Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Cellular Respiration
The process of converting glucose and oxygen into water and carbon dioxide and producing energy for the cell to use through the synthesis of ATP
Mitochondria
Where cellular respiration occurs
Redox reaction
The kind of reaction cellular respiration is
Glycolysis, Aerobic Respiration
Forms of cellular respiration (2)
Breakdown of pyruvate, Citric acid cycle, Oxidative phosphorylation
Stages of aerobic respiration (3)
Anaerobic Respiration (Fermentation)
Occurs without oxygen, produces less ATP
Glycolysis
A form of substrate level phosphorylation, Produces 2 pyruvate, 2ATP, and 2NADH
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
The direct transfer, via an enzyme, of a phosphate from an organic molecule to ADP to ATP, Glycolysis is an example of this
Cytosol
Where glycolysis occurs (since it doesn’t require oxygen)
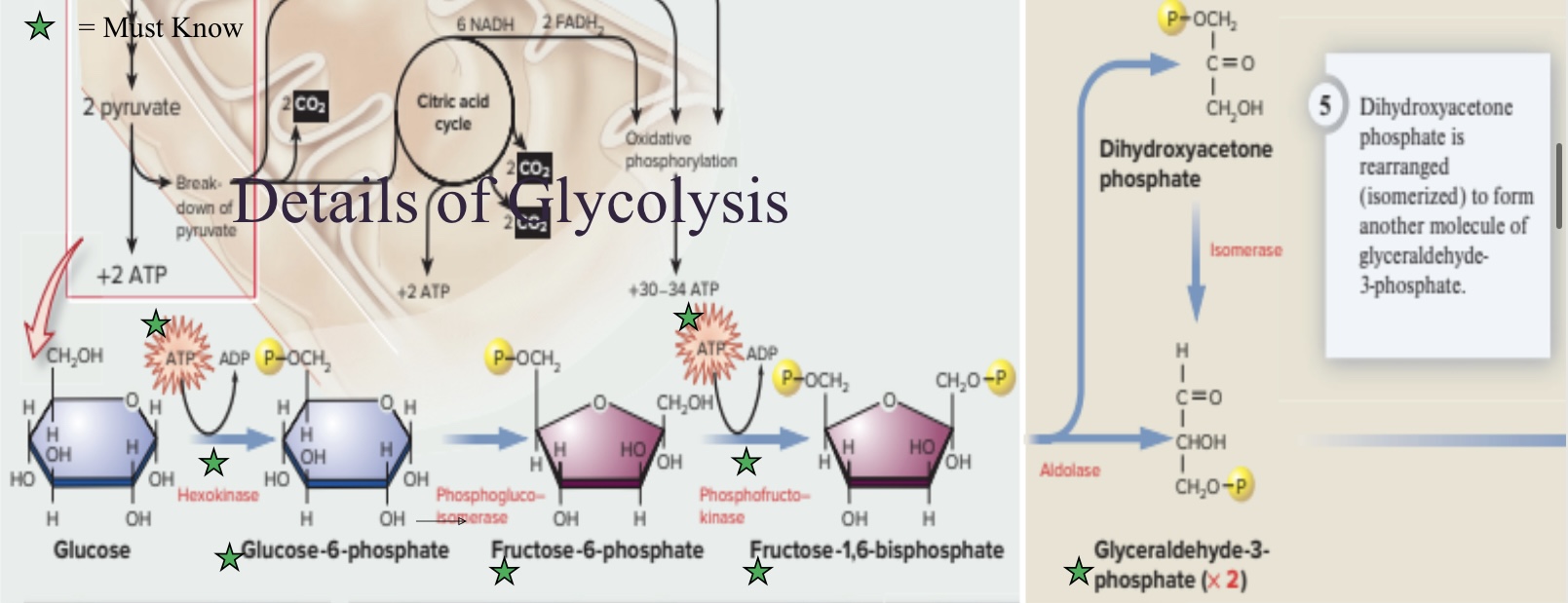
Energy investment phase, Cleavage phase, Energy liberation phase
Three phases of glycolysis
Energy Investment Phase
Phase of glycolysis that uses ATP to add a phosphate to glucose, producing fructose-1-6-biphosphate
Cleavage Phase
Phase of glycolysis that splits fructose-1-6-biphosphate into 2 molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
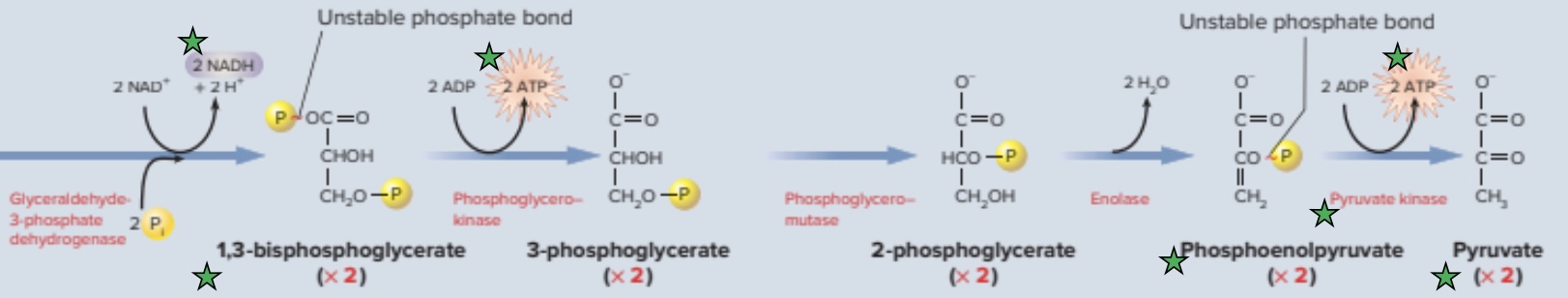
Energy Liberation Phase
Phase of glycolysis that converts glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate into pyruvate and produces ATP
2
The net production of ATP from glycolysis
Hexokinase
Enzyme utilized in the energy investment phase of glycolysis that phosphorylates glucose into glucose-6-phosphate by using a phosphate from ATP, changing it back into ADP
Glucose-6-phosphate
Phosphorylated glucose that is more easily trapped in the cell than glucose
Fructose-6-phosphate
Isomer of glucose-6-phosphate that will eventually become phosphorylated
Phosphofructokinase
Enzyme utilized during the energy investment phase of glycolysis that phosphorylates fructose-6-phosphate into fructose-1-6-biphosphate, ATP can bind to the allosteric site of this enzyme for feedback inhibition (speed it up or slow it down)
Fructose-1-6-biphosphate
Phosphorylated fructose-6-phosphate that will eventually split during the cleavage phase
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Two of this molecule forms when fructose-1-6-biphosphate is split during the cleavage phase
1,3-biphosphate
Two of this molecule form when glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidized during the energy liberation phase, 2 NADH is formed
Phosphoenolpyruvate
Two of these molecules are used to form 2 pyruvate, The phosphate group in the molecule is destabilized, so the bond will break in a highly exergonic reaction
Pyruvate Kinase
Enzyme utilized in the energy liberation phase of glycolysis that catalyzes the transfer of the phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, creating ATP and pyruvate (2x)
Energy Investment and Cleavage Phase
Which phase(s) of glycolysis is this?
Energy Liberation Phase
Which phase(s) of glycolysis is this?
Pyruvate
Two of these molecules are formed when a phosphate is removed from phosphoenolpyruvate, which is then transferred to ADP to form ATP
2 pyruvate
2 NADH
2 ATP
2 H2O
2 H+
The net production of molecules after glycolysis
Breakdown of Pyruvate
Stage of aerobic respiration where the 2 pyruvate that form during glycolysis travels to the mitochondrial matrix to be broken down
2 pyruvate + 2 CoA + 2NAD+ —> 2 Acetyl CoA + 2CO2 + 2NADH
“Chemical reaction” of pyruvate breakdown
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Enzyme utilized during breakdown of pyruvate that oxidizes pyruvate into Acetyl CoA and CO2 (2x)
2 Acetyl CoA
2 NADH
2 CO2
Net production of molecules following breakdown of pyruvate
2 Acetyl
4 NADH
2 ATP
2 CO2
2 H2O
2 H+
Net production of molecules following glycolysis AND oxidation of pyruvate
Citric Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle
A metabolic cycle that recycles different components that help continue the cyclic reaction
Mitochondrial Matrix
Where the Krebs Cycle occurs
Citrate
Forms during the first step of the Krebs Cycle when Acetyl CoA attaches to oxaloacetate
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
Enzyme utilized during the Krebs Cycle that regulates the speed of the cycle, Catalyzes the oxidation of isocitrate into alpha-ketoglutarate, NAD+ is reduced to NADH
Alpha-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase
Enzyme utilized during the Krebs Cycle that helps regulate the cycle, Catalyzes the oxidation of alpha-ketoglutarate as it combines with CoA to form succinyl CoA, CO2 and NADH are also formed, More CO2 is released soon after this stage
Oxaloacetate
A set of reactions during the Krebs Cycle, such as the phosphorylation of GDP and ADP into ATP and GTP, FAD becoming FADH2, and NAD+ becoming NADH, regenerates this starting molecule (that binds to Acetyl CoA) to restart the cycle
Citrate Synthetase
Enzyme utilized during the Krebs Cycle that catalyzes oxaloacetate and Acetyl CoA to form citrate
Inhibitors, Activators
ATP and NADH act as ______ of isocitrate dehydrogenase, while ADP and NAD+ act as ______
2 CoA
4 CO2
6 NADH
2 FADH2
2 GTP
2 ATP
6 H+
Net production of molecules after the Krebs Cycle
10 NADH
4 ATP
6 CO2
8 H+
2 FADH2
Net production of molecules after glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, AND the Krebs Cycle
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Involves the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 and ADP becomes phosphorylated via the electron transport chain and the chemiosmosis of H+ through the ATP synthase
Oxygen
The final electron acceptor following oxidative phosphorylation
Electron Transport Chain
A group of protein complexes and small organic molecules within the inner membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts and the plasma membrane of prokaryotes, The components accept and donate electrons to each other in a linear manner and produce a H+ electrochemical gradient
Chemiosmosis
A process for making ATP in which energy stored in an ion electrochemical gradient is used to make ATP from ADP and P, Transpots H+ ions through the ATP synthase
ATP Synthase
An enzyme that utilizes the energy stored in a H+ electrochemical gradient for the synthesis of ATP via chemiosmosis
NADH Dehydrogenase
Enzyme utilized during oxidative phosphorylation that transfers high-energy electrons directly to the respiratory chain, NADH becomes NAD+ here
Cytochrome Oxidase
Enzyme utilized during oxidative phosphorylation that receives some electrons from cytochrome c, Some energy is harness to pump H+ into the intermembrane space, Electrons are transferred to oxygen, Water is produced, ATP binds to the allosteric site of the enzyme to inhibit the electron transport chain
10 NAD+
2 FAD
10 H2O
30-34 ATP
Net production of molecules following oxidative phosphorylation
34-38 ATP
6 CO2
10 H2O (not through dehydration)
Net production of molecules after cellular respiration
Bacteriohodopsin
A light-driven H+ pump
Glucose
What carbs are broken down/rearranged into to enter glycolysis
Amino acids, Pyruvate, Acetyl CoA
Proteins are broken down into _____ _____ first, then they are processed differently at different points as _____, _______, or by entering the Krebs Cycle
Fatty acids, Glycerol
What fats are broken down into (2)
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, Acetyl CoA
Glycerol can become ______ and enter glycolysis, while fatty acids can become ______ and get broken down by the Krebs Cycle
NADH, NAD+
During anaerobic respiration, glycolysis produces ______ and depletes ______.
It reacts with cellular components and generates damaging free radicals
It’s necessary for glycolysis to continue in order to produce ATP
Why NAD+ is important during cellular respiration (2)
Nitrate (NO3-)
The final electron acceptor following anaerobic respiration
Muscle Fermentation, Yeast Fermentation
Two kinds of fermentation
Muscle Fermentation
Type of fermentation where pyruvate and NADH become lactic acid and NAD+
Yeast Fermentation
Type of fermentation where either pyruvate becomes CO2 and acetaldyhyde, or acetaldehyde and NADH become ethanol and NAD+