3. Merchandise Sales
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Merchandising companies must account for…
sales, sales discounts, sales returns, and allowances, and cost of goods sold.
Review
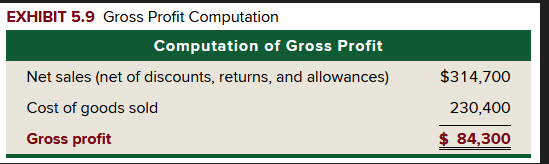
Z-Mart has three items in its gross profit computation - see the figure. This shows that customers paid $314,700 for merchandise that cost Z-Mart $230,400, yielding a cross profit of $84,300.
What does the perpetual accounting system require for each sale transaction for a merchandiser, whether for cash or credit?
It requires that it has two entries. One for revenue and one for cost.
For each sales transaction for a merchandiser, what does the revenue entry represent?
Revenue recorded (and asset increased) from the customer.
For each sales transaction for a merchandiser, what does the cost entry represent?
cost of goods sold (and asset decreased) to the customer
For both sales without a cash discount and with a cash discount, how would we record the revenue side?
debit accounts receivable and credit sales (sales is same as revenues).
Either with a cash discount or without, debit and credit the same accounts. If there is a cash discount, it is recorded later with an adjustment.
For both sales without a cash discount and with a cash discount, how would we record the cost side?
debit cost of goods sold (expense) and credit merchandise inventory
The cost side of each sale requires that…
Merchandise Inventory decreases by that item’s cost since our inventory has decreased bu that amount.
For sales with cash discounts, the gross method records sales at the…
full amount and records sales discounts if, and when, they are taken.
Review example under sales without Cash Discounts (Z-Mart)
Review Sales on Credit example under Sales with Cash Discounts.
(debit and credit same accounts as sales without cash discounts, this is just for review. Remember there is an entry for the revenue side and an entry for the cost side).
What type of account is Sales Discounts?
A contra revenue account
What is Sales Discounts a contra revenue account to?
Sales
What does it mean when Sales Discounts is a contra revenue account to Sales?
Sales Discounts account is subtracted from the Sales account (for example when computing net sales).
Does Sales Discounts have a normal debit or credit balance?
debit
Does Sales have a normal debit or credit balance?
credit
What is net sales?
The amount received from the customer.
What is the entry to record the transaction when the buyer pays within the discount period?
debit Cash (for the original amount minus discount), debit Sales Discounts (for the discount amount), and credit Accounts Receivable.
What is the entry to record the transaction when the buyer pays after the discount period?
debit cash and credit accounts receivable
When a buyer returns goods what does it impact?
The seller’s revenue and cost sides.
When a return occurs, what account should the seller debit or credit?
The seller debits Sales Returns and Allowances.
What type of account is Sales Returns and Allowances?
a contra revenue account to Sales.
Does Sales Returns and Allowances have a normal debit or credit balance?
debit
What does it mean when Sales Returns and Allowances is a contra revenue account to sales?
It is subtracted from Sales.
As an example, if a customer returns the merchandise on December 29 that sold for $15 and cost $9, what is the revenue side entry? (returned merchandise not defective)
debit Sales Returns and Allowances and credit Cash (for amount customer paid for merchandise)
As an example, if a customer returns the merchandise on December 29 that sold for $15 and cost $9, what is the cost side entry? (returned merchandise not defective)
debit Merchandise Inventory and credit Cost of goods sold (for amount you purchased the merchandise for, not how much customer paid)
When a return occurs, the seller must…
reduce the cost of sales.
Which transactions using the perpetual system, requires both a revenue side and a cost side when you are selling merchandise?
The sale of merchandise and when a customer returns merchandise.
When might there be a buyer granted allowance?
If a buyer is not satisfied with the goods, the seller might offer a price reduction for the buyer to keep the goods.
Is there a cost-side entry when the buyer grants an allowance and why?
No because the inventory is not returned
What is the revenue-side entry for buyer granted allowances?
debit Sales Returns and Allowances and credits Cash or Accounts receivable depending on whats agreed.
If the seller has already collected cash for the sale, if the buyer gives a price reduction for the buyer to keep the goods (buyer grants allowance), what does the revenue-side entry look like?
debit Sales Returns and Allowances and credit cash instead of accounts receivable.
If paying freight for FOB destination what would be the entry to record this transaction as the seller?
debit Delivery expense and credit cash
Review Need-To-Know 5-3