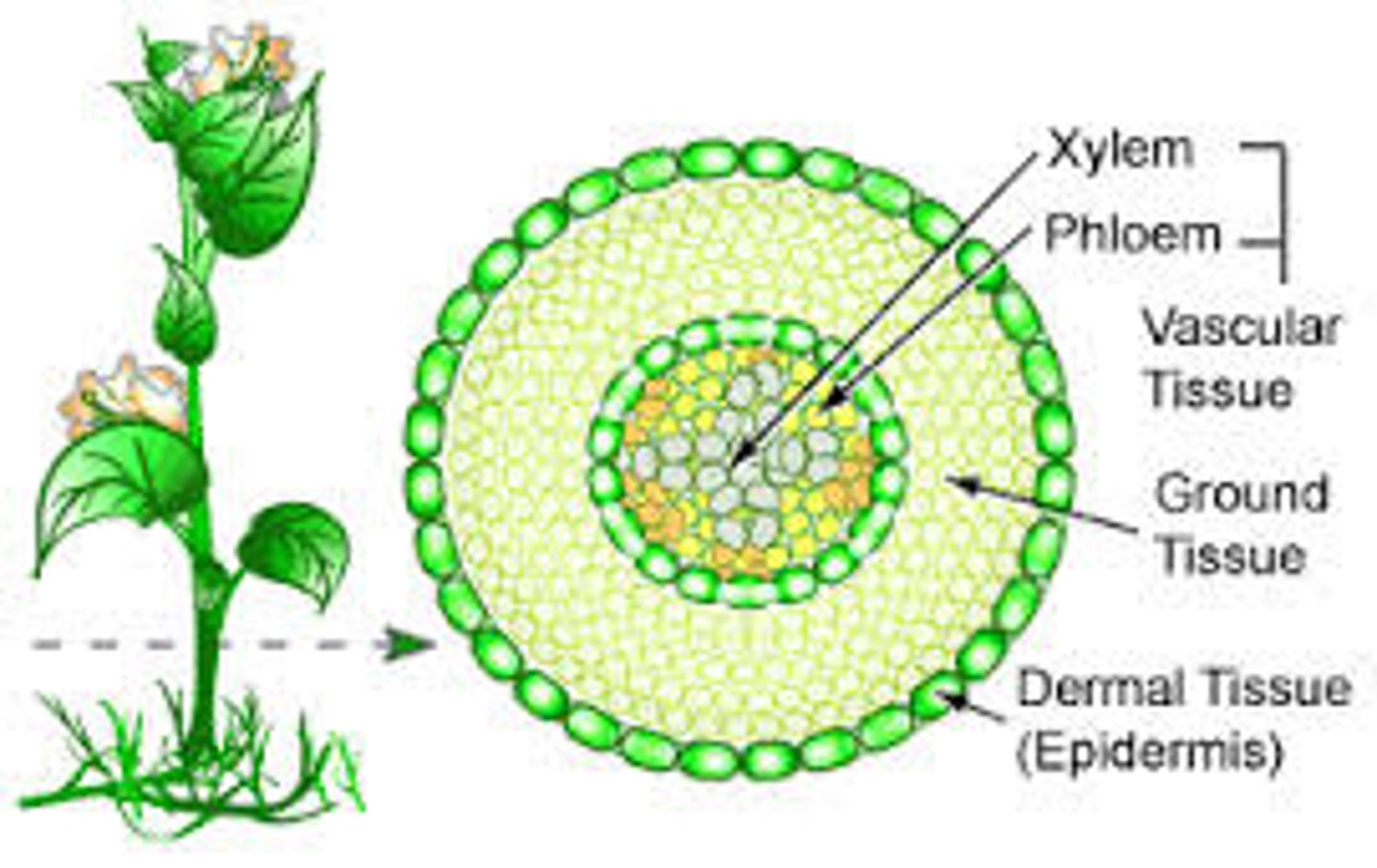
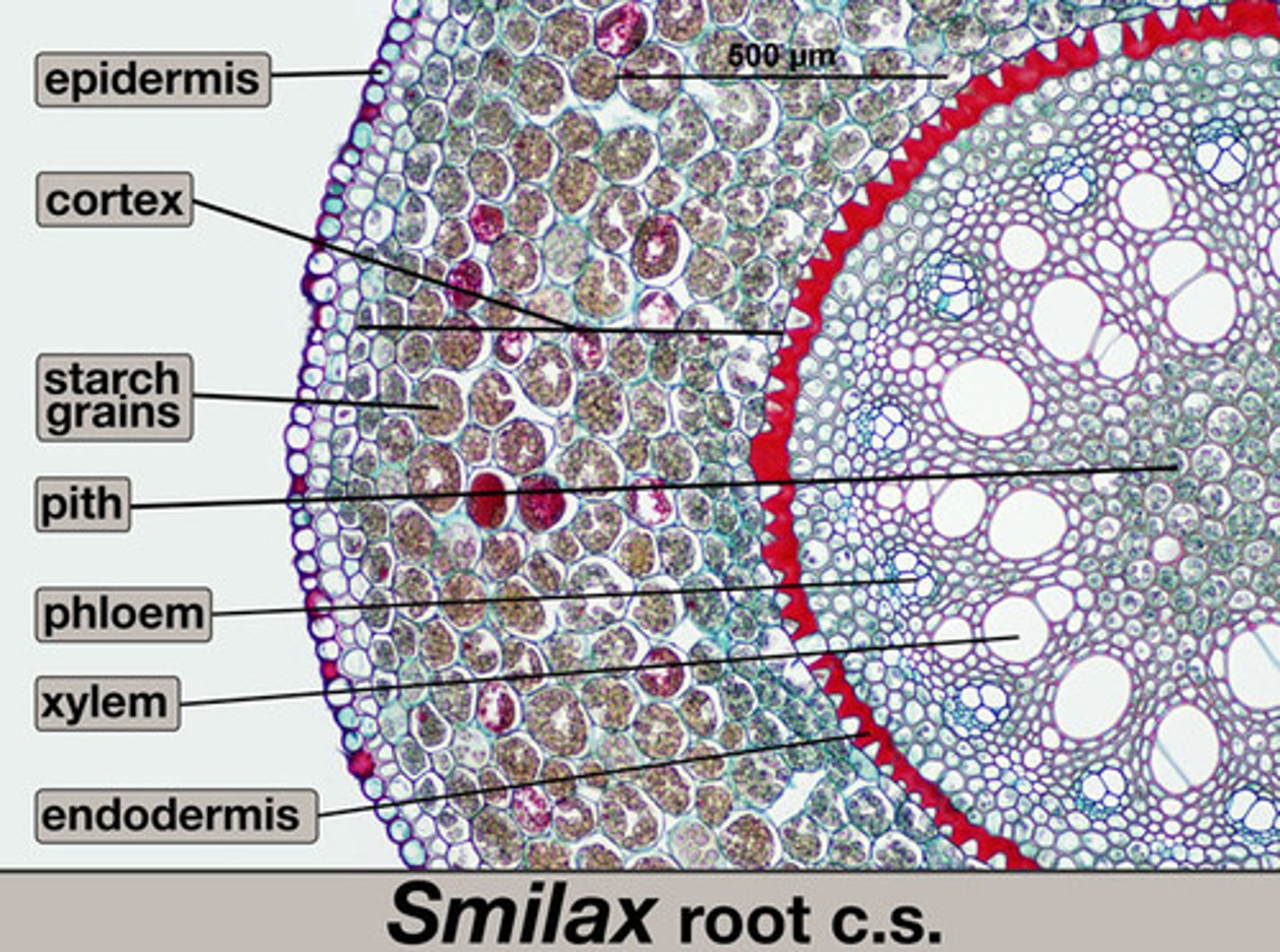
dermal tissue
tissue of the plant that makes up the waxy outer layer of the plant
plant epidermis
outermost layer of flattened cells that covers and protects all parts of the plant
ground tissue
tissue system that makes up the majority of a plant
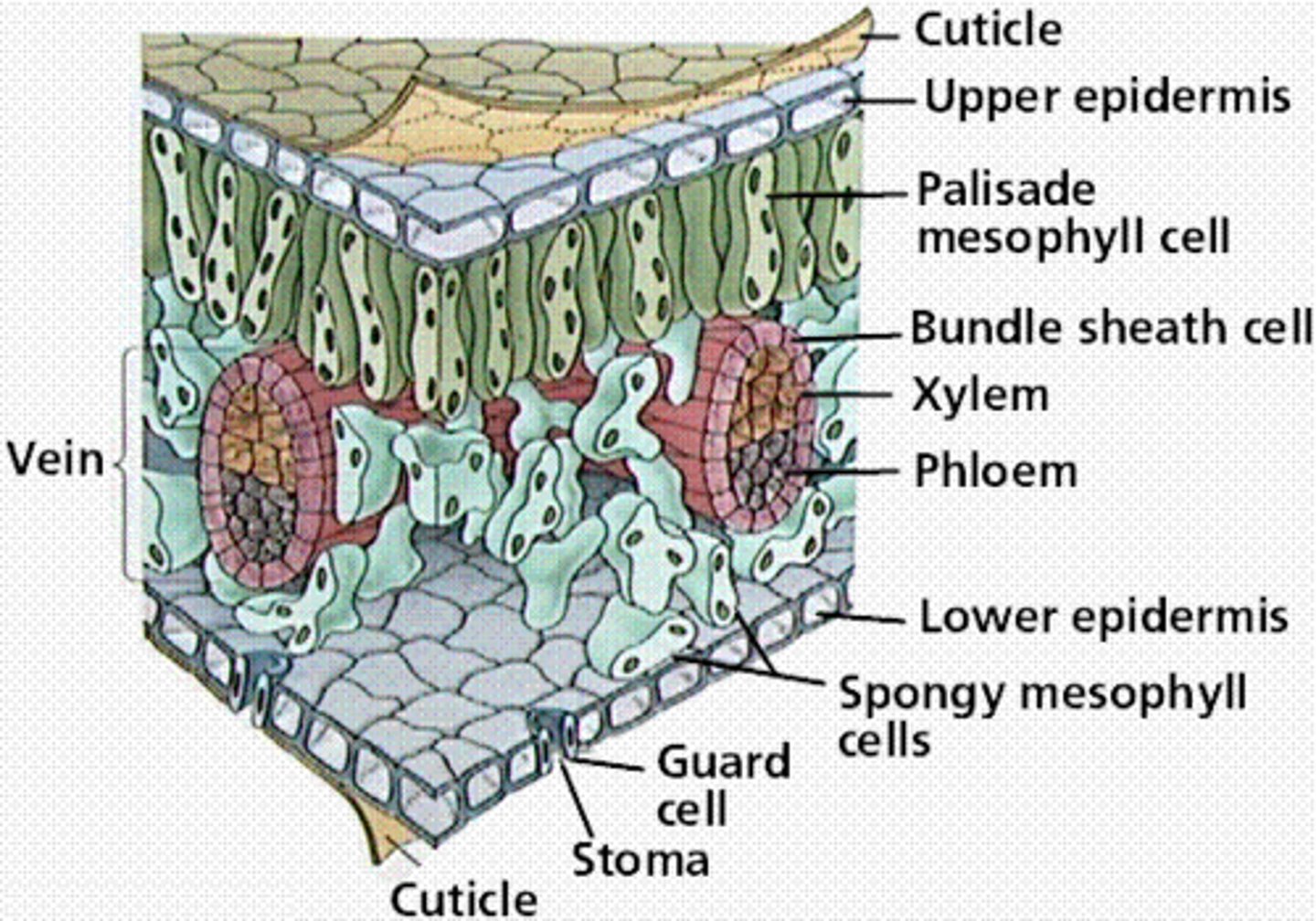
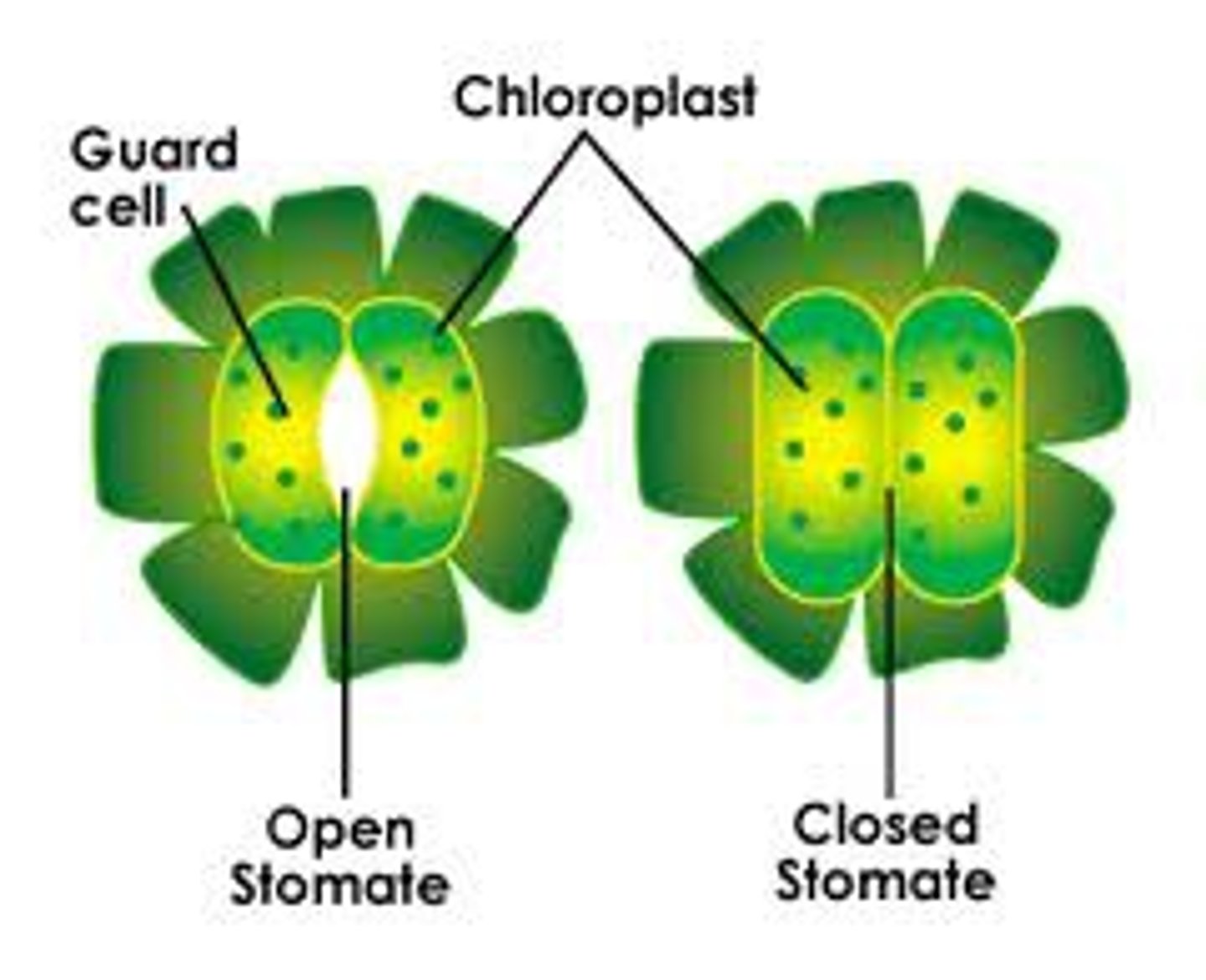
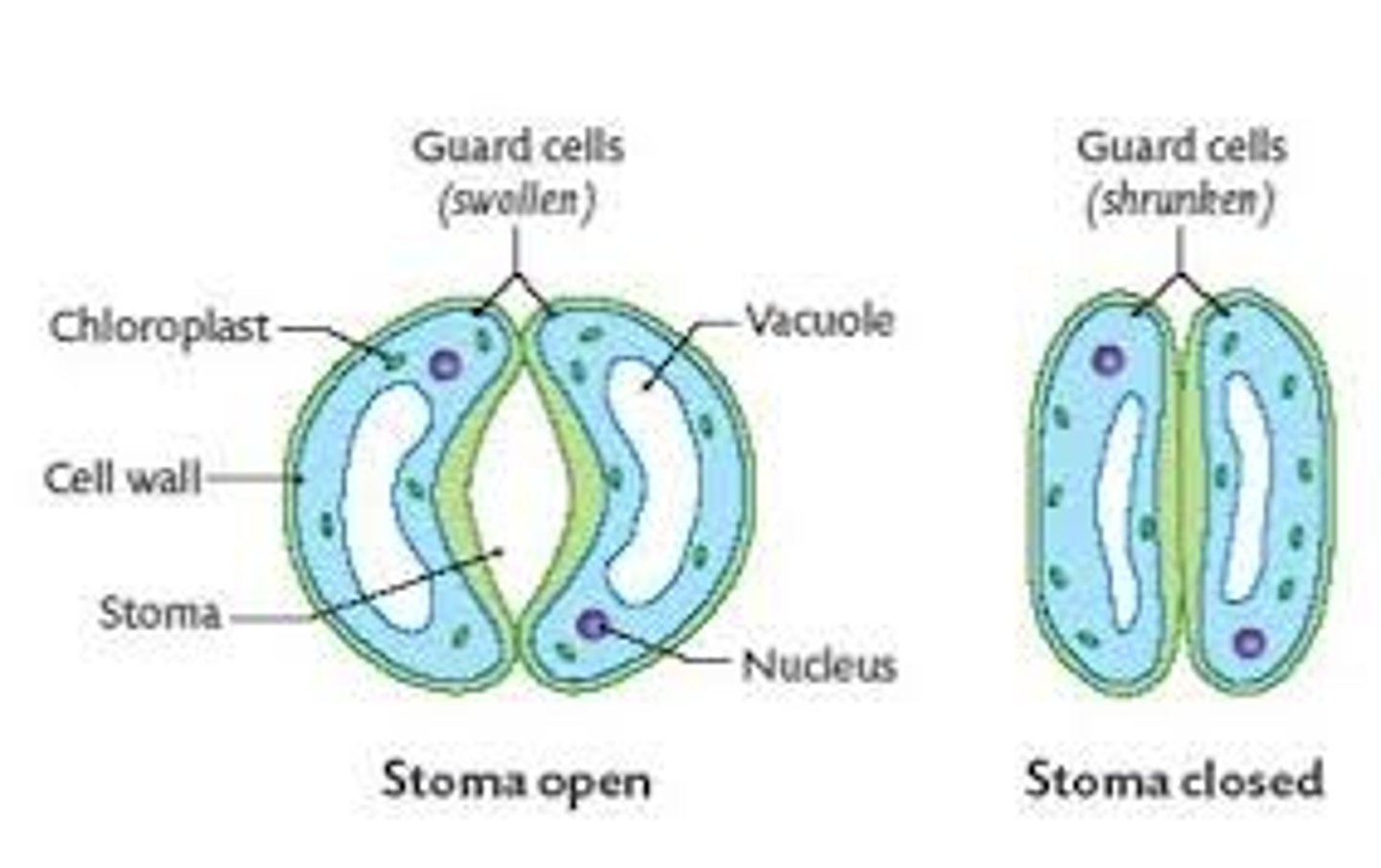
guard cell
Pairs of cells that surround stomata and control their opening and closing.
meristematic tissue
plant tissue found only in the tips of shoots and roots; responsible for plant growth

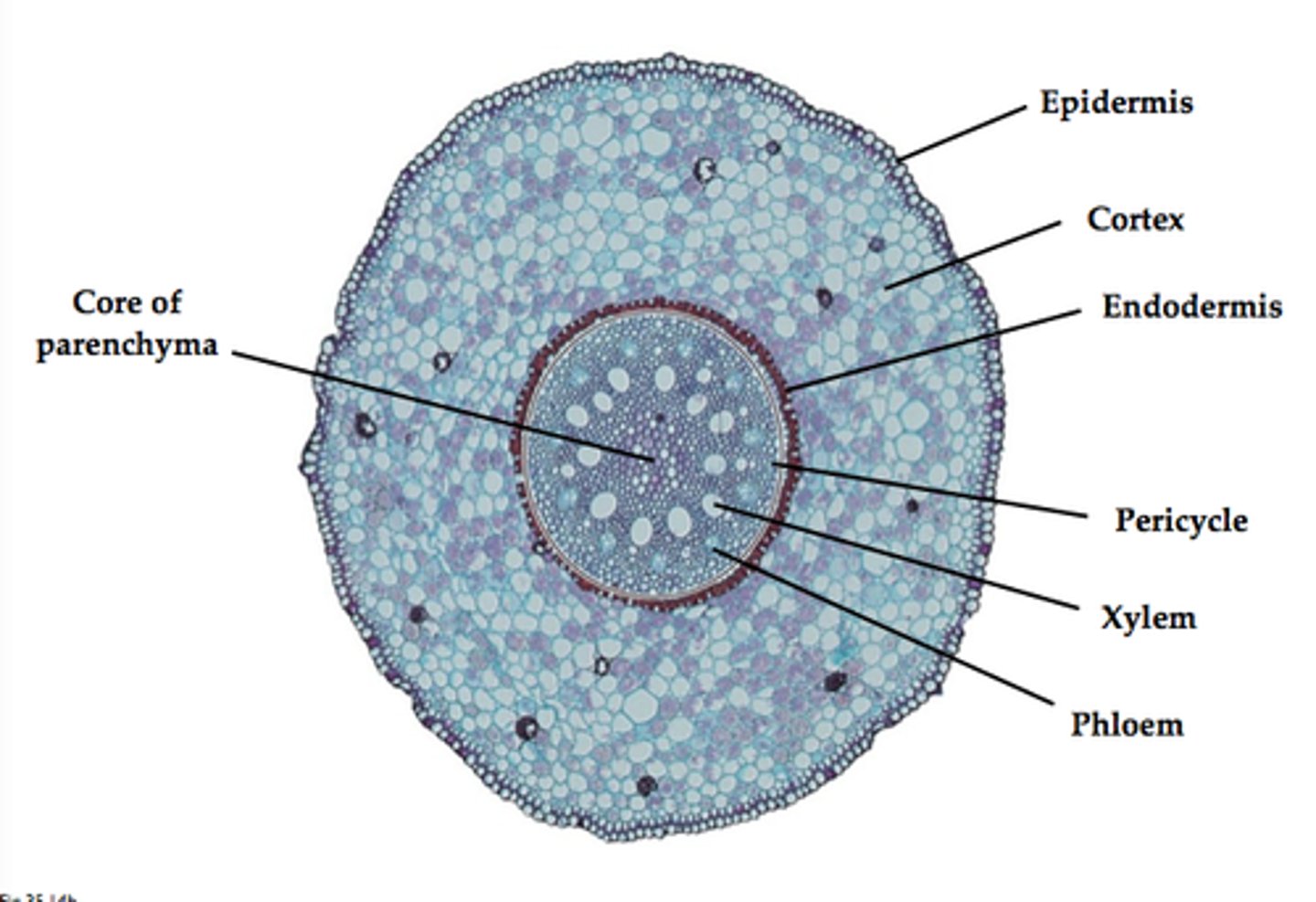
phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
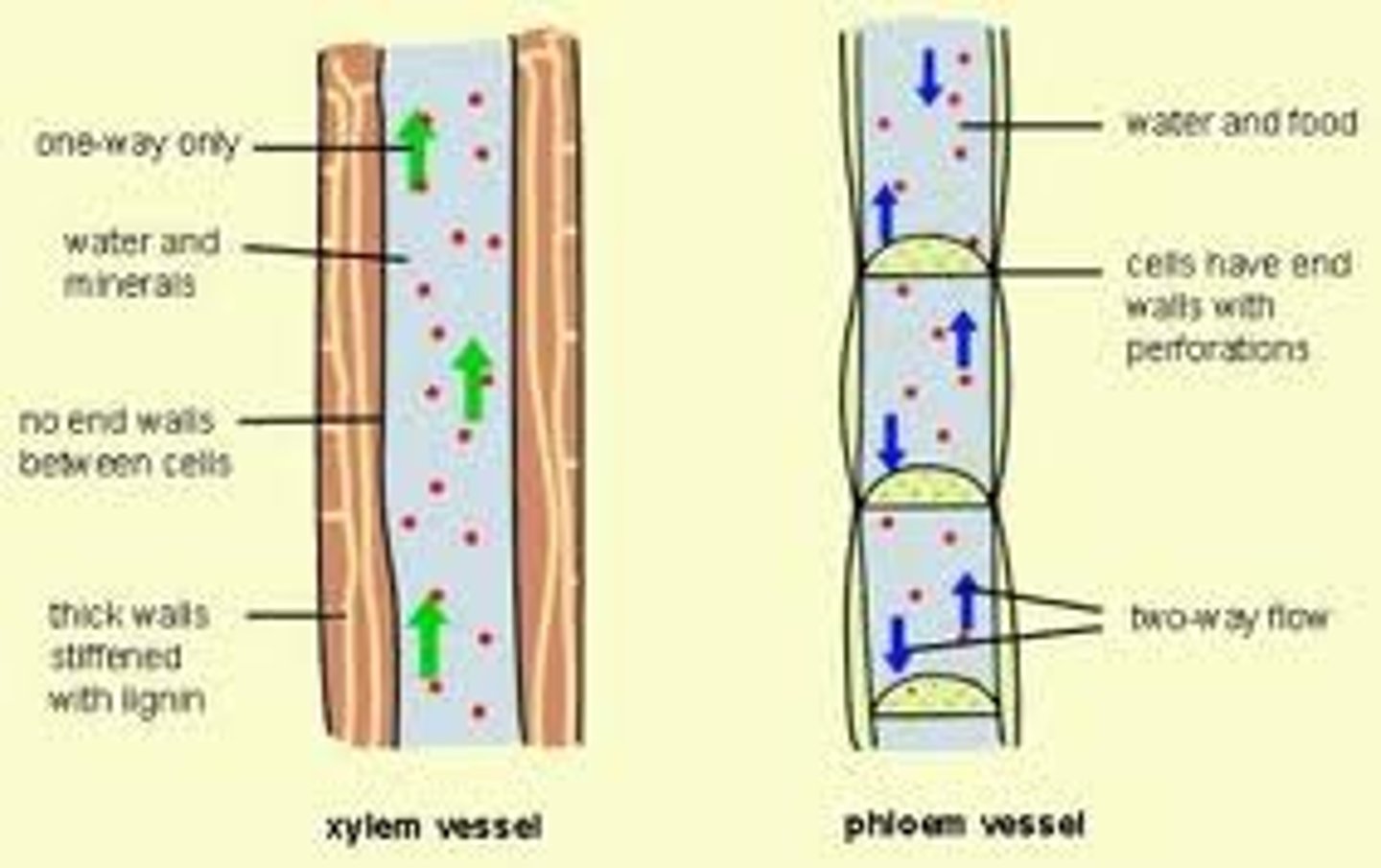
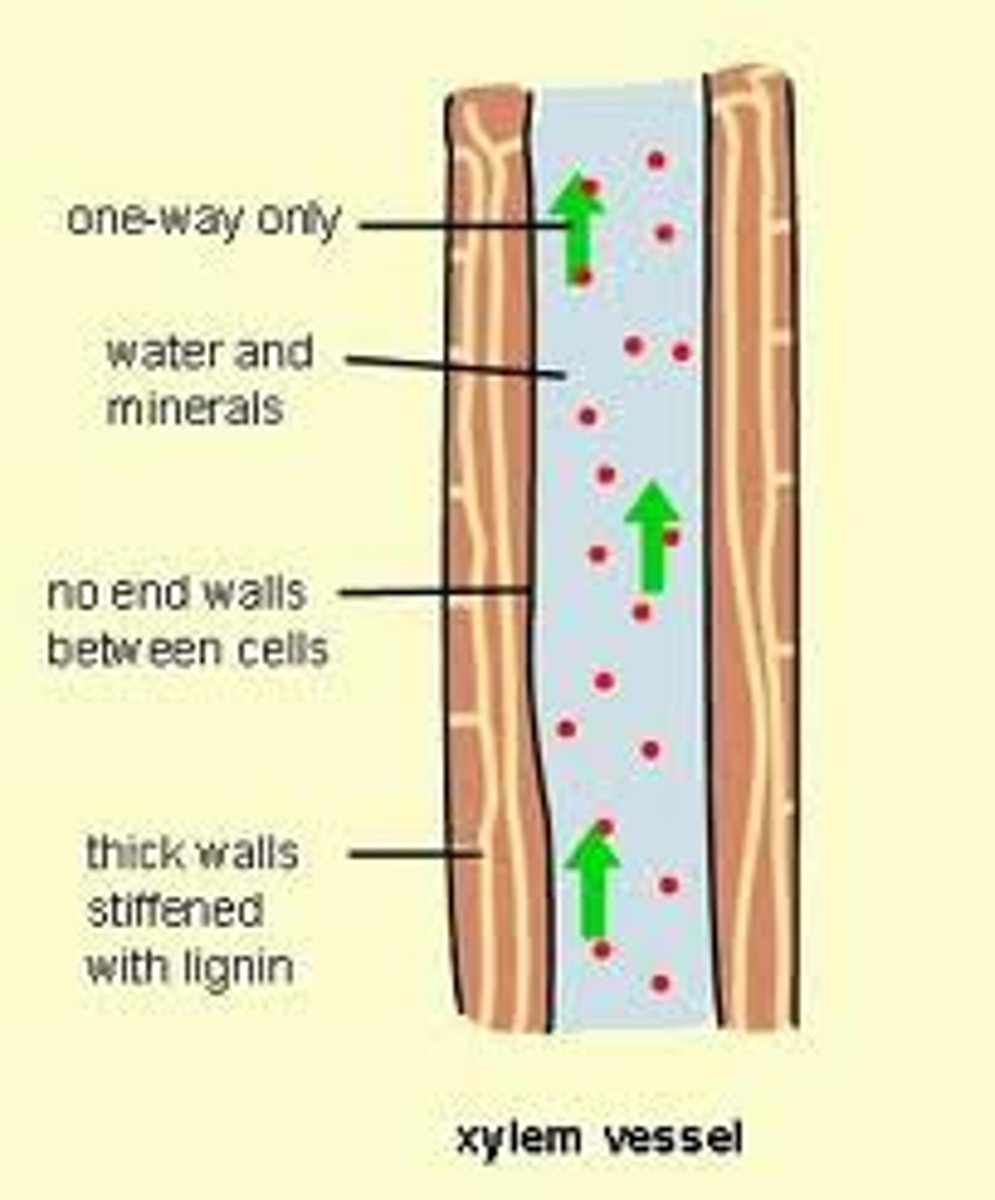
xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
stoma of plants
entrance to the plant that opens and closes for gas exchange
controls water loss
when open water leave and co2 enters, this dehydrates the plant
shoot system
The aerial portion of a plant body, consisting of stems, leaves, and (in angiosperms) flowers.
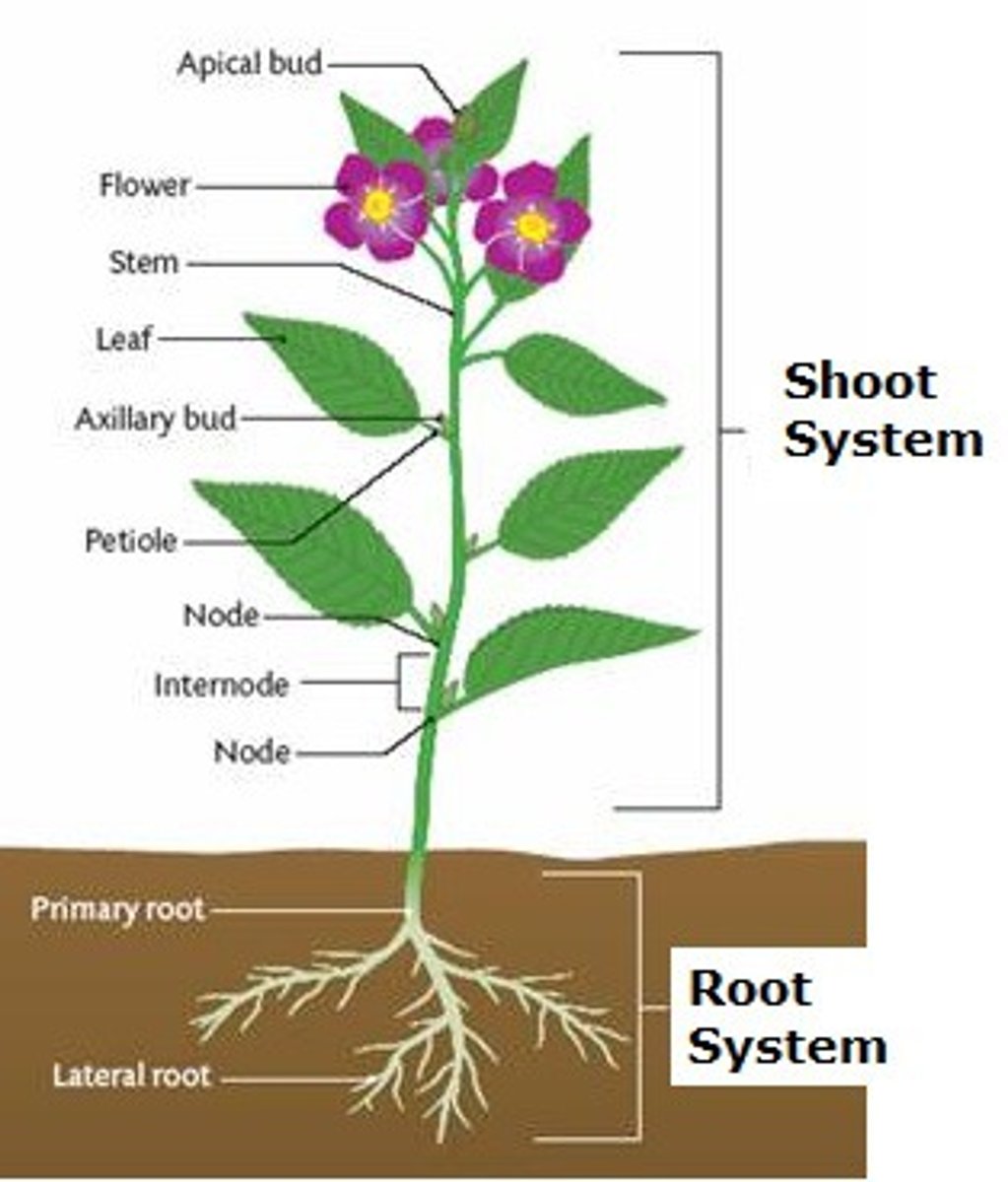
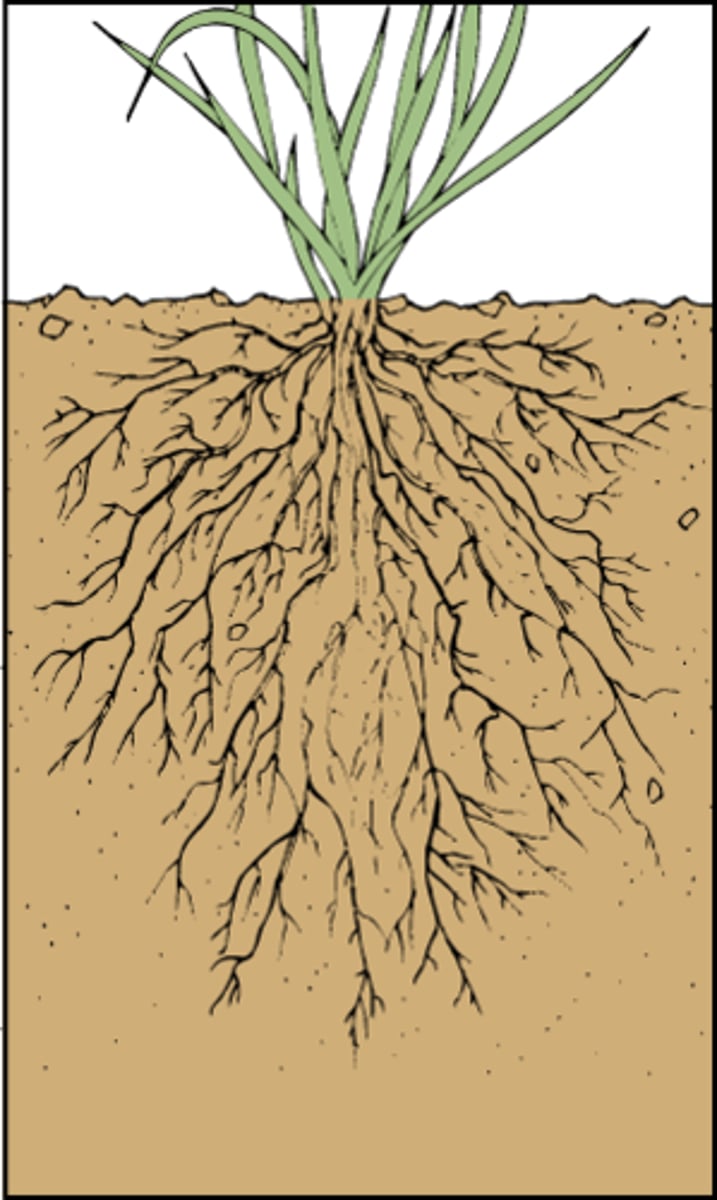
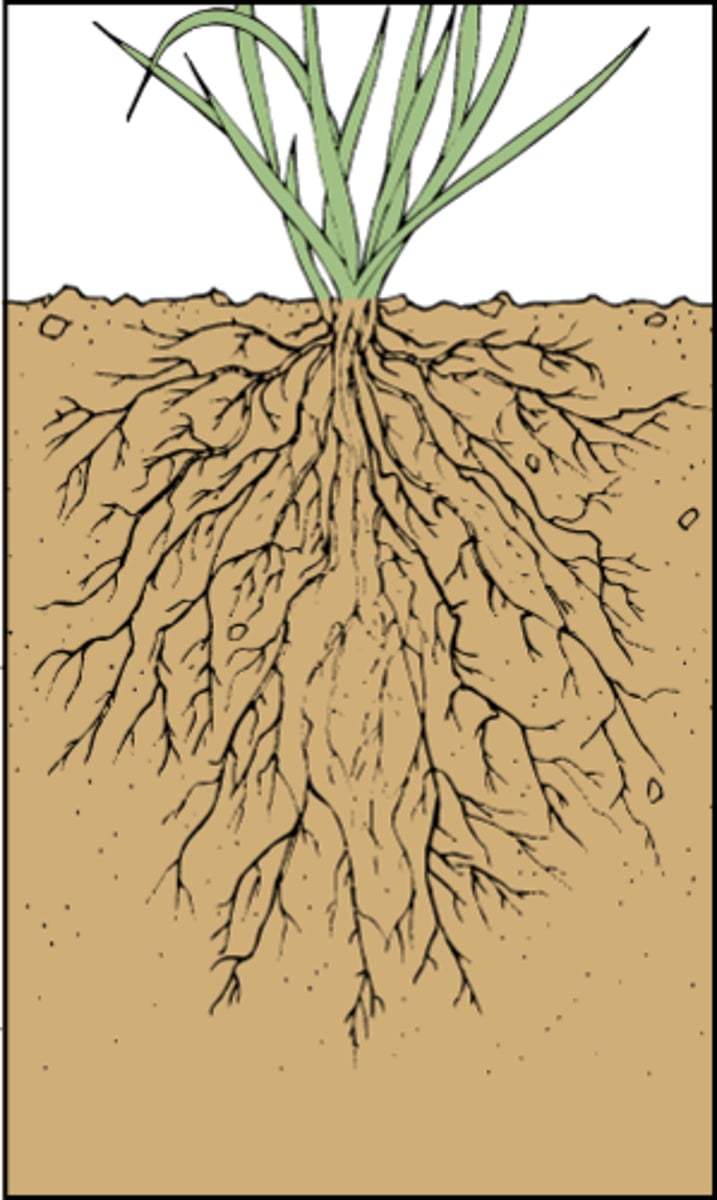
root system
All of a plant's roots, which anchor it in the soil, absorb and transport minerals and water, and store food.
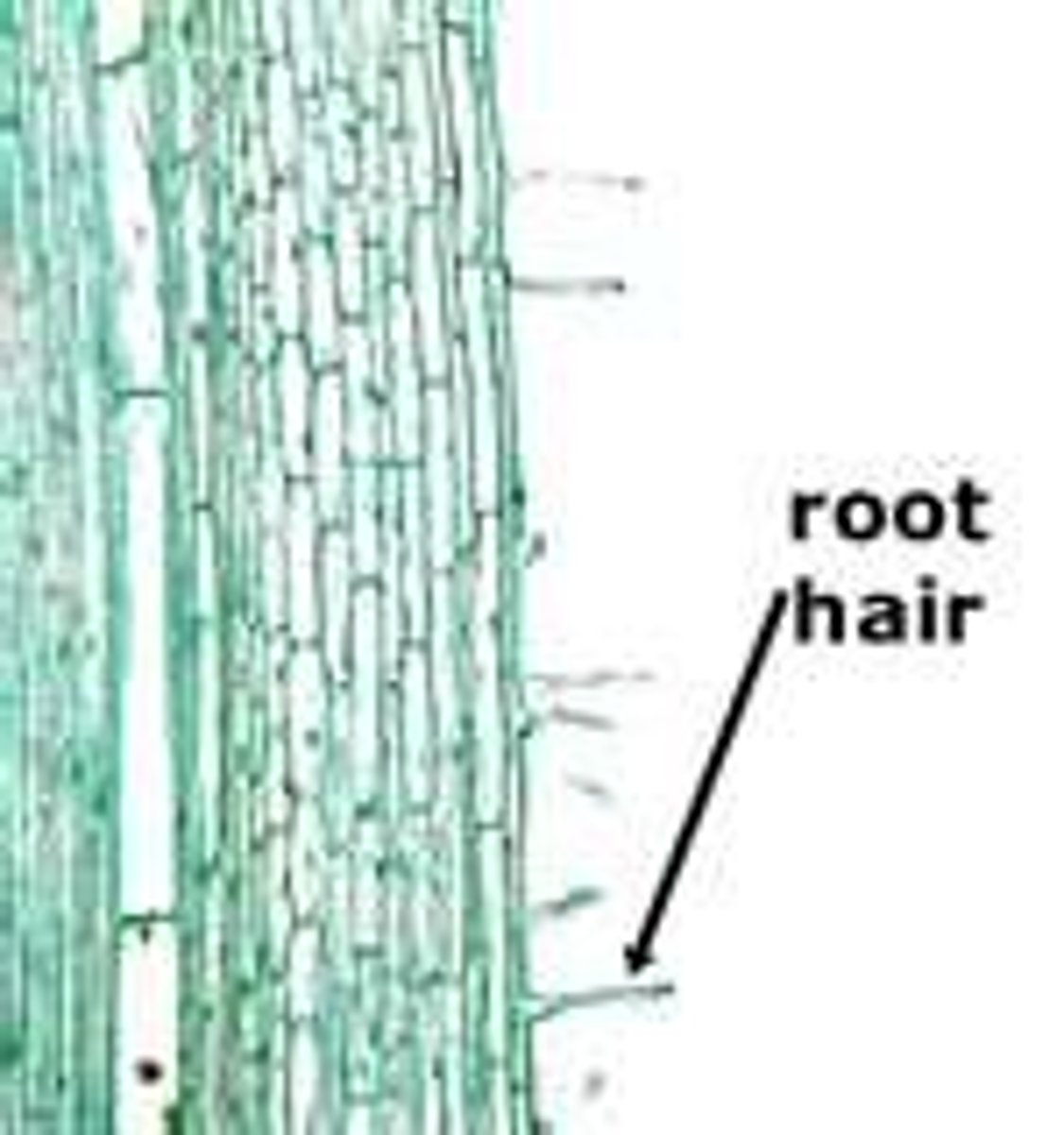
root hairs
tiny hair-like extensions that increase the surface area of the root allowing it to absorbs more water and nurtients
roots
Absorbs water and minerals from the ground. Anchors plant in ground.
aerenchyma
a soft plant tissue containing air spaces, found especially in many aquatic plants
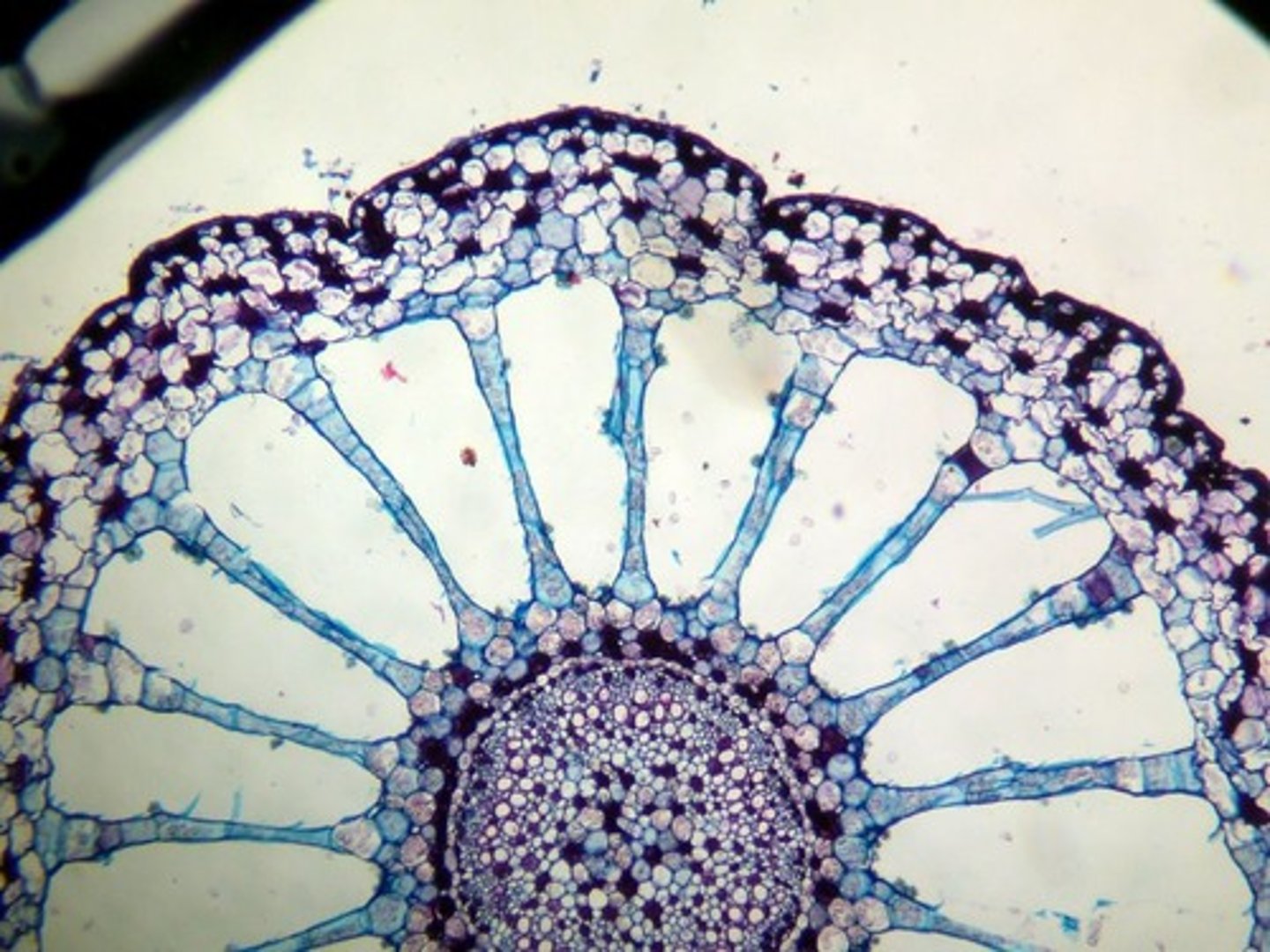
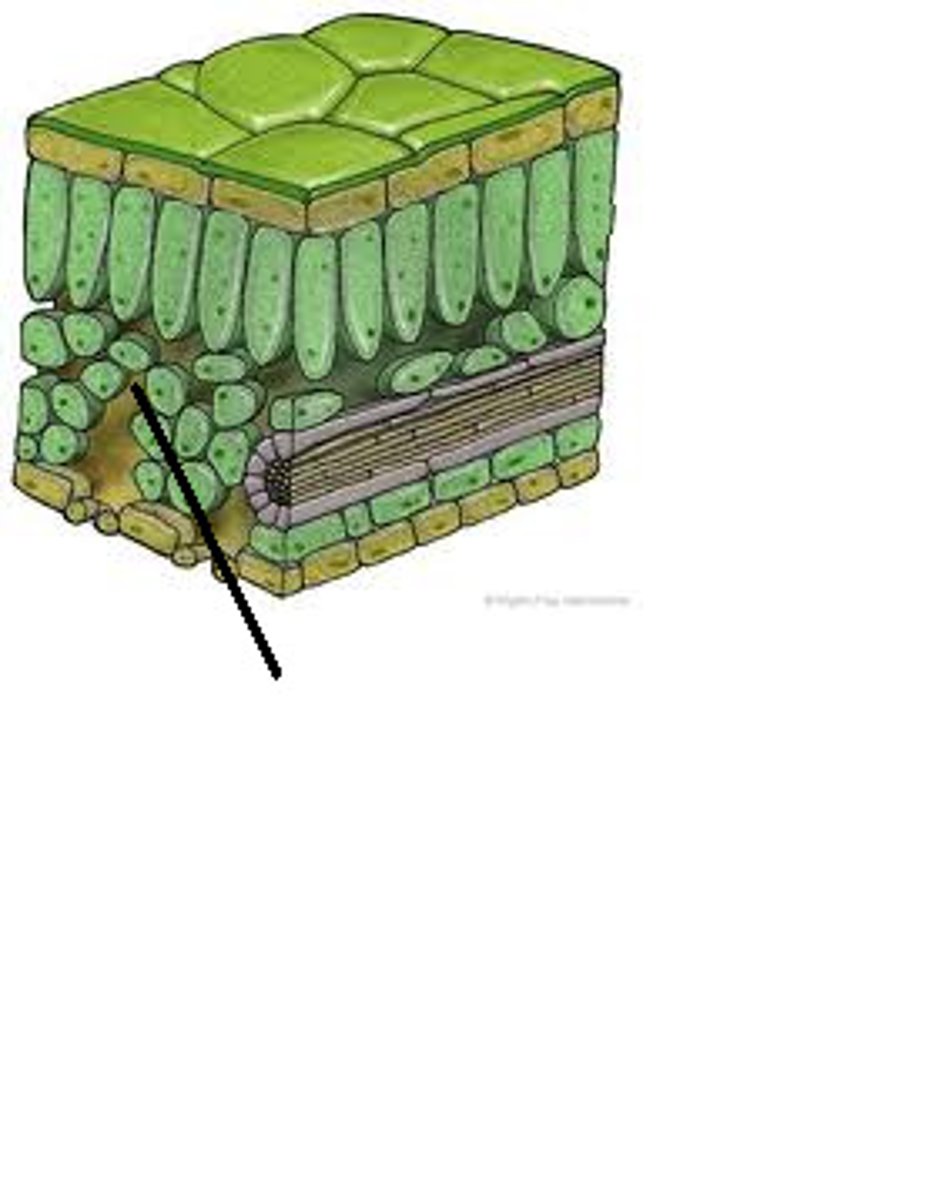
Cortex (plants)
layer below the epidermal layer; composed of ground tissues; water and nutrients move through this layer on the way to vascular tissues
cuticle
A waxy covering on the surface of stems and leaves that acts as an adaptation to prevent desiccation in terrestrial plants.
endodermis
The innermost layer of the cortex in plant roots; a cylinder one cell thick that forms the boundary between the cortex and the vascular cylinder.
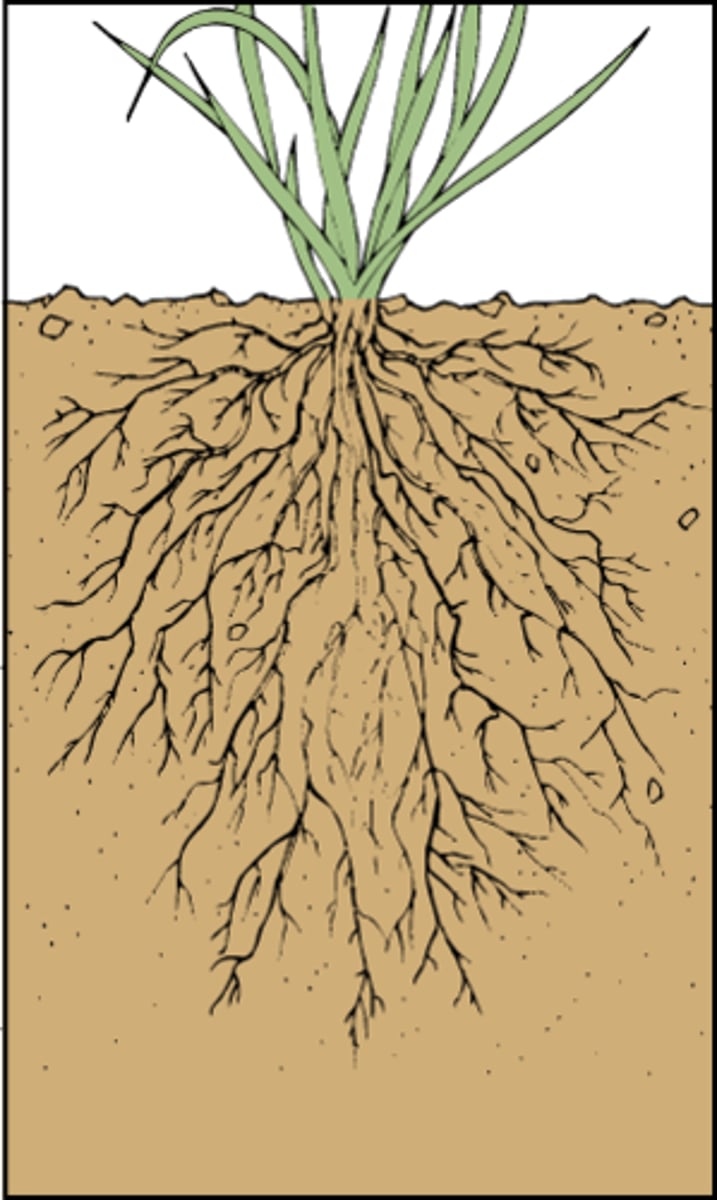
fibrous root
part of a root system in which roots branch to such an extent that no single root grows larger than the rest
mesophyll
The ground tissue of a leaf, sandwiched between the upper and lower epidermis and specialized for photosynthesis.
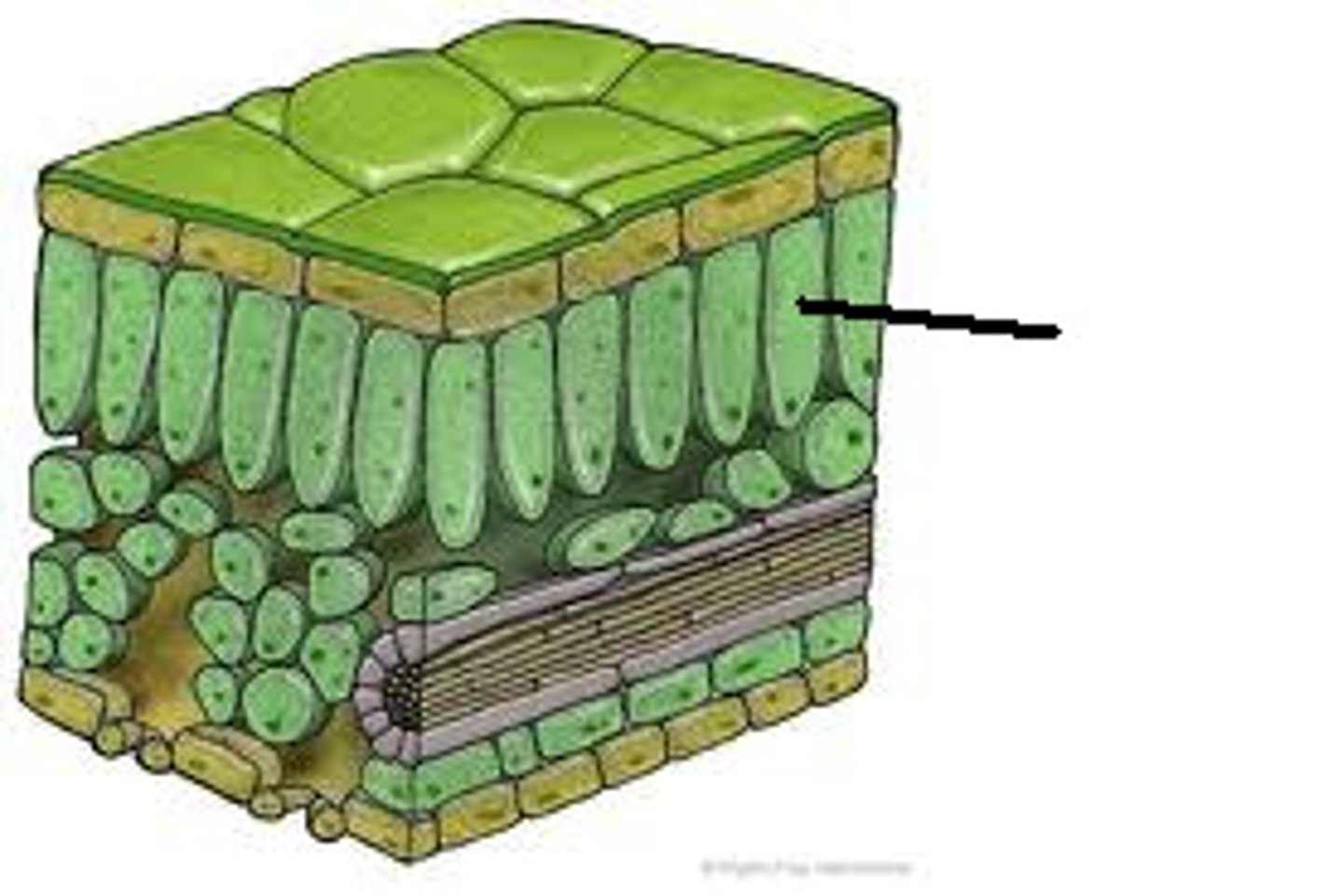
palisade mesophyll
Layer of tall, column-shaped mesophyll cells just under the upper epidermis of a leaf
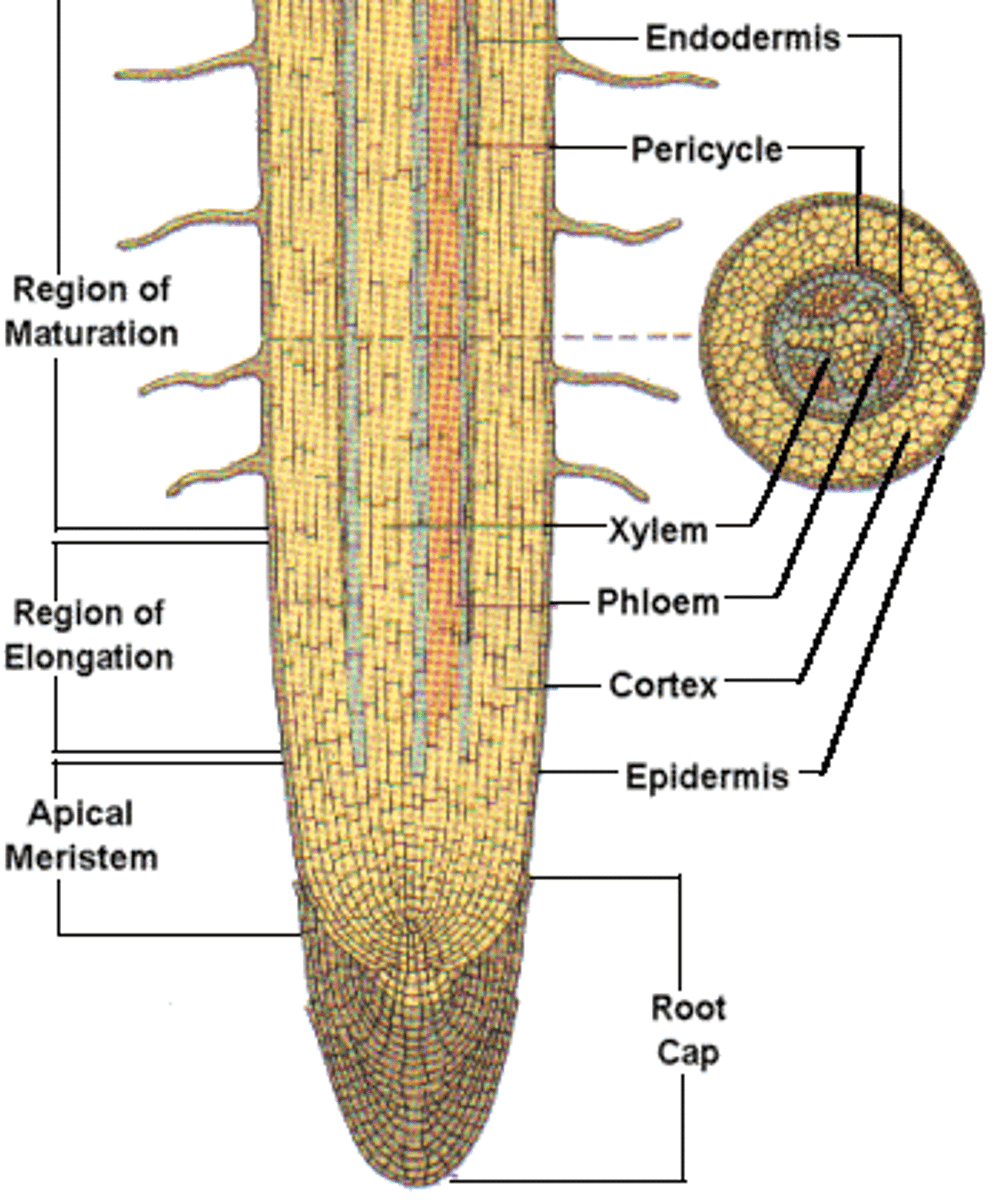
root cap
a structure that covers the tip of a root, protecting the root from injury
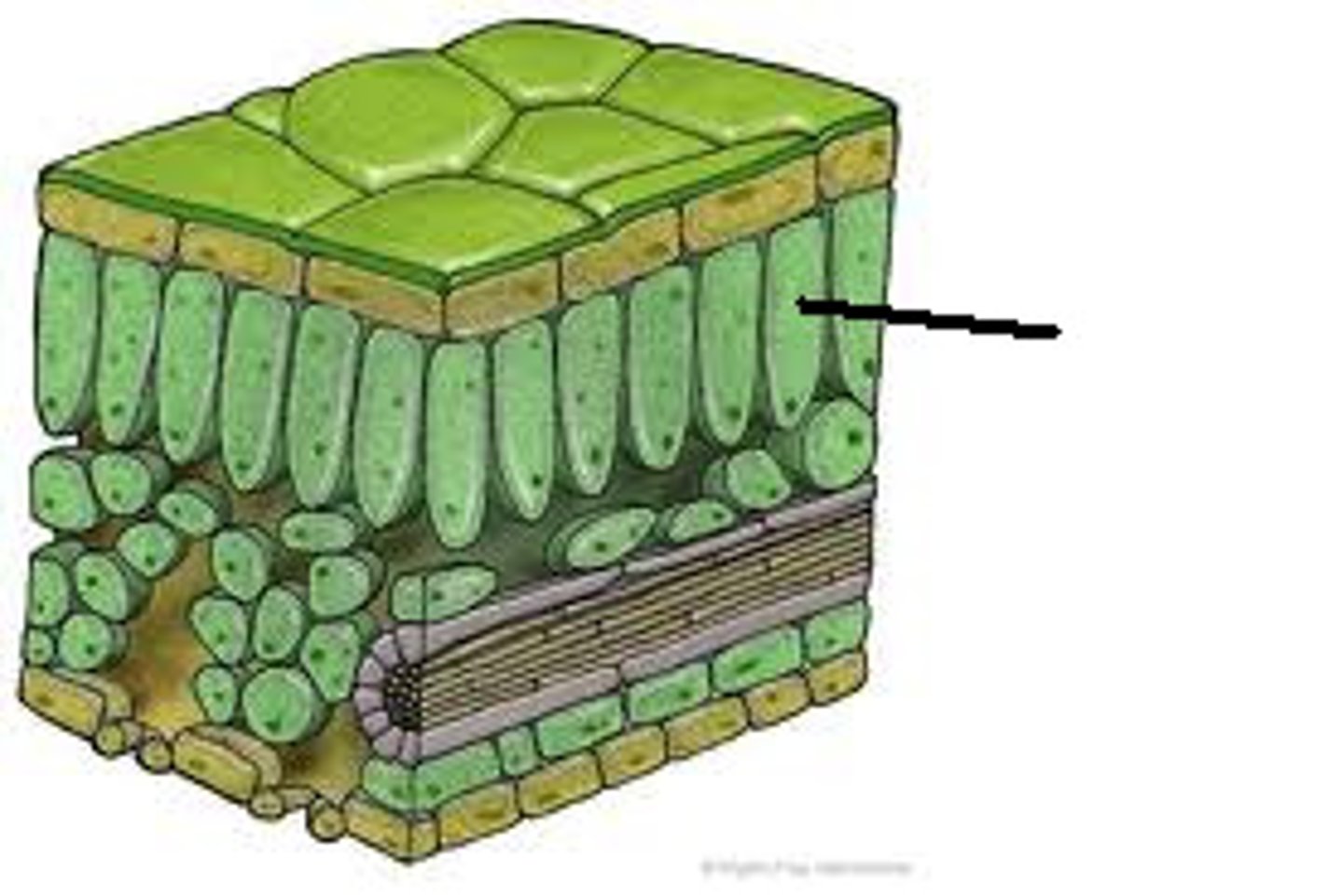
spongy mesophyll
Loose tissue beneath the palisade layer of a leaf; has many air spaces between its cells
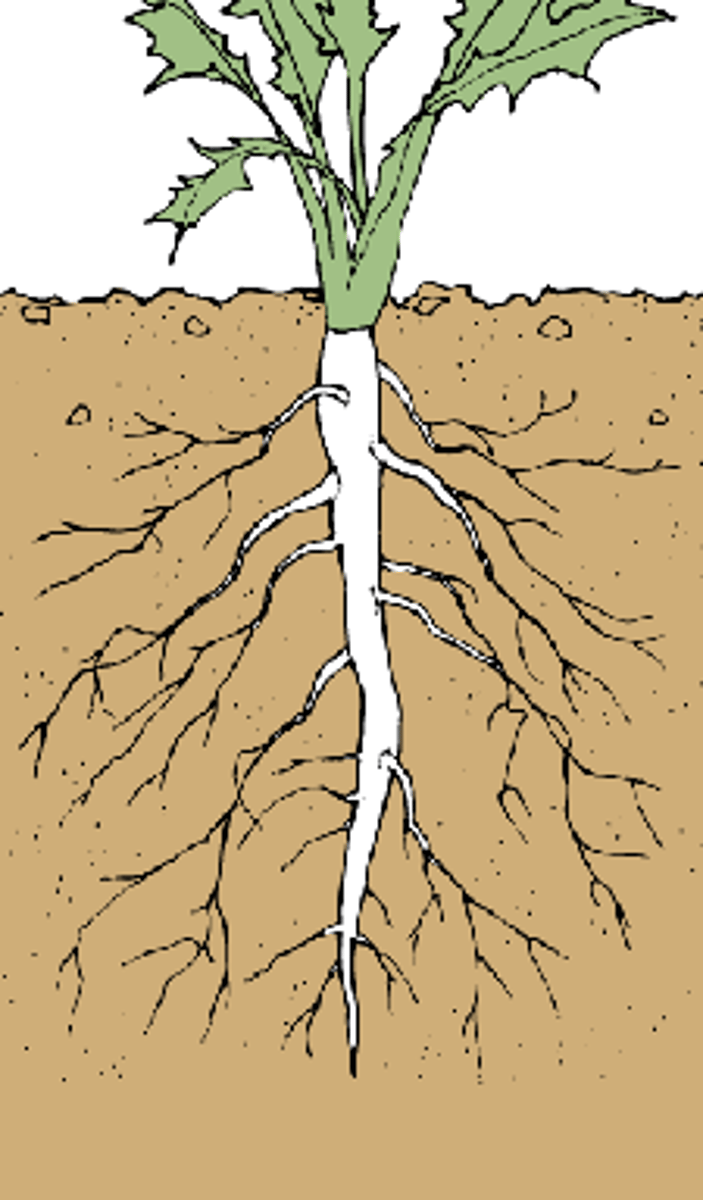
taproot
primary root found in some plants that grows longer and thicker than other roots
venation
the arrangement of veins in a leaf

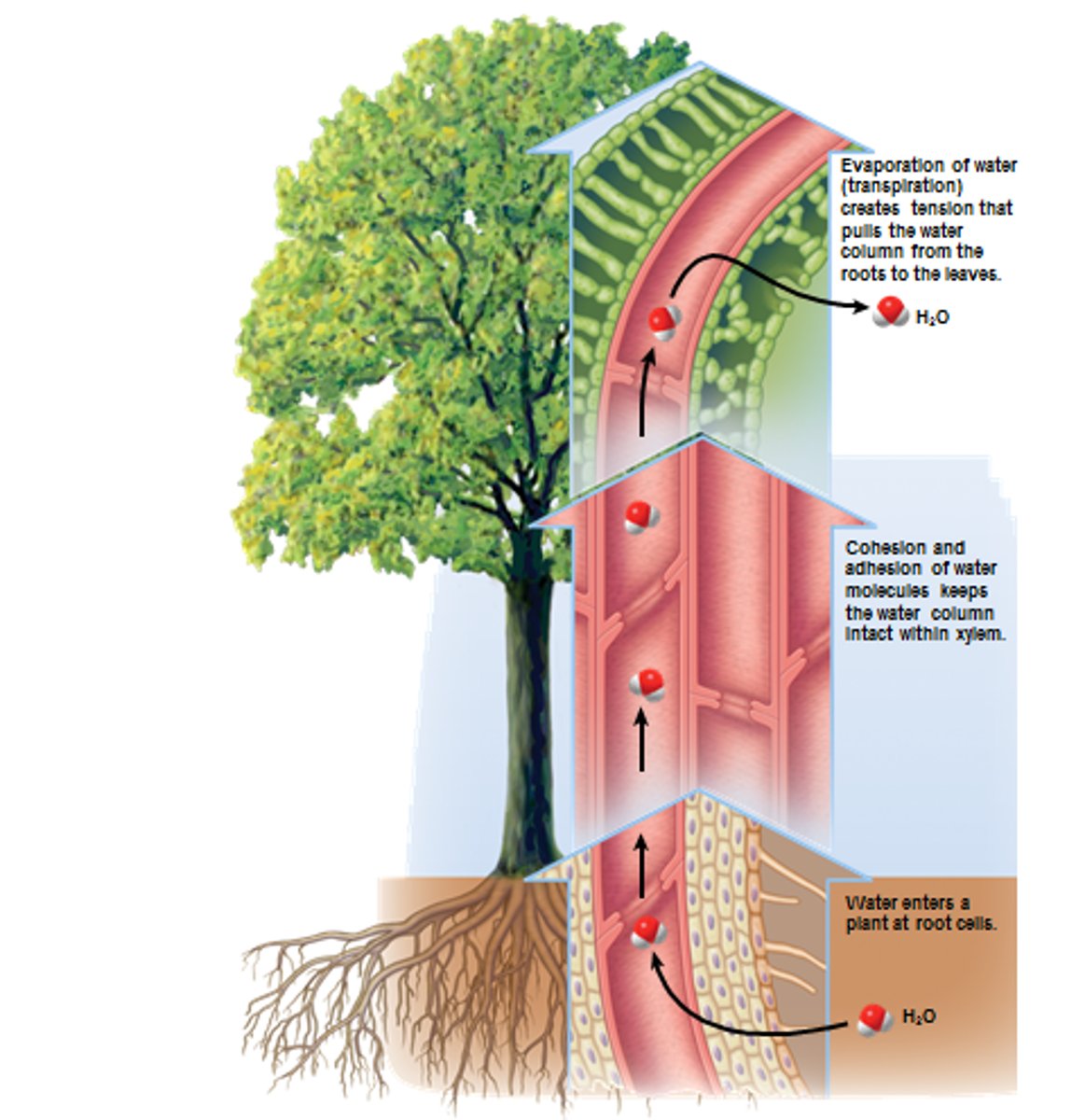
cohesion-tension model
explanation for upward transport of water in xylem based upon transpiration-created tension and the cohesive properties of water molecules
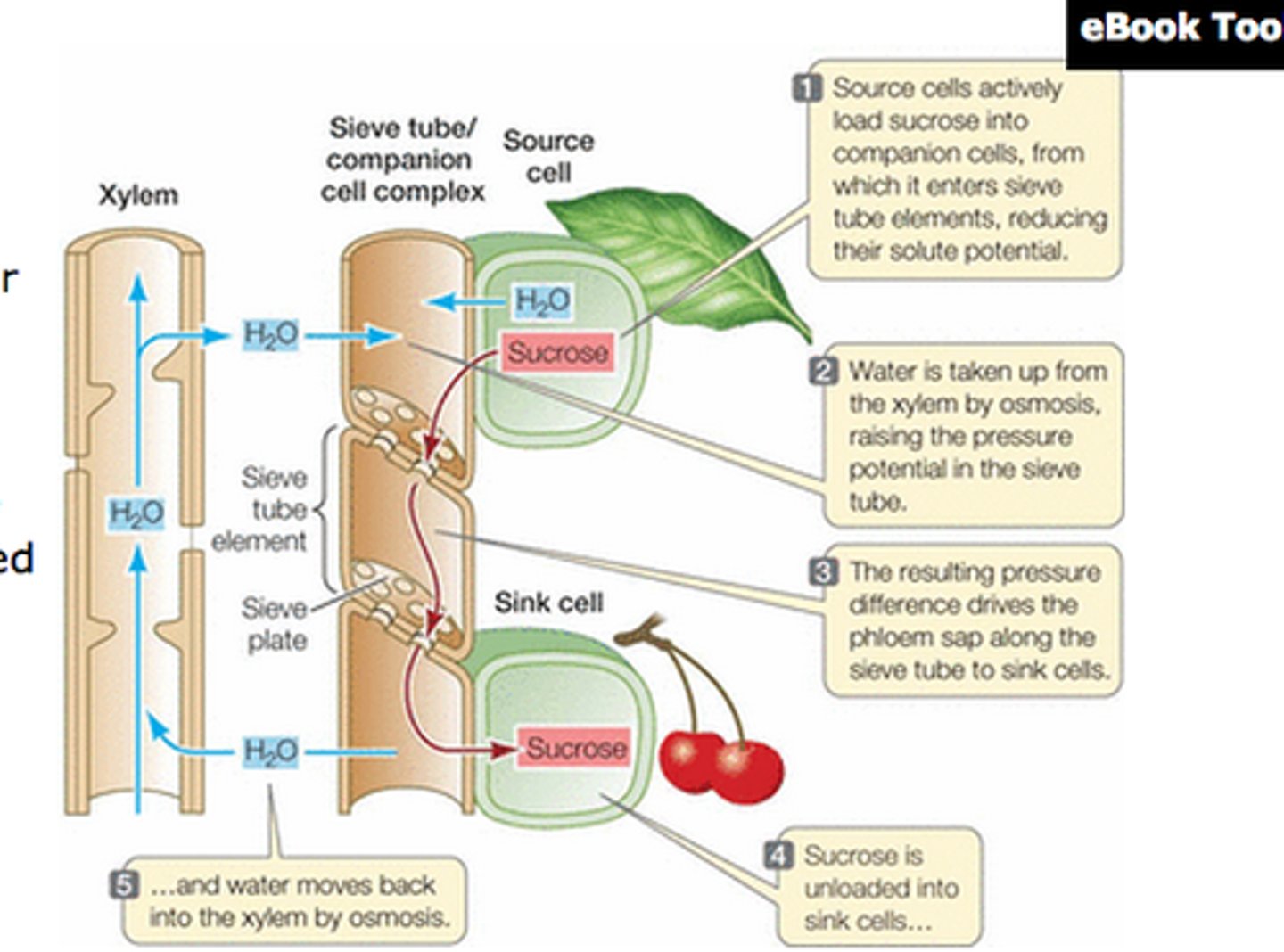
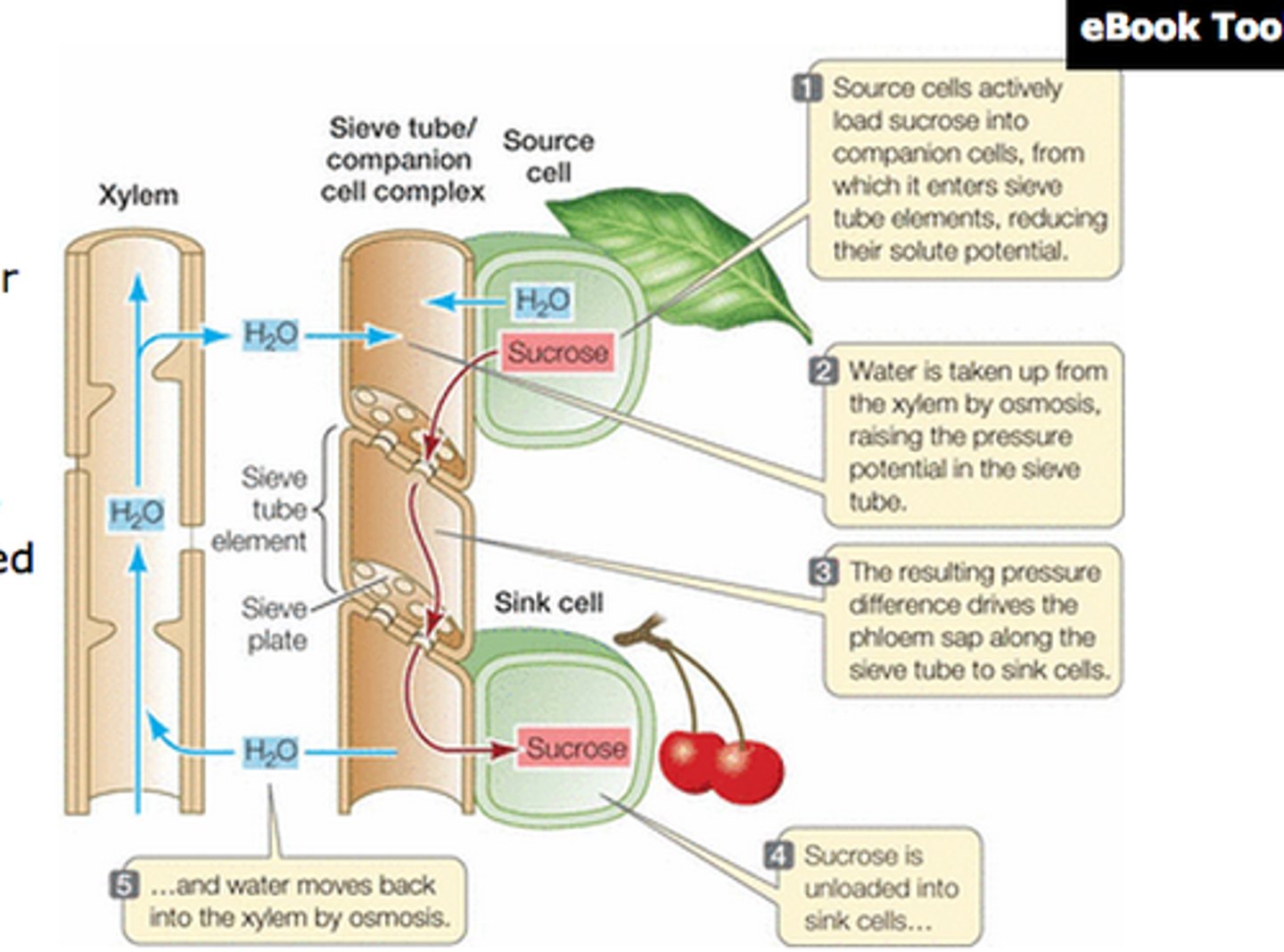
pressure-flow model
an explanation for how carbohydrates are translocated in plants
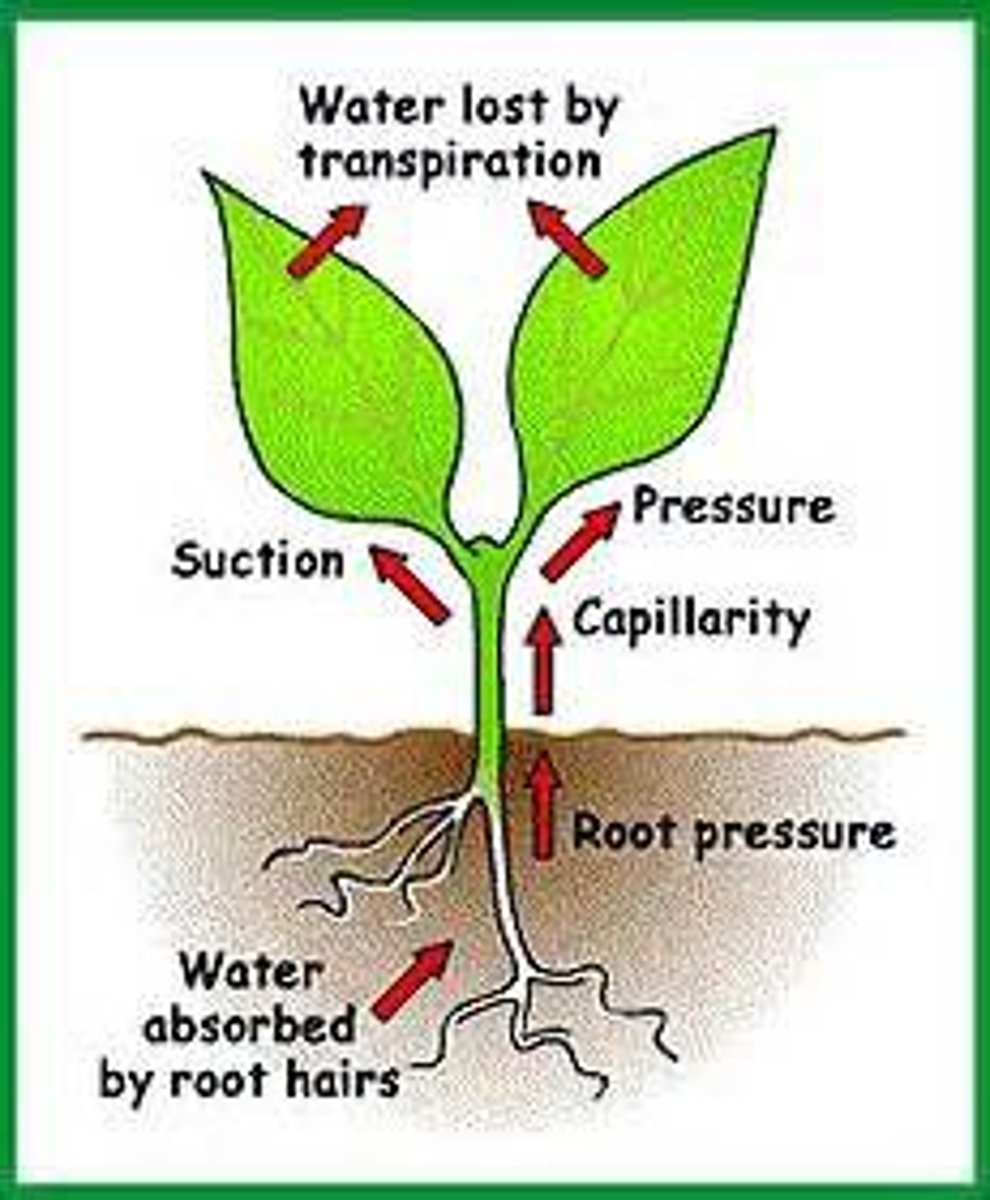
root pressure
The upward push of xylem sap in the vascular tissue of roots.
Translocation (plants)
phloem carry sugar from leaves to rest of plant
requires energy
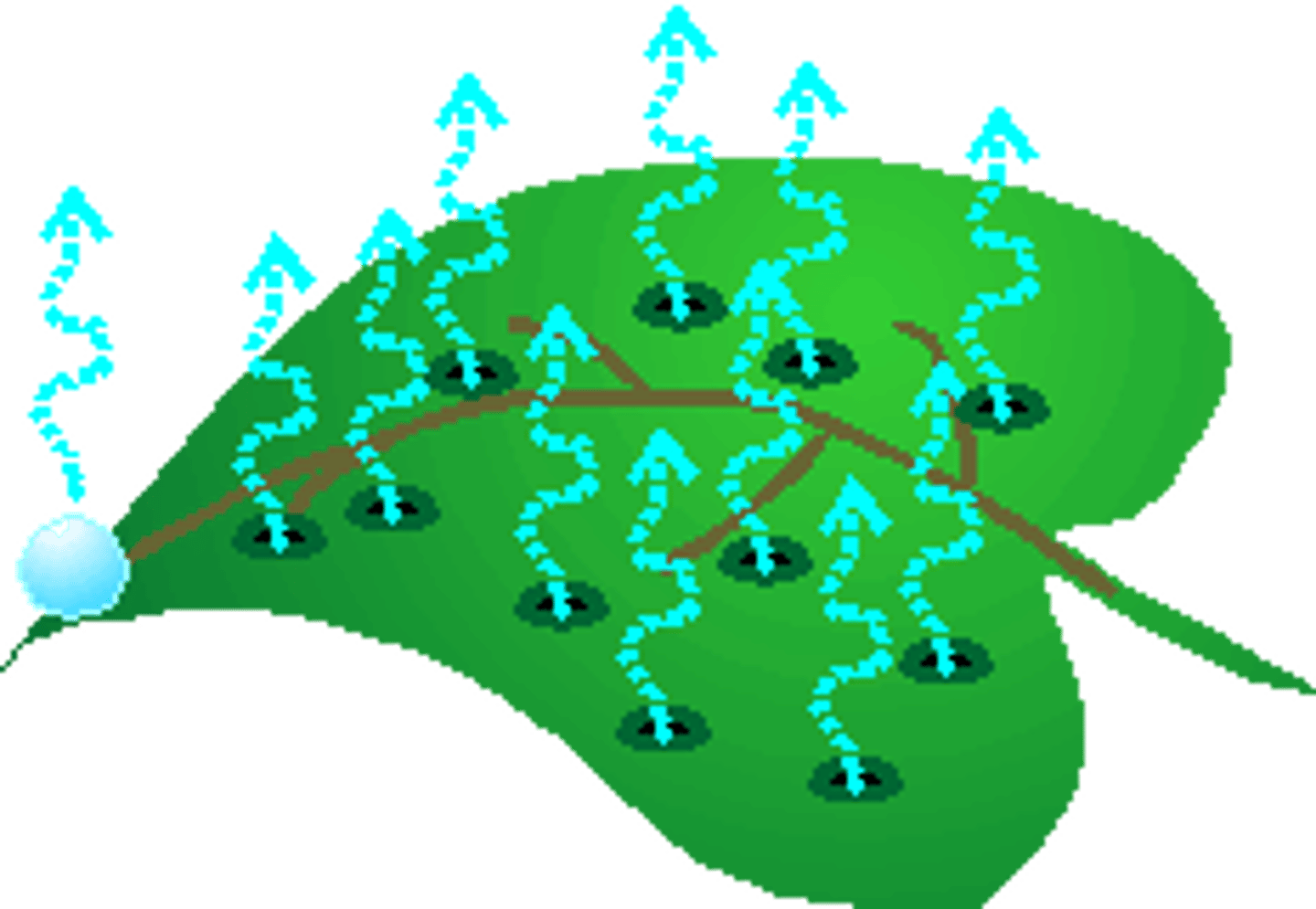
transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
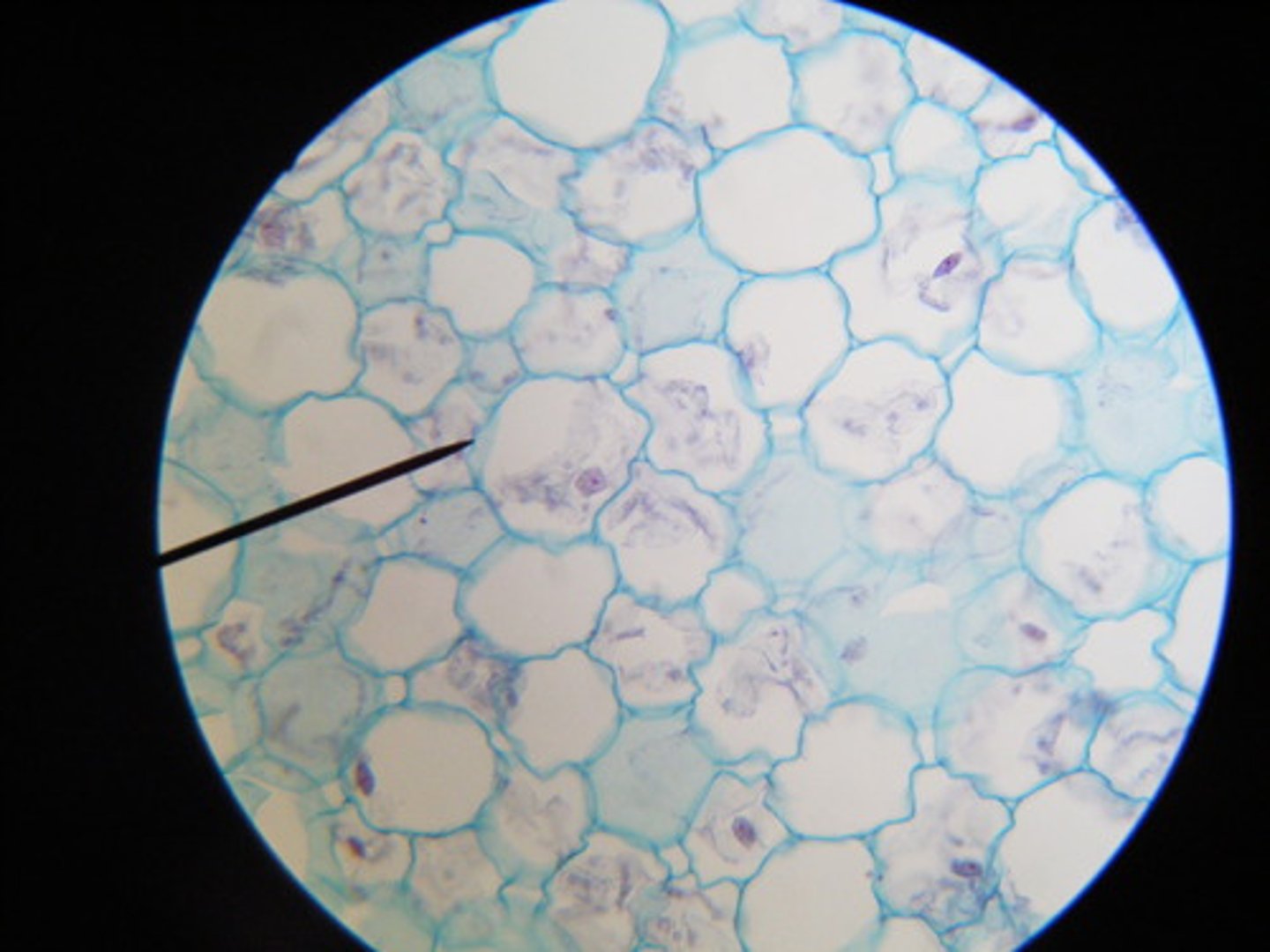
parenchyma cells
play a role in storage, secrection, and photosynthesis in cells
collenchyma cells
provide flexible and mechanical support; found in stems and leaves
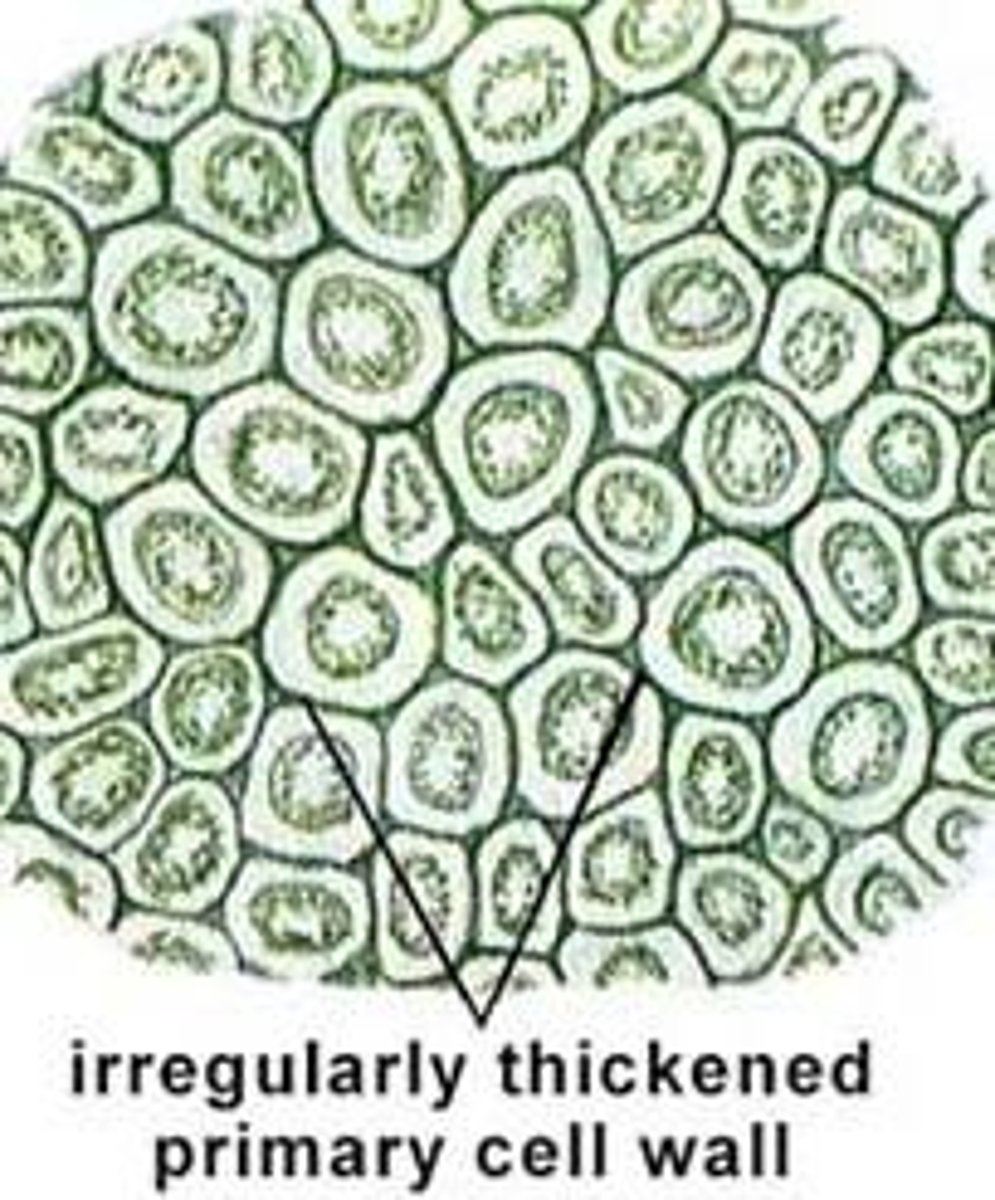
sclerenchyma cells
A rigid, supportive plant cell type usually lacking protoplasts and possessing thick secondary walls strengthened by lignin at maturity.
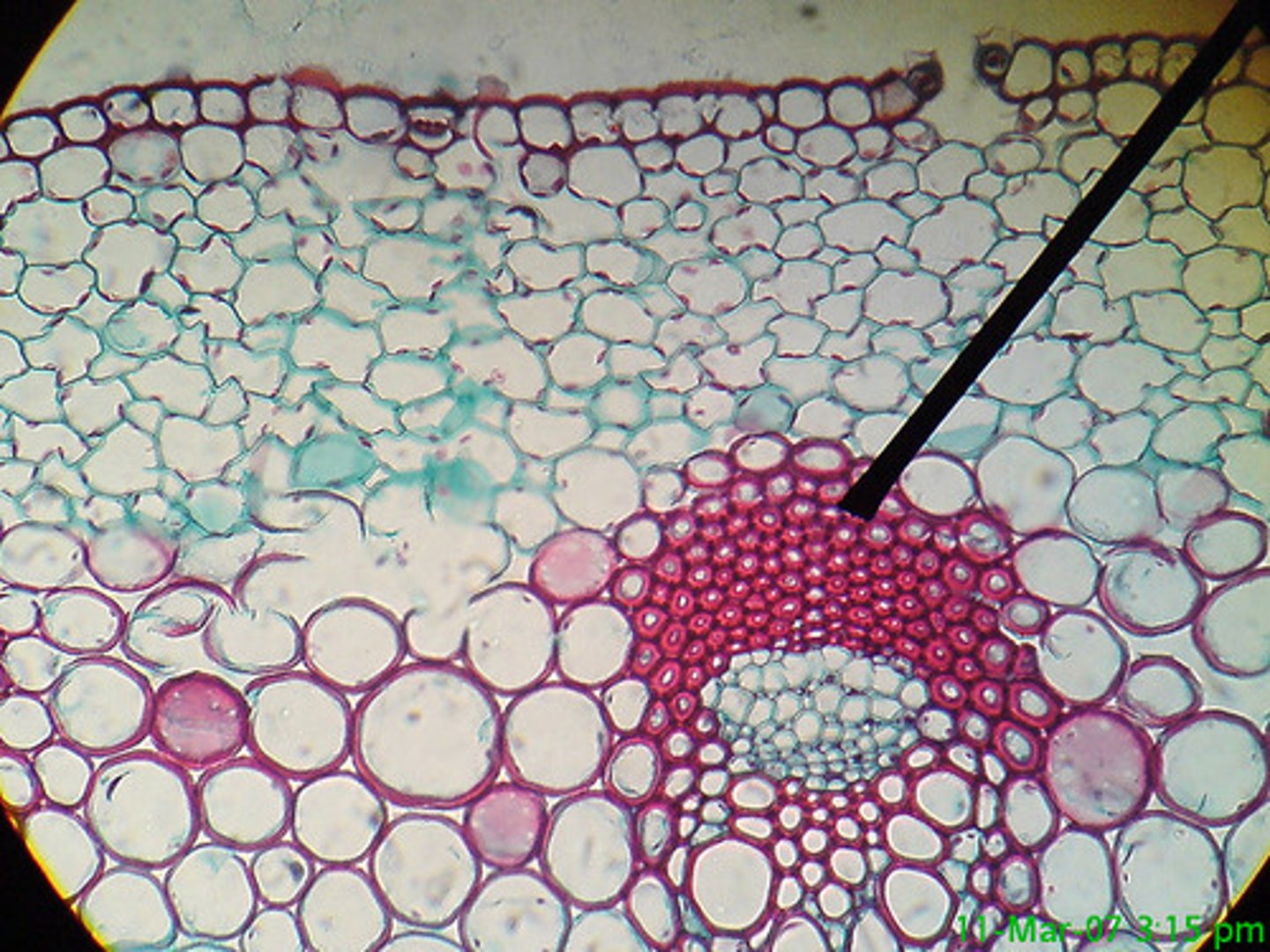
tuber
An enlargement at the end of a rhizome in which food is stored.

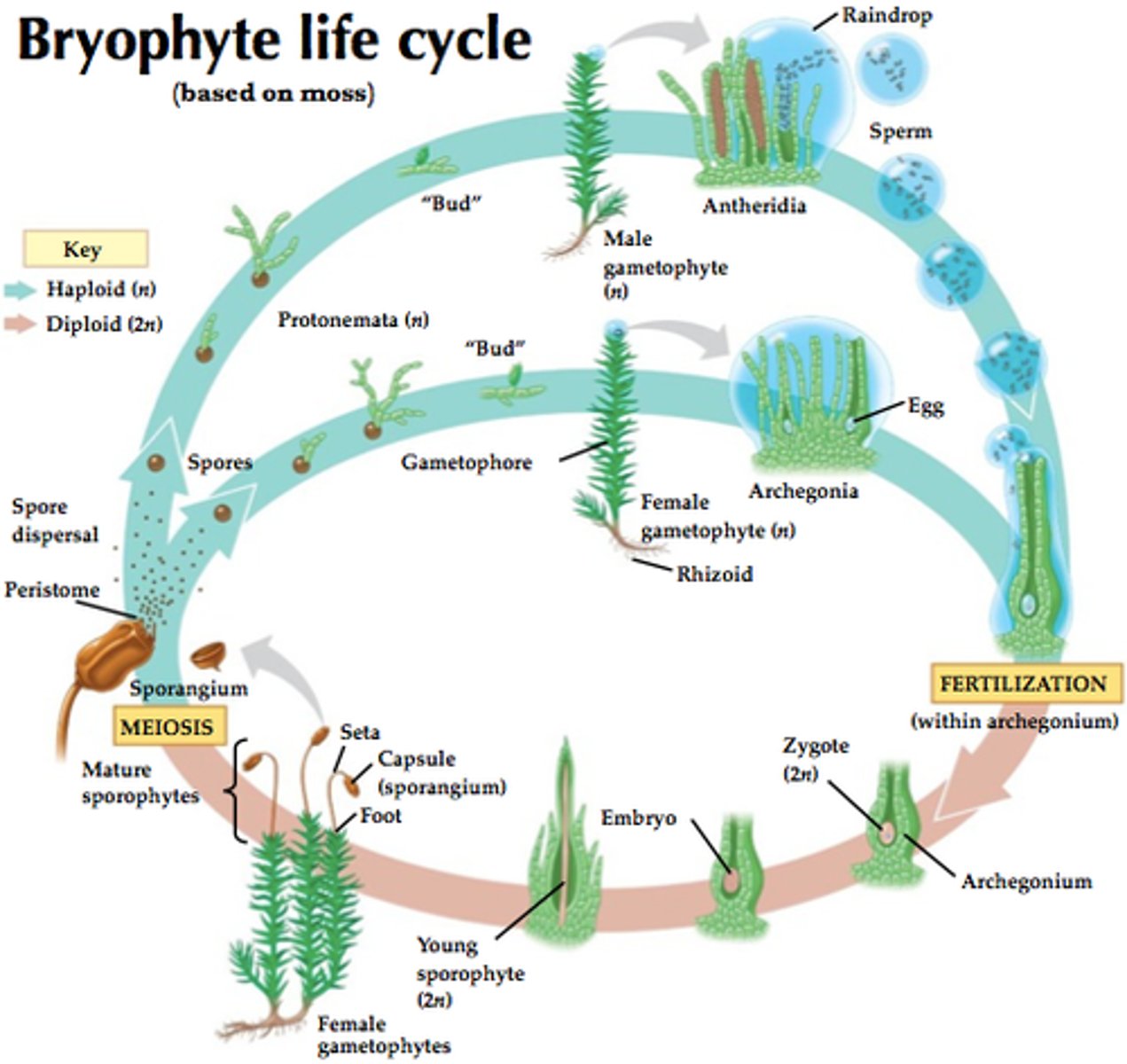
bryophyte
nonvascular plant; examples are mosses and their relatives
seedless vascular plants
lycophytes and monilophytes

lycophytes
club mosses and their relatives

monilophytes
ferns and their relatives

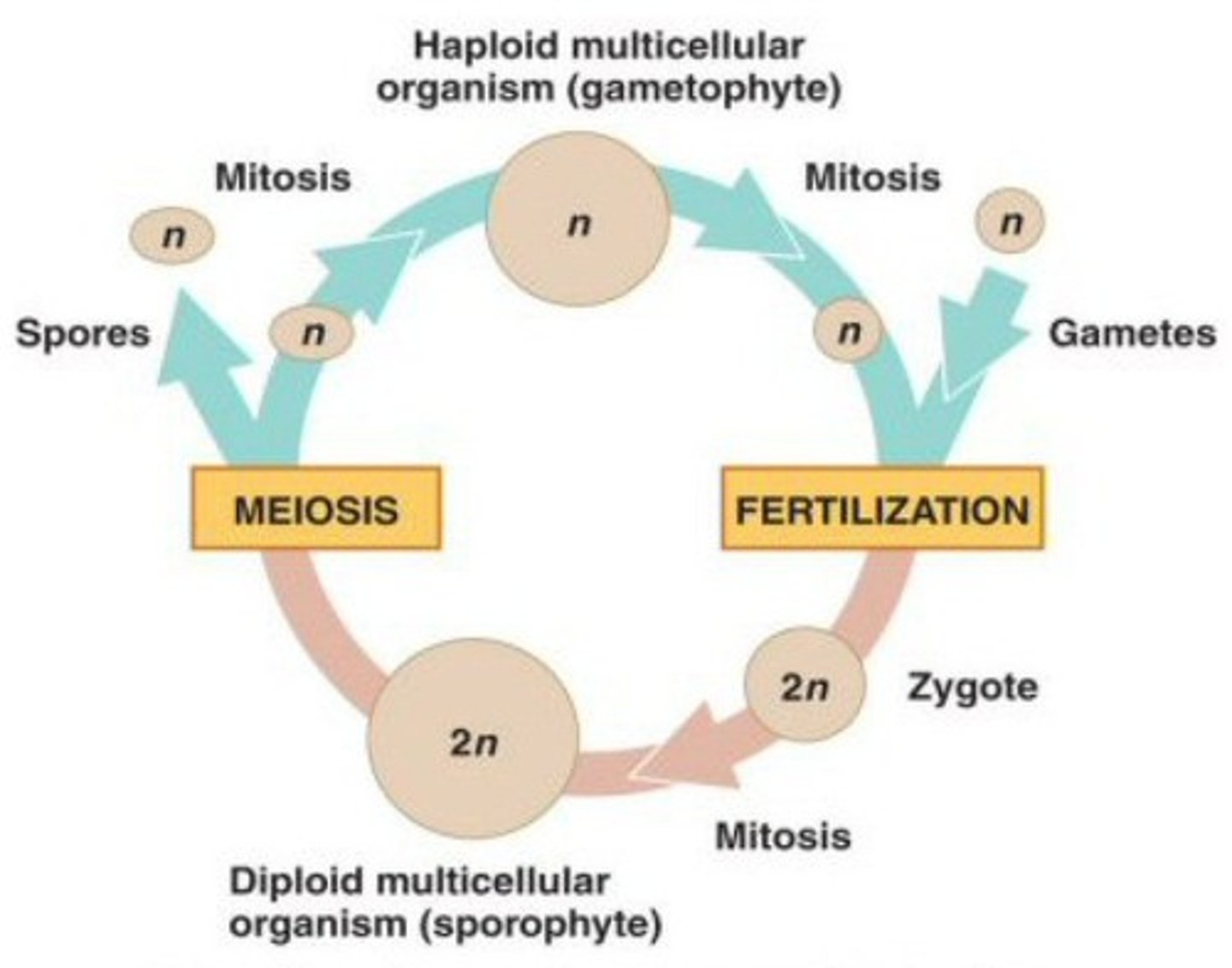
sporophytes
The multicellular diploid form in the life cycle of organisms undergoing alternation of generations; results from a union of gametes and meiotically produces haploid spores that grow into gametophytes generation
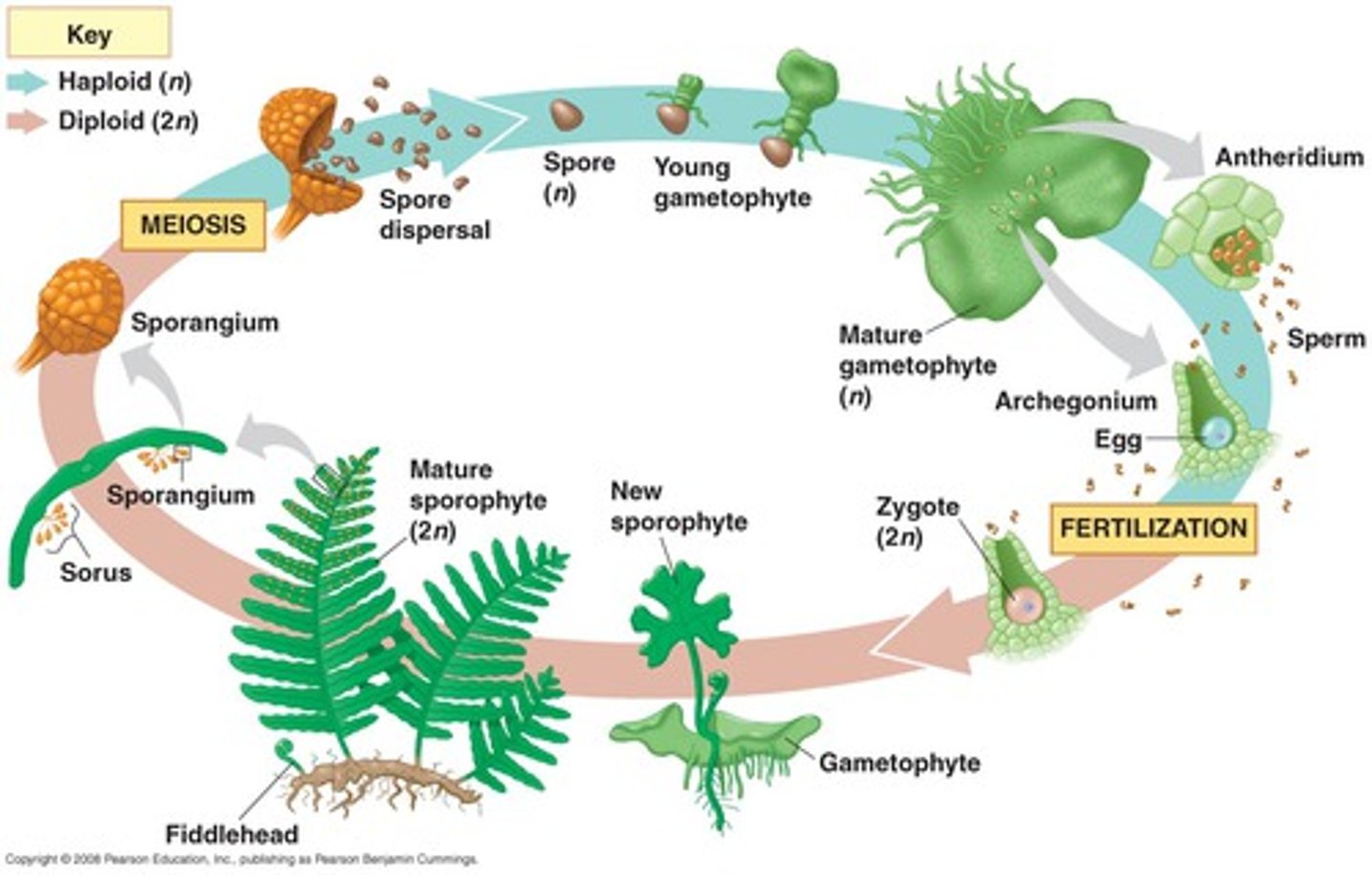
life cycle of a fern
1.) Sporangia release spores (n). Ferns produce a single type of spore that develops into a bisexual photosynthetic gameteophyte
2.) each gametophyte develops both a sperm-producing antheridium and and egg-producing archegoniums
3.) Flagellated- sperm swim to eggs in archegonia (fertilization)
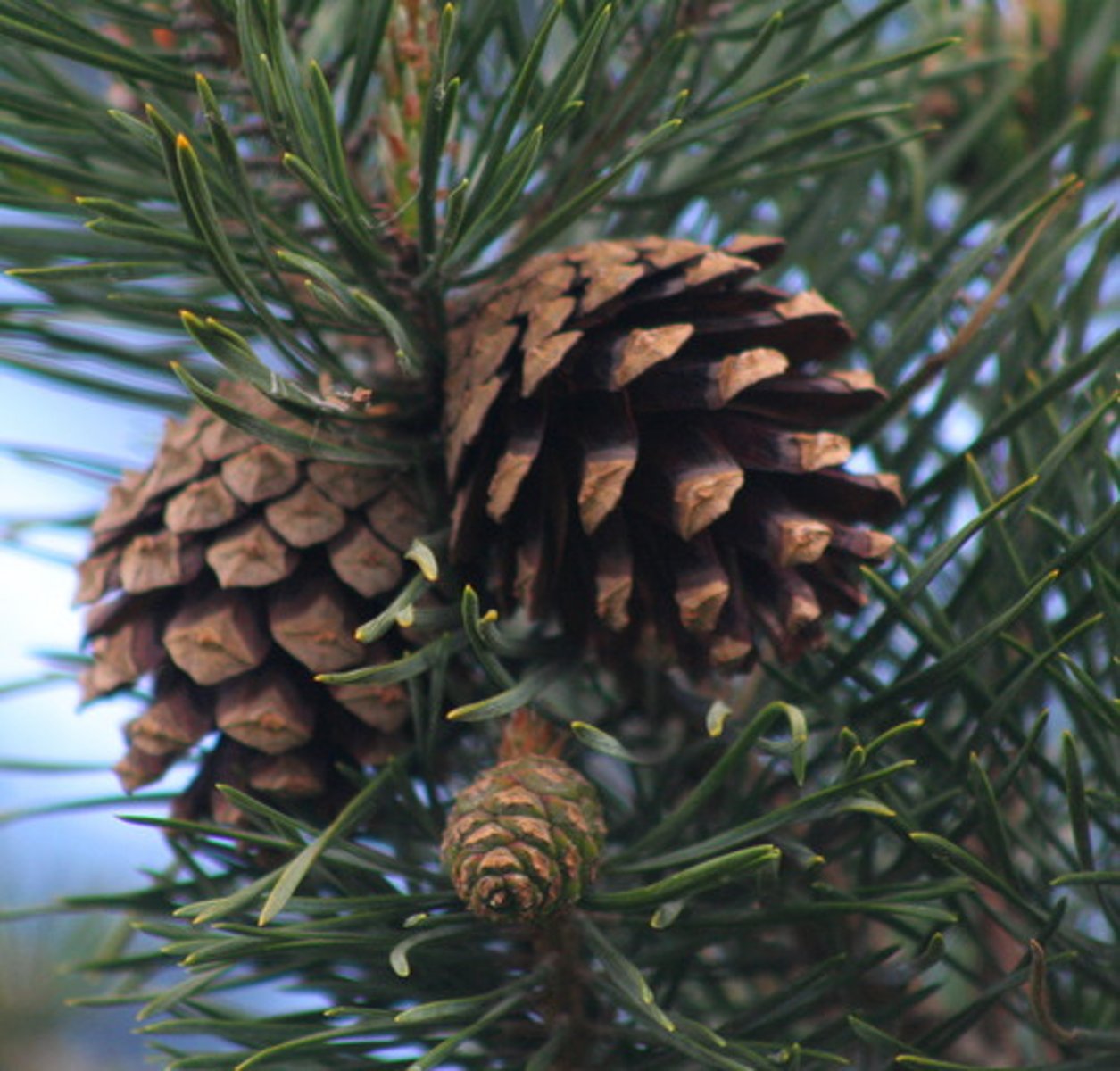
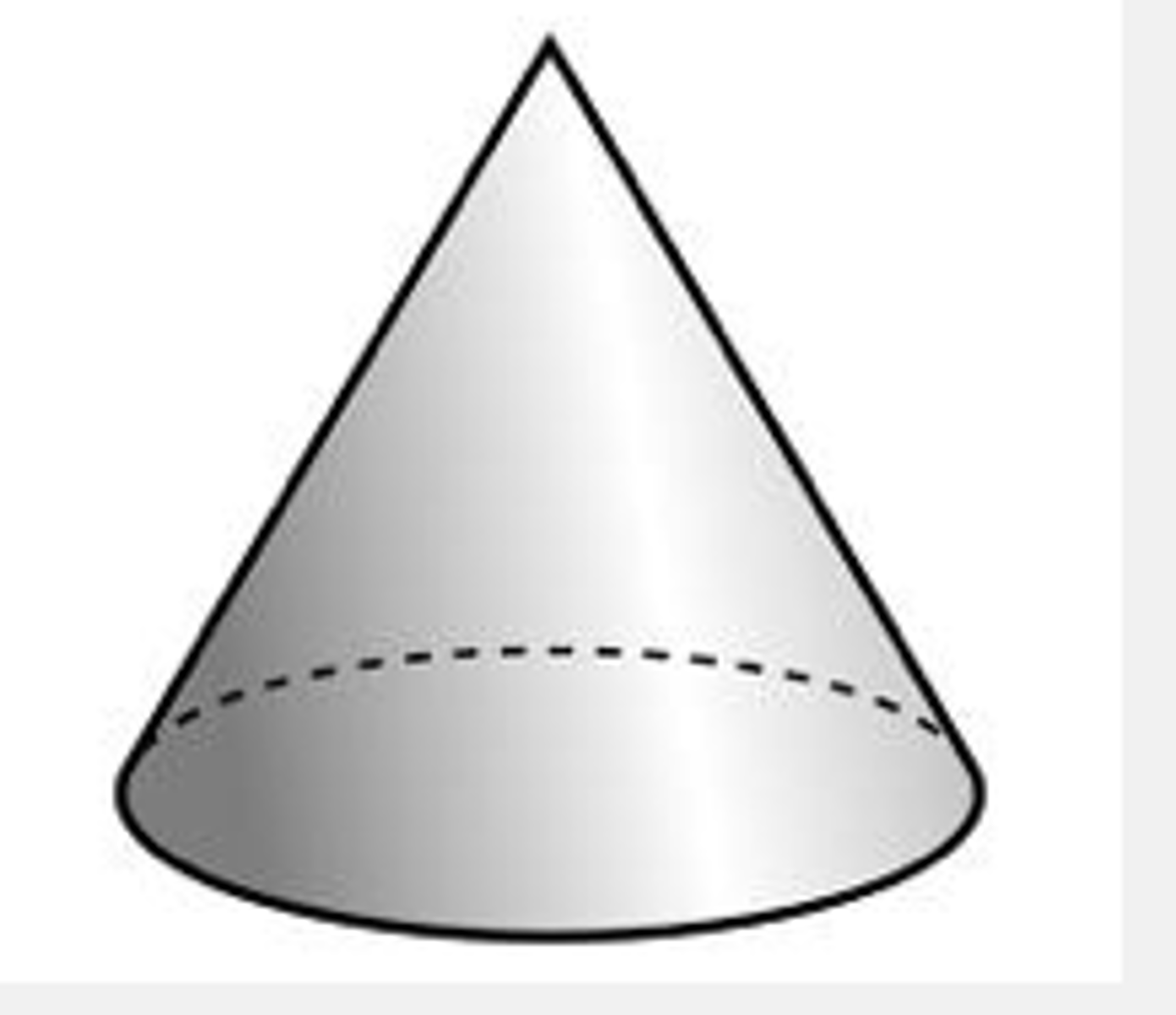
gymnosperm
"Naked seeds", such as pine cones and other conifers.

Angiosperms
A flowering plant which forms seeds inside a protective chamber called an ovary.

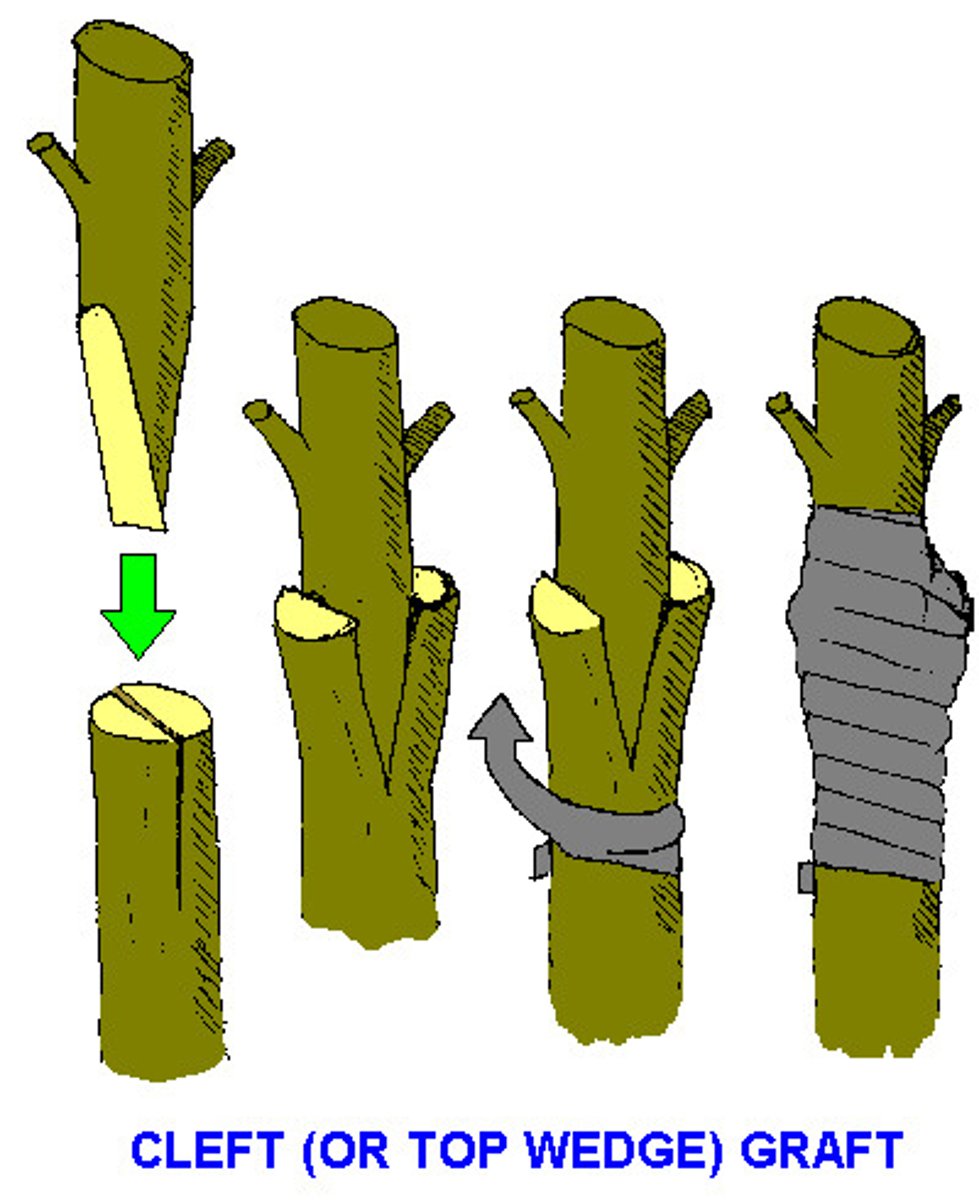
artificial propagation
The creation of new plants (clones) through human manipulation e.g. cuttings.
cone
The reproductive structure of a gymnosperm.
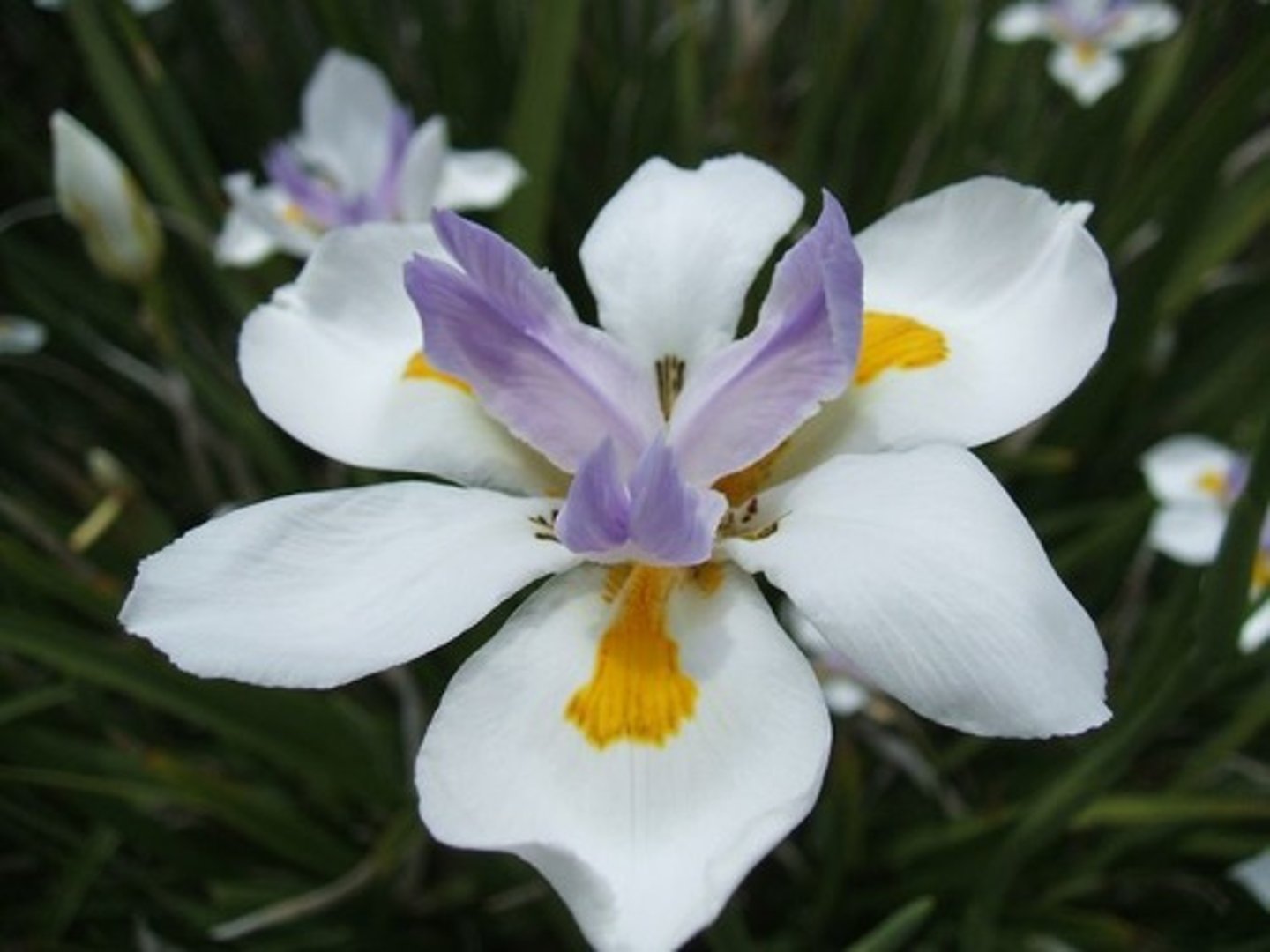
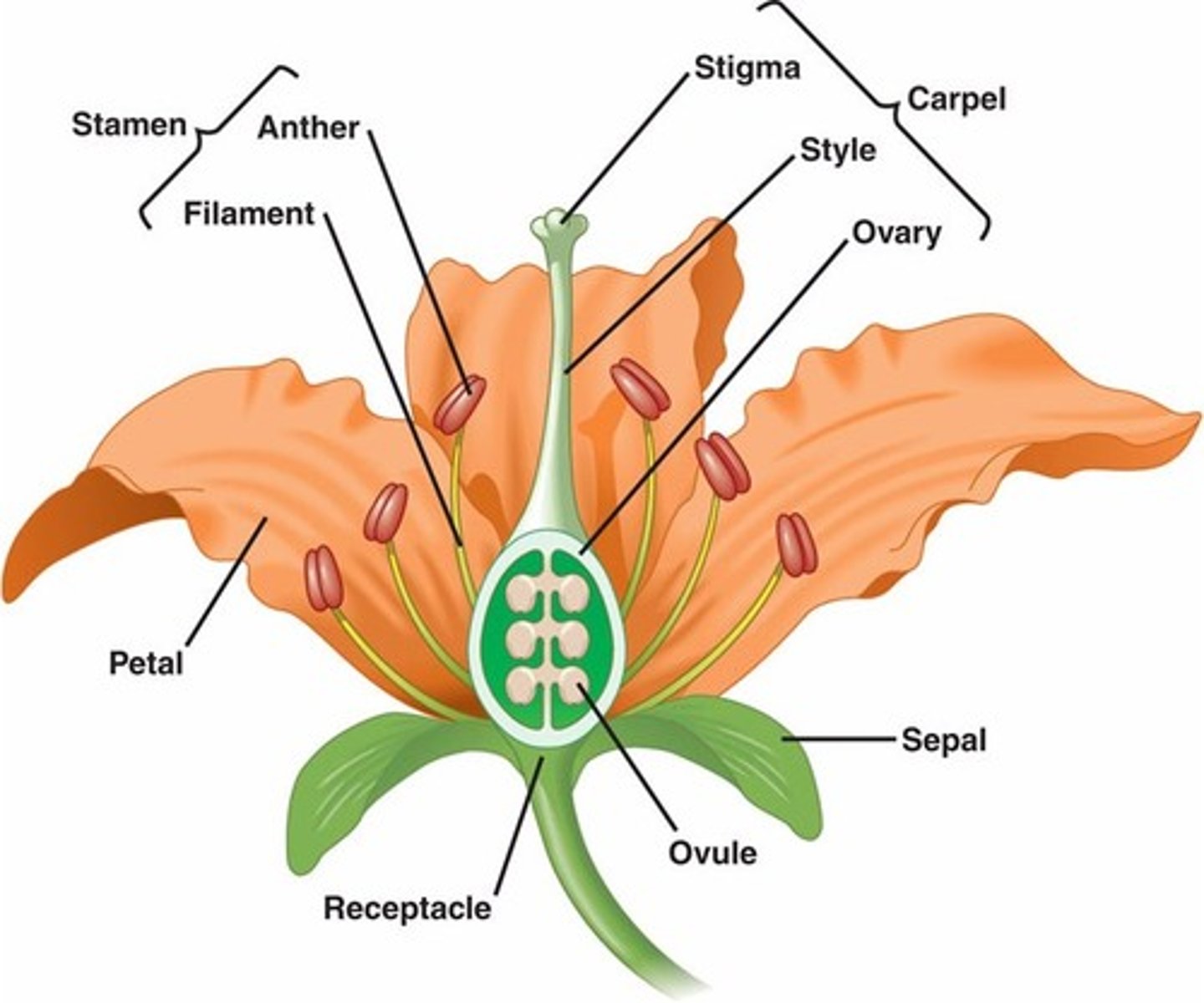
flower
The reproductive structure of an angiosperm

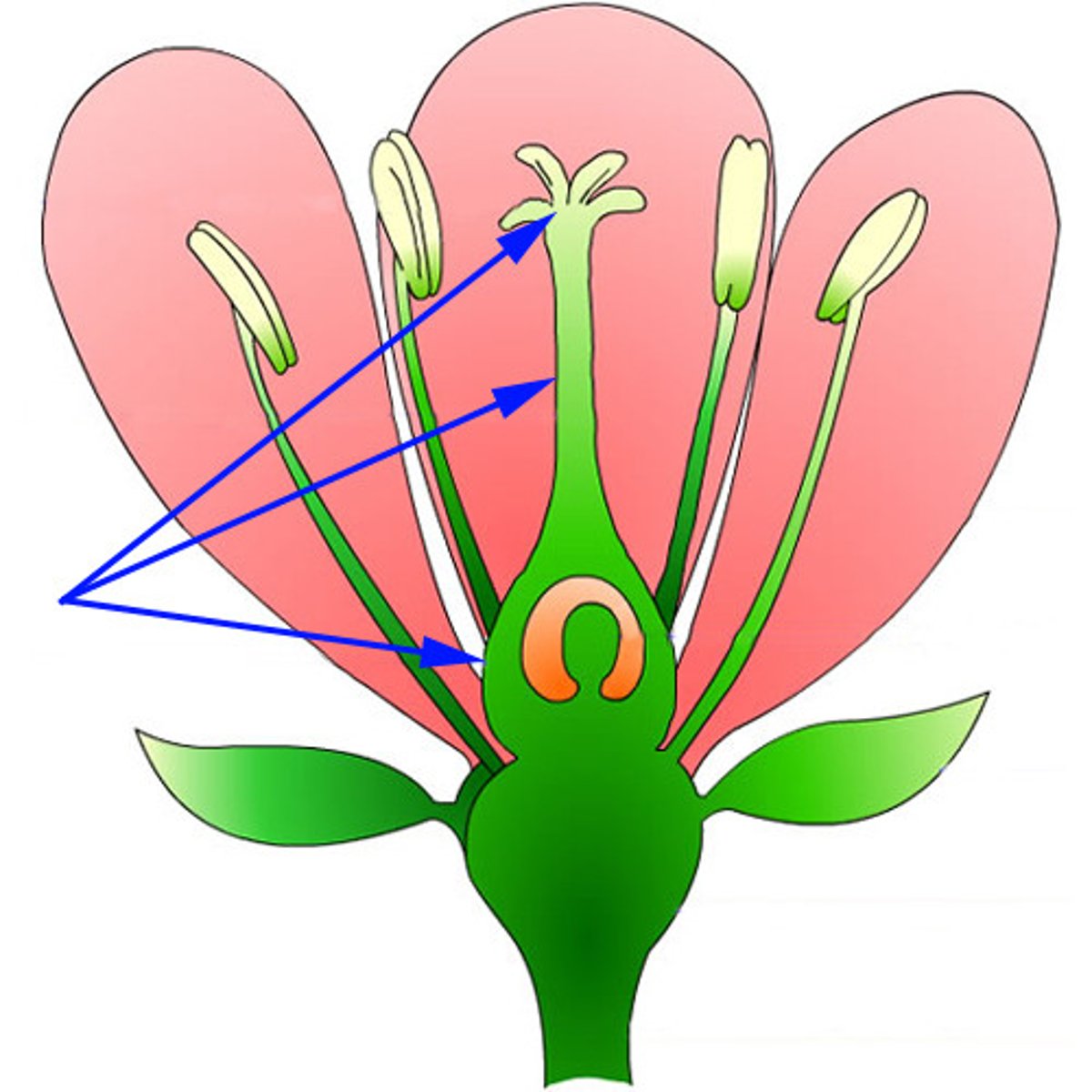
anther
the part of a stamen that contains the pollen.
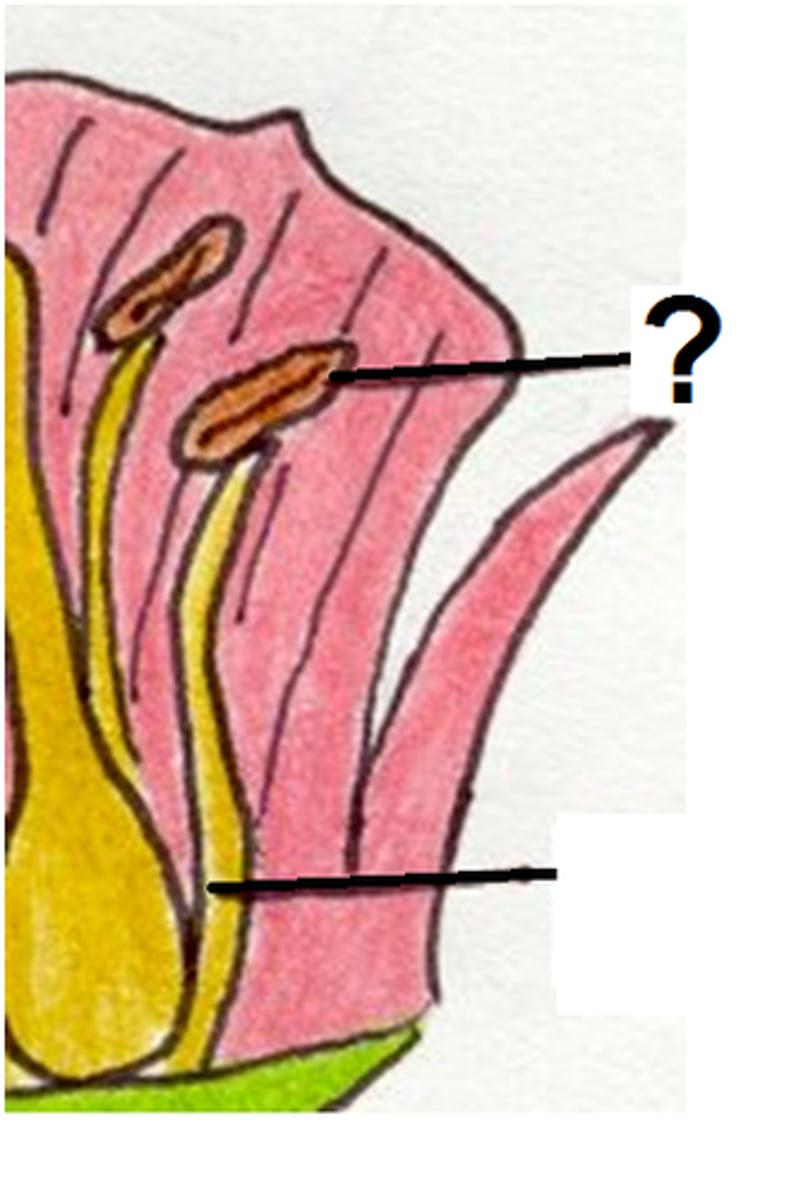
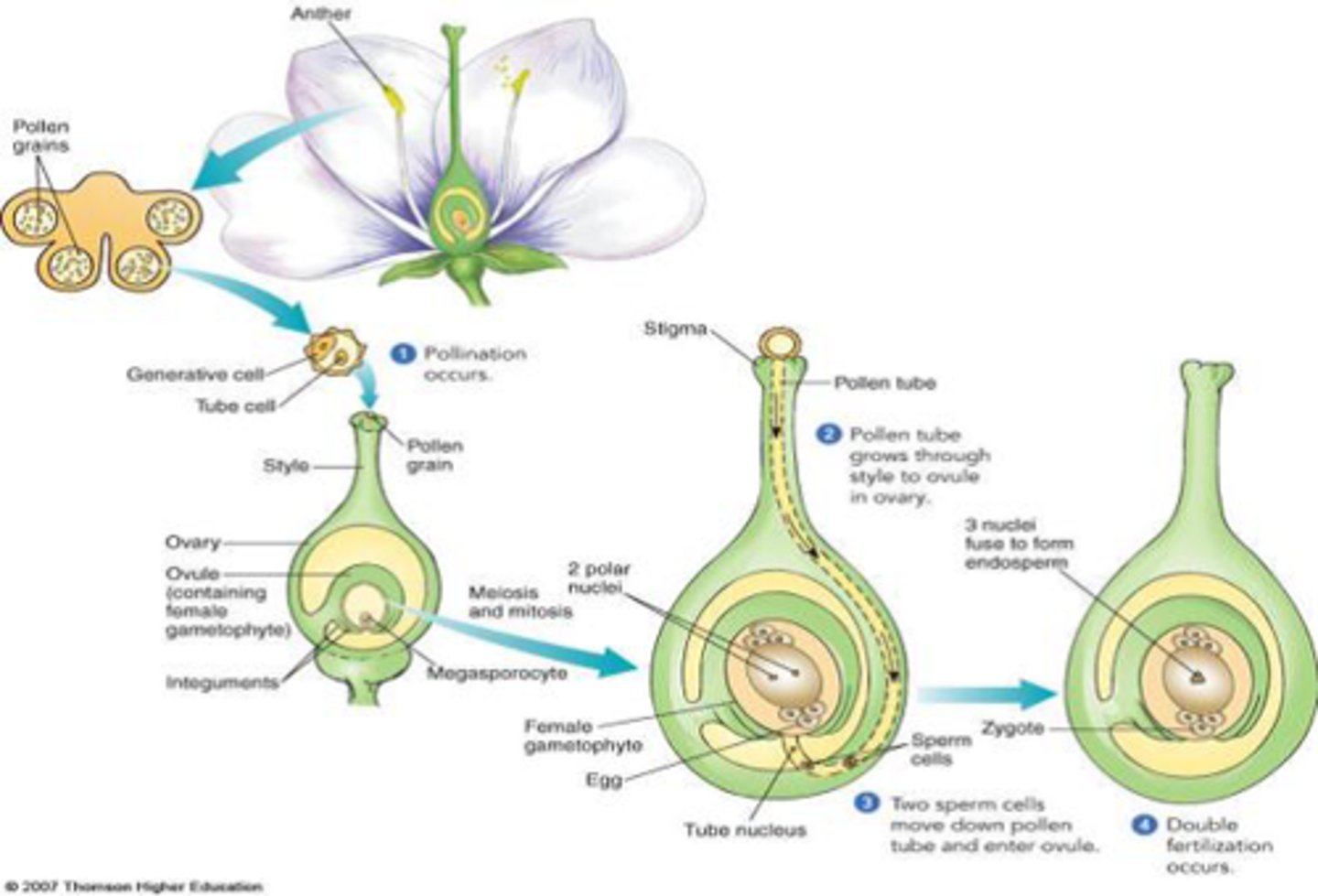
pollen
A fine dust that contains the sperm of seed-producing plants

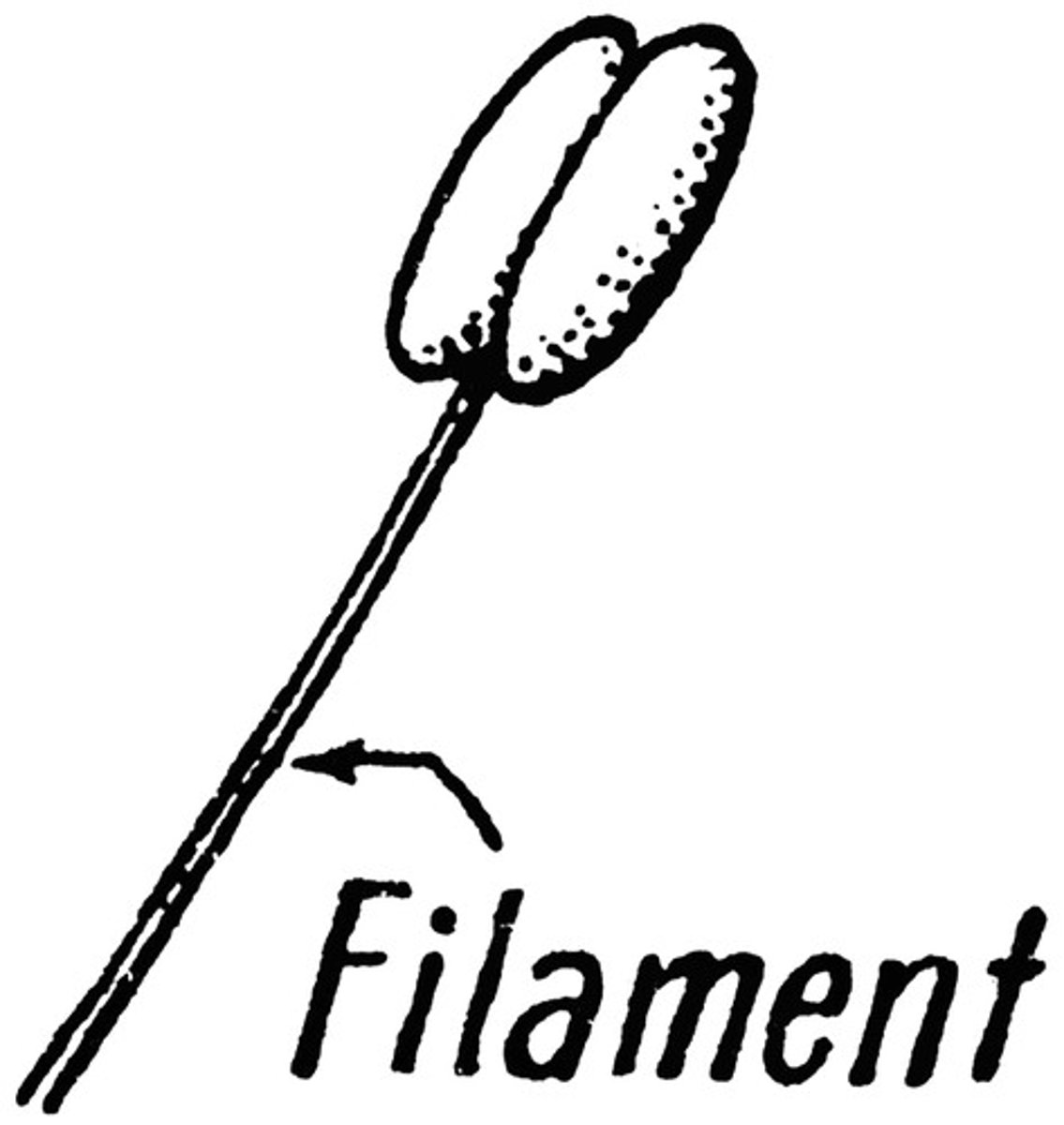
filament stalk
Supports the anther
stigma (plants)
In plants, the region of a carpel serving as a receptive surface for pollen grains, which germinate on it.

style (plants)
a long, slender stalk that connects the stigma and the ovary
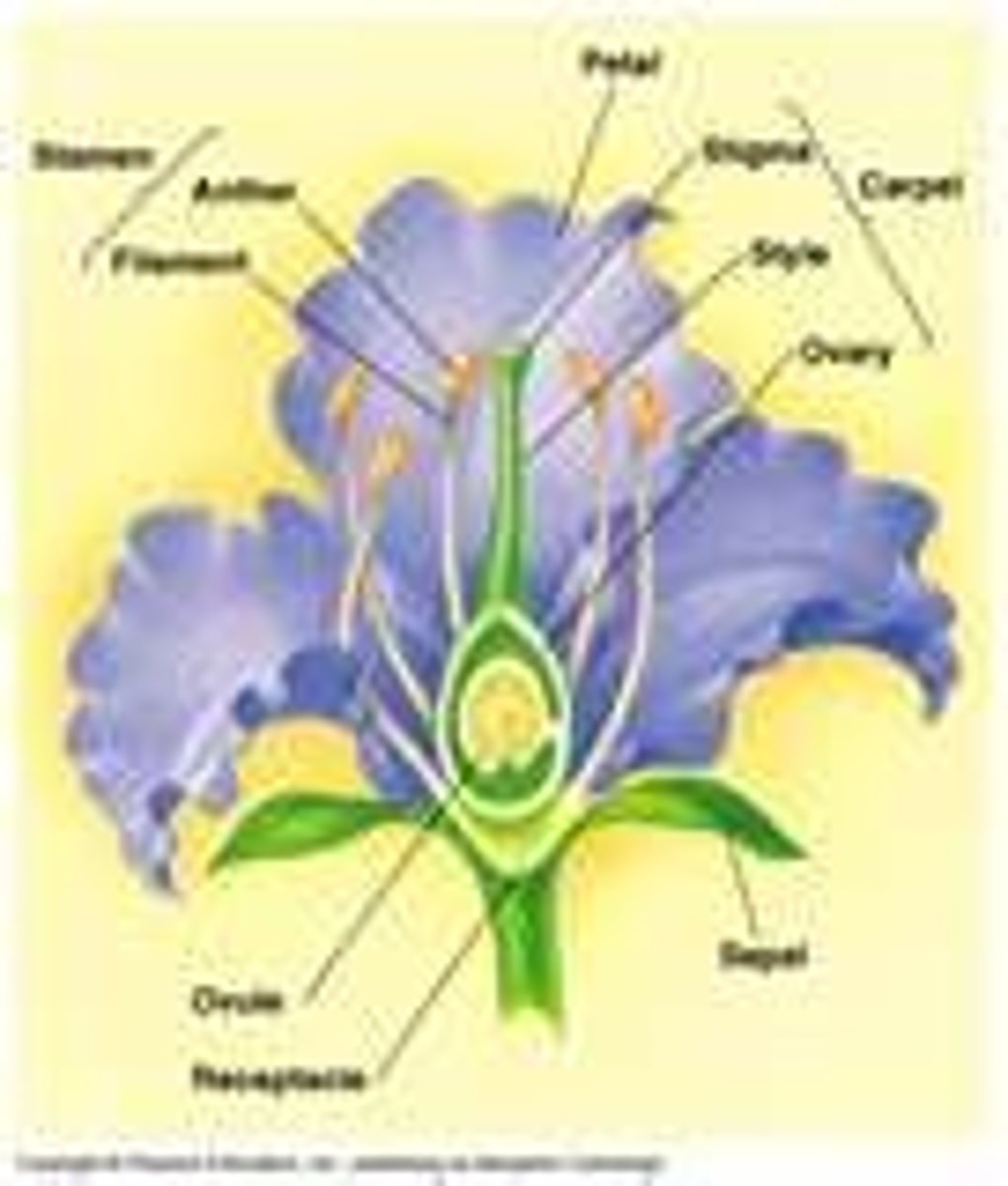
ovary in plants
A protective structure in plants that encloses the developing seeds
ovules in plants
organ that forms the seed of flowering plants
fruit
A mature ovary of a flower that protects dormant seeds and aids in their dispersal.

sporic reproduction
sexual reproduction that alternates between a gamete-making individual and a spore-making individual
alga
A protist that produces its food by photosynthesis.

Protists
A eukaryotic organism that cannot be classified as an animal, plant, or fungus.

embryo (plants)
a young multicellular diploid sporophyte that develops from a single-celled zygote by mitosis, produced following the fertilization of an egg and depend on maternal issues for food, unique to land plants, takes place inside a seed.

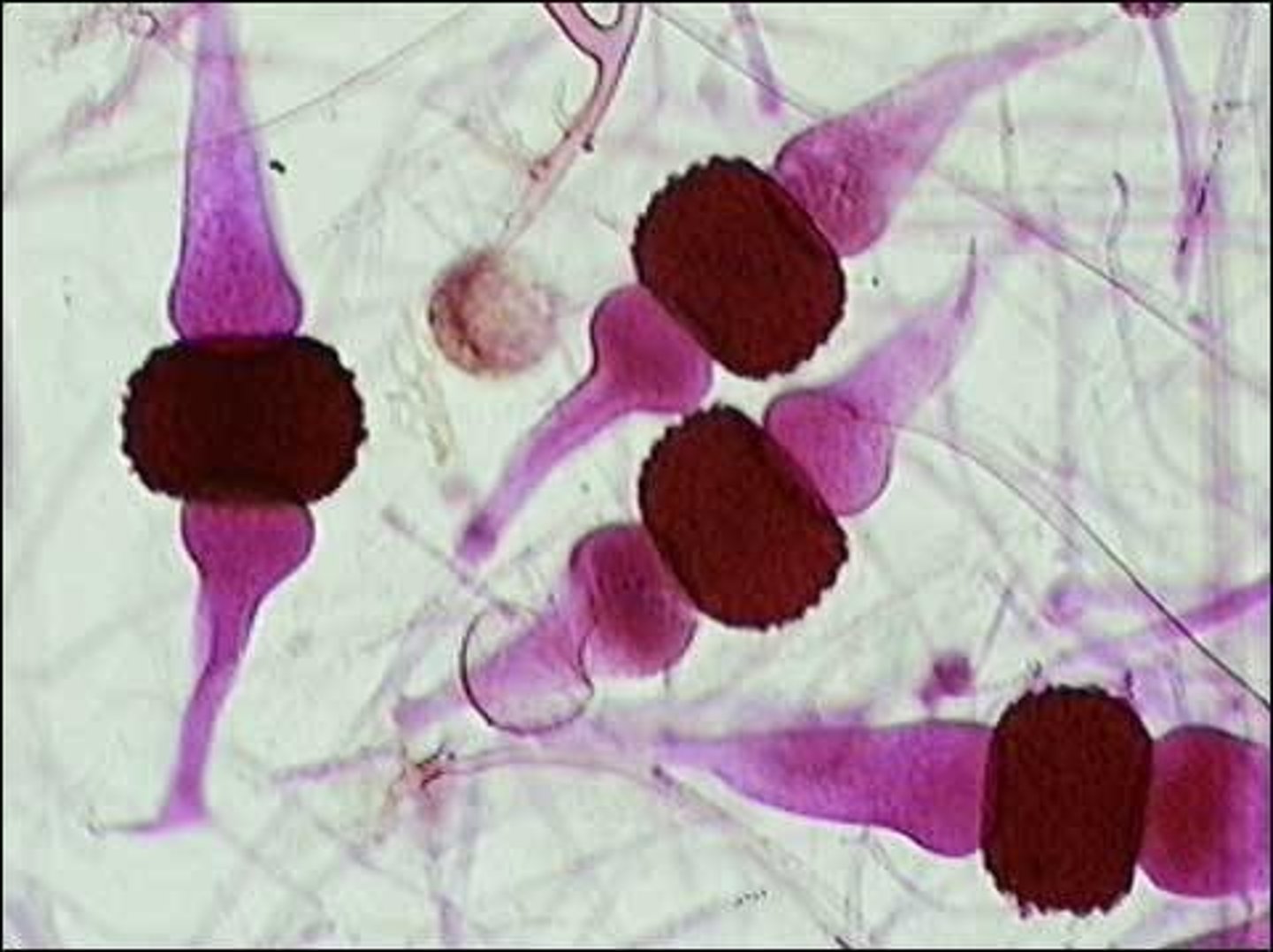
ascus
the reproductive structure where spores develop on sac fungi
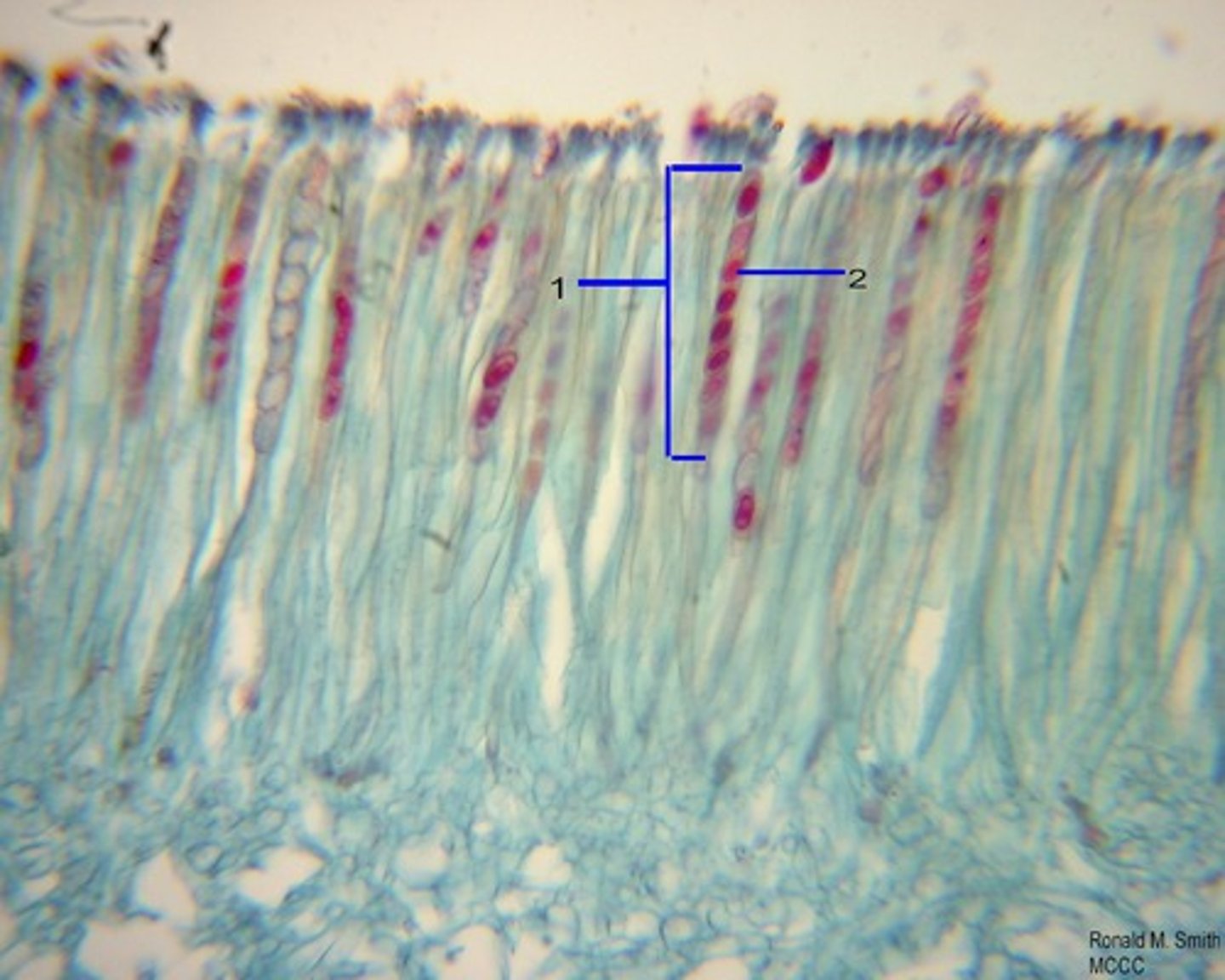
sac fungi
single celled fungi that reproduces by budding (ascomyota)
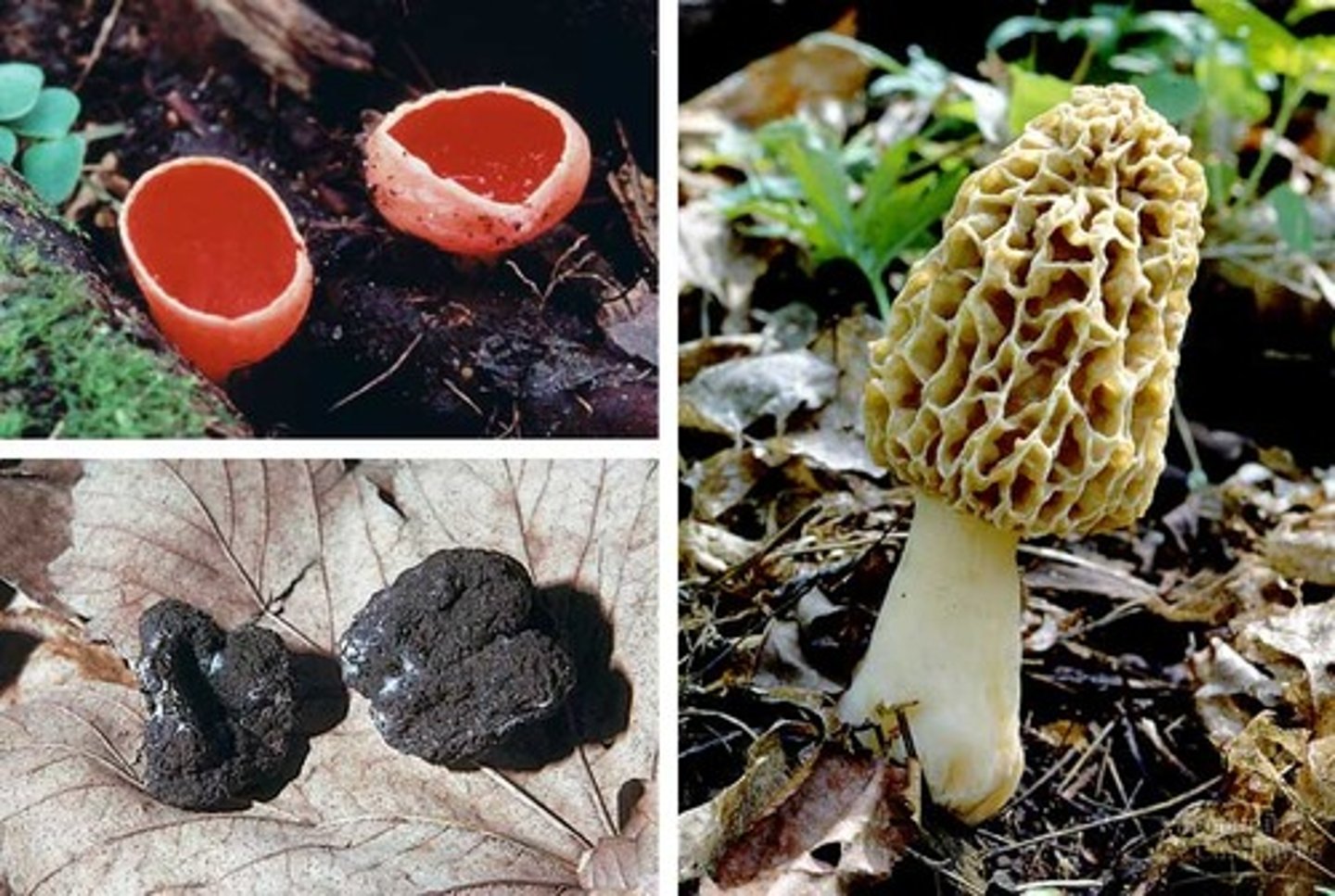

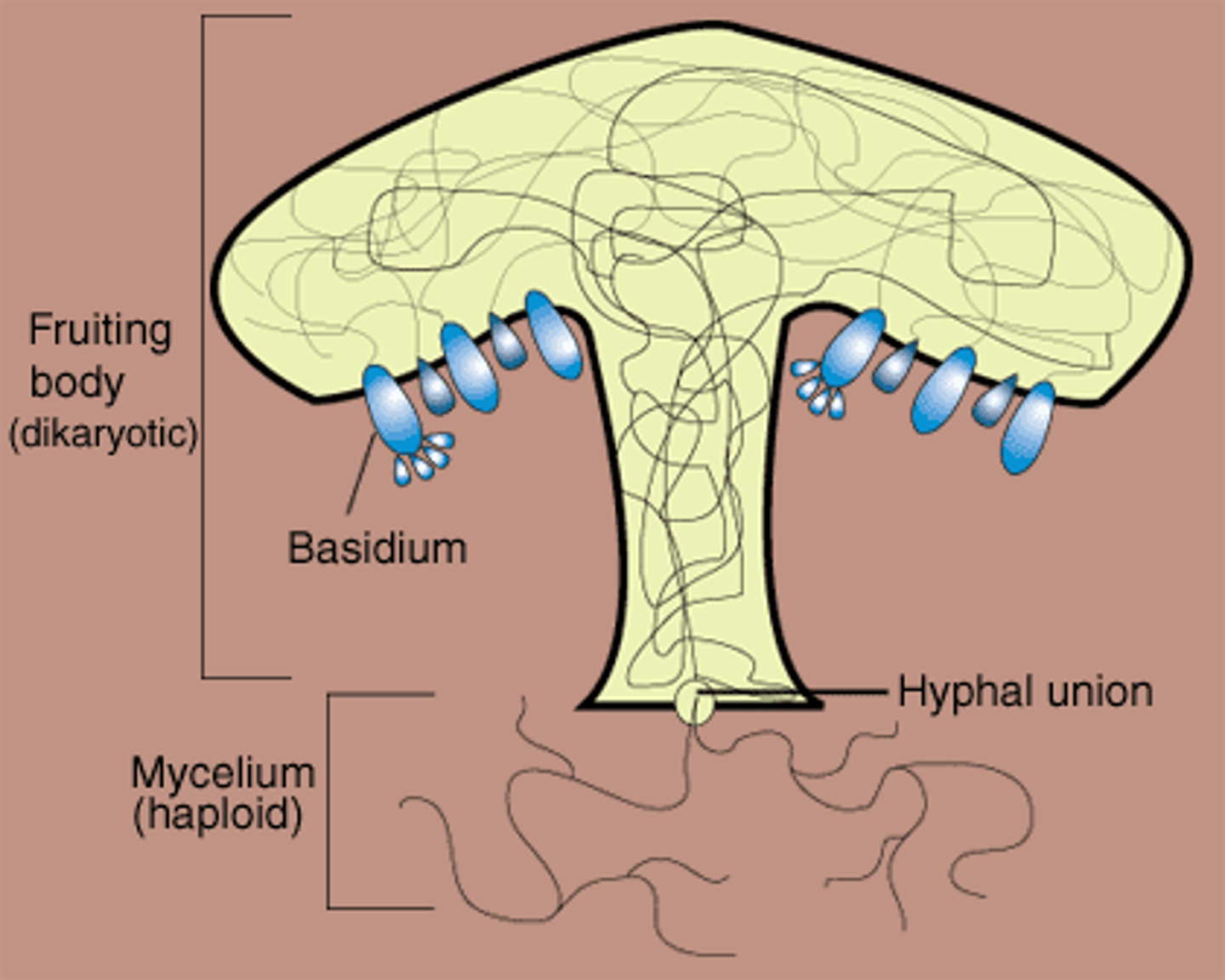
basidium
Club-shaped, reproductive structure in which club fungi produce spores
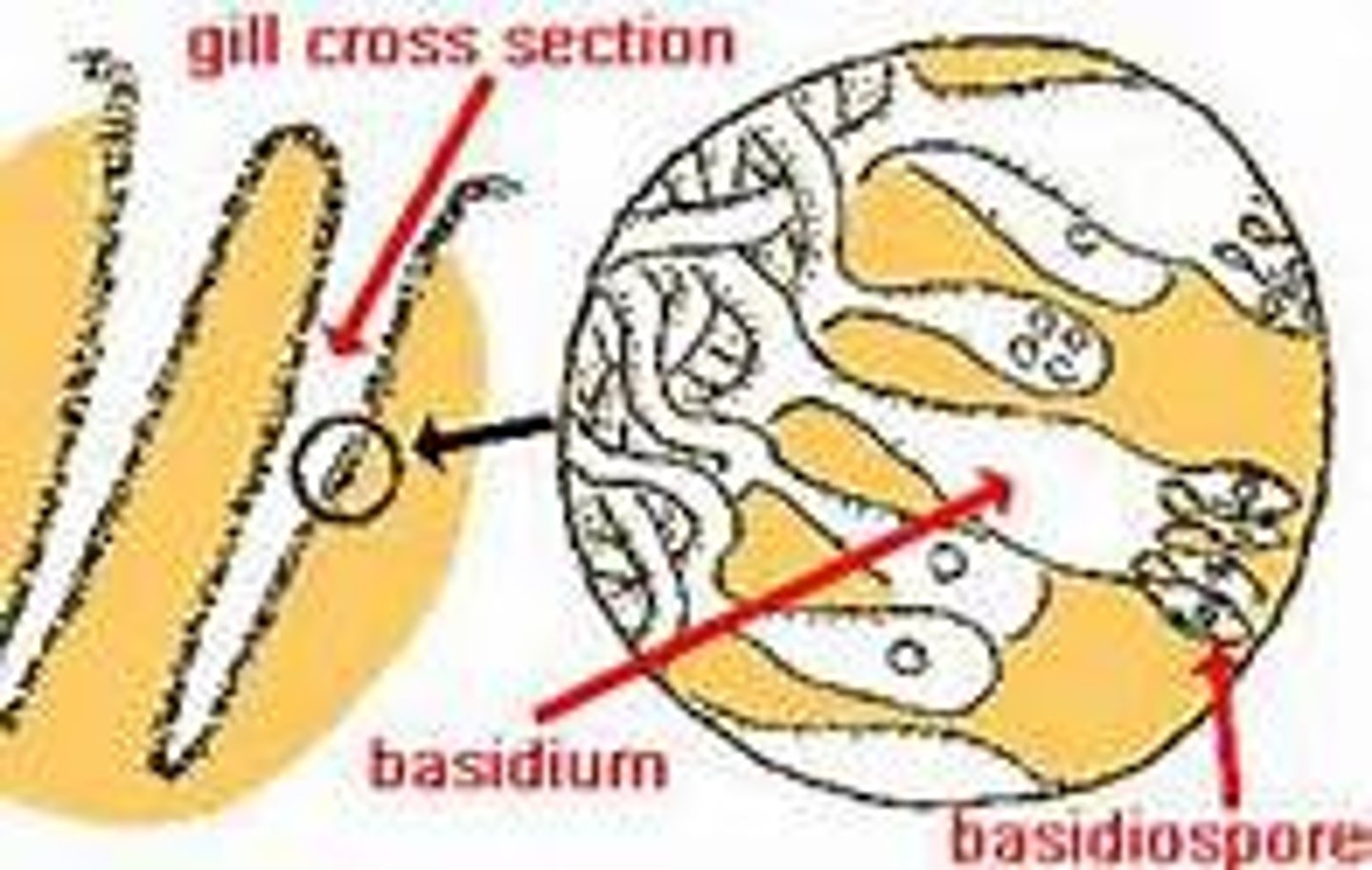
club fungi (basidiomycota)
Fungi that, if multicellular, bear the products of meiosis on club-shaped basidia and possess a long-lasting dikaryotic stage. Some are unicellular.

fungus
a parasitic plant lacking chlorophyll and leaves and true stems and roots and reproducing by spores
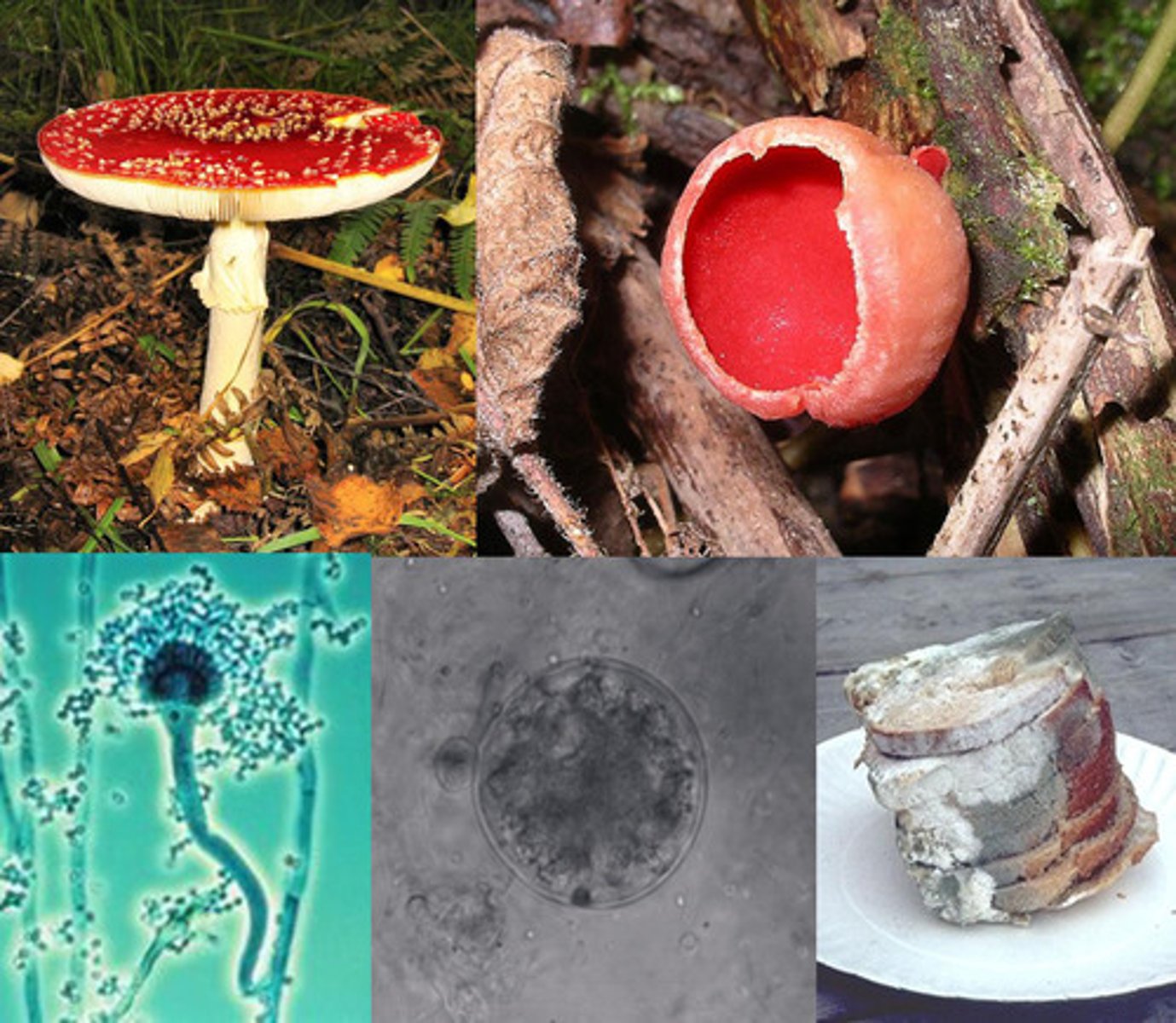

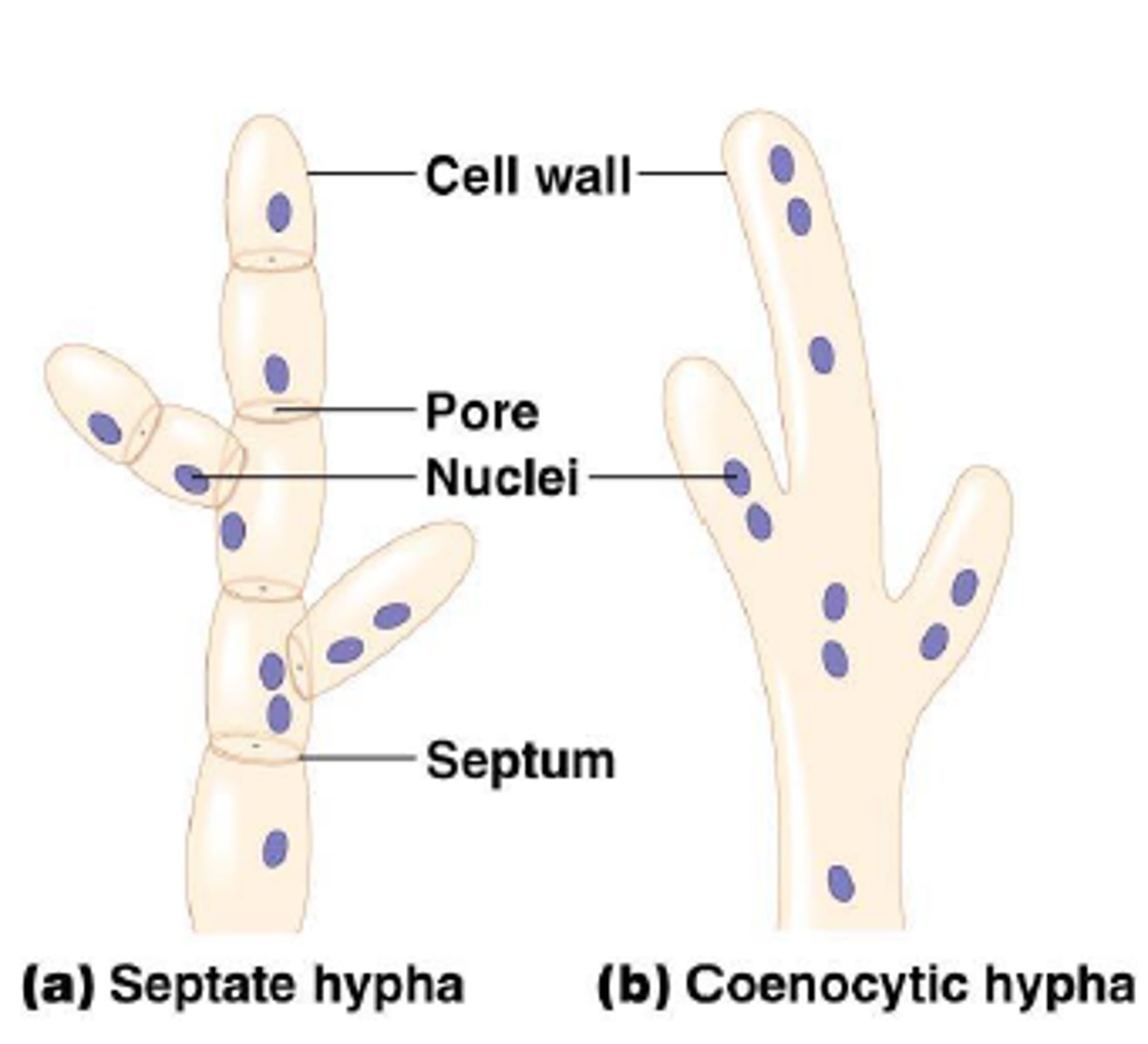
hypha
tiny filament that makes up a multicellular fungus or a water mold
parasitic
living at the expense of another; sponging

predatory
inclined to prey on others

mutualistic
both organisms benefit

saprobial
feeds on dead organisms or organic waste

asexual reproduction in fungi
fragmentation, budding, spores
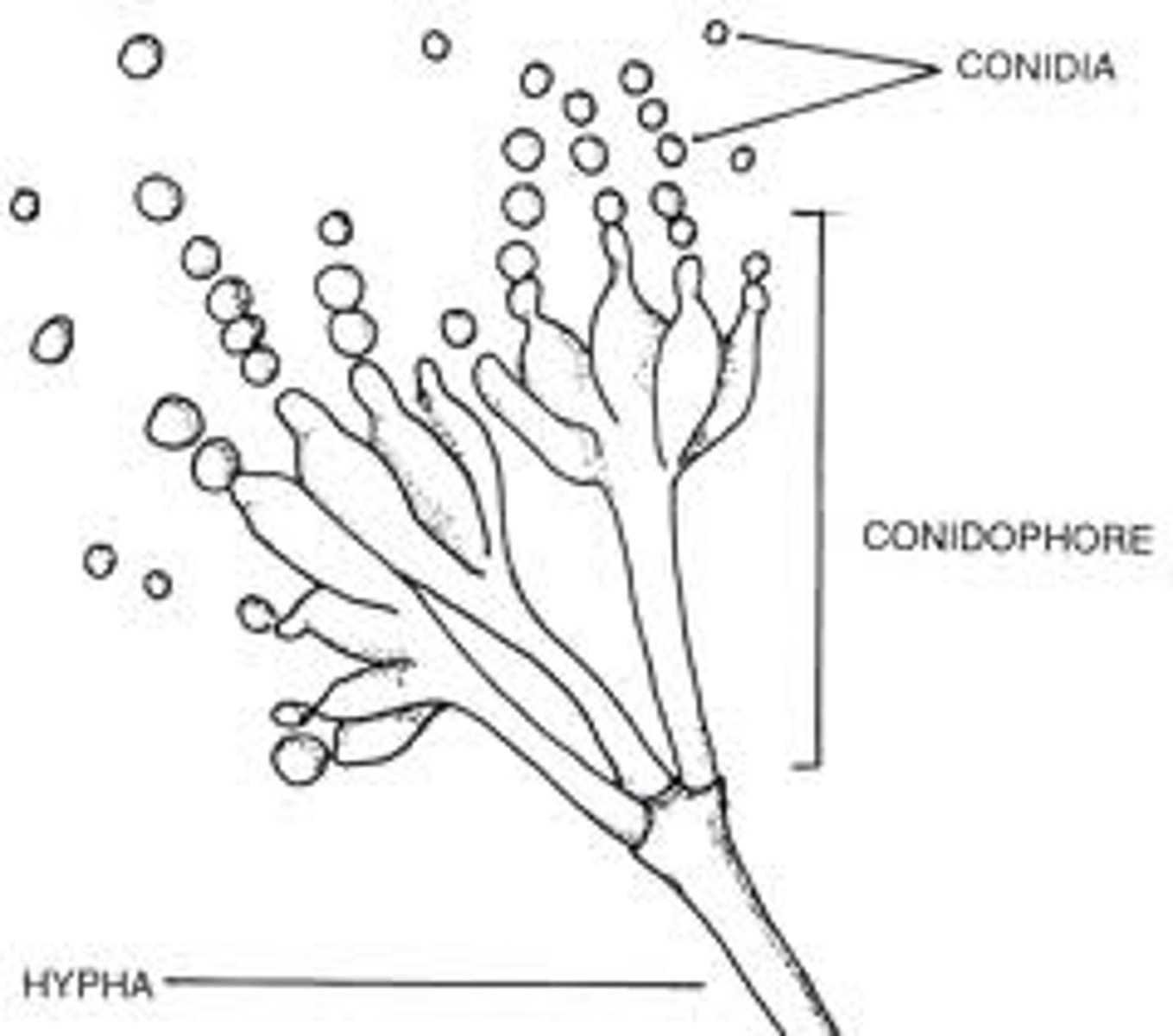
sexual reproduction in fungi
plasmogamy, karyogamy, meiosis
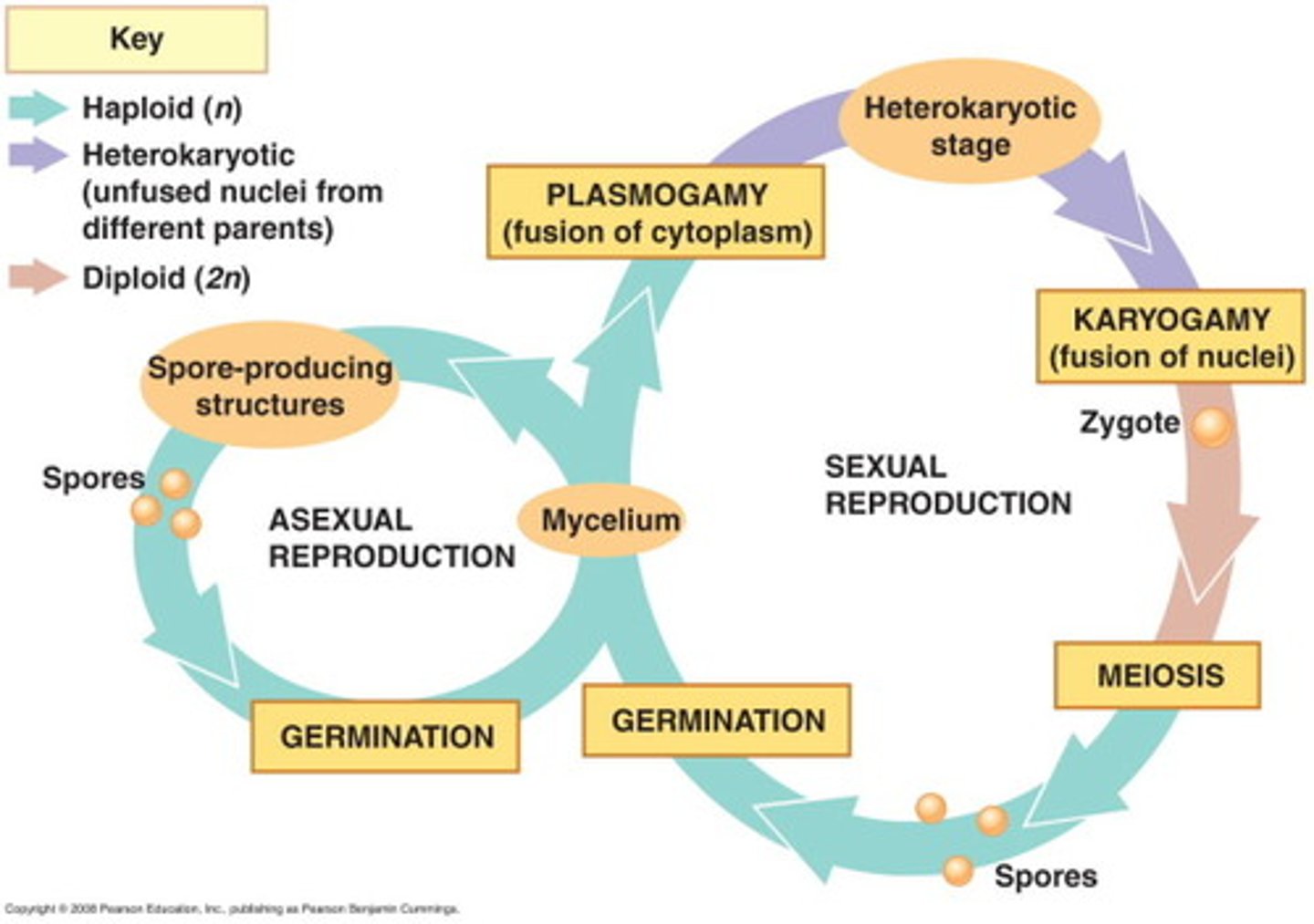
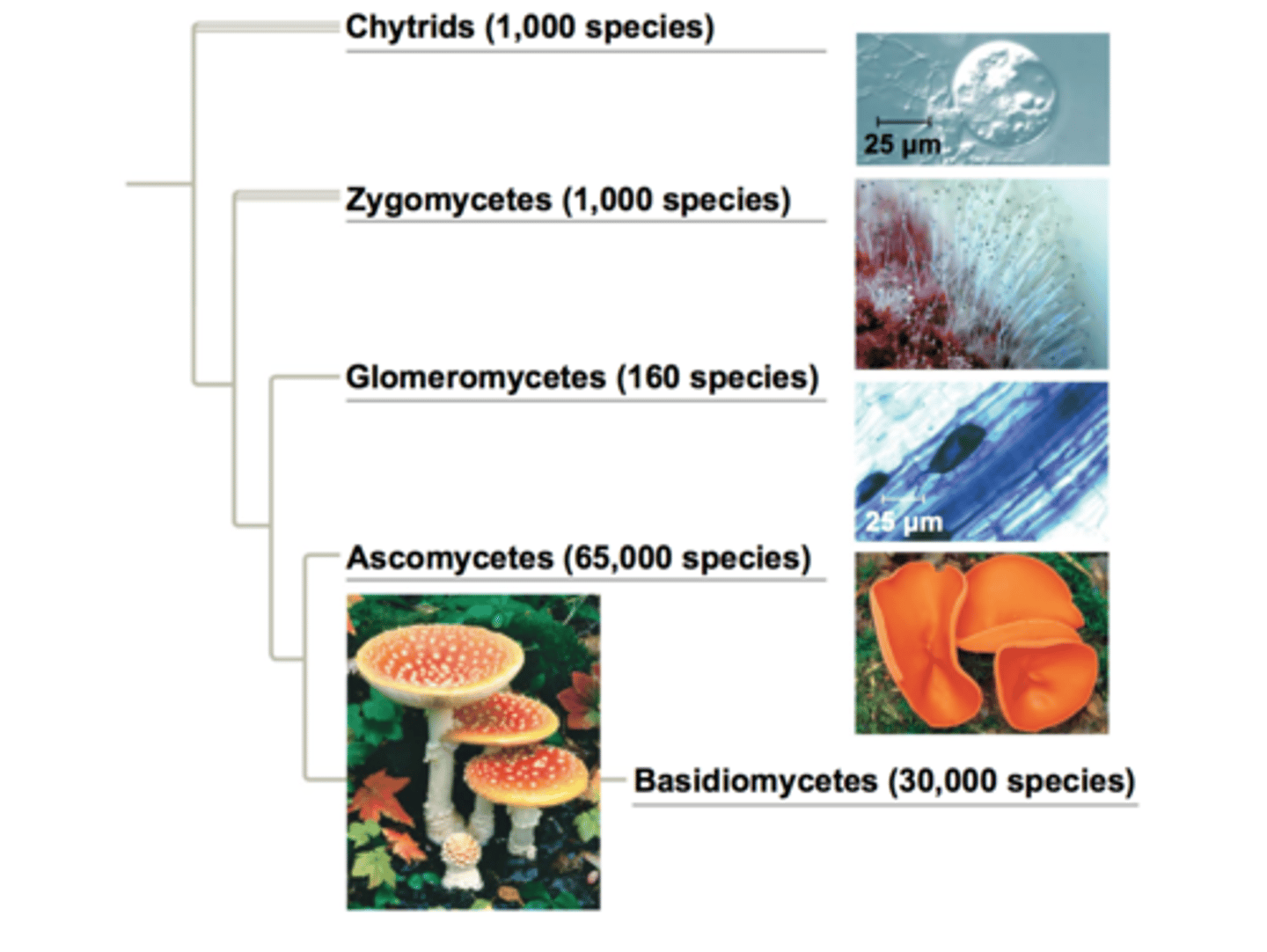
5 groups of fungi
1. Chytrids
2. Zygomycetes
3. Glomeromycetes
4. Ascomycetes
5. Basidiomycetes
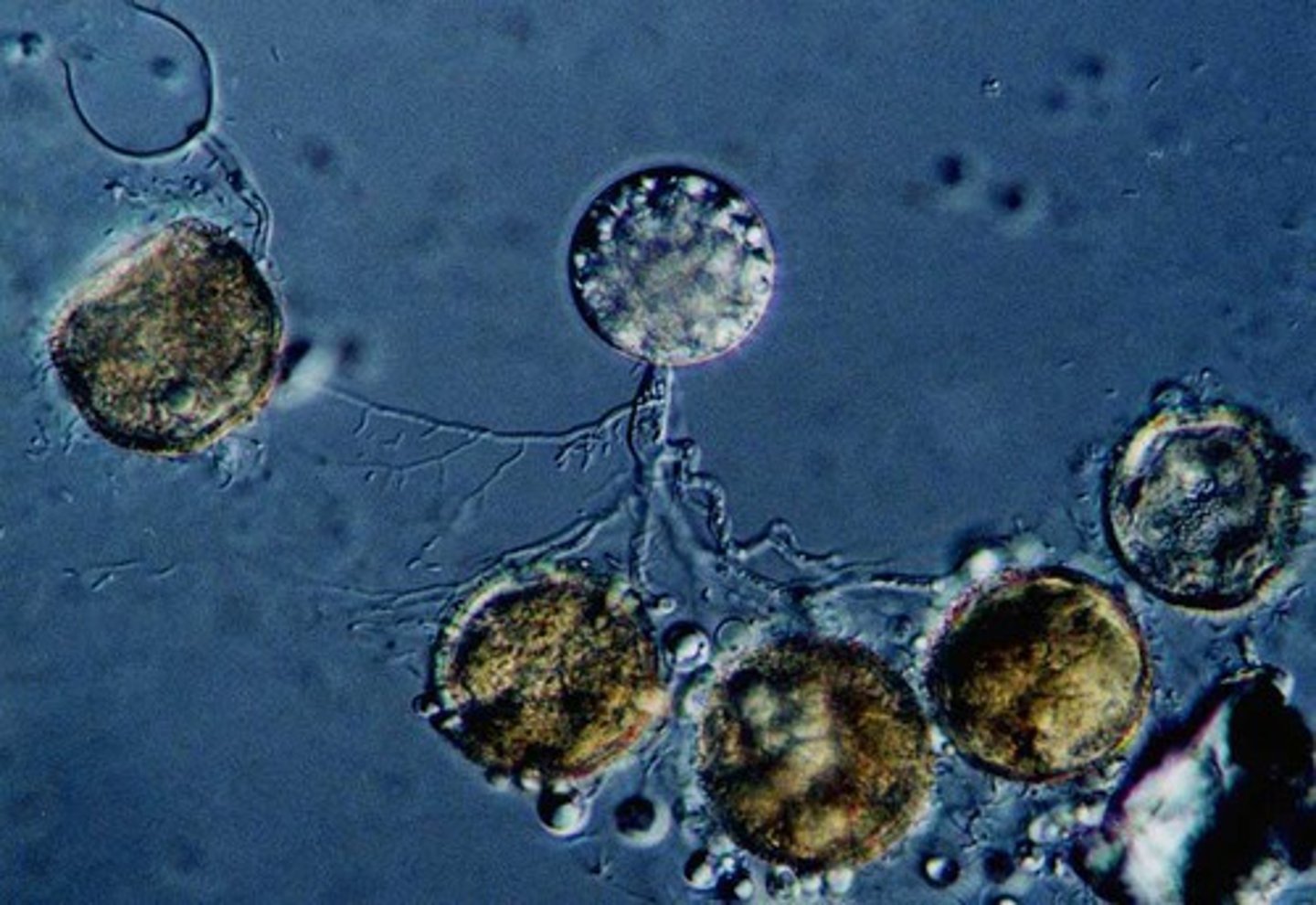
chytrids
aquatic and produce flagellated spores; they were the first fungi
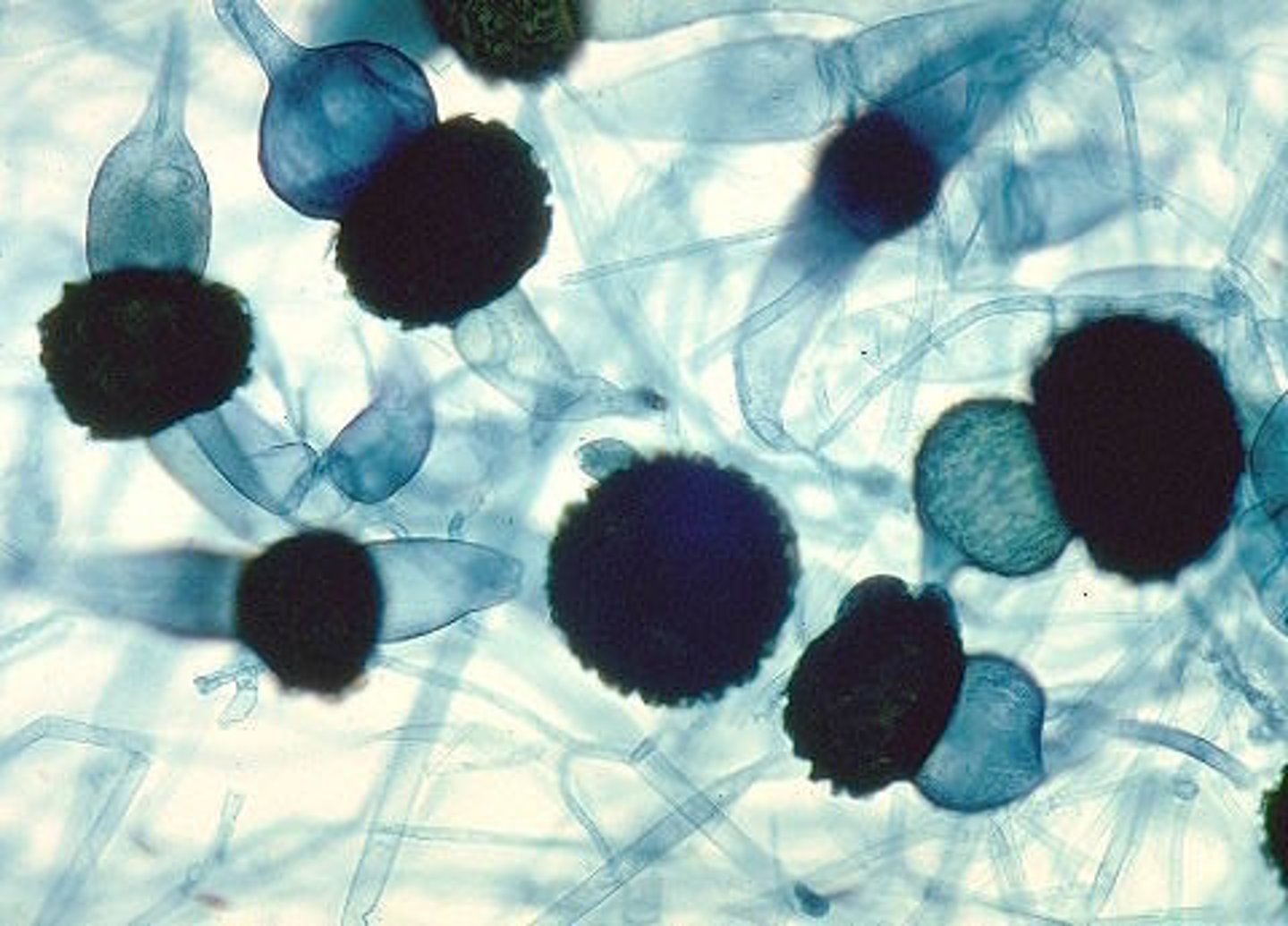
zygomycetes
a fungal group that is not very pathogenic; complex life cycle consisted on sexual and asexual fungal groups...fungi spend most of their time as haploids; black bread mold;
glomeromycetes
Member of the fungal phylum Glomeromycota, characterized by a distinct branching form of mycorrhizae called arbuscular mycorrhizae.
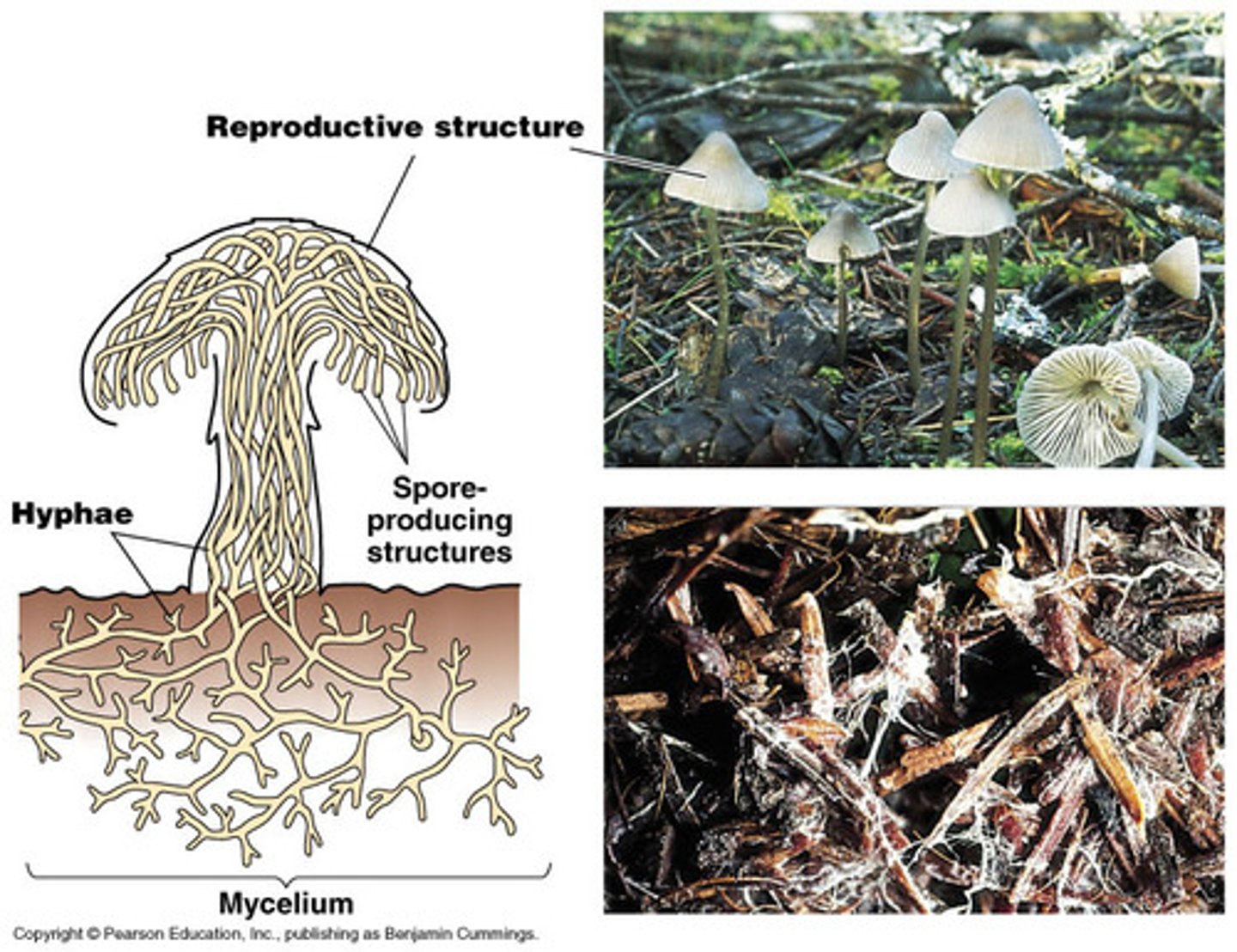
mycelium
densely branched network of the hyphae of a fungus
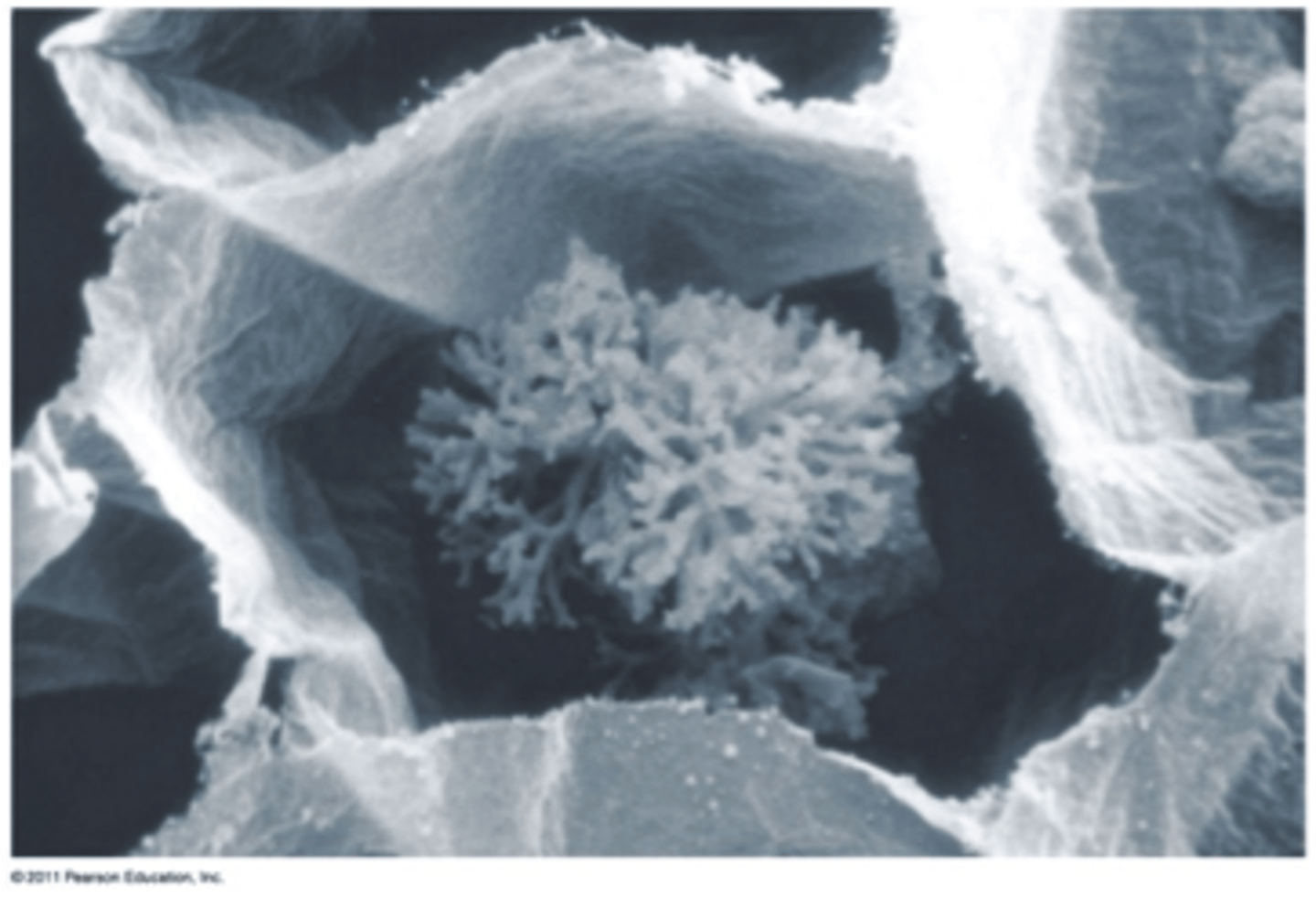
zygospore
resting spore that contains zygotes formed during the sexual phase of a mold's life cycle
fruiting body
The reproductive structure of a fungus that contains many hyphae and produces spores
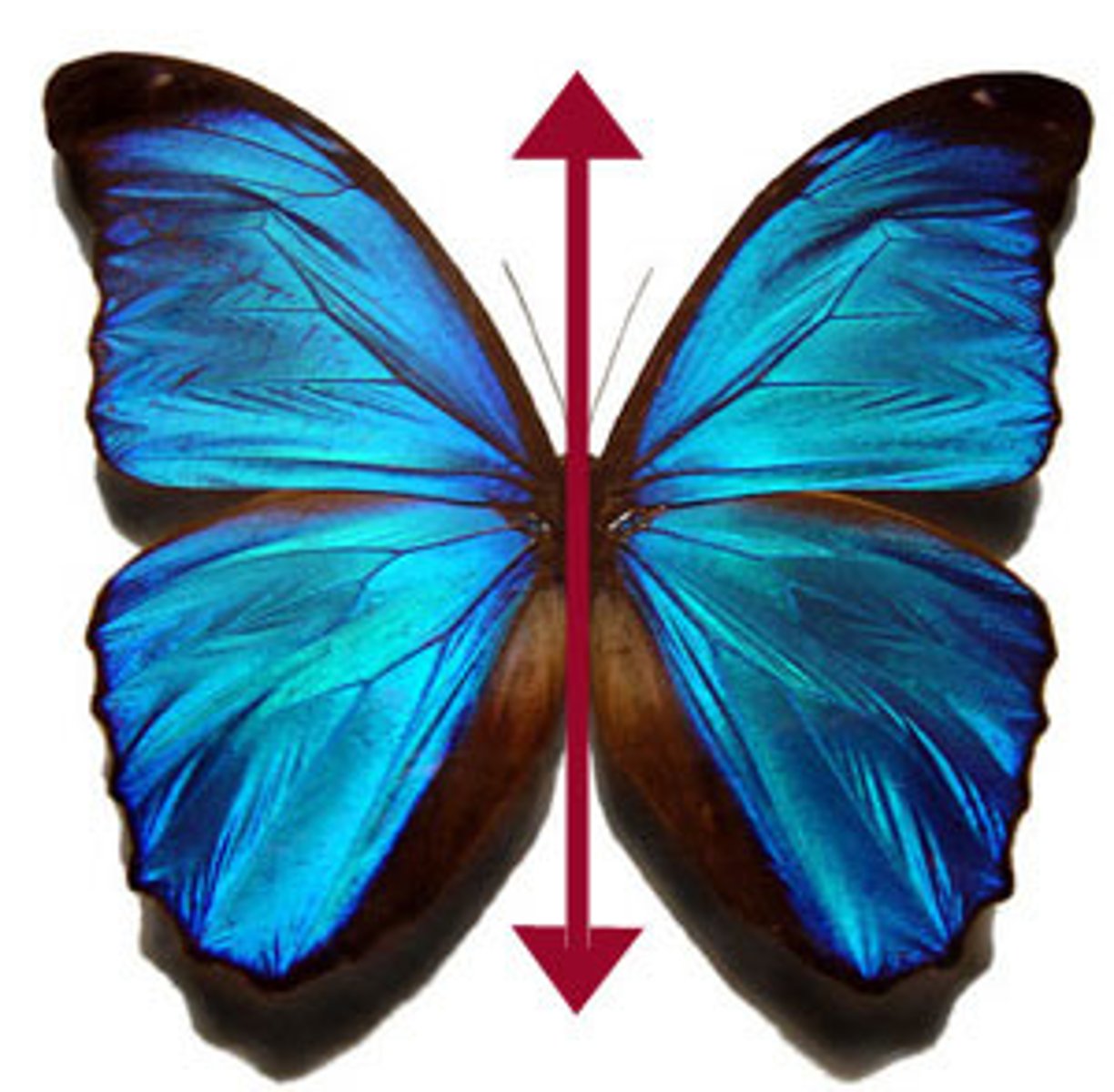
bilateral symmetry
Body plan in which only a single, imaginary line can divide the body into two equal halves.

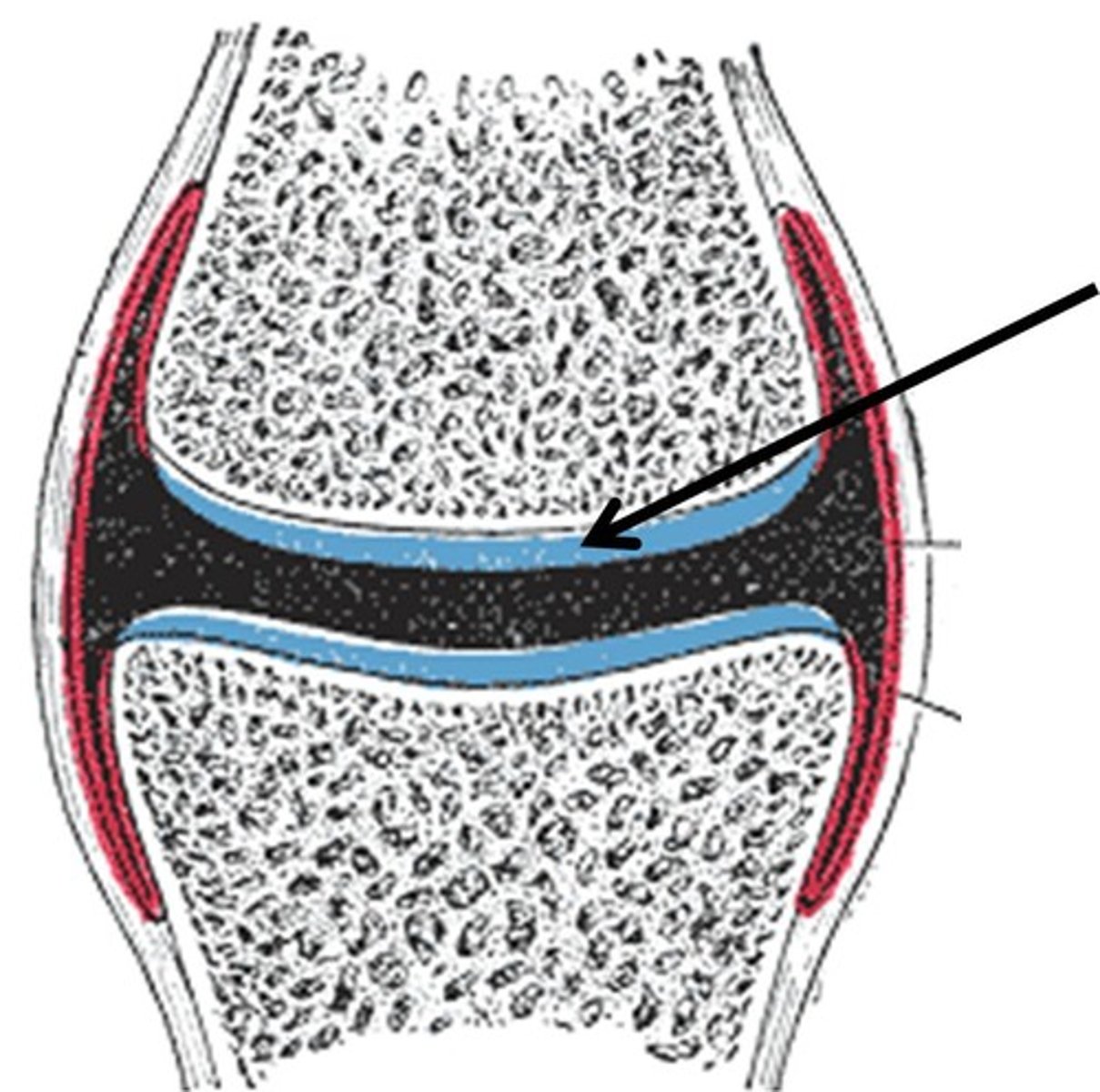
Cartilage
A connective tissue that is more flexible than bone and that protects the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together.
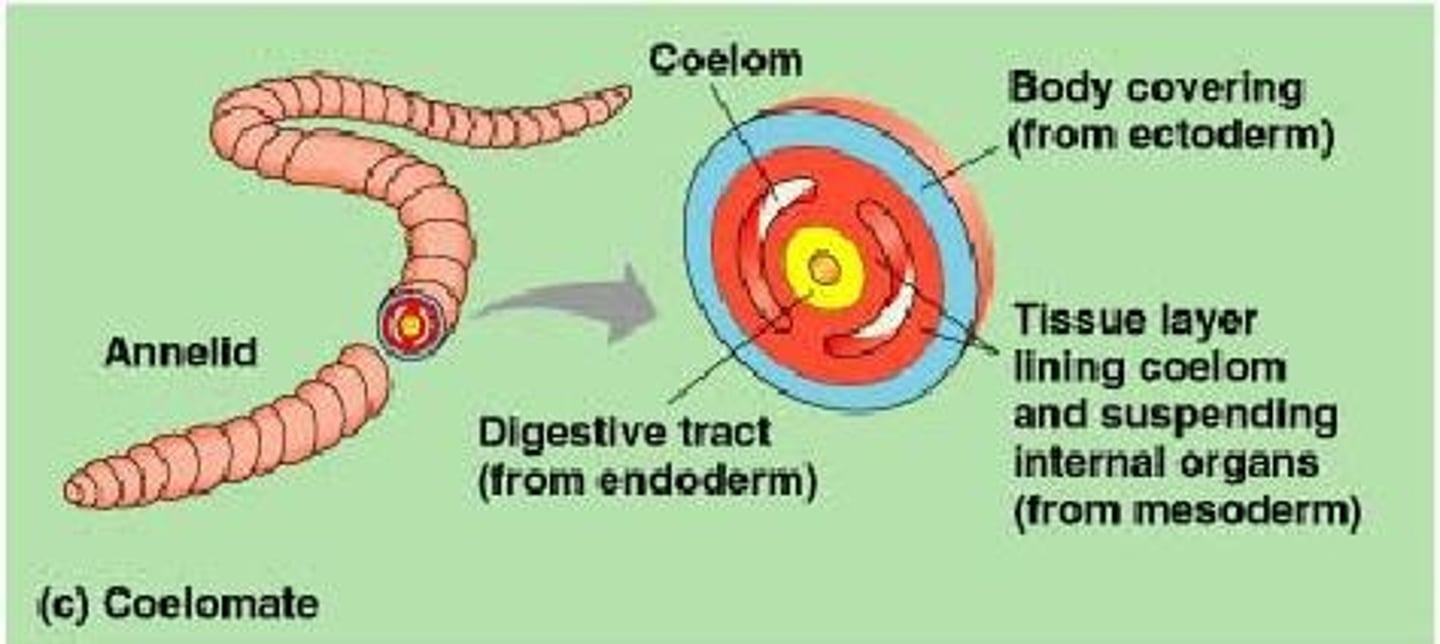
coelom
fluid-filled body cavity lined with mesoderm
ectothermy
Determination of body temperature primarily by external thermal conditions.

endothermy
Organisms with bodies that are warmed by heat generated by metabolism. This heat is usually used to maintain a relatively stable body temperature higher than that of the external environment

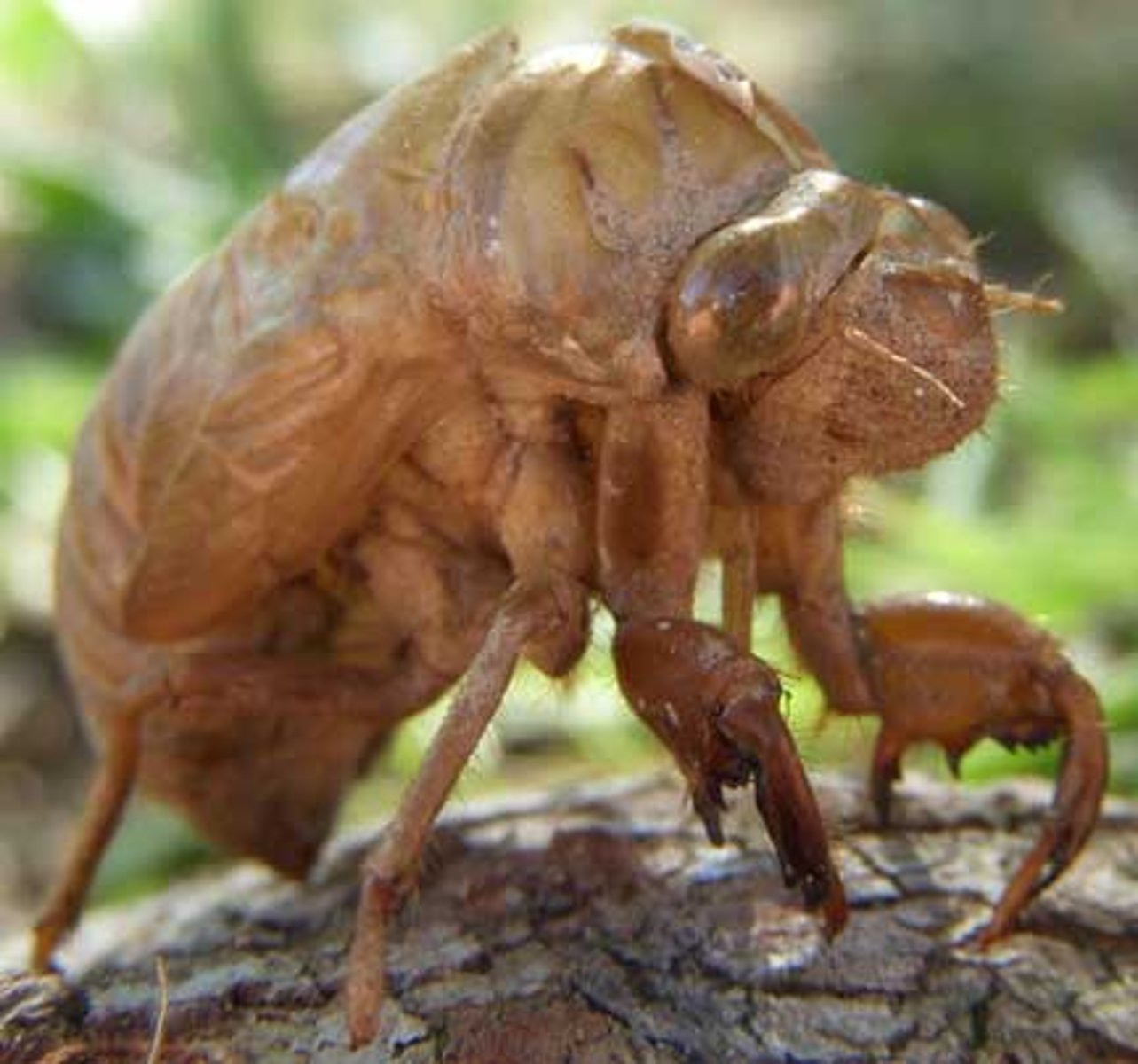
exoskeleton
A body covering, typically made of chitin, that provides support and protection

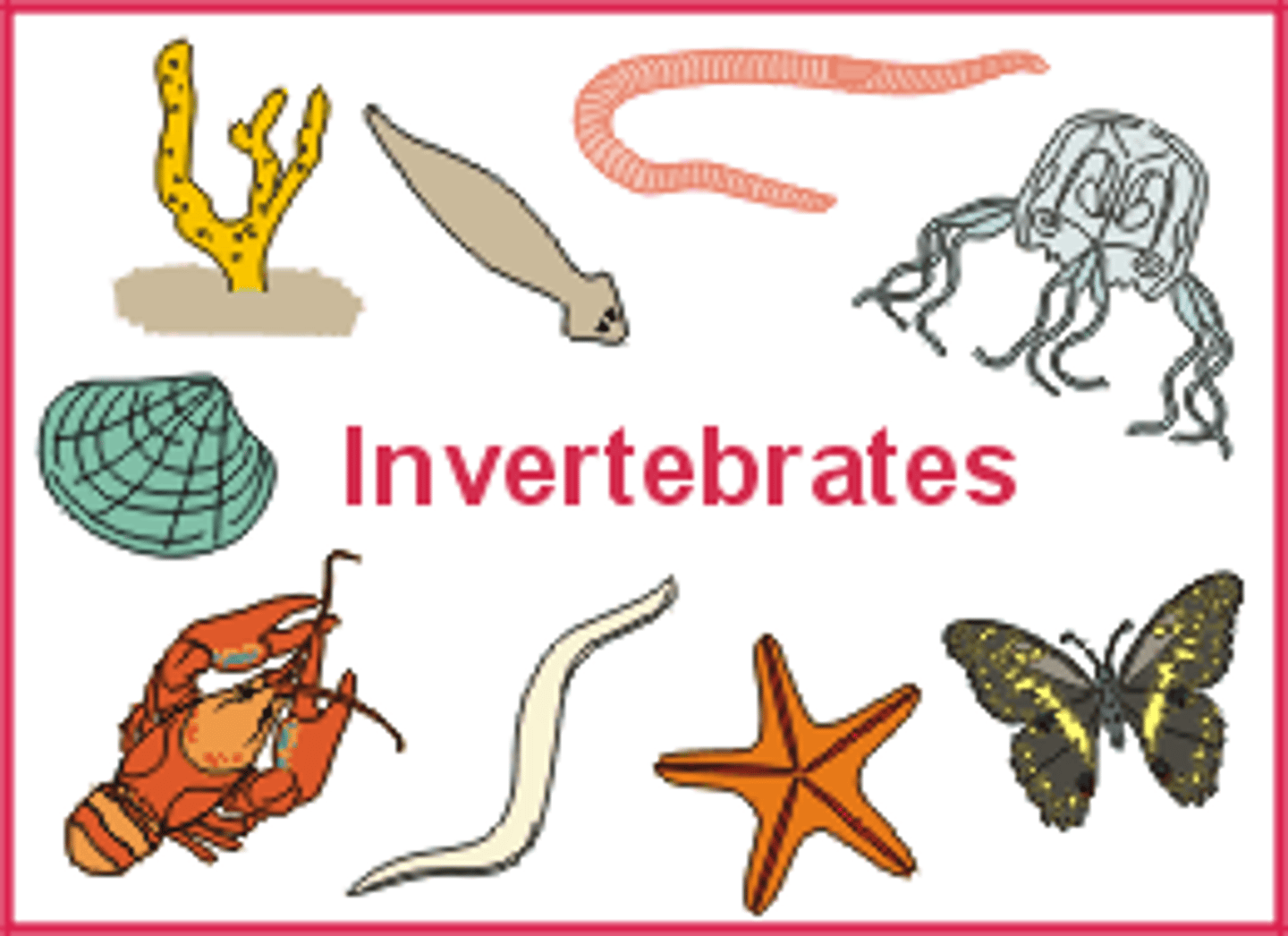
invertebrate
An animal without a backbone

mammary gland
An organ in female mammals that produces milk for the mammal's young.
mantle
refers to a soft, fleshy layer of tissue found in mollusks and some other invertebrates. It's a dorsal body wall that covers the visceral mass (internal organs) and, in many mollusks, secretes the shell.
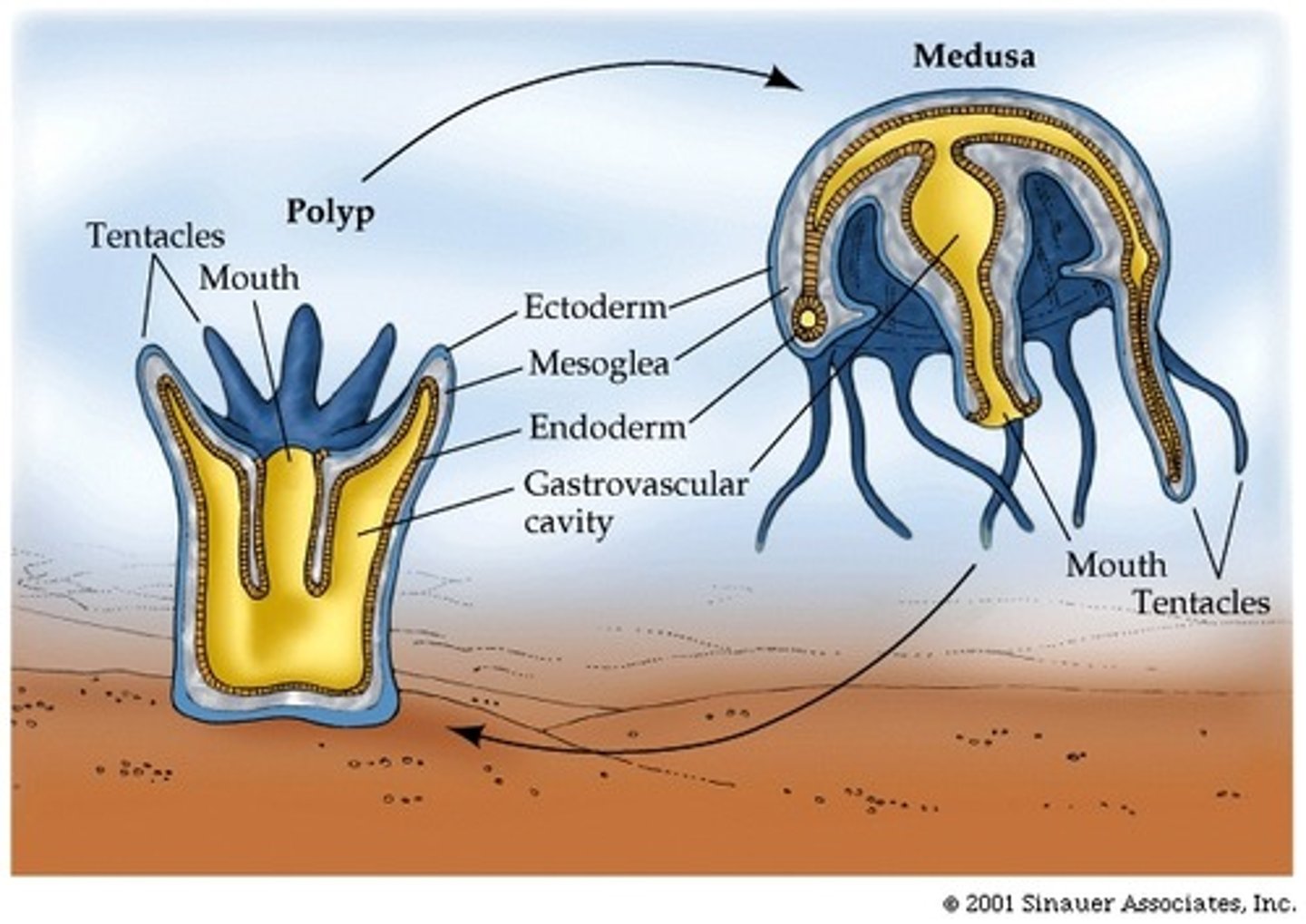
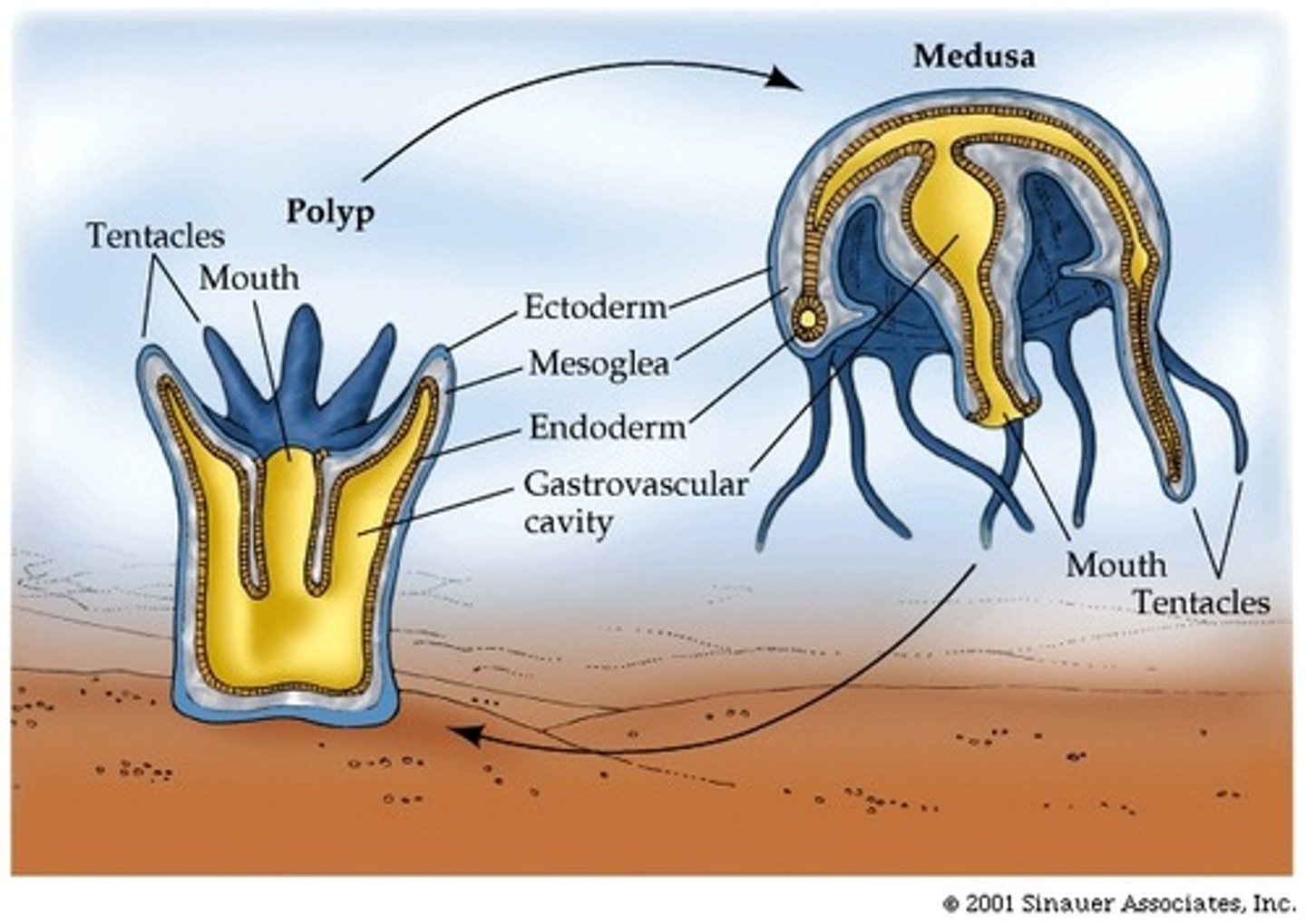
medusa
A free-swimming cnidarian with a bell-shaped body and tentacles
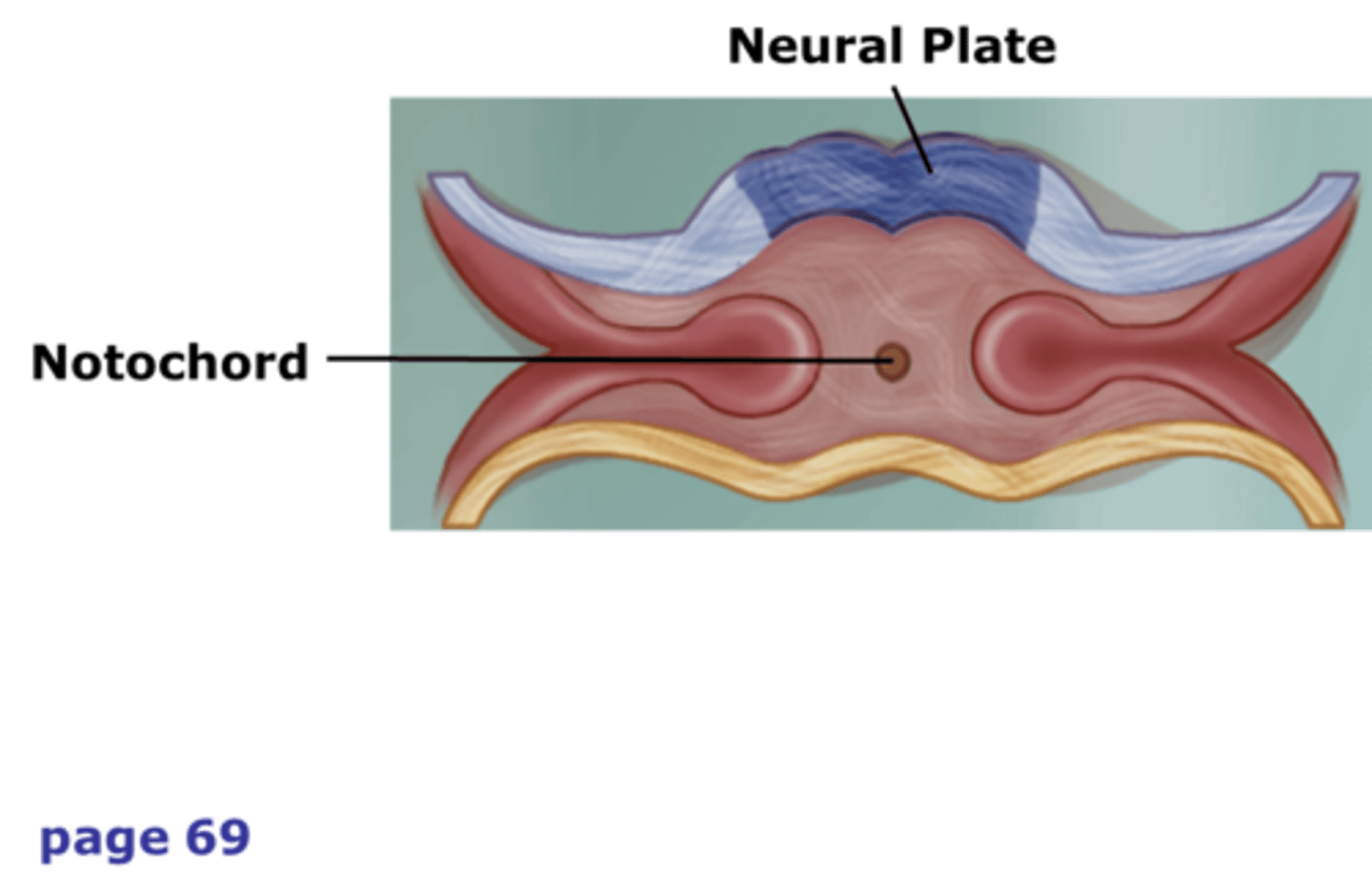
Notochord
A flexible rod that supports a chordate's back
polyp
The sessile, tubular form of a cnidarian with a mouth and tentacles at one end and a basal disk at the other
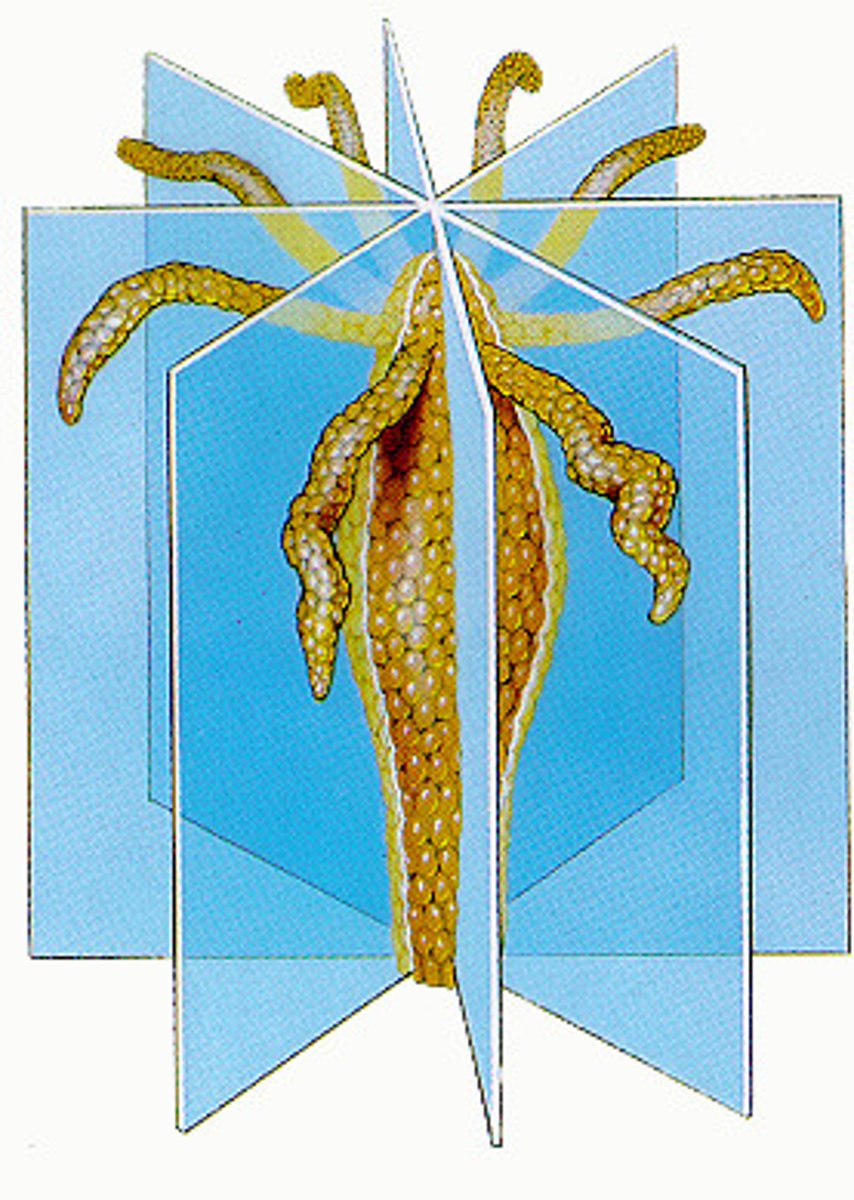
radial symmetry
body plan in which body parts repeat around the center of the body
segmentation
the division of the body of an organism into a series of similar parts
tetrapod
vertebrate with four limbs
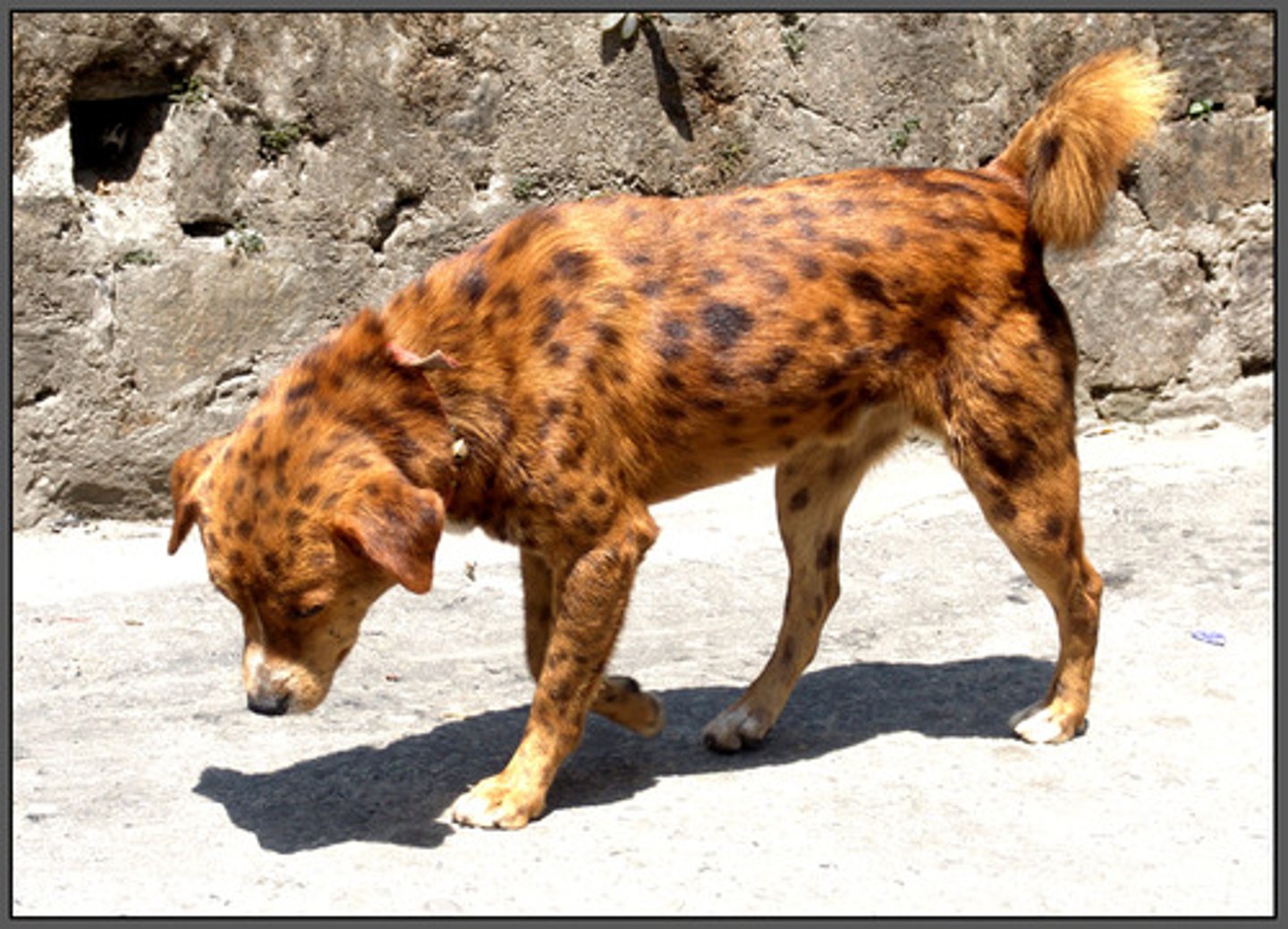

vertebrate
An animal with a backbone
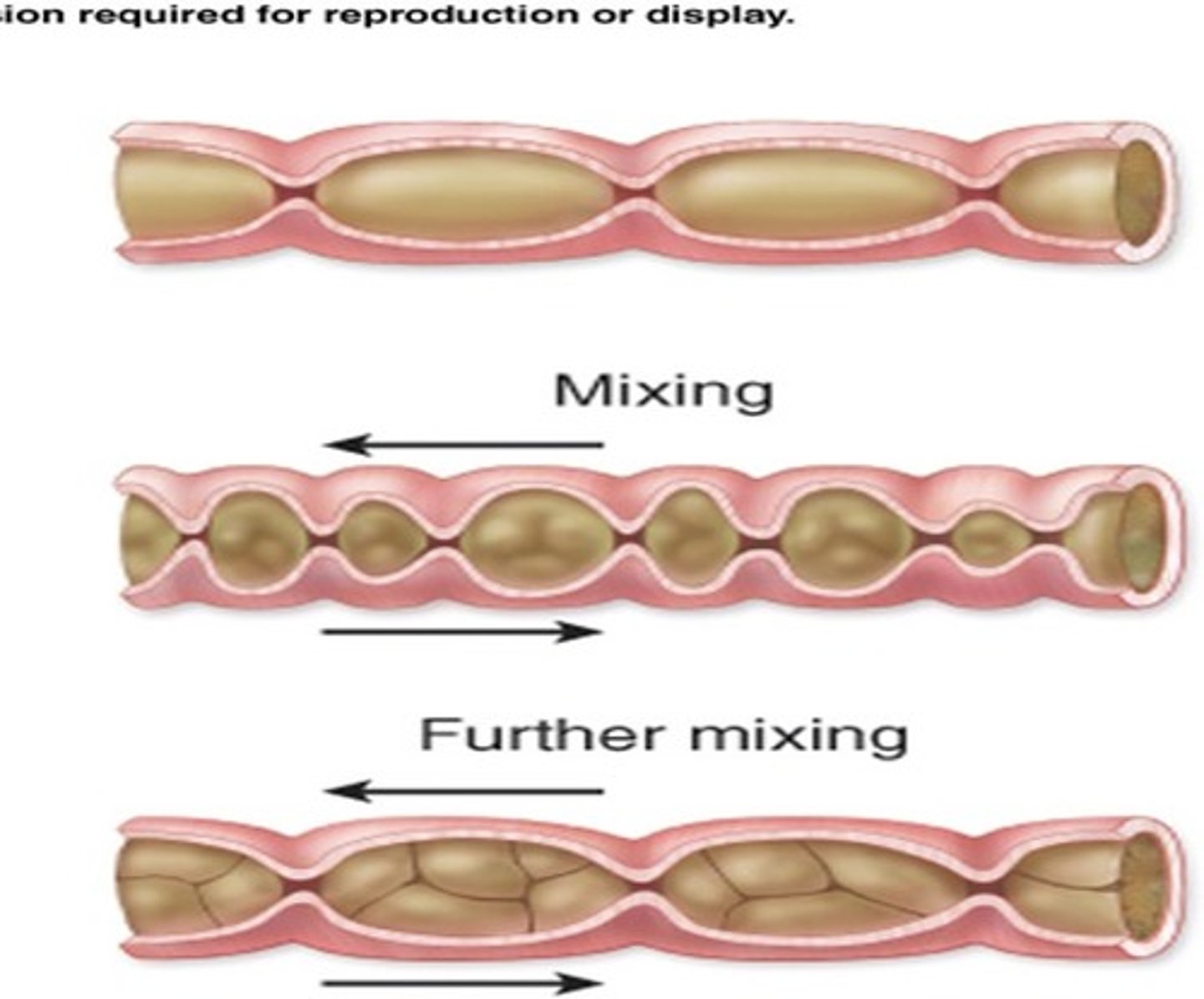
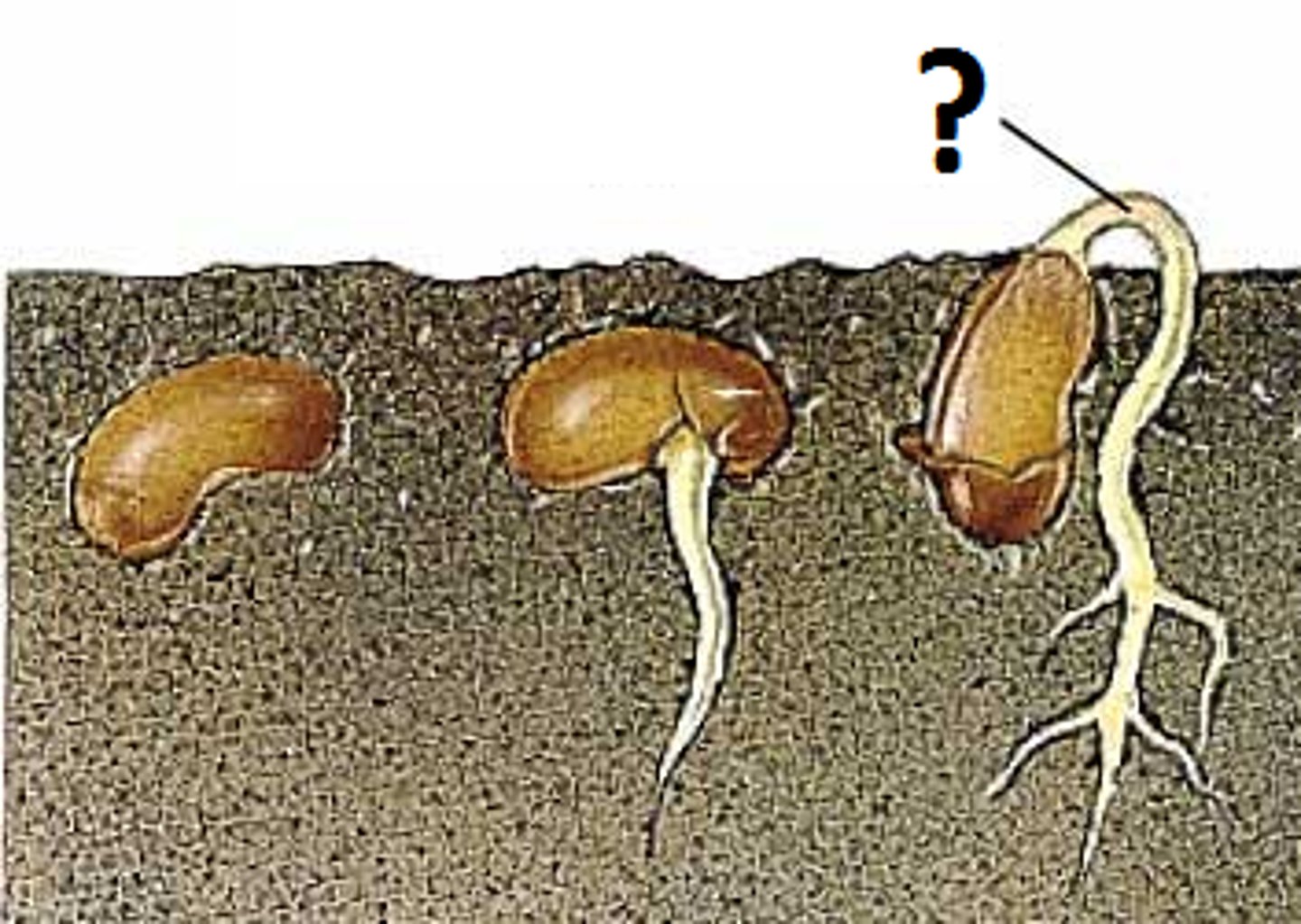
Germination
the process whereby seeds or spores sprout and begin to grow
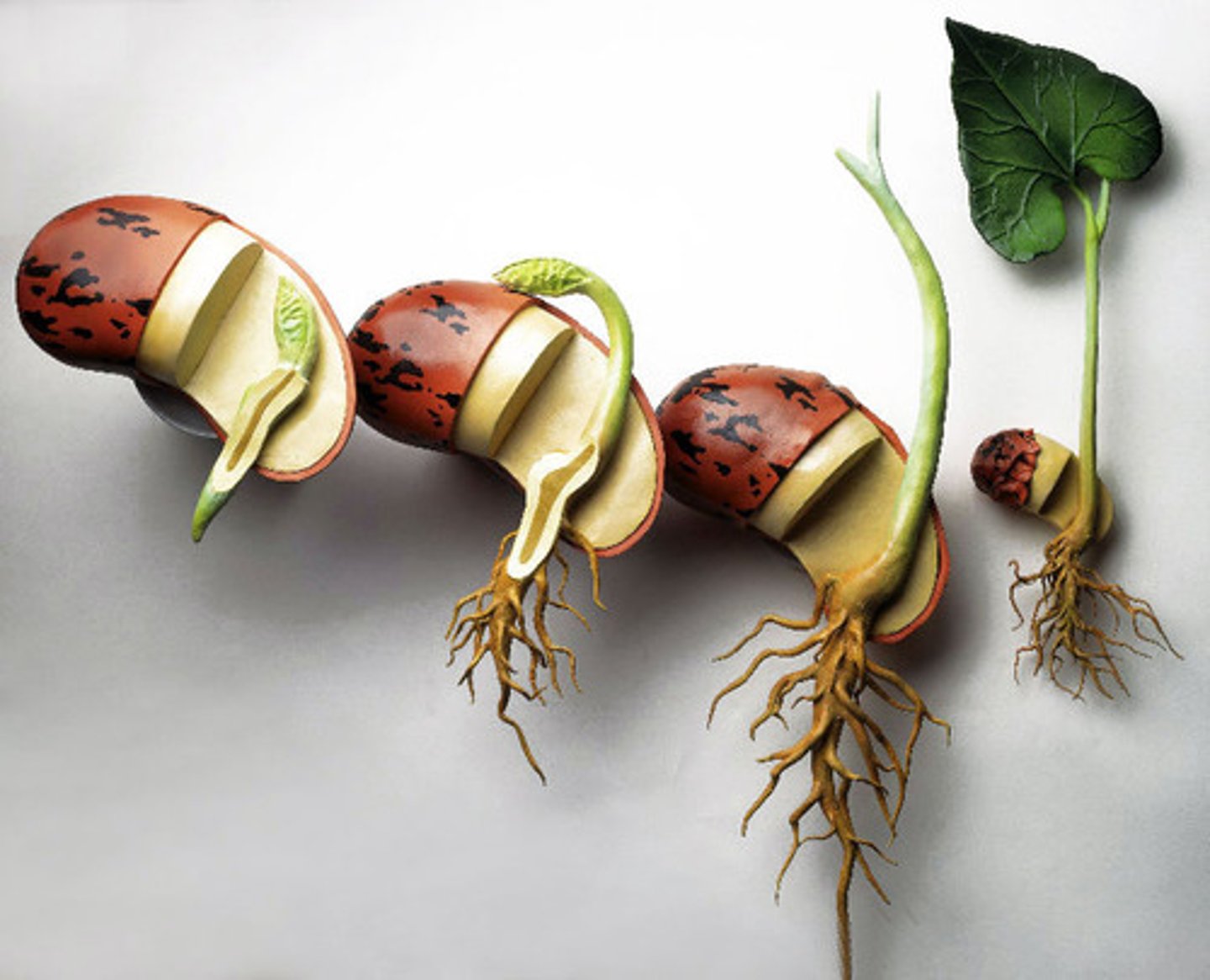

hypocotyl
The part of a plant embryo directly below the cotyledons, forming a connection with the radicle.

petal
A modified leaf of a flowering plant; petals are the often colorful parts of a flower that advertise it to insects and other pollinators.
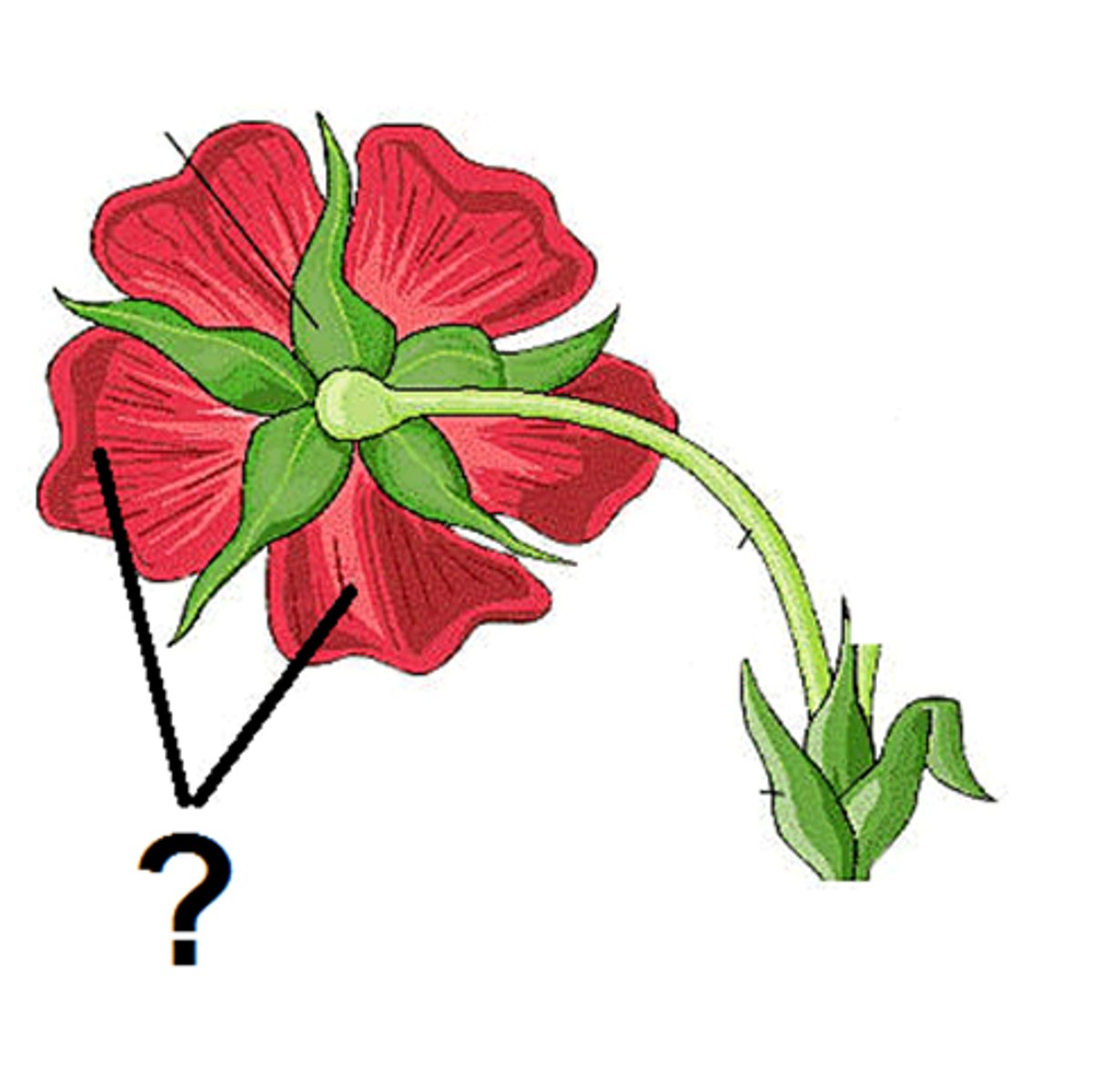
Pistil
The female reproductive part of a flower