Cancer Genetics, DNA Repair and Genome Maintenance
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
DNA damage leads to
mutations
What are the two main types of DNA damage?
Single-stranded break (SSB)
Double-stranded break (DSB)
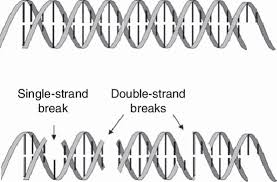
Which type of DNA damage can cause chromosome rearrangements?
Double-stranded break
What can unrepaired DNA damage can result in?
apoptosis (ageing)
senescence (ageing)
escape from growth suppression (cancer)
unregulated cell division (cancer)
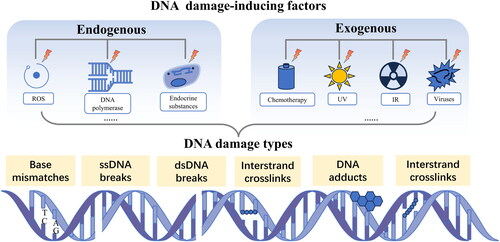
What are the two main sources of DNA damage?
exogenous (ionising radiation, UV from sun, chemotherapy, x-rays, viruses)
endogenous (errors during DNA replication, ROS, alkylation)

A famous example of exogenous DNA damage caused by release of ionising radiation is the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster. As a result, there was a significant increase in the number of which type of cancer?
early childhood thyroid cancer
What are the four main types of DNA repair mechanisms?
BER (base-excision repair)
NER (nucleotide-excision repair)
Recombinational repair
Homologous repair (HR)
Non-homologous end joining (NEJ)
Mismatch repair
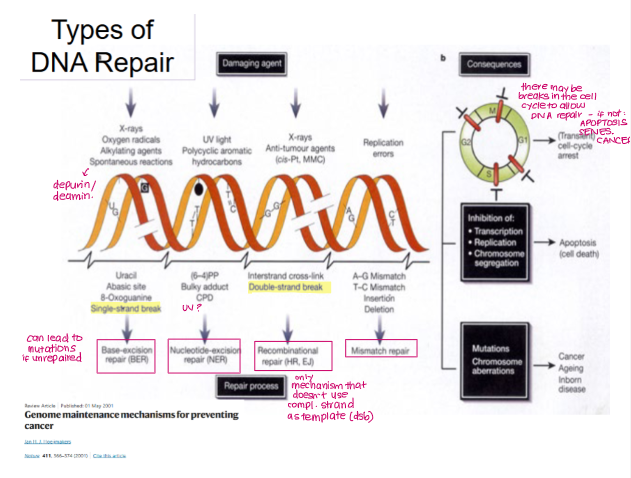
The choice of repair mechanism depends on?
type of lesion
stage of cell cycle
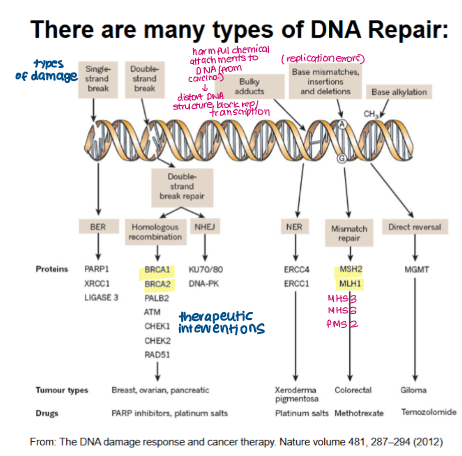
Examples of inherited human syndromes linked to defects in DNA repair
MSH2/3/6, MLH1, PMS2 (BER) → colon cancer
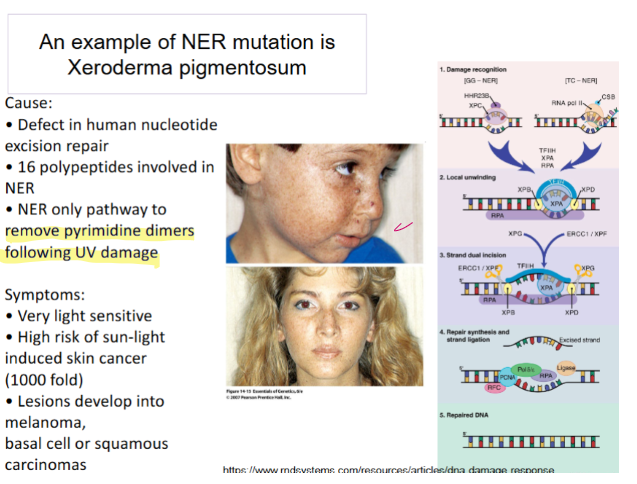
Xeroderma pigmentosum (NER) → skin cancer
BRCA1/2 (HR) → breast/ovarian cancer
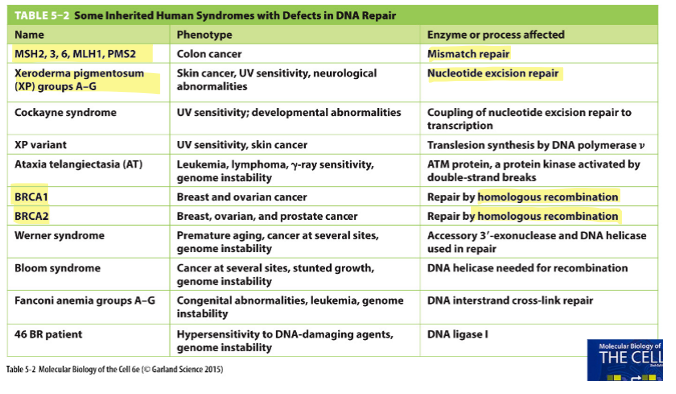
What are the three basic steps involved in DNA repair?
Excision
Resynthesis
Ligation
Which types of DNA damage are repaired by BER mechanism?
ROS
Spontaneous depurination and deamination
Alkylating agents
X-rays
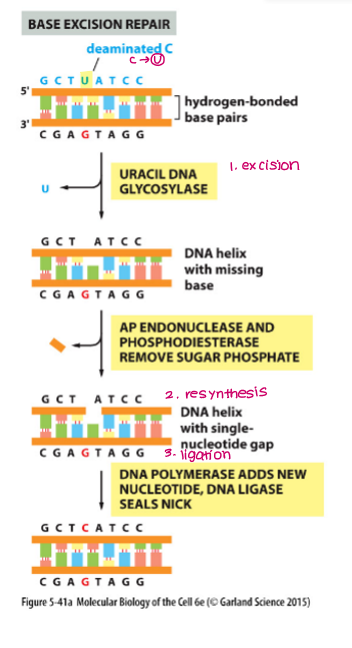
Explain how the BER mechanism repairs DNA damage.
Excision
Damaged base removed by DNA glycosylase
Strand incision by AP endonuclease
Remaining nucleotide excised by dRpase exonuclease
Resynthesis and Ligation
DNA polymerase fills in gaps using intact strand as a template
DNA ligase seals nicks in strand
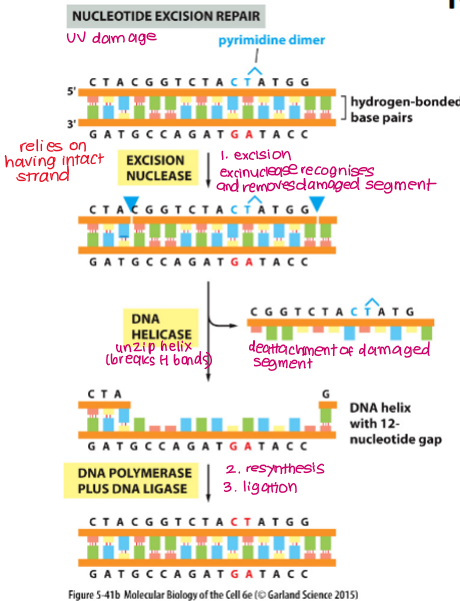
Explain how the NER mechanism repairs DNA damage.
Pyrimidine dimer is removed along with many other adjacent bases
Excision
Exonuclease recognises and removes damaged segment
DNA helicase unzips helix and removes damaged segment
Resynthesis and Ligation
DNA polymerase fills in gaps using intact strand as a template
DNA ligase seals nicks in strand
The NER mechanism is used exclusively to repair DNA damage caused by?
UV
What is a common consequence of NER mutation?
xeroderma pigmentosum
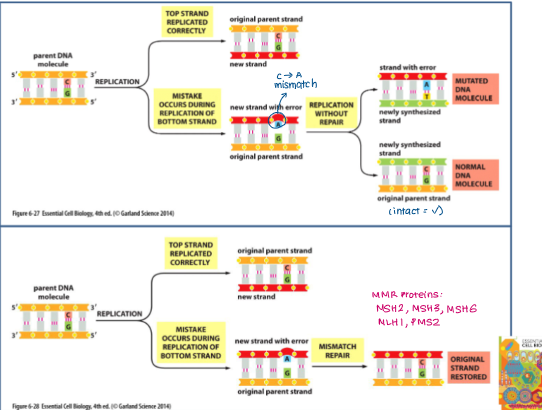
Mismatch repair mechanism repairs which kind of DNA damage?
DNA damage caused by errors in DNA replication (insertion, deletion, mismatched base)
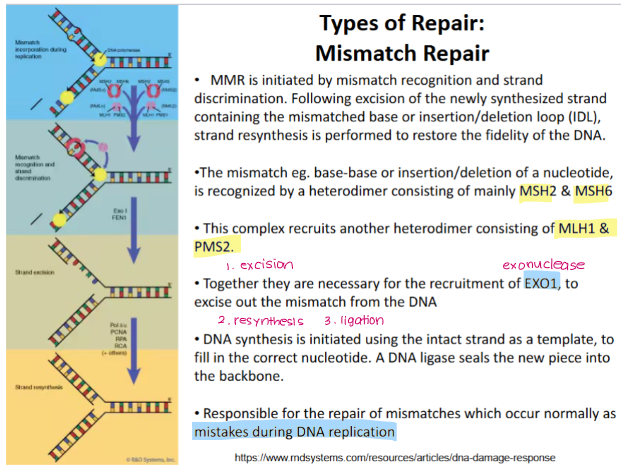
Name the five mismatch proteins
MSH2 and MSH6 (forms dimer)
MLH1 and PMS2 (forms dimer)
MSH3
Explain how the mismatch repair (MMR) mechanism repairs DNA damage.
Excision
Dimer (MSH2 and MSH6) recognises mismatch
Complex recruits another dimer (MLH1 and PMS2)
Both dimers together recruit EXO1 (exonuclease) which excises the mismatch out from the strand
Resynthesis and Ligation
DNA polymerase fills in gaps using intact strand as a template
DNA ligase seals nicks in strand
What is a common consequence of MMR mutation?
HNPCC (hereditary non-polyposis colon caner)
MMR mutation causes microsatellite instability in coding regions of cancer associated genes
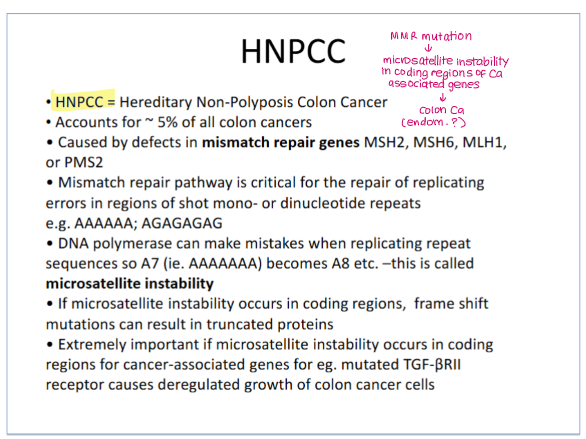
Recombination repair mechanism repairs which kind of DNA damage?
Double-stranded breaks (DSB)
Prevent use of complementary strand as a template
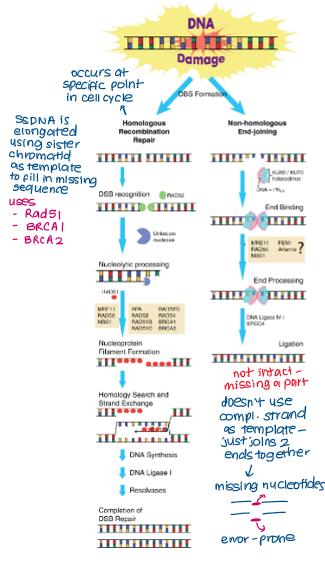
What are the two types of recombination repair?
homologous recombination (HR)- uses sister chromatids as template
non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)- no template used, just joins ends together
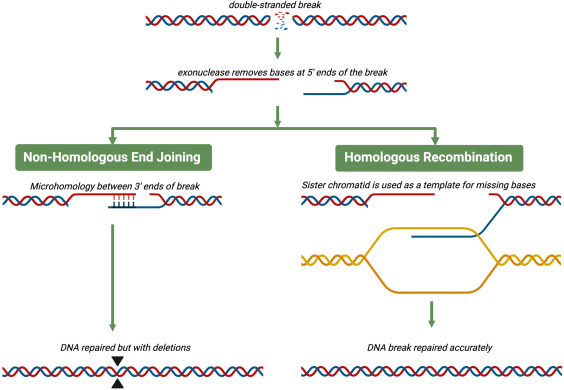
Explain how the homologous recombination (HR) mechanism repairs DNA damage.
Resection: A DSB is processed, creating single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) tails with free 3' ends.
Filament Formation: RAD51 protein loads onto the ssDNA to form a helical filament, with help from BRCA2 and other factors.
Homology Search & Invasion: The RAD51 filament searches for and invades a homologous (identical) intact DNA molecule (sister chromatid or homologous chromosome) to find a template.
DNA Synthesis: The invading 3' end acts as a primer, and DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA, copying the template sequence to fill the gap.
Resolution: The resulting DNA structures (like Holliday junctions) are resolved by nucleases and ligases, restoring two intact DNA molecules.
Uses RAD51, BRCA1/BRCA2
BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations account for what percentage of:
a) hereditary breast cancers
b) all breast cancers
c) ovarian cancers
a) 20-25%
b) 5-10%
c) 15%

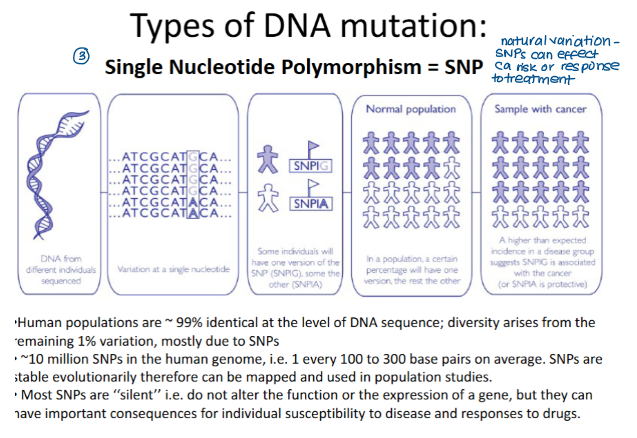
What are the three main categories of DNA mutation.
Base-pair (substitution, insertion, deletion, frameshift)
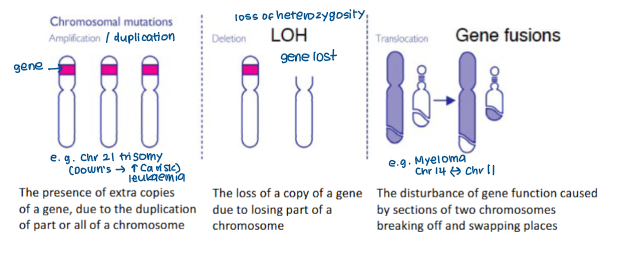
Chromosomal (translocation, duplication, deletion)
SNPs
Translocation between chromosome 14 and 11/4 is associated with with type of cancer?
multiple myeloma
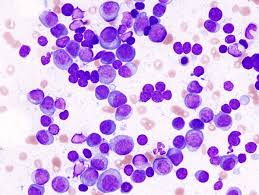
Duplication of chromosome 21 (trisomy) is associated with which syndrome and has an increased risk of developing which type of cancer?
Downs syndrome
Increased risk of leukaemia
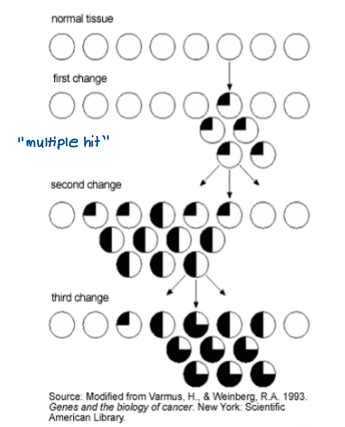
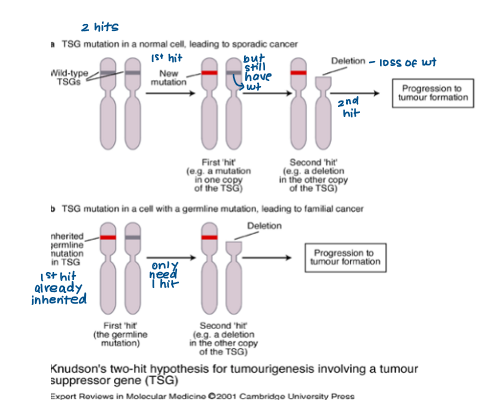
What did Knudson’s two-hot hypothesis of tumorigenesis (1971) suggest?
Inherited retinoblastoma vs sporadic retinoblastoma
inherited cases occur earlier
inherited cases developed in both eyes
“Two hits” needed- in inherited cases, first hit already present (inherited mutation) so only one more needed (deletion)
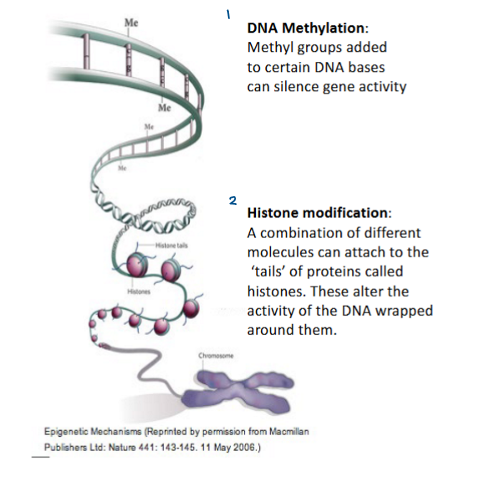
Mutations can also be caused by epigenetic modifications. Give two examples.
DNA methylation
Histone modification
Cancer is a genetic disease resulting from the accumulation of multiple mutational events. What is the relationship between mutation and cancer progression?
Cells with higher DNA mutation rates will tend to progress faster
e.g. BRCA1/2 mutation → develop breast cancer earlier