Overview of Prosthetics
4.9(12)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
New cards
Prosthetists
provide care to patients with partial or total absence of limbs by designing, fabricating, and fitting prosthesis or artificial limbs.
2
New cards
* Creating the design to fit the individual’s particular functional and cosmetic needs
* Selects the appropriate materials and components
* Makes all necessary casts, measurements, and modifications, evaluates the fit and function of the prosthesis on the patient
* Teaches the patient how to care for the prosthesis
* Selects the appropriate materials and components
* Makes all necessary casts, measurements, and modifications, evaluates the fit and function of the prosthesis on the patient
* Teaches the patient how to care for the prosthesis
roles of the prosthetist.
3
New cards
Prosthesis
\- is used to provide an individual who has an amputated limb with the opportunity to perform functional tasks, particularly ambulation, which may not be possible without the limb
\- may also be made for use during activities or sports
\- determined largely by the extent of an amputation or loss and location of the missing extremity
\- may also be made for use during activities or sports
\- determined largely by the extent of an amputation or loss and location of the missing extremity
4
New cards
Amputation
\- absence of all or part of a limb as result of surgery, trauma, or disease
\- congenital or acquired
\- congenital or acquired
5
New cards
* Trauma
* Vascular Disease
* Infection
* Tumors
* Thermal, Chemical, or Electrical Injury
* Vascular Disease
* Infection
* Tumors
* Thermal, Chemical, or Electrical Injury
etiology of amputation.
6
New cards
* Trauma
* Disease and Tumors
* Disease and Tumors
etiology of amputation for UE.
7
New cards
* PVD
* Trauma
* Tumors
* Trauma
* Tumors
etiology of amputation for LE.
8
New cards
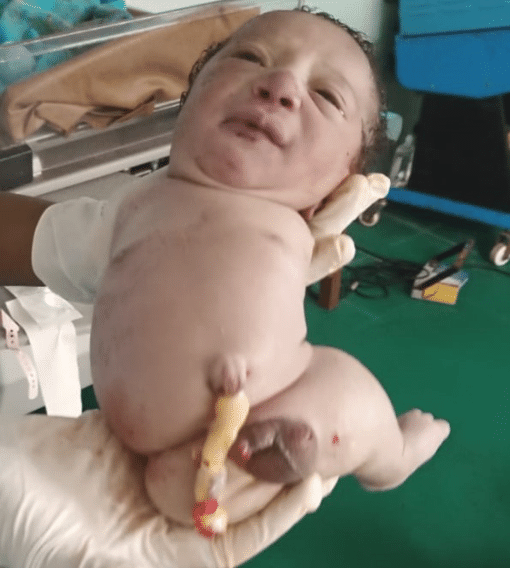
Amelia
absence of a limb.
9
New cards
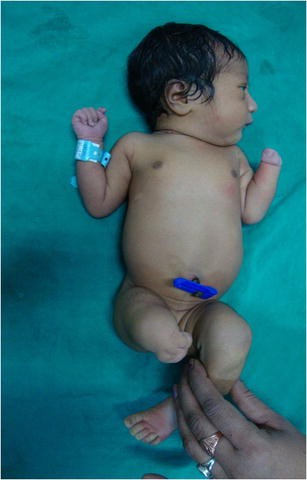
Meromelia
partial absence of a limb.
10
New cards
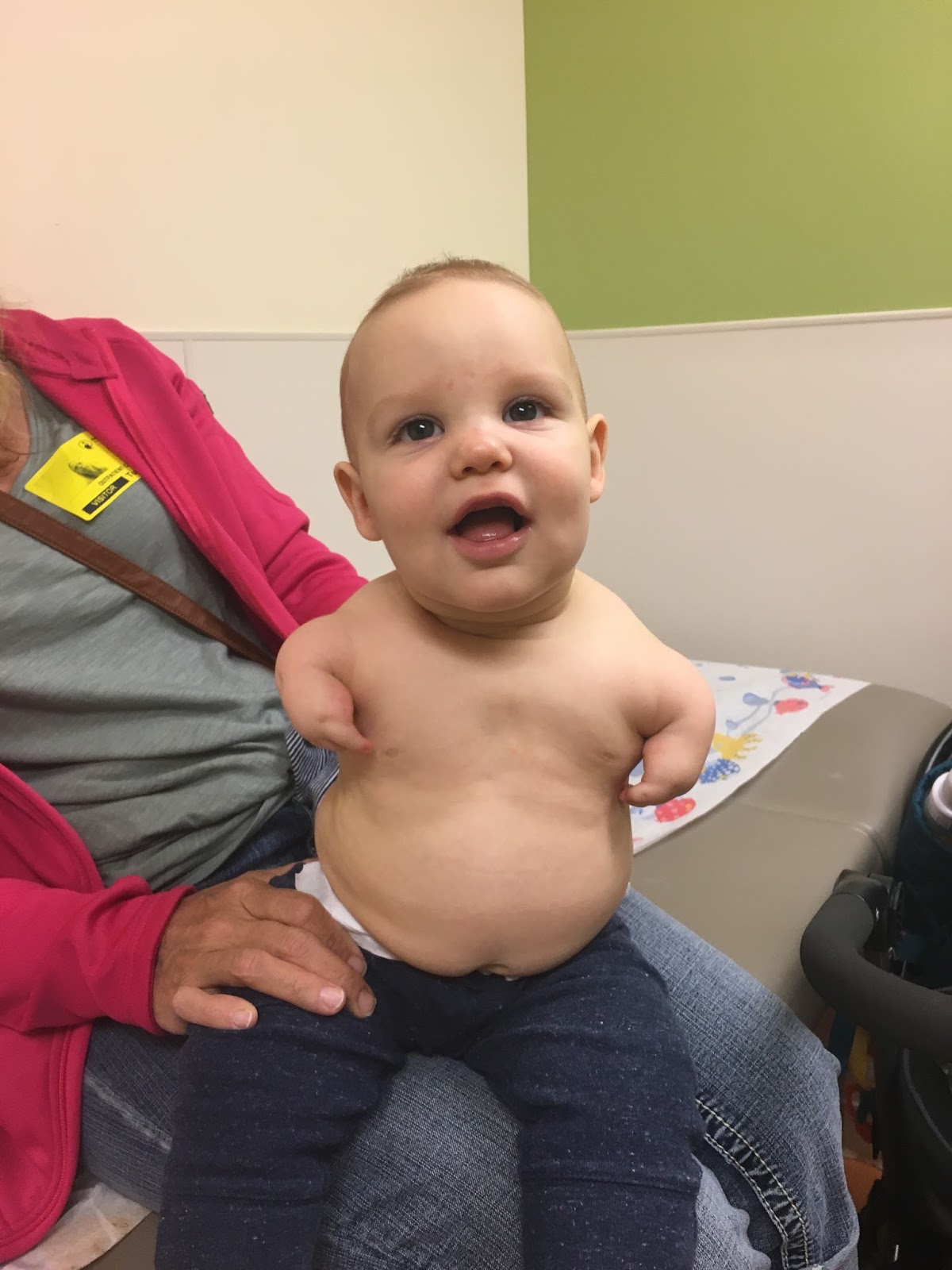
Phocomelia
flipper like appendage attached to the trunk.
11
New cards
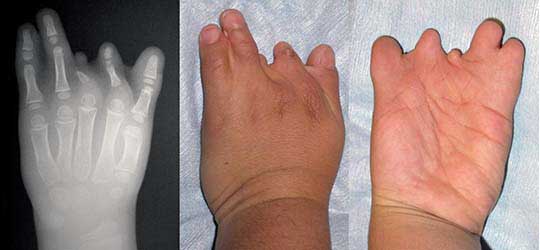
Adactayly
absent metacarpal or metatarsal.
12
New cards
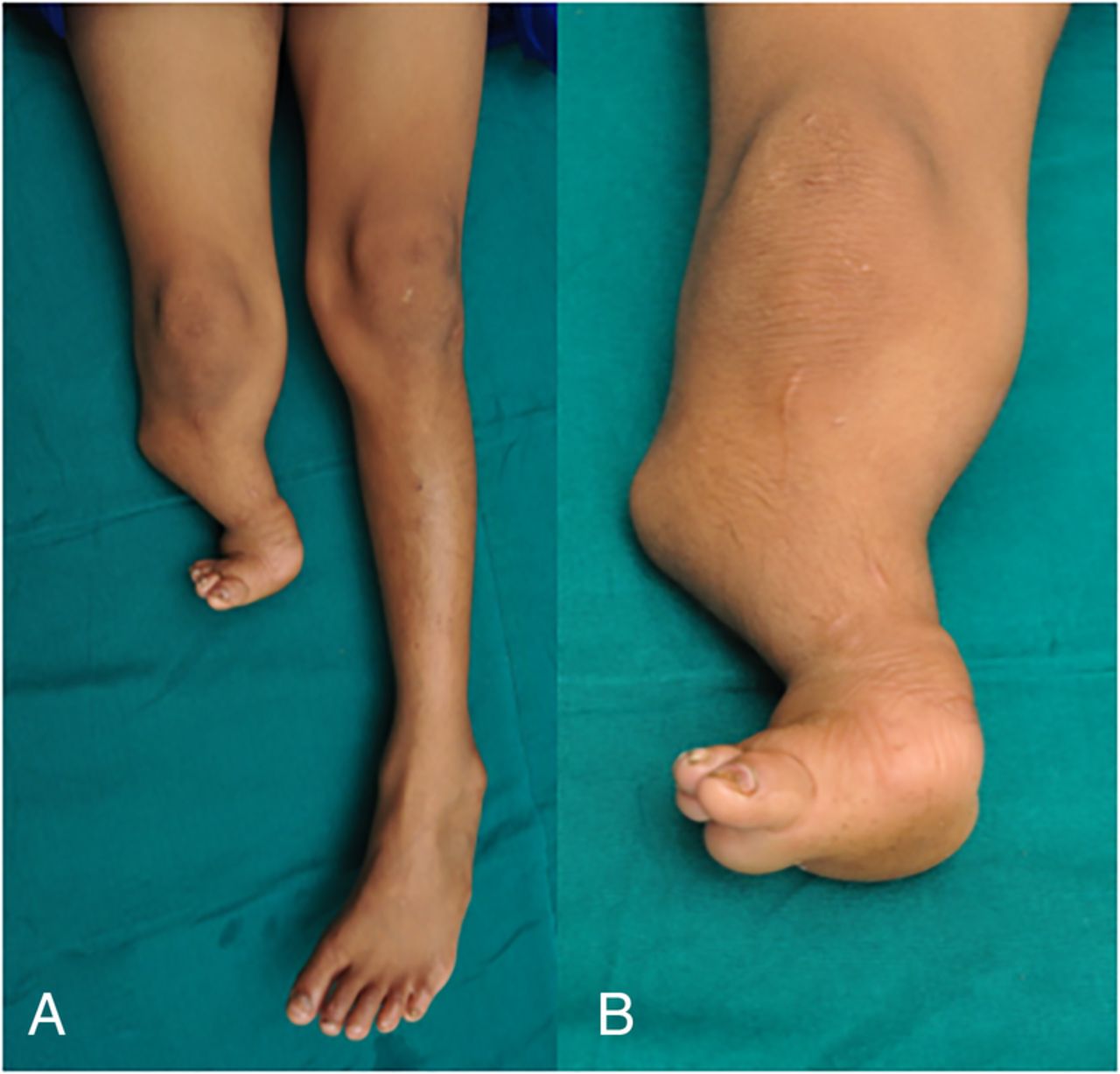
Hemimelia
absence of half a limb.
13
New cards
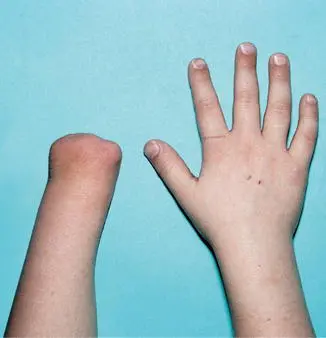
Acheiria
missing hand or foot.
14
New cards
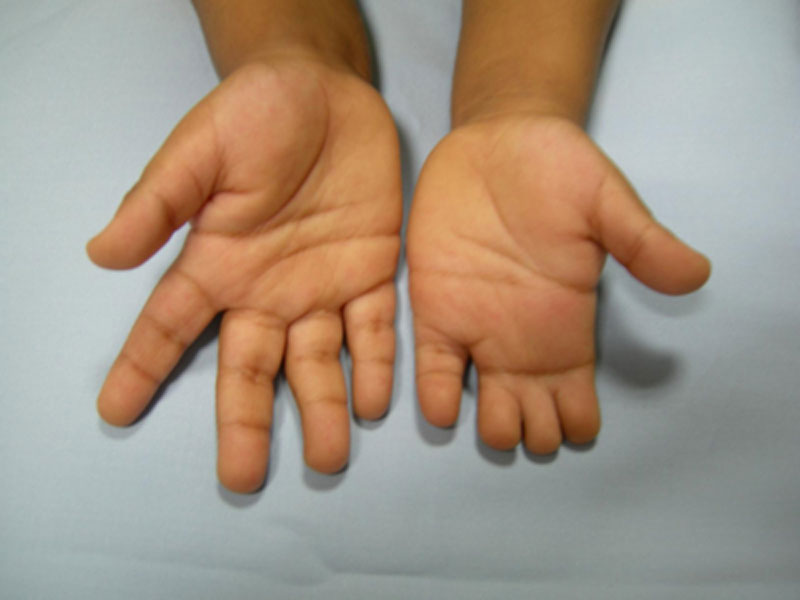
Aphalangia
absent finger or toe.
15
New cards
* Open Amputation (Guillotine Amputation)
* Closed Amputation
* Minor and Major Amputation
* Closed Amputation
* Minor and Major Amputation
types of amputation
16
New cards
Open Amputations
\- first of at least 2 operations required to construct a satisfactory stump
\- must followed by secondary closure, reamputation, revision or plastic repair
\- must followed by secondary closure, reamputation, revision or plastic repair
17
New cards
* Infections
* Severe traumatic wounds with extensive destruction of tissue and gross contamination by FB te
* Severe traumatic wounds with extensive destruction of tissue and gross contamination by FB te
indications of open amputation.
18
New cards
* Inverted skin flap
* Circular open amputations with post operative skin traction
* Vacuum assisted closure
* Circular open amputations with post operative skin traction
* Vacuum assisted closure
techniques in open amputation
19
New cards
* Amputation level
* Contour of the residual limb
* Expected function of the prosthesis
* Cognitive function of the patient
* Vocation of the patient
* A vocational interest of the patient
* Cosmetic importance of the prosthesis
* Financial resources of the patient
* Contour of the residual limb
* Expected function of the prosthesis
* Cognitive function of the patient
* Vocation of the patient
* A vocational interest of the patient
* Cosmetic importance of the prosthesis
* Financial resources of the patient
considerations when choosing a prosthesis.
20
New cards
* Poor fitting of the prostheses
* Walking with prosthesis on takes extra energy
* The stump should be checked every day for redness, blisters, soreness, or swelling
* Prosthesis need to be adjusted several times before it fits well
* Walking with prosthesis on takes extra energy
* The stump should be checked every day for redness, blisters, soreness, or swelling
* Prosthesis need to be adjusted several times before it fits well
problems may occur when using prosthesis.
21
New cards
Interscapulothoracic Amputation
\- used less frequently
\- only made necessary as part of the surgical intervention to remove a malignant lesion or the result of severe trauma
\- most difficult to fit with a functional prosthesis due to:
* *number of joints to be replaced*
* *multiple DOF available for control*
* *problems related to maintaining secure suspension of the prosthesis*
\- only made necessary as part of the surgical intervention to remove a malignant lesion or the result of severe trauma
\- most difficult to fit with a functional prosthesis due to:
* *number of joints to be replaced*
* *multiple DOF available for control*
* *problems related to maintaining secure suspension of the prosthesis*
22
New cards
Shoulder Disarticulation
\- in this amputation, the rotator cuff tendons should be sutured together over the glenoid wing; the deltoid is attached to the inferior glenoid and lateral scapular border to fill the subacromial space
\- it involves unique and challenging prosthetic problems - incorporates the greatest number of prosthetic components
\- prosthetics components are similar to those for the transhumeral prosthesis with the addition of a shoulder unit, which allows passive positioning of the shoulder joint in **flexion-extension and abduction-adduction**
\- it involves unique and challenging prosthetic problems - incorporates the greatest number of prosthetic components
\- prosthetics components are similar to those for the transhumeral prosthesis with the addition of a shoulder unit, which allows passive positioning of the shoulder joint in **flexion-extension and abduction-adduction**
23
New cards
* Complete enclosure shoulder socket
* X-frame shoulder socket
* X-frame shoulder socket
commonly used designs for shoulder disarticulation.
24
New cards
Transhumeral Amputation
\- most common satisfactory amputation in the upper extremity
\- above elbow
\- the more humeral length is preserved, the more optimal the prosthetic restoration
* *very short*
* *short*
* *standard*
* *long*
\- above elbow
\- the more humeral length is preserved, the more optimal the prosthetic restoration
* *very short*
* *short*
* *standard*
* *long*
25
New cards
Short
transhumeral amputation that preserves 30% to 50% of length, which results in loss of GH motion because of the inhibition of the prosthetic socket that encompasses the acromion.
26
New cards
Long
transhumeral amputation that preserves 50% to 90% of length relative to the sound side, GH motions are preserved and uninhibited by the prosthetic socket.
27
New cards
Internal Elbow Joint
\- the standard elbow component for the transhumeral prosthesis
\- allow for 135 degrees of flexion and can be manually locked into a number of preset flexed positions
\- incorporated a turntable that allows passive internal or external rotation of the forearm
\- allow for 135 degrees of flexion and can be manually locked into a number of preset flexed positions
\- incorporated a turntable that allows passive internal or external rotation of the forearm
28
New cards
Elbow Disarticulation
\- a variant of the transhumeral prosthesis; the socket is flat and broad distally to conform to the anatomic configuration of the epicondyles of the distal humerus
\- provides some self suspension and allows the individual with an amputation active rotation of the prosthesis
\- advantages:
* reduction in surgery time and blood loss
* provides improved prosthetic self suspension
* reduces the rotation of the socket on the residual limb
\- disadvantages:
* marginal cosmetic appearance caused by the required external elbow mechanism
* current limitations in technology which impede the use of externally powered elbow mechanism
\- provides some self suspension and allows the individual with an amputation active rotation of the prosthesis
\- advantages:
* reduction in surgery time and blood loss
* provides improved prosthetic self suspension
* reduces the rotation of the socket on the residual limb
\- disadvantages:
* marginal cosmetic appearance caused by the required external elbow mechanism
* current limitations in technology which impede the use of externally powered elbow mechanism
29
New cards
Transradial Amputation
\- preferred in most cases
\- most common level because it allows the highest level of functional recovery
\- most common level because it allows the highest level of functional recovery
30
New cards
Short BE
defined as **0% to 35%** preservation, which results in difficult prosthetic suspension and the additional loss of full ROM at the elbow.
31
New cards
Medium BE
\- preserves **35% to 55%** length, but pronation and supination with a prosthesis are lost
\- elbow flexion is reduced because of the inhibiting prosthesis
\- elbow flexion is reduced because of the inhibiting prosthesis
32
New cards
Long BE
\- preserves **55% to 90%** length,
\- allows up to **60% degrees of supination and pronation** with a prosthesis, and maintains strong elbow flexion
\- allows up to **60% degrees of supination and pronation** with a prosthesis, and maintains strong elbow flexion
33
New cards
Short Transradial Amputation
\- can complicate suspension
\- limit elbow flexion strength and elbow ROM
\- limit elbow flexion strength and elbow ROM
34
New cards
Medium Forearm Residual Limb
\- preferred when optimal externally powered prosthetic restoration is the goal
\- length typically permits good function and cosmesis
\- length typically permits good function and cosmesis
35
New cards
Long Forearm Residual Limb
\- preferred when optimal body-powered prosthetic restoration is the goal
\- ideal level for the patient who is expected to perform physically demanding work
\- ideal level for the patient who is expected to perform physically demanding work
36
New cards
Krukenberg Amputation
\- converts transradial amputation to radial and ulnar pincers
\- indicated for blind people
\- indicated for blind people
37
New cards
Wrist Disarticulation
\- not commonly done:
* *difficult socket fabrication.*
* *conventional wrist units are too long and cannot be used*
* *harder to fit with a myoelectric prosthesis*
* *difficult socket fabrication.*
* *conventional wrist units are too long and cannot be used*
* *harder to fit with a myoelectric prosthesis*
38
New cards
Hemicorporectomy
\- amputation of the lower limbs and the pelvis (translumbar amputation)
\- during this procedure the bony pelvis, pelvic contents, lower extremities, and external genitalia are removed following disarticulation of the lumbar spine and transection of the spinal cord
\- a last resort for life-threatening conditions such as advanced pelvic tumors, pelvic osteomyelitis, crushing pelvic trauma, or intractable decubitis in the pelvic region
\- during this procedure the bony pelvis, pelvic contents, lower extremities, and external genitalia are removed following disarticulation of the lumbar spine and transection of the spinal cord
\- a last resort for life-threatening conditions such as advanced pelvic tumors, pelvic osteomyelitis, crushing pelvic trauma, or intractable decubitis in the pelvic region
39
New cards
Hemipelvectomy
\- resection of the lower half of the pelvis (hip disarticulation; transpelvic amputation)
\- they vary greatly in the amount of bone removed, they range from focal osteotomy to a complete transaction of the pelvis that spares only the sacrum
\- the prosthesis for this resembles that for the hip disarticulation except in the interior configuration of the socket
\- most of the weight is borne by the soft tissues on the amputated side, with some of the weight being borne by the sacrum, the rib cage, and the opposite ischial tuberosity
\
\- they vary greatly in the amount of bone removed, they range from focal osteotomy to a complete transaction of the pelvis that spares only the sacrum
\- the prosthesis for this resembles that for the hip disarticulation except in the interior configuration of the socket
\- most of the weight is borne by the soft tissues on the amputated side, with some of the weight being borne by the sacrum, the rib cage, and the opposite ischial tuberosity
\
40
New cards
Hip Disarticulation
amputation through the hip joint with pelvis intact.
41
New cards
Transfemoral Amputation
\- Above knee amputation (AKA)
* *short above knee*
* *middle above knee*
* *supracondylar amputation*
\- the primary surgical goal is to stabilize the femur while retaining maximal femur length
\- there are two standard socket design (prosthesis) for this type of amputation:
* *quadrilateral design*
* *ischial containment design*
* *short above knee*
* *middle above knee*
* *supracondylar amputation*
\- the primary surgical goal is to stabilize the femur while retaining maximal femur length
\- there are two standard socket design (prosthesis) for this type of amputation:
* *quadrilateral design*
* *ischial containment design*
42
New cards
Knee Disarticulation
\- amputation through the knee joint with whole femur still intact
\- similar to the syme amputation, full weight bearing on the distal end of the KD residual limb is usually possible and the anatomic flare of the femoral condyles can be used for self-suspension of the prosthesis, because of the improved distal weight bearing, the KD amputation does not require an ischial weight-socket leading to enhanced comfort and sitting tolerance as does a transfemoral amputation
\- similar to the syme amputation, full weight bearing on the distal end of the KD residual limb is usually possible and the anatomic flare of the femoral condyles can be used for self-suspension of the prosthesis, because of the improved distal weight bearing, the KD amputation does not require an ischial weight-socket leading to enhanced comfort and sitting tolerance as does a transfemoral amputation
43
New cards
Gritti-Stokes Amputation
in which the femoral condyles are transecting just proximal to the joint and the patella is attached to the metaphyseal bone.
44
New cards
Below Knee Amputation
\- transtibial amputation
\- the most common amputaiton level seen in general practice
* Long BKA
* Medium BKA
* Short BKA
* Very Short BKA
\- the most common amputaiton level seen in general practice
* Long BKA
* Medium BKA
* Short BKA
* Very Short BKA
45
New cards
Long BKA
\- are sometimes performed to give patients a longer lever arm and more surface area for load distribution
\- no functional muscle attachments are saved with this, and it is associated with multiple complications and poorer cosmesis
\- no functional muscle attachments are saved with this, and it is associated with multiple complications and poorer cosmesis
46
New cards
Syme Amputation
\- transmalleolar amputation
\- ankle disarticulation with attachment of the heel pad to the distal end of the tibia
\- its goal is to have **significant distal load bearing available**, the amount of distal loading that is available is dependent on the individual
\- advantage: *there is a long residual limb and that it is an end weight bearing amputation*
\- disadvantage: the *poor prosthetic cosmesis (because the distal residual limb is quite bulbous with a socket) and the limited prosthetic foot options*
\- ankle disarticulation with attachment of the heel pad to the distal end of the tibia
\- its goal is to have **significant distal load bearing available**, the amount of distal loading that is available is dependent on the individual
\- advantage: *there is a long residual limb and that it is an end weight bearing amputation*
\- disadvantage: the *poor prosthetic cosmesis (because the distal residual limb is quite bulbous with a socket) and the limited prosthetic foot options*
47
New cards
Boyd and Pirogroff Amputation
\- are variations of the Syme’s where part of the calcaneus is fused to the distal tibia to lengthen the limb further and reduce limb length discrepancy
\- these amputations also allow distal weight bearing, but the minimal limb shortening makes prosthetic fitting very challenging in adults
\- these amputations also allow distal weight bearing, but the minimal limb shortening makes prosthetic fitting very challenging in adults
48
New cards
Boyd Amputation
amputation at the ankle with removal of the talus and fusion of the tibia and inferior calcaneus.
49
New cards
Pirogoff’s Amputation
amputation of the foot at the ankle, posterior part of the calcaneus being left in the stump.
50
New cards
Chopart Amputation
amputation at the level of the midtarsals.
51
New cards
Lisfranc’s Amputation
amputation of the foot between the metartasus and tarsus.
52
New cards
Transmetatarsal Amputation
\- is a very successful amputation
\- in this case, the forefoot is transversely amputated through the shaft of the metatarsals. The remaining portions are usually beveled inferiorly with a predominantly plantar skin flap
\- in this case, the forefoot is transversely amputated through the shaft of the metatarsals. The remaining portions are usually beveled inferiorly with a predominantly plantar skin flap