I&I: practice questions (week 6)
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
mycology, helminths, & protozoans
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What are some general characteristics of fungi?
Eukaryotic, heterotrophic, non-motile, uni/multicellular, aerobic, larger than bacteria, asexual/sexual, lack chlorophyll
What are the cell walls of fungi made up of?
Chitin
What are the morphological classifications of fungi?
Yeast, mold, dimorphic
What is the morphology of yeasts & how do they grow on media?
Unicellular + round/oval, grow on solid media → often appear as mucoid colonies
What are some examples of yeasts?
Candida (thrush, skin/nail infections, enteritis, vaginitis) & Malassezia (otitis externa, chronic dermatitis)
What is the morphology of molds & how do they grow on media?
Filamentous, grow on solid media & usually fluffy/cottony → produce hyphae & spores
What is an example of a mold?
Aspergillus (brooder pneumonia in chicks, guttural pouch mycosis in horses)
How can a mycotic infection be transmitted?
Direct contact (ringworm)
Inhalation
Ingestion (mycotoxins)
What is the pathogenesis of most fungi?
-Low morbidity/contagiousness rate (minus ringworm)
-Resist phagocytosis w/ capsules (biofilm)
-Chronic nature (granulomatous response)
What enzymes do fungi release to damage the host?
Keratinase, elastase, collagenase
Where should a sample be taken from at a mycotic/fungal infection site?
Periphery of infection
What are some methods of diagnosis for a fungal infection?
Wood’s lamp (UV) test
Wet mount (10% KOH)
Culture on Sabouraud dextrose agar (1-4wks @ 25-37C)
What are the main hosts for the fungi Microsporum (M. canis)?
Dogs, cats
What is the organism that is associated with ringworm, alopecia, erythema, & crusts?
Microsporum spp.
What are the main hosts for the fungi Trichophyton (T. mentagrophytes)?
Horses, dogs, cats
How are dermatophytes properly diagnosed?
Plucked hair samples @ periphery of lesion
What are the clinical signs of a dermatophyte infection?
Alopecia (skin lost)
A 2-year old dog develops itchy skin & loss of hair in various parts of the body. What is the most reliable lab methods to confirm their skin infection?
KOH & culture on fungal culture medium
What are some examples of dimorphic fungi?
Cryptococcosis, Blastomycosis, Histoplasmosis, Coccidioidomycosis, & Zygmomycosis
What is a common source of fungal infection of Cryptococcus neoformans?
Bird droppings in the soil
What are some symptoms of Cryptococcus neoformans?
Sneezing, snuffling, mucopurulent/hemorrhagic nasal discharge
-mainly in cats
What are the main species affected by Blastomycosis & how is it transmitted?
Dogs/humans & aerosol inhalation from the soil
What is the main species affected by Histoplasmosis & how is it transmitted?
Dogs & inhalation from soil w/ bird or bat droppings
What is the main species affected by Coccidioidomycosis (“Valley Fever”) & how is it transmitted?
Dogs & inhalation from soil/dust
-barrel-shaped
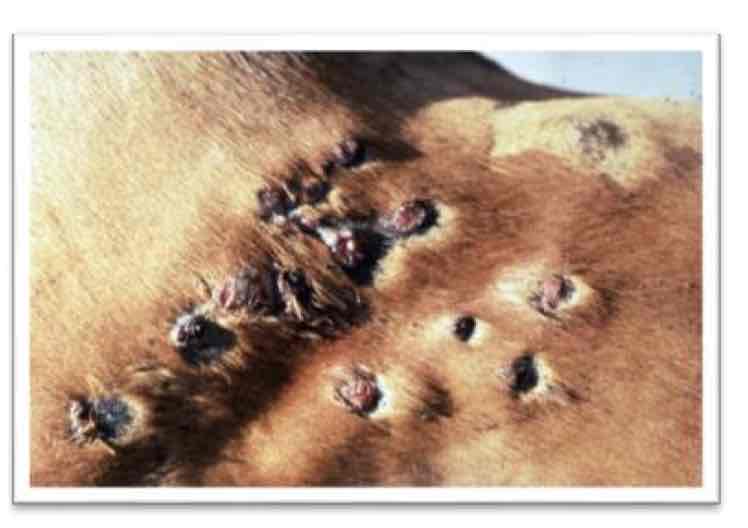
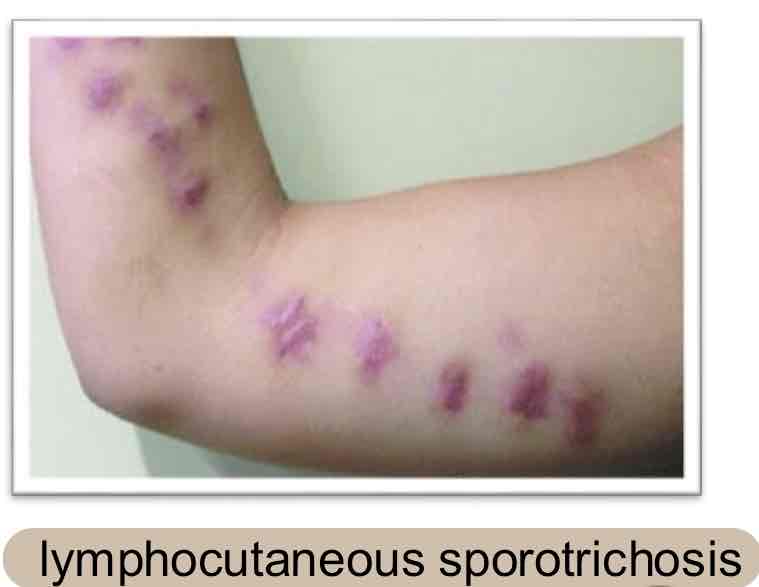
What are the main species affected by Sporotrichosis (“Rose Gardeners Disease”) & how is it transmitted?
Horses/mules & via skin wounds → lymphatic spread
What is the consequence of ingestion of grains or forage containing mycotoxins produced by certain fungi?
Mycotoxicosis
How are mycotoxins transmitted?
Mold-contaminated feed (grains, corn, peanuts) or direct contact
Which fungal infections in animals have no transmission?
Aspergillosis, Mucormycosis, Candidiasis, & Cryptococcoses
Which fungal infections in animals are indirectly transmitted from the environment?
Coccidioidomycosis, Histoplasmosis, Blastomycosis, & Para-coccidioidomycosis
What animals are potential hosts for Microsporum canis?
Dogs, cats, & many other mammals
What animals are potential hosts for Microsporum gypseum?
Horses, dogs
What species of Malassezia is a non-lipid-dependent species?
Malassezia pachydermatitis
Is a fungal infection of the skin classified as a local or systemic infection?
Local
What phylum does tapeworm belong to?
Platyhelminthes
What are the two classes in the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms)?
Class Trematoda (flukes) & Class Cestoda (tapeworms)
What kind of worms are in the phylum Nematoda?
Roundworms
What is the outward appearance of Nematodes, Trematodes, & Cestodes?
Nematodes: Worm-like/round
Trematodes: Leaf-like/flat
Cestodes: Tape-like/flat
What is the cross-section of Nematodes, Trematodes, & Cestodes?
Nematodes: Cylindrical
Trematodes: Flattened
Cestodes= Flattened
What kind of body cavities do Nematodes, Trematodes, & Cestodes have?
Nematodes: Fluid-filled (pseudocoelomates)
Trematodes: Absent
Cestodes: Absent
What kind of gut do Nematodes, Trematodes, & Cestodes have?
Nematodes: True gut (both mouth + anus)
Trematodes: Blind sac (only a mouth)
Cestodes: No gut (absorb thru cuticle)
What kind of reproduction do Nematodes, Trematodes, & Cestodes undergo?
Nematodes: Dioecious/sexual/polyandrous
Trematodes: Monoecious/asexual/hermaphrodite
Cestodes: Monoecious/asexual/hermaphrodite (outcrossing + self-fertilization)
What kind of life cycles do Nematodes, Trematodes, & Cestodes have?
Nematodes: Direct & Indirect
Trematodes: Indirect
Cestodes: Indirect
What is the goal of a worm in the host-parasite relationship?
To reproduce & co-evolve (do not directly cause mortality)
What are three ways a helminth can invade its host?
Ingestion of infective stage (most common)
Direct penetration thru skin
Penetration thru skin wound by insect vector
What is the infective stage of most Nematodes?
L3
What is the infective stage of most Trematodes?
Metacercaria
What is the infective stage of most Cestodes?
Metacestode
Which host is where the parasite matures & reproduces?
Definitive host (DH)
Which host is where immature stages develop with parasites in indirect lifecycles & is essential for completion of the lifecycle?
Intermediate host (IH)
Which host takes up immature form but does not retain it (no development) & is not essential for completion of the lifecycle?
Transport host
Which host is where immature stages are retained in host tissue but there is no development?
Accidental host
Which helminth is the most successful type of animal on earth (80% of all species) & lives in a variety of different habitats?
Nematodes (roundworms)
Which helminth is covered by a tough chitinous cuticle?
Nematodes
What is significant about the way Nematodes move around?
Thrash from side to side (solely longitudinal body wall muscles)
How do circulation & respiration occur in a Nematode?
Circulation: fluids slosh around in the pseudocoel
Respiration: diffusion of gases across cuticle
What statement about Nematodes is true?
Some are oviparous & some are larviparous
What is the time taken in a definitive host from infection to presence of reproducing adults & determines treatment interval to suppress fecal egg output?
Pre-patent period
Where can Nematodes be located in the host?
GI tract, respiratory tract, CVR system, & skin
What is an example of a physiological Nematode where the larvae enters hypo biotic state in the tissues & are then reactivated ~3 weeks prior to parturition & migrate to infect the fetus?
Toxocara canis
What is an example of a seasonal Nematode where the larvae is ingested in autumn, stays dormant in the gastric glands of the abomasum in winter, & then larvae development resumes again in the spring?
Ostertagia ostertagi
What is always the first host for a Trematode (fluke)?
Mollusk (usually a snail)
What is the most important Trematode pathogen in humans?
Schistosoma spp.
What happens in the terrestrial life cycle of a Trematode?
Egg is ingested by snail (IH)
What happens in the aquatic life cycle of a Trematode?
Miracidium hatches from egg & penetrates into snail (IH)
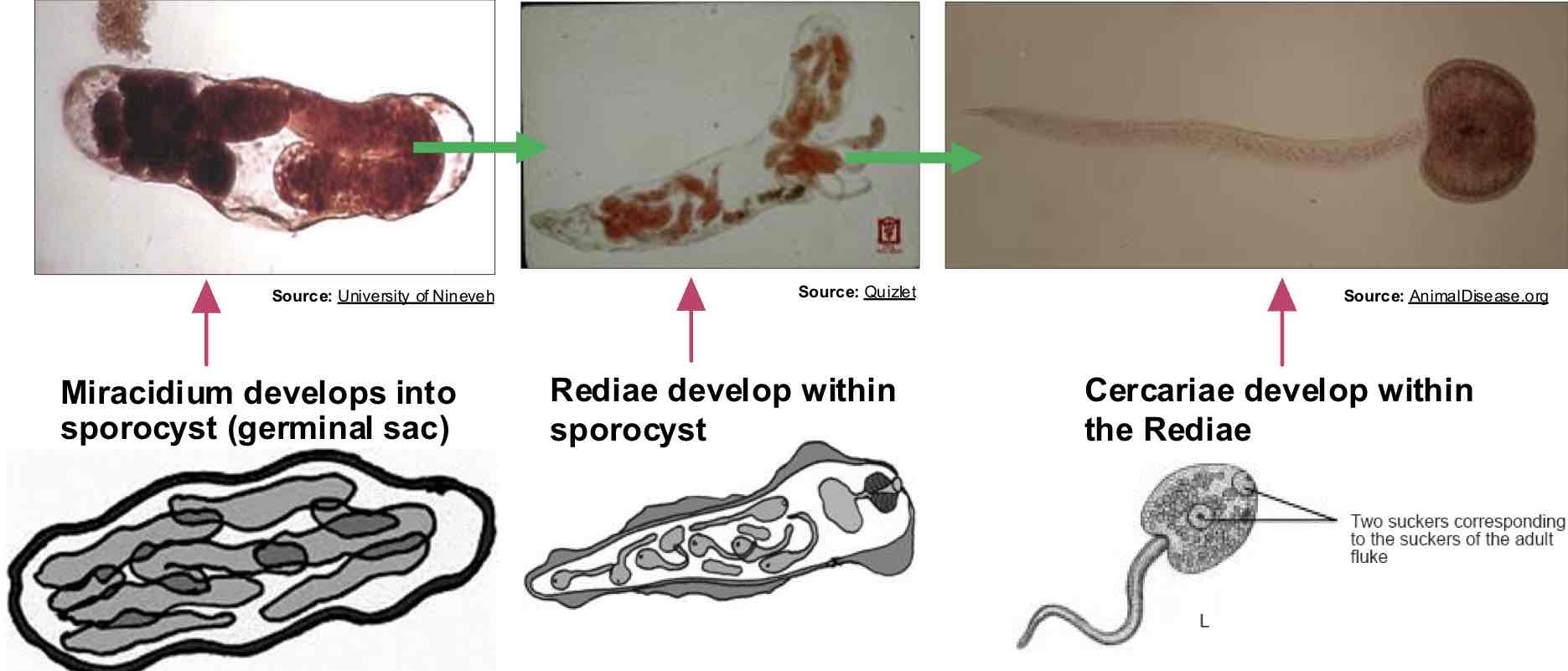
What happens once the miracidium of a Trematode is in the snail tissues?
Reproduce asexually → 1 miracidium becomes a large # of cercariae → cercariae shed tail + coat & develop into metacercaria (infective stage)
Where are Cestodes typically found in the host?
DH’s intestine
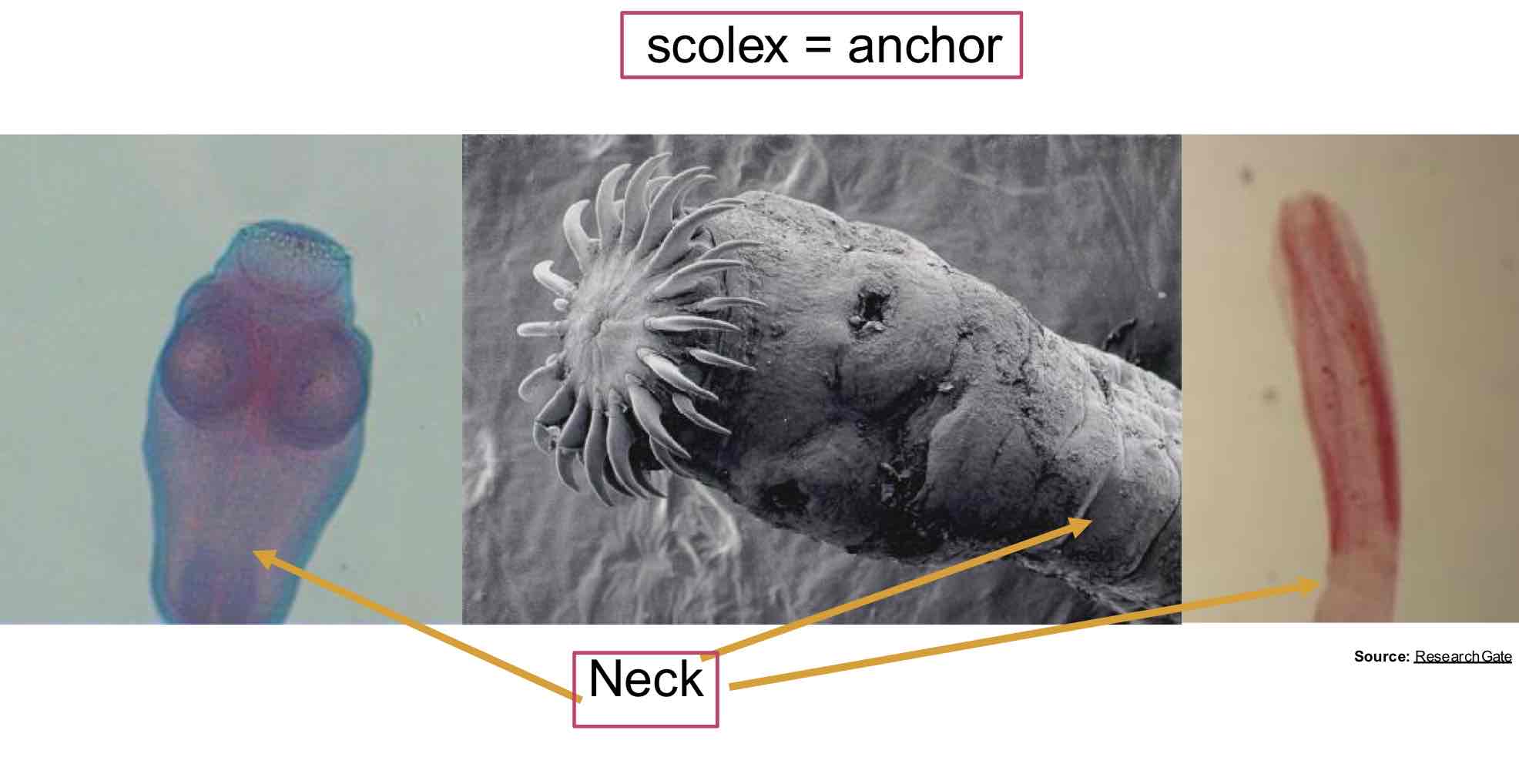
What are the parts of a Cestode’s body?
Scolex → Neck → Strobila (proglottid is a single segment)
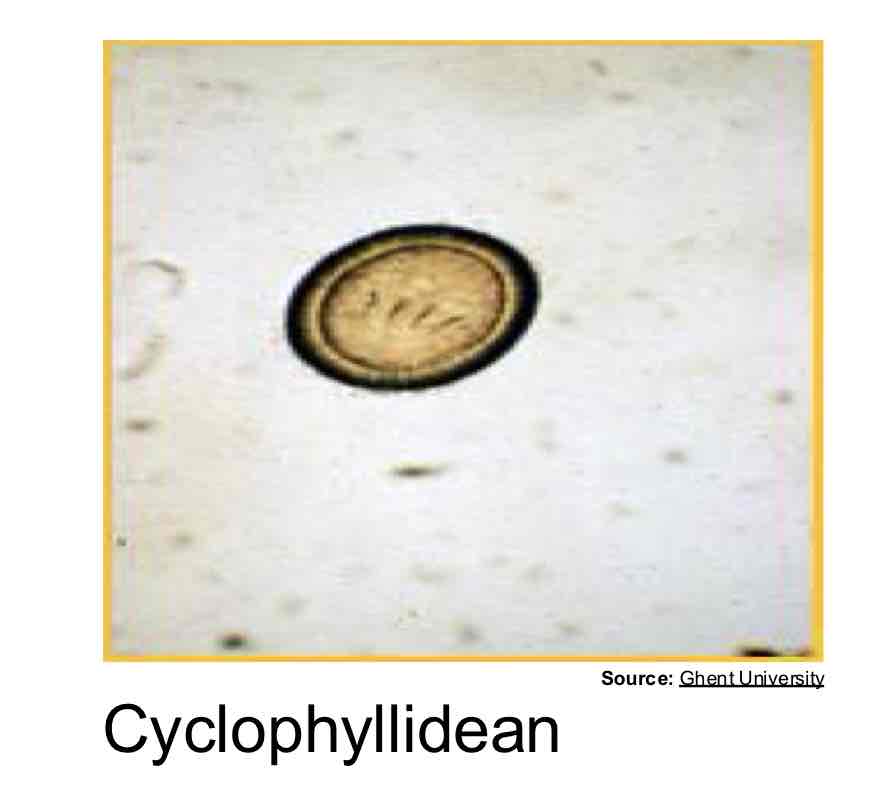
Which group of Cestodes are “true”, have suckers/hooks, only 1 IH, contain oncosphere operculate eggs (hexacanth that becomes hook), & diverse larval types?
Cyclophyllidean (most common)

Which group of Cestodes are “primitive”, have bothria (slits/grooves), 2+ IH, & multiple larval stages?
Pseudophyllidean
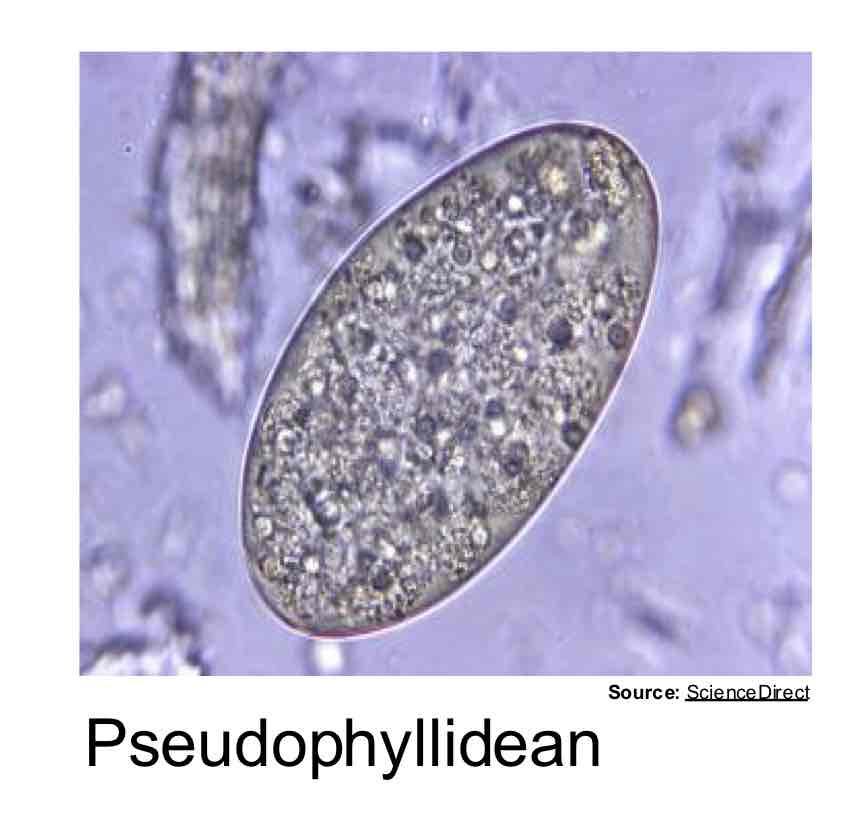
What definition best describes a protozoa?
A single-celled, microscopic, eukaryotic organism that can live extracellular or intracellular
T/F: Certain protozoa can be transmitted by arththropods.
True (ex: malaria by mosquitoes)
What is the function of the flagella in protozoa?
Locomotion
What are some examples of zoonotic Protozoa?
Giardia, Toxoplasma gondii, & Cryptosporidium
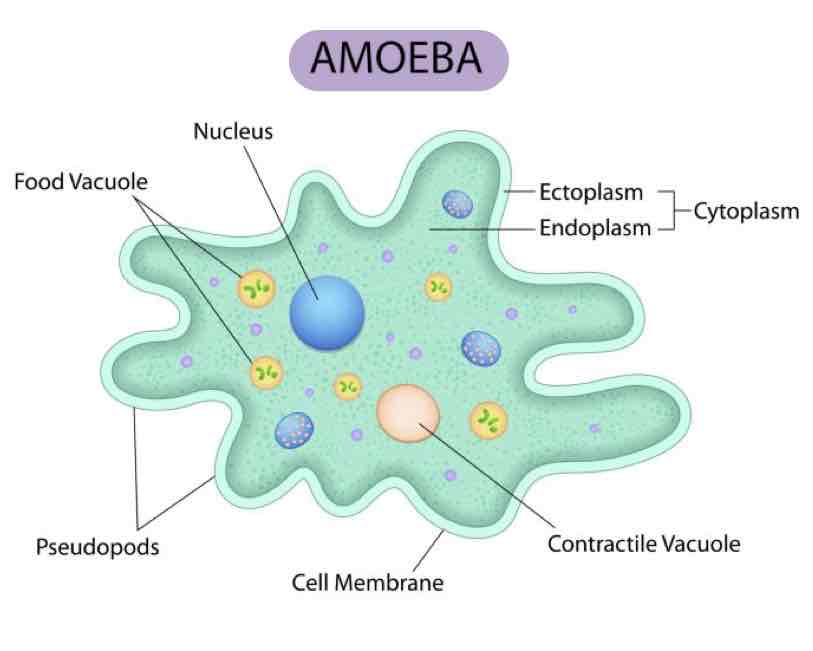
Which group of Protozoa are amoeba-like, use pseudopodia for motion & feeding, feed by phagocytosis extracellularly, reproduce asexually (binary fission), & have a direct life cycle?
Rhizopod
-ex: Entamoeba histolytica & E. invadens
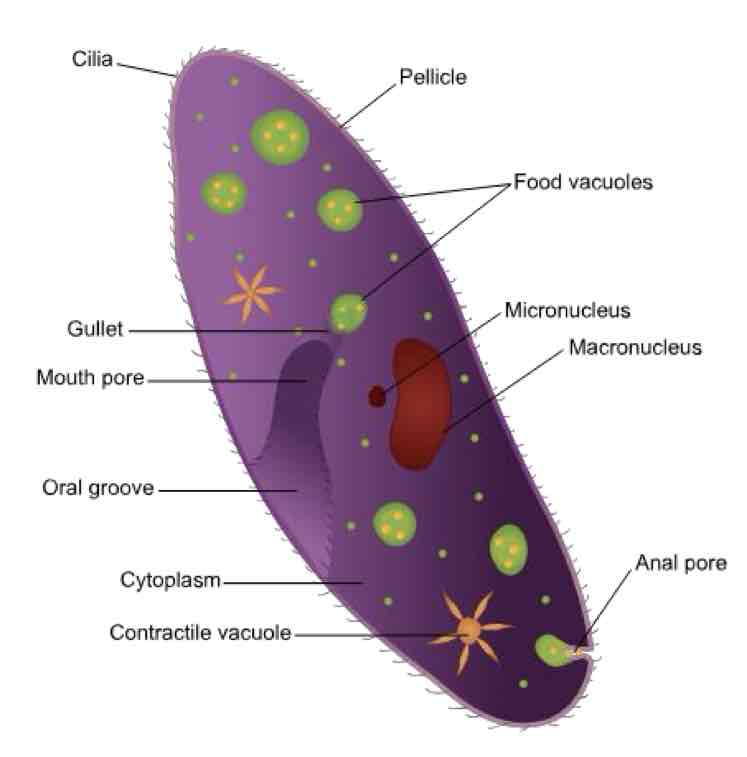
Which group of Protozoa have cilia for locomotion + feeding, two types of nuclei (macro/micronucleus), reproduce both sexually (conjugation) + asexually (binary fission/budding), & have a direct life cycle?
Ciliates
-ex: Balantidium coli & Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
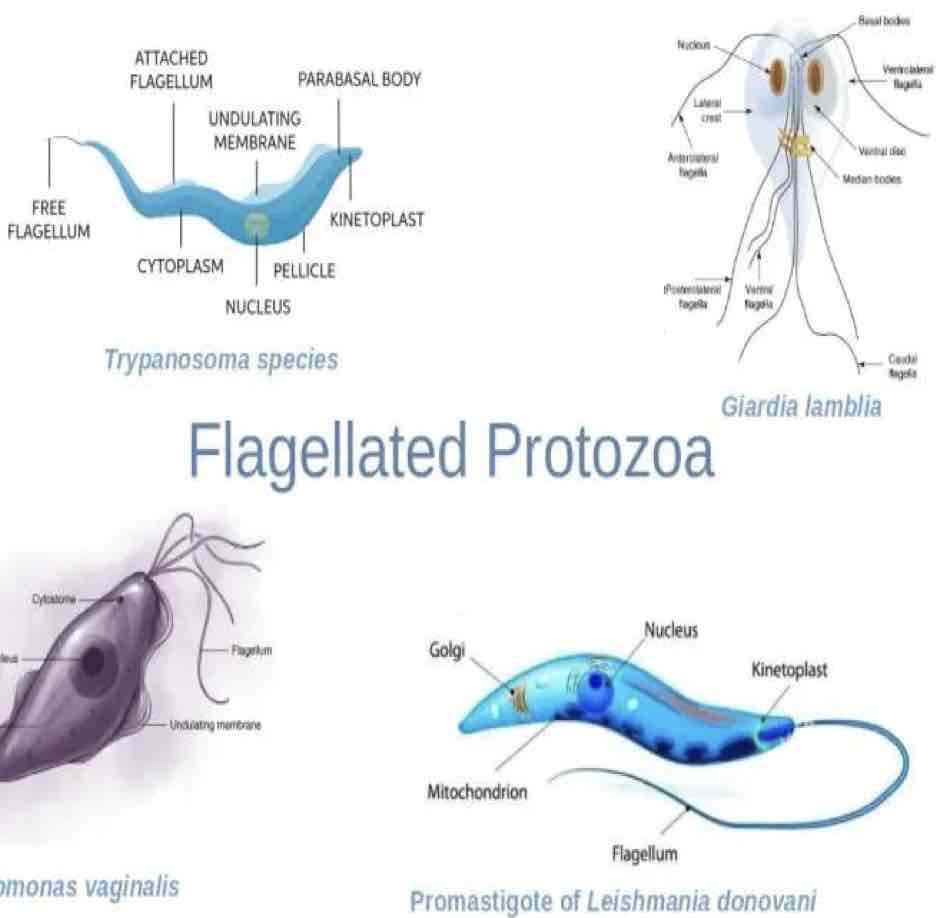
Which group of Protozoa have 1+ flagella for locomotion, reproduce asexually (binary fission), & have both a direct & indirect life cycle?
Flagellates
-ex: Trypanosoma spp., Leishmania spp., Giardia spp., & Tritrichomonas spp.
Which group of Protozoa have no motion, reproduce both sexually & asexually (schizogony), & have both direct & indirect life cycles?
Sporozoan
-ex: Eimeria spp., Isospora spp., Cryptosporidium spp., & Toxoplasma gondii
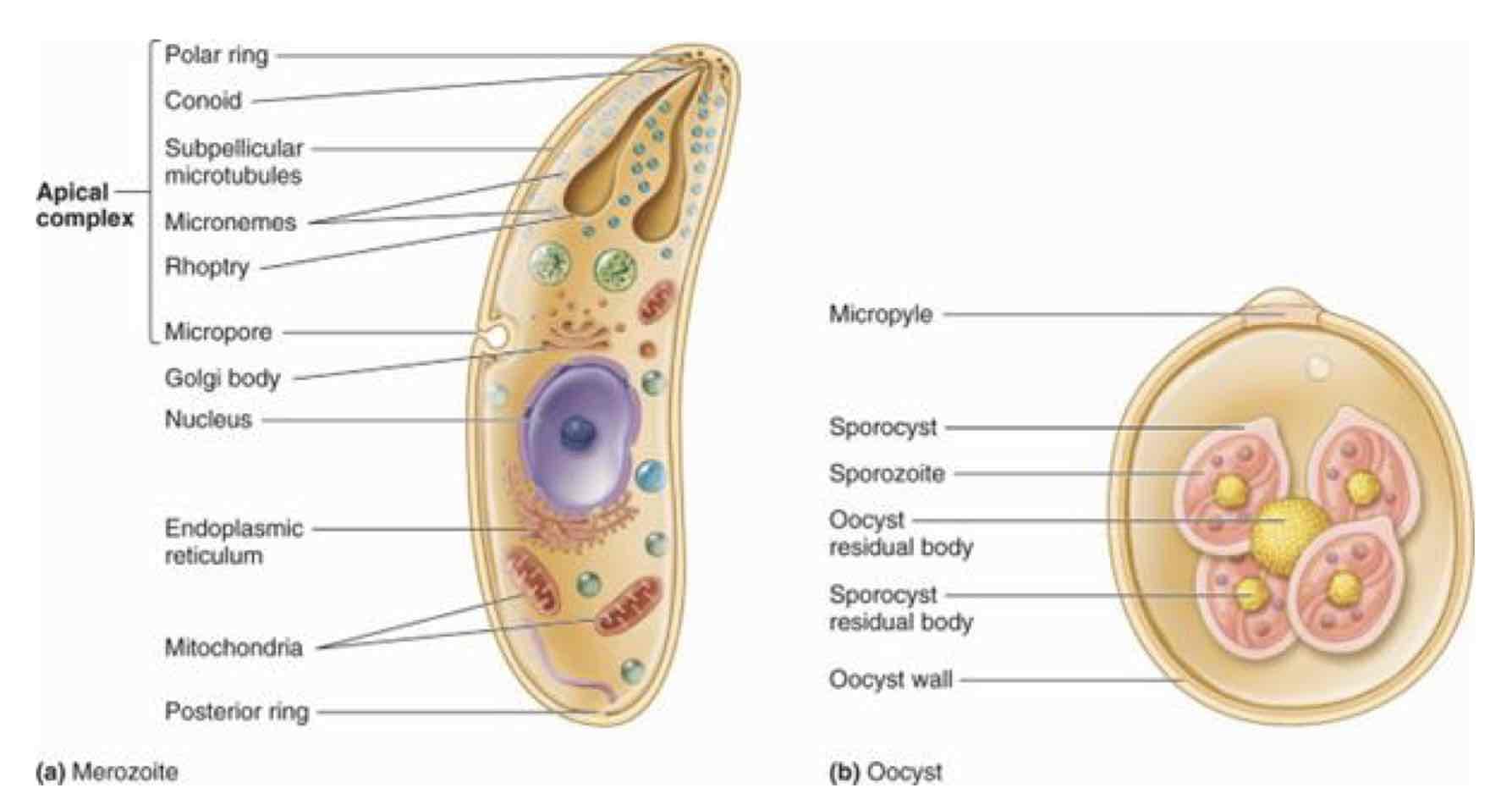
What is the organelle used by Entamoeba histolytica (Rhizopod) for locomotion?
Pseudopodia
What are some modes of transmission of Protozoa?
Fecal-oral (most common)
Ingestion
Vector-borne
Sexual contact btwn hosts
Vertical transmission
Blood transfusion
Autoinfection
Iatrogenic
What type of sexual reproduction in Protozoa involves the exchange of genetic material between two cells leading to the temporary fusion of these cells?
Conjugation
What type of sexual reproduction in Protozoa involves complete fusion of genetic material from two gametes which fertilize to form a zygote & encysts to form an oocyst?
Syngamy
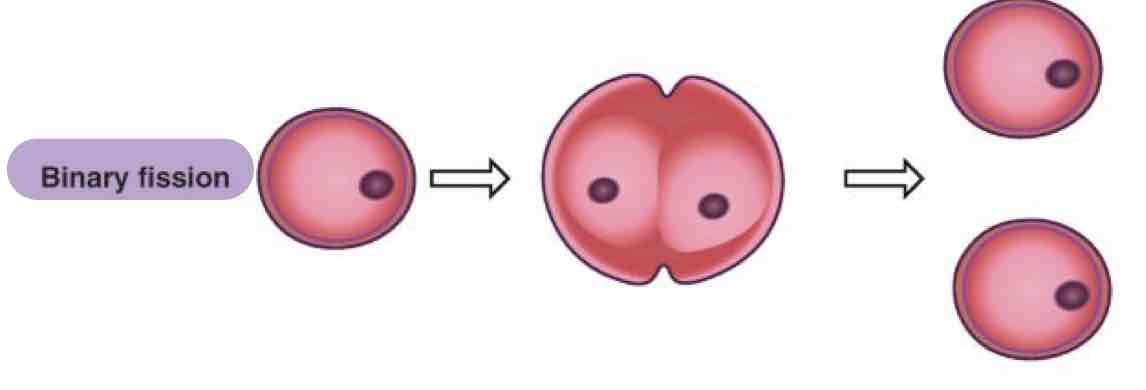
What type of asexual reproduction in Protozoa is where organelles duplicate & the Protozoa divides into two complete organisms?
Binary fission
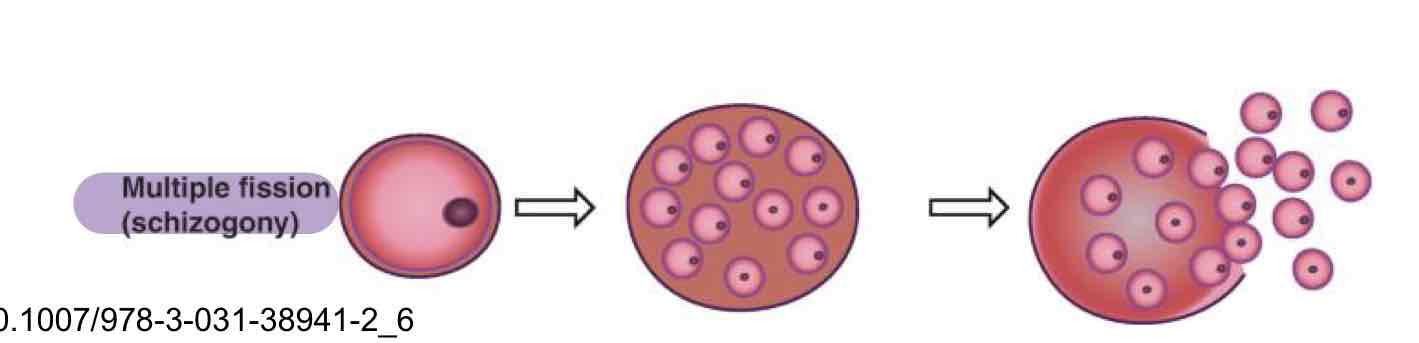
What type of asexual reproduction in Protozoa is where the nucleus divides repeatedly before the cytoplasm divides resulting in formation of smaller uninucleate merazoites?
Multiple fission (Schizogony)
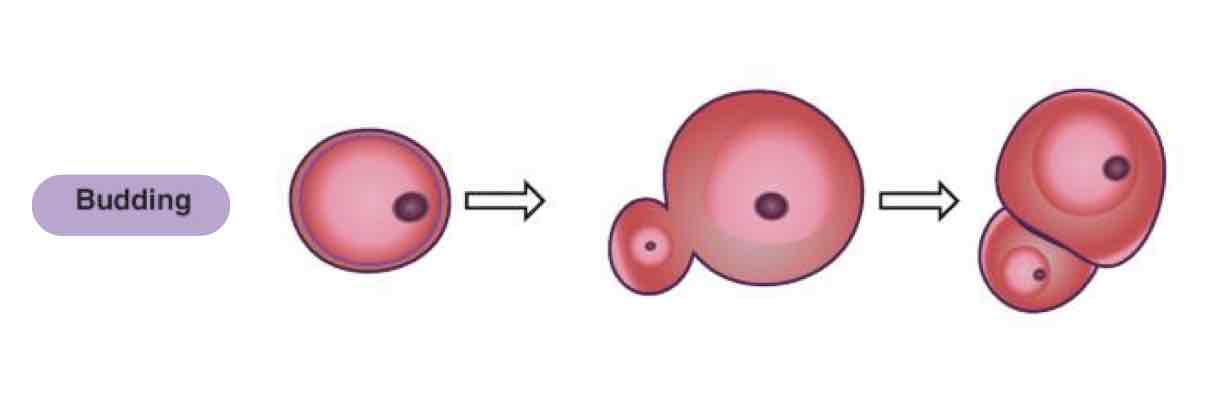
What type of asexual reproduction in Protozoa is where a new organism is produced from small outgrowth from the parent cell & is ejected when mature?
Budding
What specific Protozoa is transmitted by a mosquito vector & has an indirect life cycle?
Leishmania spp.
What specific Protozoa is transmitted by a tick vector & has an indirect life cycle?
Babesia spp.
What are some diagnostic methods for diagnosing Protozoa?
Wet mount/fecal smear (motile stage)
Fecal flotation/centrifugation (resistant/cyst stage)
Blood smears
PCR
What is an advantage of the wet mount/smear diagnostic test?
Allow observation of the motile stage
T/F: Protozoa parasites present with unique clinical signs making diagnosis easy.
False
What is the name of the motile, feeding protozoa stage?
Trophozoite