Unit 4 Circulatory system
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
The cardiovascular system
Composed of the heart, blood vessels and blood
Delivers oxygen and other nutrients to all body cells
Removes carbon dioxide and other waste products from them
Can be compared to a muscular pump equipped with one-way valves and a system of large and small plumbing tubes within which blood travels
The heart
Approximately the size of a clenched fist
Weighs less than one pound
Located in the medial cavity of the thorax and is flanked by the lungs
The more pointed apex is directed toward the left and rests on the diaphragm at the fifth intercostal space
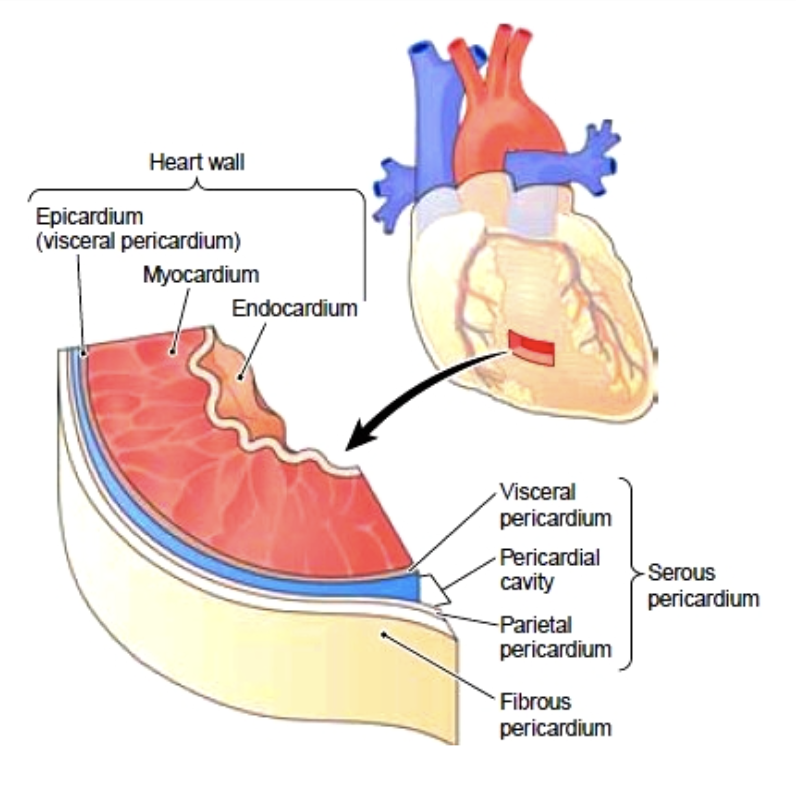
Pericardium
A double-walled sac that encloses the heart
Keeps the heart contained in the chest cavity
Prevents the heart from over-expanding when blood volume increases
Limits heart motion
Contains lubricating fluid that allows the heart to beat easily
The three layers of the heart’s walls
Epicardium:
Outer layer
Myocardium:
Thick bundles of cardiac muscle
The layer that contracts
Endocardium:
Thin sheet that lines the heart chambers
Chambers of the heart
4 Chambers:
Two atria (left and right)
Two ventricles (left and right)
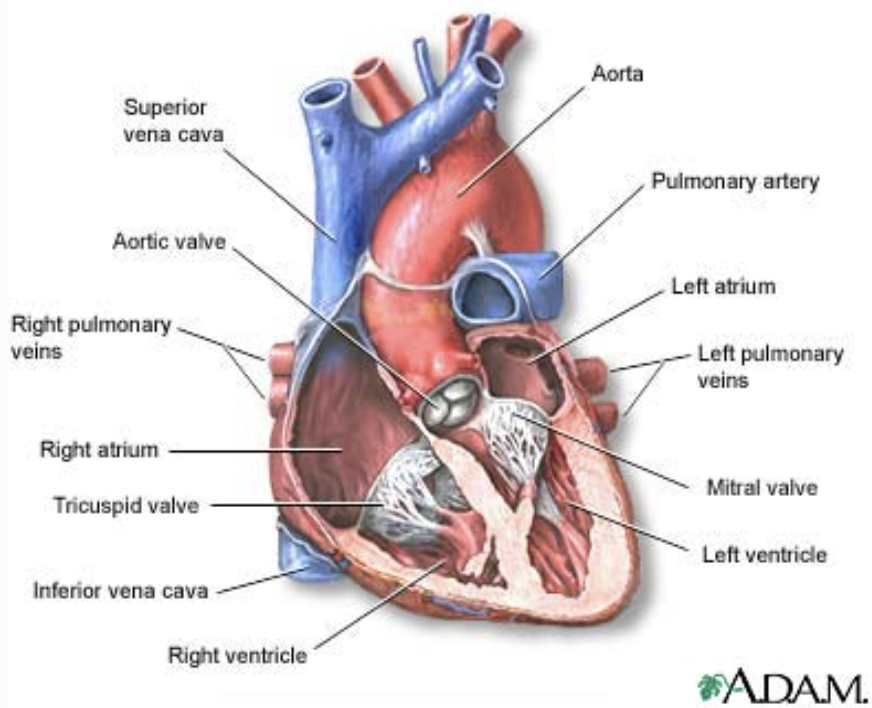
Atria (singular atrium)
“receiving chambers”
Blood flows into the atria from the veins under low pressure and then continues on to fill the ventricles
Ventricles
“discharging chambers”
When they contract blood is propelled out of the heart and into the circulation
Right ventricle forms most of the heart’s anterior surface
Left ventricle forms the apex
The chambers are divided longitudinally by a septum
External anatomy of the heart
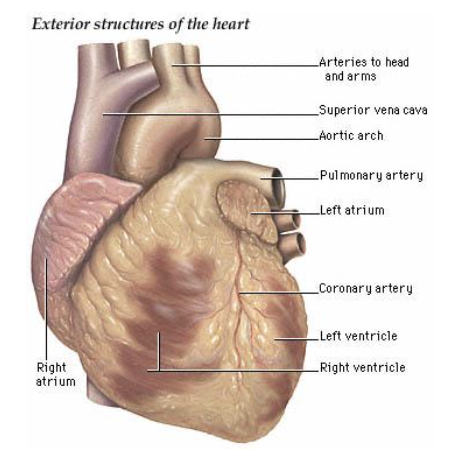
Pulmonary circulation
Happens in the right side of the heart
Oxygen-poor blood is transported from the right atrium and ventricle to the lungs for gas exchange
Then returned to the heart
Systemic circulation
Happens in the left side of the heart
Blood moves from the left side through the body tissues and back to the right side of the heart
It supplies oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to all body organs
The valves
Allow blood to flow in only one direction through the heart chambers
From atria through ventricles and out the greater arteries leaving the heart
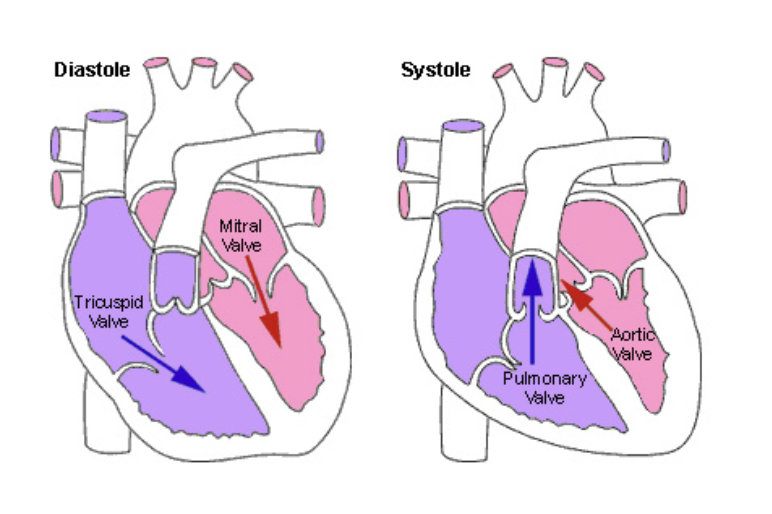
Atrioventricular Valves
Located between the atria and ventricles
Prevent backflow into the atria when the ventricles contract
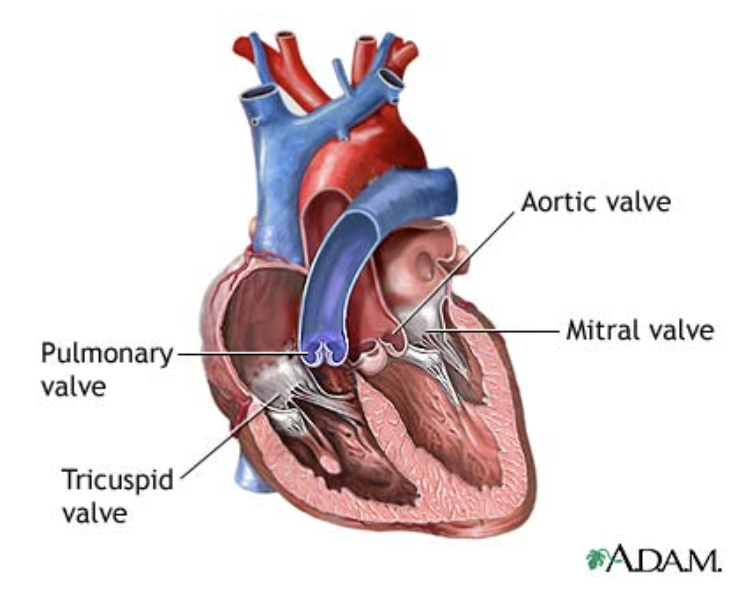
Left AV valve
Bicuspid (mitral) valve
Two flaps of endocardium
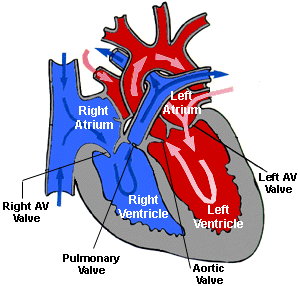
Right AV valve
Tricuspid
Three flaps of endocardium
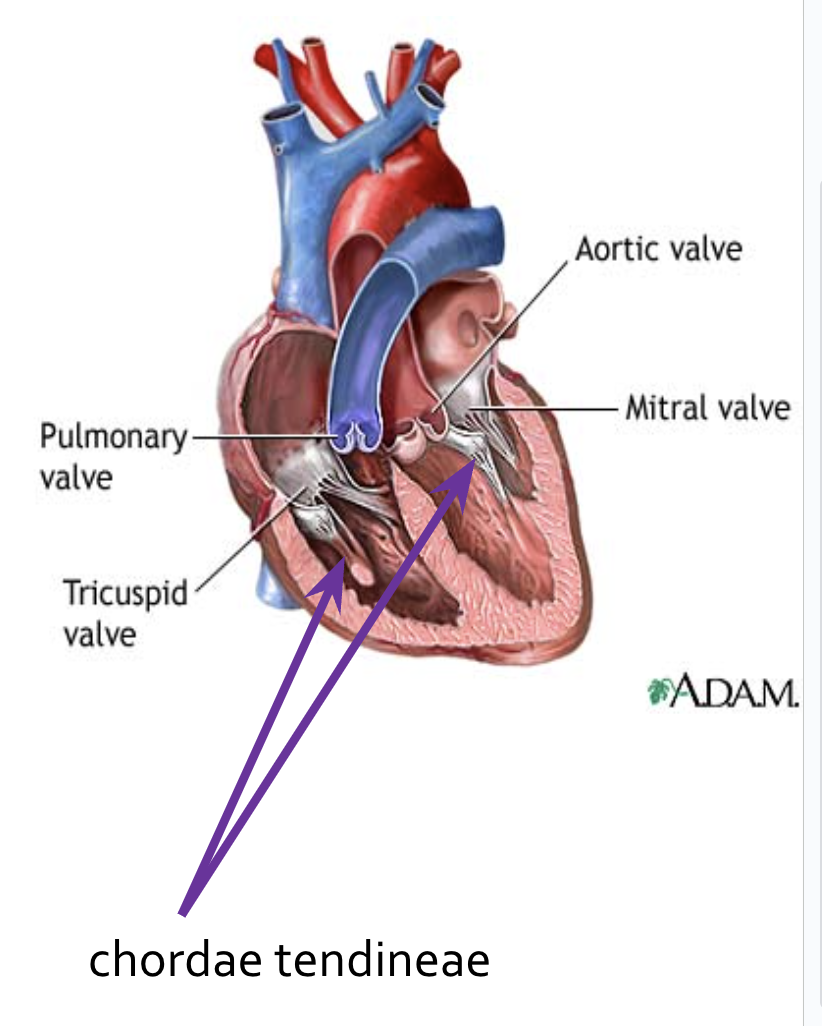
The chordae tendineae (“tendinous cords”)
Anchor the flaps to the walls of the ventricles
When the heart is relaxed and blood is passively filling its chambers the AV flaps hang limply into the ventricles
As the ventricles contract, they press on the blood in their chambers and the pressure begins to rise
This forces the AV flaps upward closing the valves.
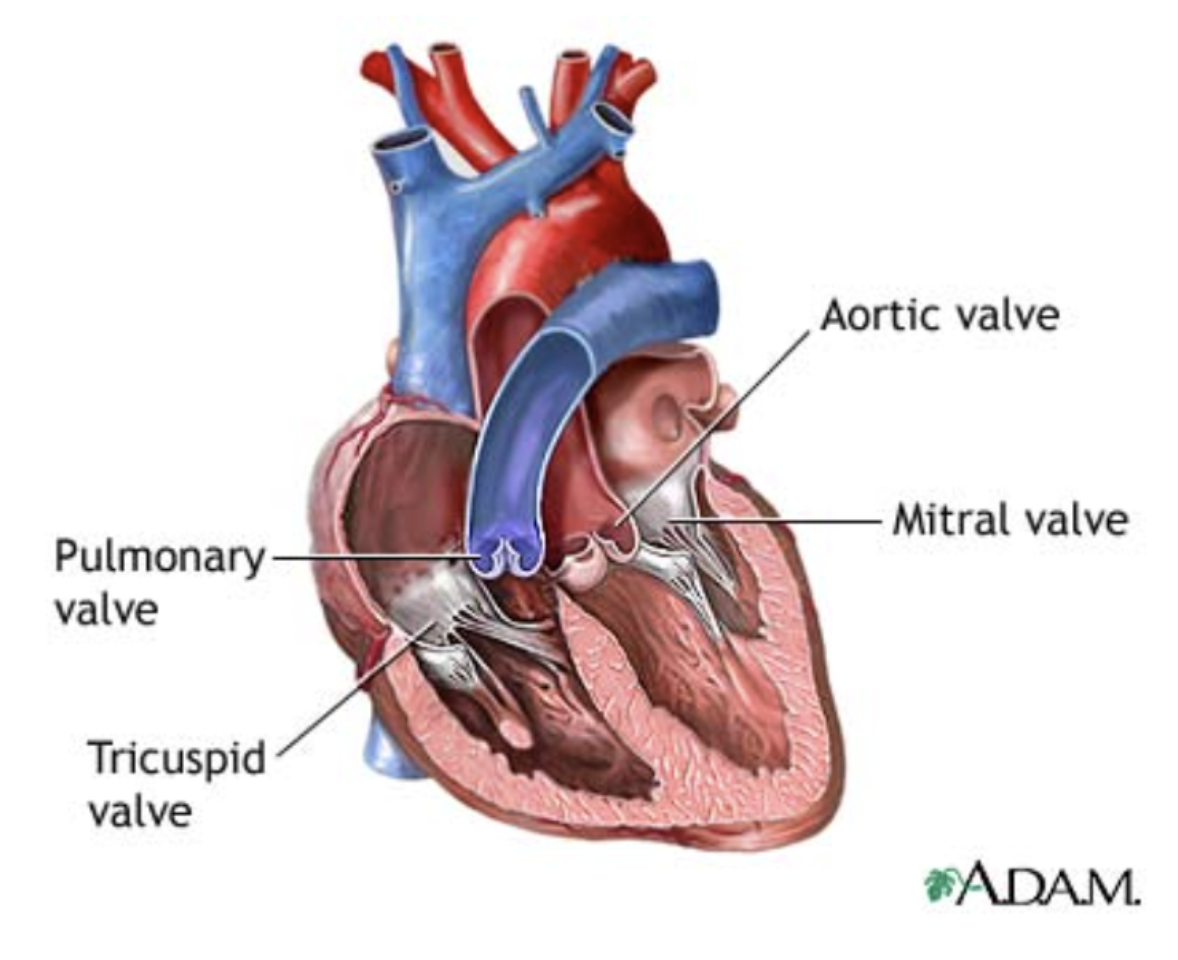
Semilunar Valves
Pulmonary and Aortic Semilunar Valves
Each has three leaflets
When the ventricles are contracting, the leaflets are forced open and flatten against the walls of the arteries
When the ventricles relax, the blood begins to flow backward toward the heart and the leaflets fill with blood closing the valves
The AV valves..
Open during heart relaxation and close during ventricular contractions
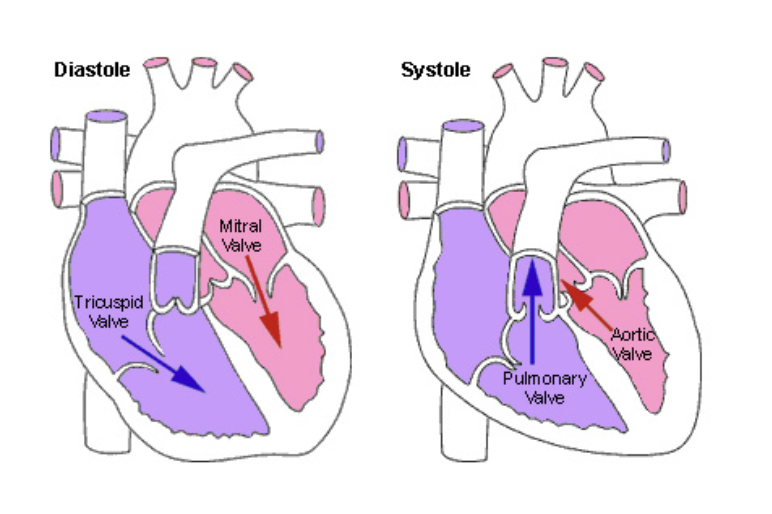
The semilunar valves..
Are closed during relaxation and are forced open when the ventricles contract
The Cardiac Cycle
The heart beats or contracts approximately 70 times per minute.
One heartbeat, or cardiac cycle, includes atrial contraction and relaxation, ventricular contraction and relaxation, and a short pause
Normal cardiac cycles (at rest) take 0.8 seconds
Systole
Contraction of the heart muscle
Diastole
Relaxation of the heart muscle
Auscultation
The sound of the heart contracting and the valves opening and closing produces a characteristic "lub-dub" sound
Lub is associated with closure of the AV valves
Dub is associated with closure of the SL valves
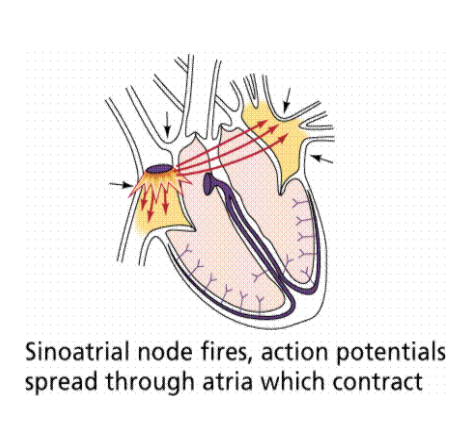
Sinoatrial node (SA node)
Where human heartbeats originate from near the right atrium
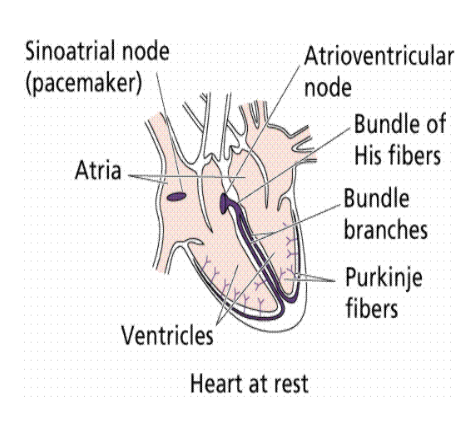
Atrioventricular node (AV node)
Where modified muscle cells contract that send a signal to other muscle cells in the heart to contract
The signal then spreads to this node
Signals carried are slightly delayed, through bundle of His fibers and Purkinjie fibers cause the ventricles to contract (almost) simultaneously
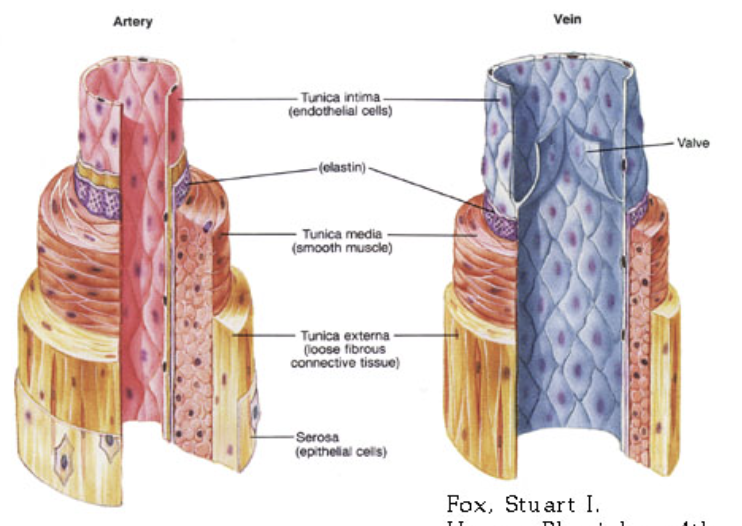
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart to the tissues of the body
Composed of (outer layer) connective tissue, (middle layer) smooth muscle, and (inner layer) epithelial cells
Are strong and elastic to withstand the pressure of the fluid they carry
Artery expansion is felt as a pulse
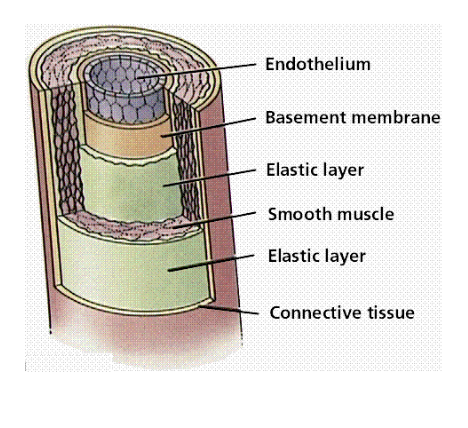
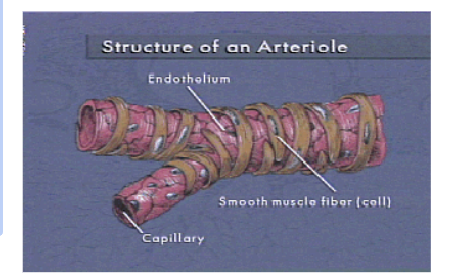
Arterioles
Formed by branching arteries
Smooth muscle in the arterioles may contract or relax which is controlled by the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Important in maintaining constant body temperature
Vasoconstriction
When the diameter of blood vessels decreases
Vasodilation
When the diameter of blood vessels increases
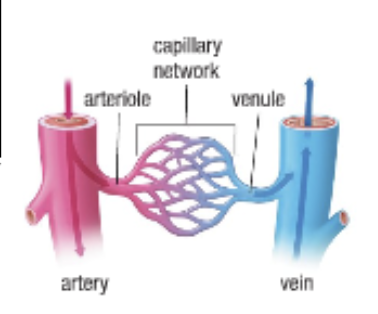
Capillaries
Branching of arterioles form capillary beds
Site of fluid and gas exchange
Extremely small in diameter so that RBC move through in single file
Extremely high total cross sectional area slows the flow of blood providing time for diffusion
Capillaries merge in a “mirror image” of the way they branched from the arterioles forming the venous side of a capillary network
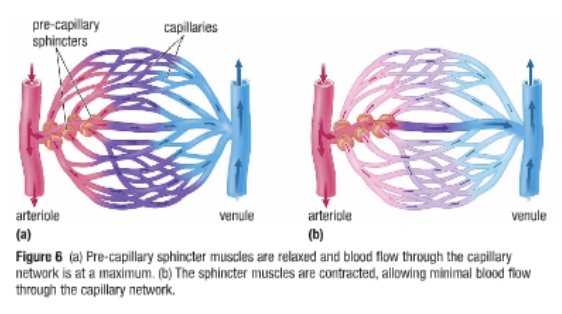
Controlling Blood Flow in the Capillaries
Capillaries lack smooth muscles
There are pre-capillary sphincter muscles
If blood is not needed in a particular capillary network the sphincters contract and reduce blood flow
Veins and Venules
Return blood to the heart
Composed of smooth muscle, and one-way valves to return low pressure blood to heart
Not as thick as arteries and the walls are not as elastic
The internal diameter of veins is therefore greater than arteries
Contraction of skeletal muscles help push blood back to heart
Gravity pulls blood down and causes pooling, veins may become larger and bulge → varicose veins
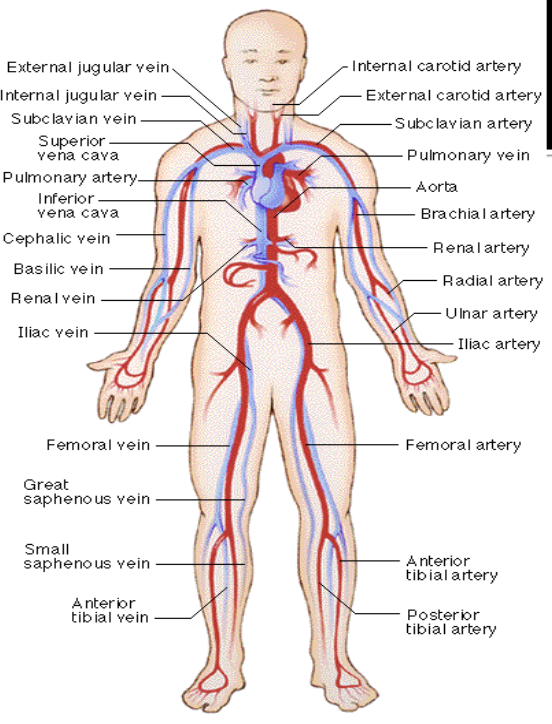
Major Vessels of the Body
Blood pressure can be affected by..
Diameter of the vessels
Physical activity
Temperature
Body position
Diet
Stress
Age
Certain medications
Hypertension
A condition of consistently elevated blood pressure (i.e. high blood pressure)
“Silent Killer”
Dangerous because is forces the heart to work harder to pump the blood around the body
Hypertension can be caused by..
Kidney disease (causes more fluid to be retained in the blood)
Some medications
Age (vessels lose elasticity as we age)
Diet
Blood
Whole blood is a mixture of blood cells and plasma.
Plasma is a yellowish fluid in which the cells are suspended
Components of The Blood
Red blood cells (RBCs)
White blood cells (WBCs)
Platelets
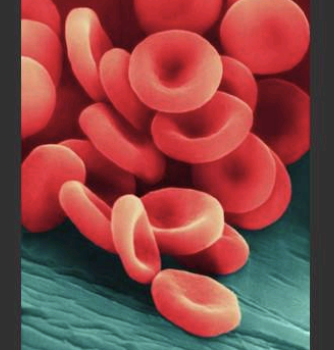
Red Blood Cells (erythrocytes)
Shaped like slightly indented, flattened disks
Contain the iron-rich protein hemoglobin
Blood gets its bright red color when hemoglobin picks up oxygen in the lungs
As the blood travels through the body, the hemoglobin releases oxygen to the tissues
Life span of about 4 months
White Blood Cells (leukocytes)
The body's system for defending itself against infection
Can move in and out of the bloodstream to reach affected tissues
There are several types and their life spans vary from a few days to months.
New cells are constantly being formed in the bone marrow
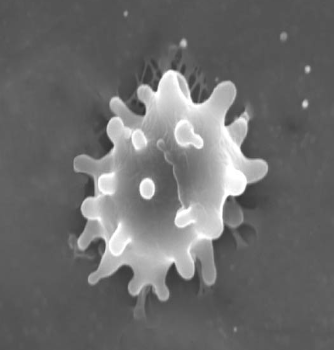
Platelets (thrombocytes)
Oval-shaped cells made in the bone marrow
Help in the clotting process
When a blood vessel breaks, they gather in the area and help seal off the leak
Survive only about 9 days in the bloodstream and are constantly being replaced by new cells
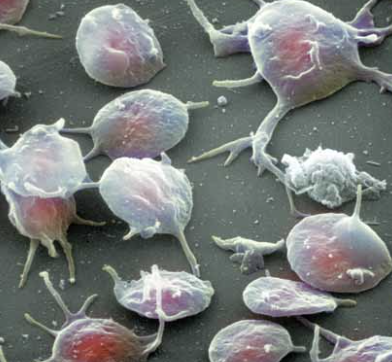
The Rh System
“D antigen” (protein) on red blood cells’ surface
When present, the person is Rh positive (85% Canadians)
When absent, the person is Rh negative (15% Canadians)
If you are Rh positive…
You can receive Rh positive or Rh negative blood
If you are Rh negative…
You can receive only Rh negative blood
“Anti-D antibodies”: produced when an Rh-negative person is exposed to red blood cells from an Rh-positive donor
Creating a transfusion reaction
Arrhythmia
An abnormal heart rhythm
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is the most common type
Bradycardia
Less than 60 beats per minutes
Tachycardia
More than 100 beats per minute
Fibrillation
Uncoordinated contractions
Angina
When your heart doesn’t get as much blood and oxygen as it needs because one or more of its arteries (coronary arteries) is blocked
A warning signal that you are at increased risk of a heart attack, cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death
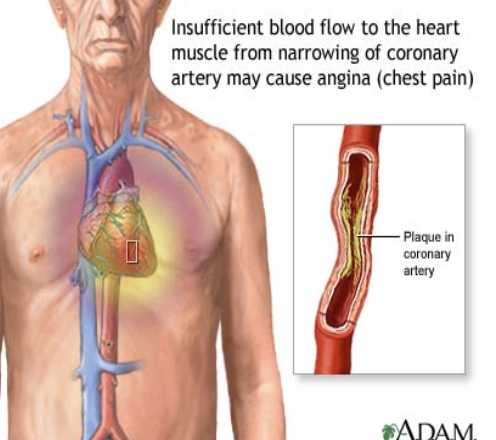
What is a heart attack?
When the blood supply to the heart is slowed or stopped because of a blockage
May also occur when a coronary artery temporarily contracts or goes into a severe spasm, effectively shutting off the flow of blood to the heart
The length of time the blood supply is cut off will determine the amount of damage to the heart
Signs of MI (myocardial infarction)
Pressure in center of chest
Pain in shoulders, neck, or arms
Chest discomfort with fainting, sweating, ot nausea
Pain radiating down left arm
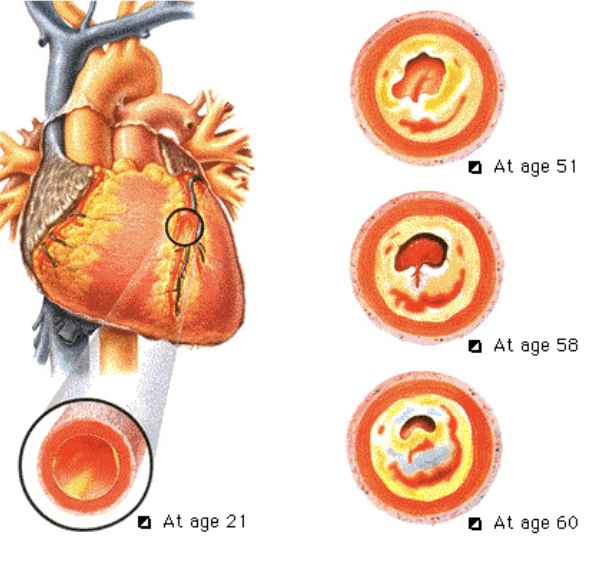
Artherosclerosis
The narrowing of coronary arteries due to plaque build-up
Causes more than 90% of heart attacks.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA)
A condition in which the heart stops beating suddenly and unexpectedly due to a malfunction in the heart’s electrical system
Caused by ventricular fibrillation
It is not a heart attack
The probability of survival declines by 7% to 10% as time passes
When CRP and defibrillation are used together, survival rates may increase to more than 50%
How does ventricular fibrillation happen?
The heart’s rhythm is so chaotic (called “fibrillating”) that the heart quivers, and is unable to pump blood to the body and brain
First loses their pulse, then consciousness, and finally the ability to breathe
Causes of cardiac arrest or ventricular fibrillation
Heart disease
Drowning
Stroke
Electrocution
Suffocation
Drug overdose
Motor vehicle or other injury
Defibrillation
A heart in ventricular fibrillation must be defibrillated
To defibrillate the heart an electrical shock must be applied
Defibrillation administered within the first few minutes after collapse has the highest chance of success
Stroke
Most are Ischemic
They are caused by the interruption of blood flow to the brain due to a blood clot.
The build-up of plaque (fatty materials, calcium and scar tissue) narrows the arteries that supply blood to the brain, interfering with, or blocking the flow of blood
Thrombotic strokes
Are caused by a blood clot that forms in an artery directly leading to the brain
Embolic strokes
Occurs when a clot develops somewhere else in the body and travels through the blood stream to the brain
Signs somebody may have had a stroke
FAST:
FACE: Facial numbness or weakness especially on one side
ARM: Arm numbness or weakness especially on one side
SPEECH: Difficulty speaking or understanding others or a loss of speech
TIME: Call EMS/911 immediately
Heart Disease Prevention
Quitting smoking
Healthy diet
Exercise