Chapter 21: Digestion単語カード | Quizlet
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What are four processes of digestion?
Digestion
Motility
Secretion
Absorption
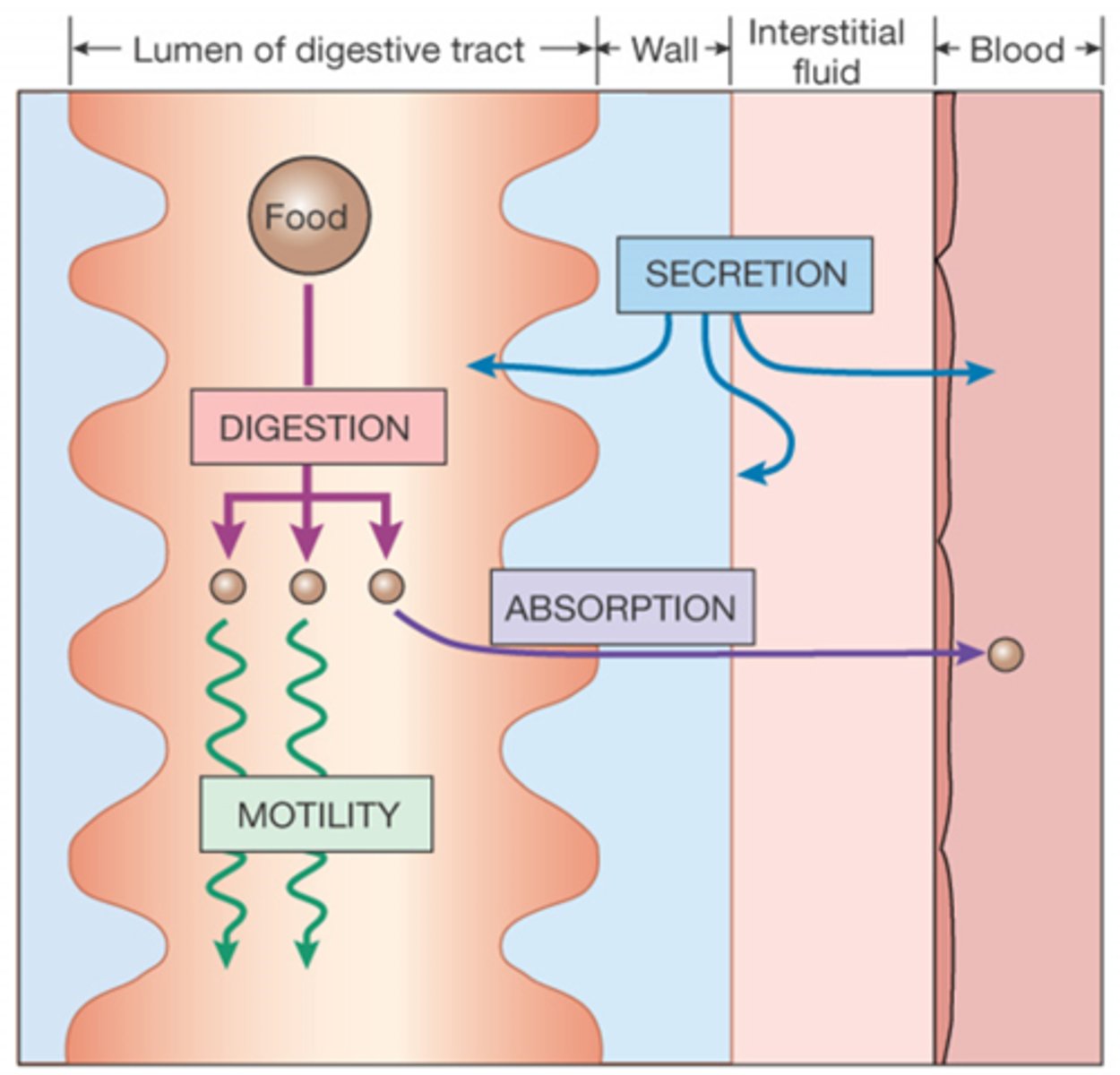
What is digestion?
chemical and mechanical breakdown of food into absorbable units
What is secretion?
movement of material from cells into lumen or ECF
What is absorption?
movement of material from GI lumen to ECF
What is motility?
movement of material through the GI tract as a result of muscle contraction
What are the components of the digestive system?
Oral cavity
Salivary glands
Esophagus
Liver
Stomach
Pancreas
SI
LI
Rectum
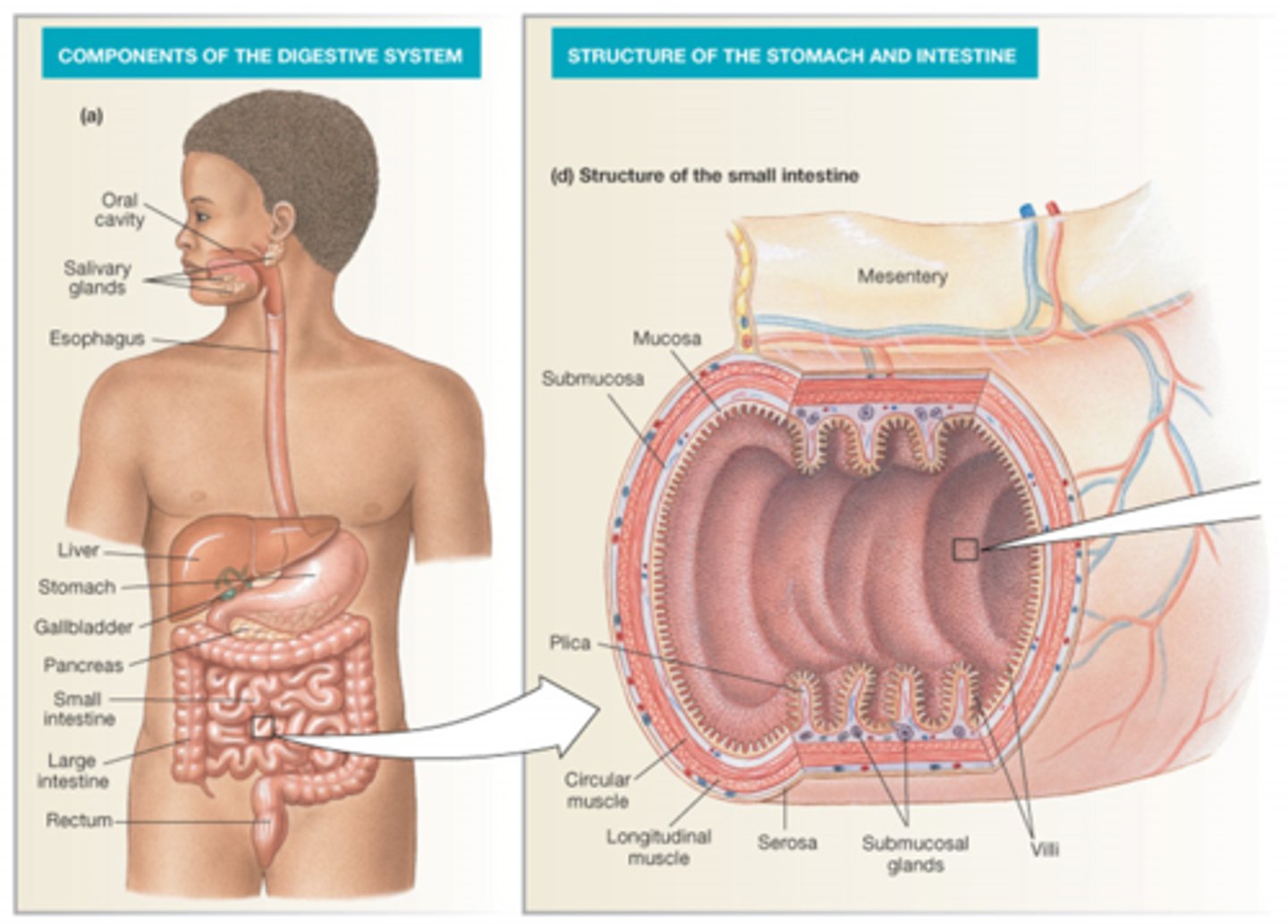
What are two ways food is moved throughout the body?
Peristalsis
Segmentation
What is peristalsis
wave-like muscle contractions
When is peristalsis used?
To move move your food down the GI tract
Segmentation
Random contractions along the GI tract
When is segmentation used
To mix your food in the GI tract
What is total input and output of the lumen?
9 L/day
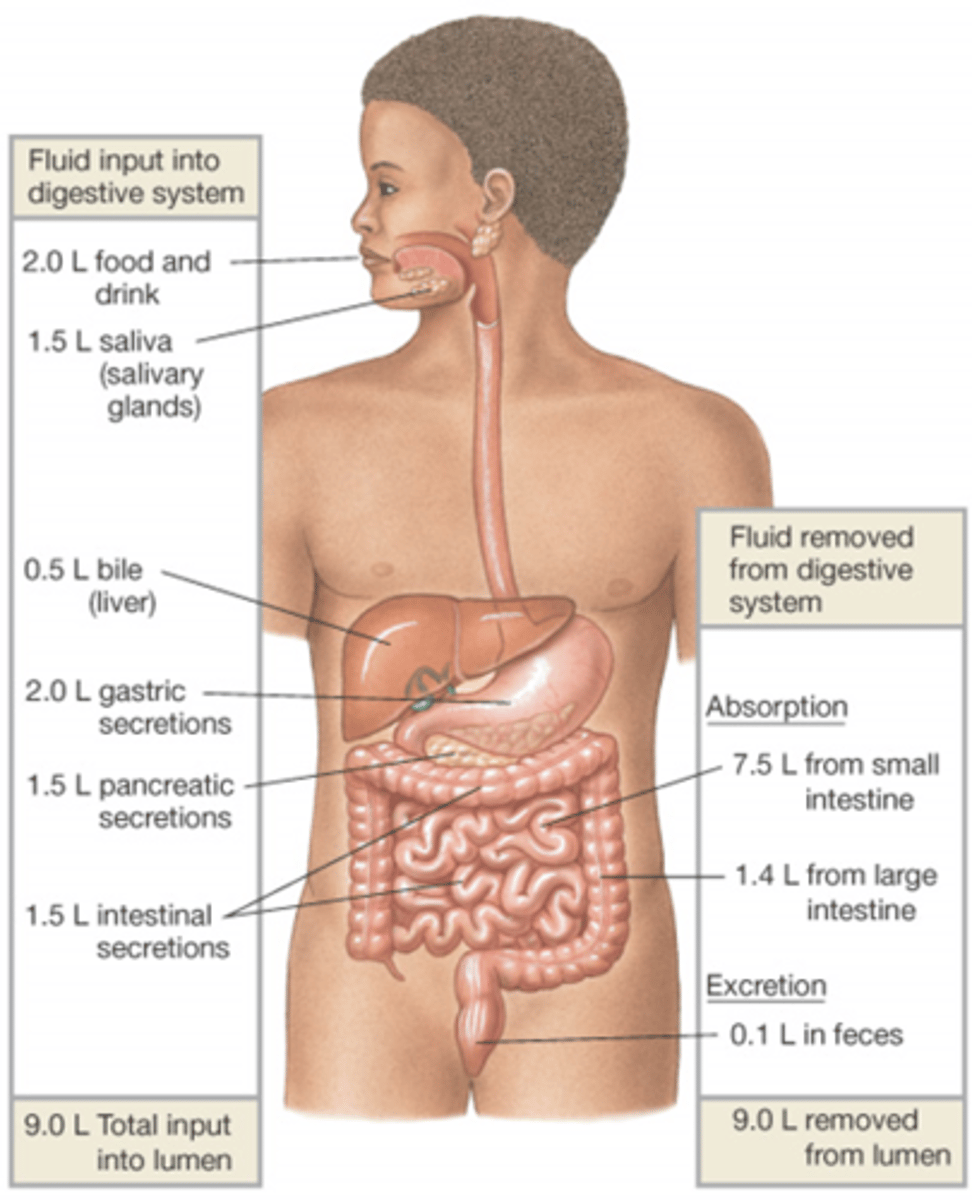
What are the two ways we input fluid into the lumen?
Ingestion (food and drink) - 2 L/Day
Secretions (from cells to lumen) - 7 L/Day
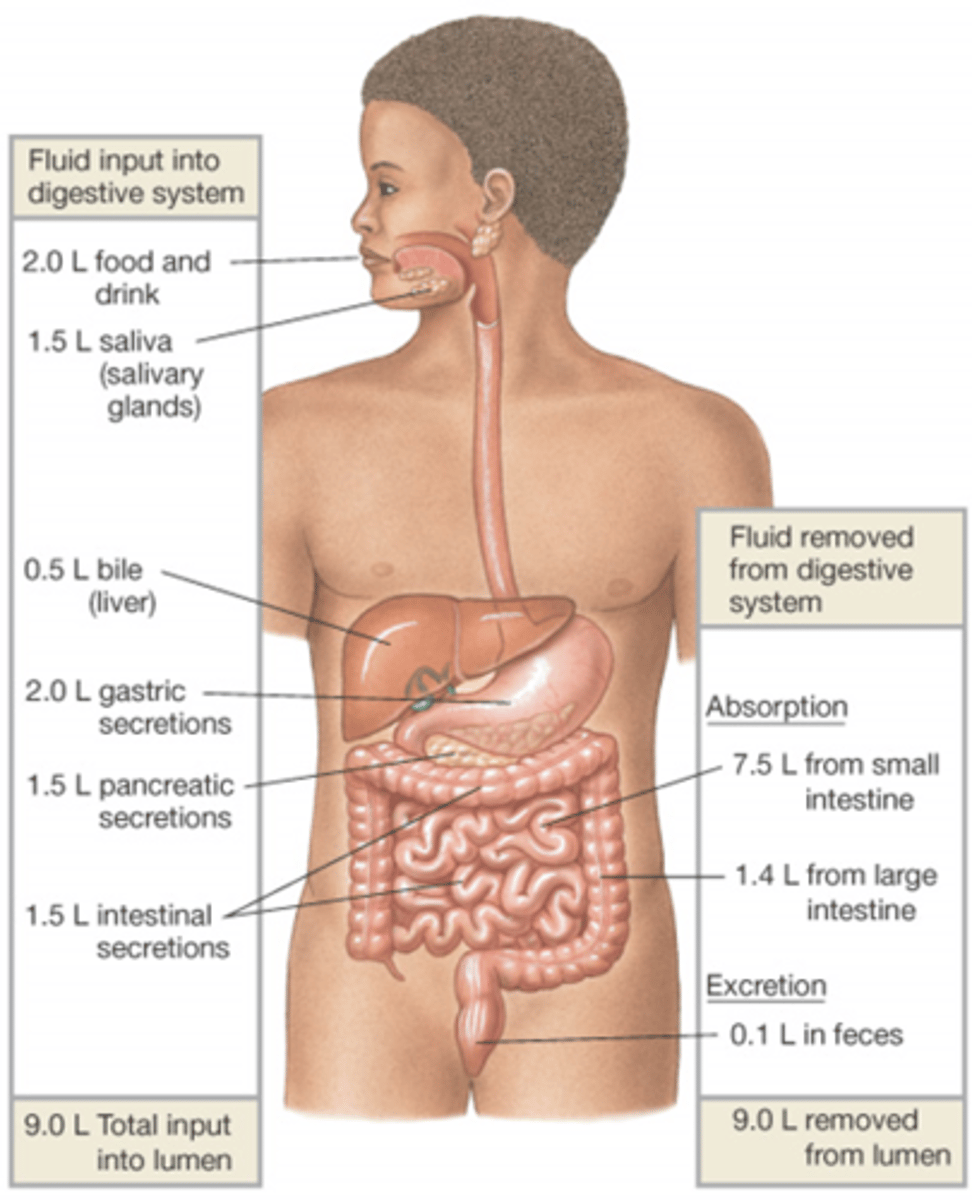
What are the two ways we remove fluid from the lumen?
Absorption
Excretion
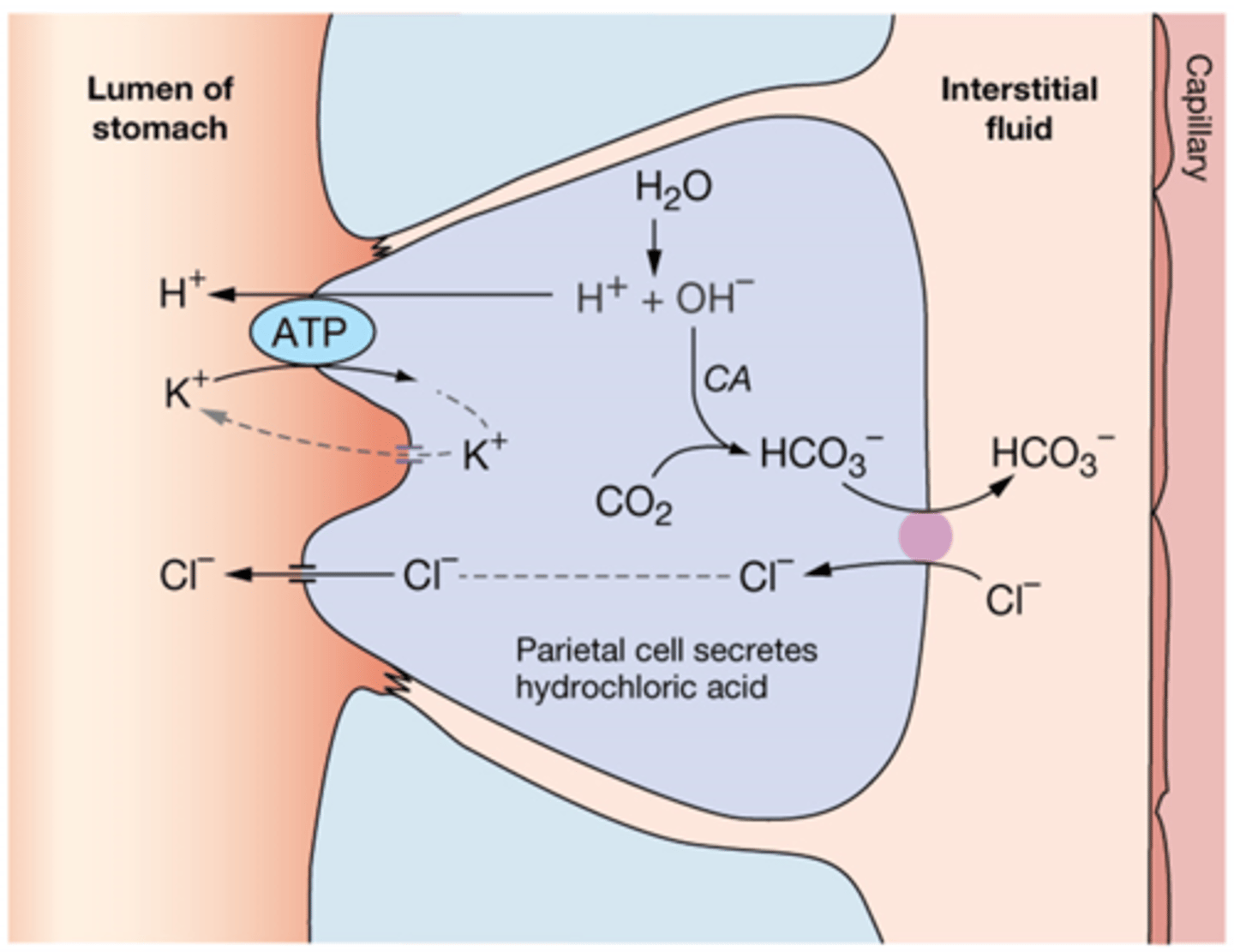
What cells line the stomach?
Parietal Cells
What do parietal cells secrete?
HCl
What the transporters on the apical and basolateral side of the parietal cell?
basolateral side - Chloride and bicarb (antiporter)
Apical - K+ H+ ATPase, Chlorine transporter
What are the two functions of the pancreas?
endocrine and exocrine
What are the exocrine functions of the pancreas?
secretes pancreatic juice and digestive enzymes
What are the endocrine functions of the pancreas?
To secrete hormones like glucagon and insulin
What do duct cells in the pancreas secrete?
sodium bicarbonate
What is the CFTR channel?
Controls the movement of water in cells which produce mucus, sweat, saliva, tears, and digestive enzymes.
Where is the CFTR gene located?
pancreas
What happens when the CFTR channel is mutated?
Cystic Fibrosis

What is the function of the liver
Make bile
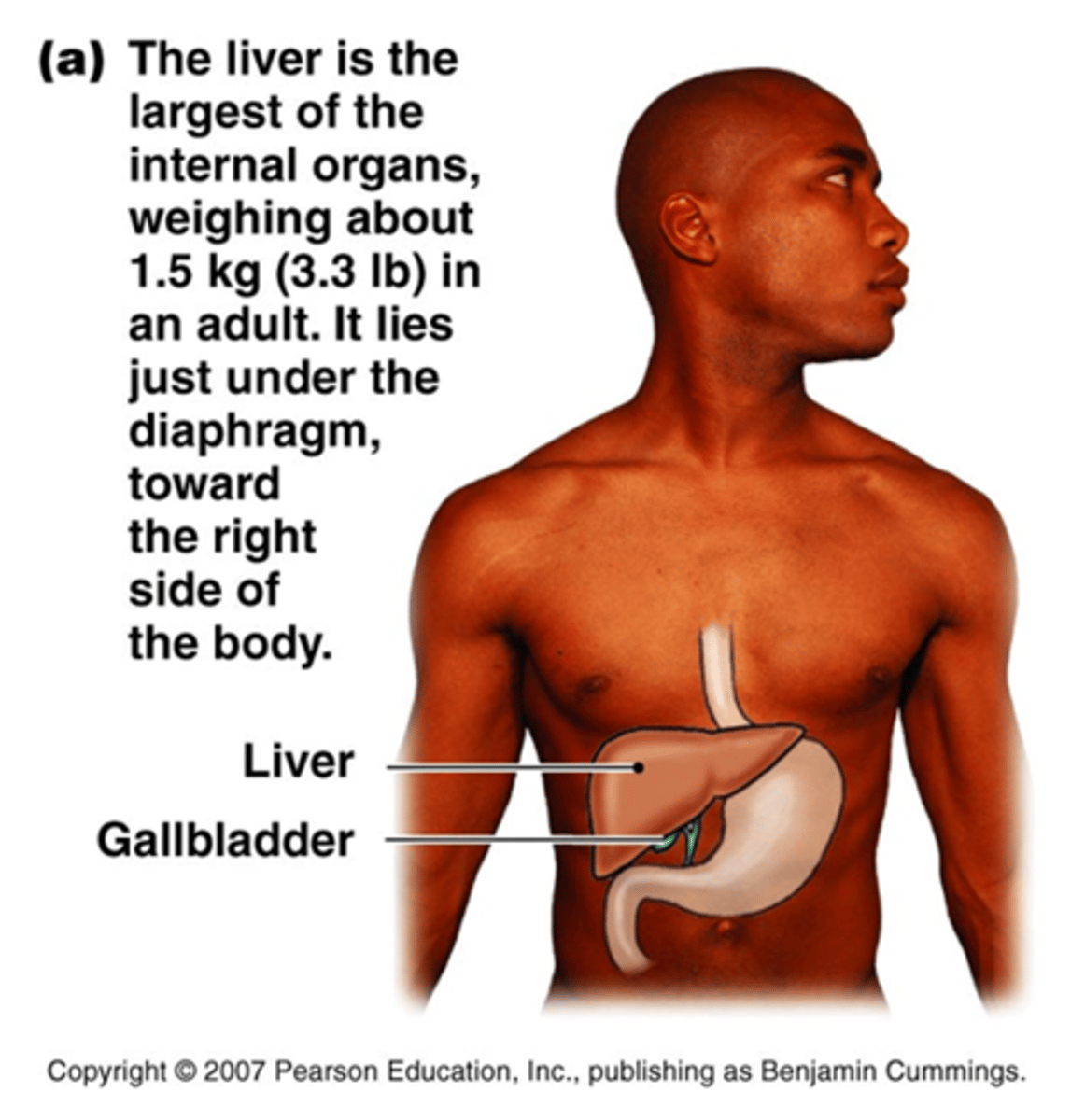
What is the function of the gallbladder
Stores bile
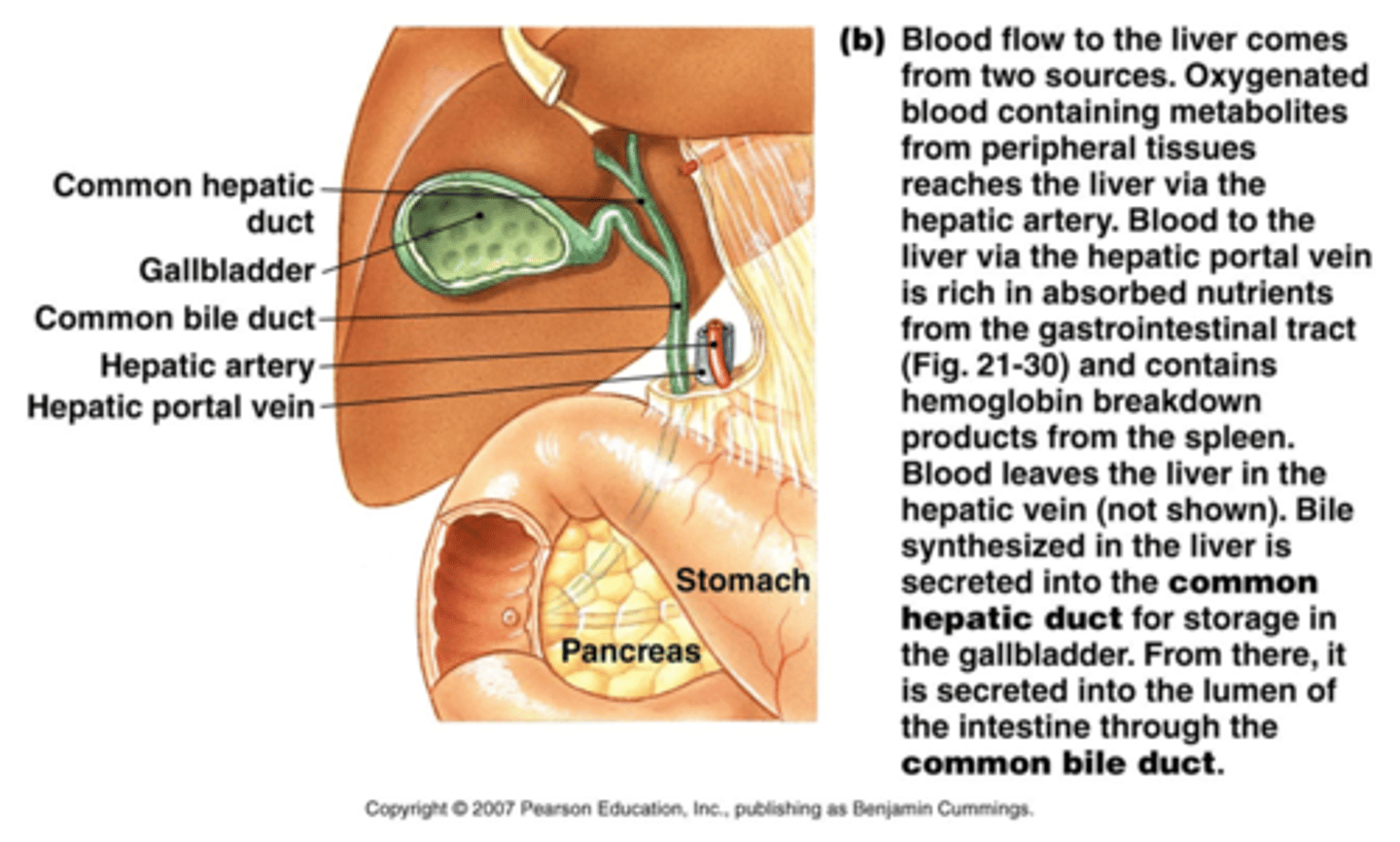
What are the two vessels of transport for the liver?
The hepatic portal vein and the hepatic duct
Where does the Hepatic duct go?
Away from the liver
Where does the Hepatic portal vein go?
To the liver
Sphincter of Oddi
Where the ducts of the pancreas and the gallbladder meet up and enter the duodenum
Pyloric Valve
controls the release of stomach contents into the intestine. So it's closed when food is in the stomach being digested
What are the two regulators of the digestive system?
The cephalic brain
Enteric nervous system
Sugars begin as ____________________ and are broken down into ______________________ and then into _________________ by __________________ .
polysaccharide
dissaccharide
Monosaccharide
amylase
The from of sugars which are able to cross the epithelium, which means they can be digested, are ______________________.
Monosaccharides
Once carbs or proteins become monosaccharides or amino acids, they travel to the liver via.......
The hepatic portal vein
Proteins begins as ____________________ and are broken down into ______________________ and then into _________________ by __________________ or _______________
Polypeptides
Dipeptides
Amino acids
Endopeptidases
Exopeptidases
If they are not broken down into AA polypeptides can cross the epithelium via ______________________
Transcytosis
What does an endopeptidase do?
cut peptide bonds in the middle of the polypeptide
What does an exopeptidase do?
cuts the peptide bond at the end of polypeptide
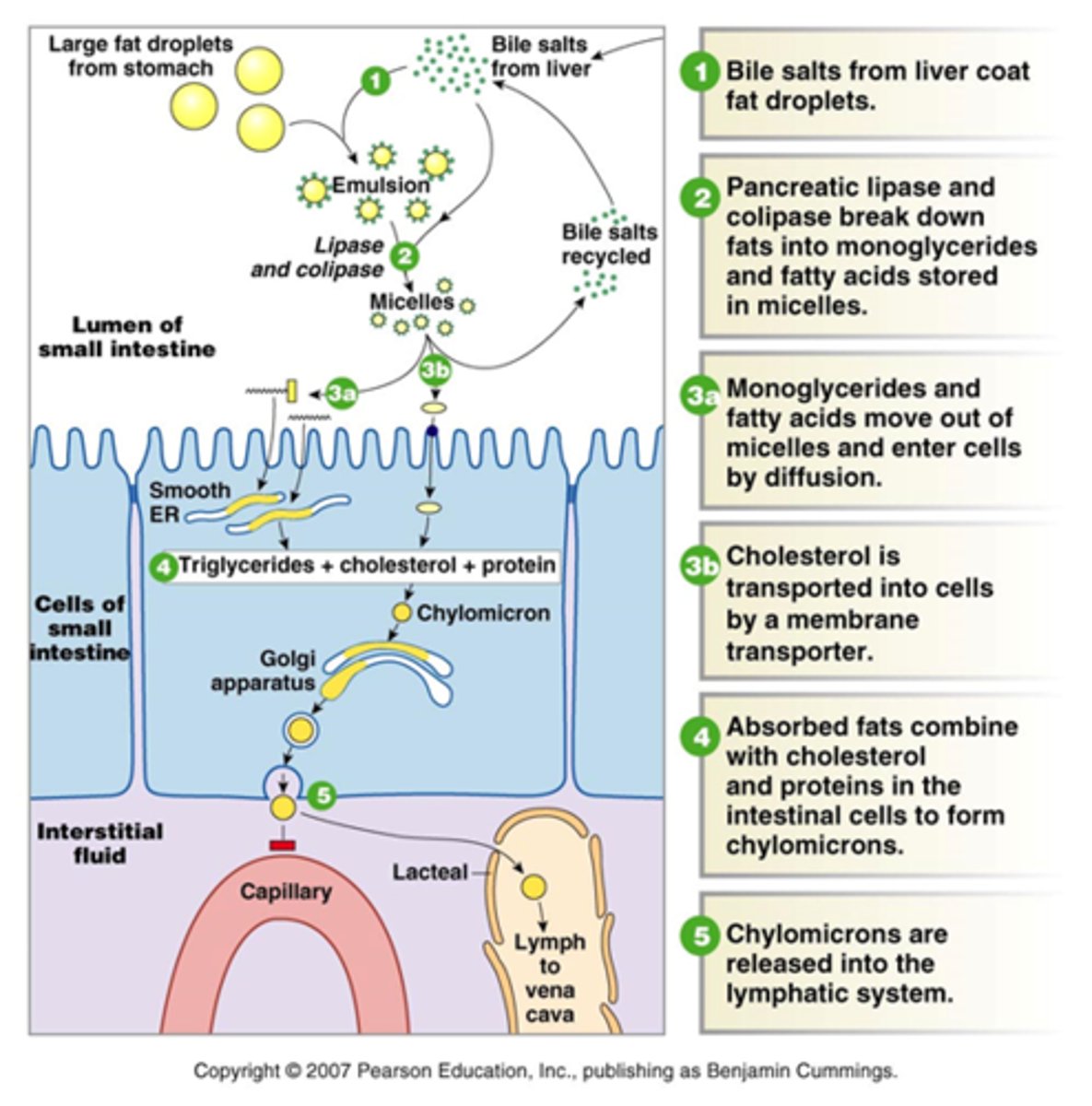
How are fats digested?
Large fat droplets + bile
Micelles via colipase + liapses
Cholesterol into SI cells
Monoglycerides into SI cells - smooth ER makes triglycerides
Cholesterol + protein + Triglycerides to make chylomicrons
Chylomicrons into Golgi - vesicle - exocytosis
into Lacteal to Vena Cava
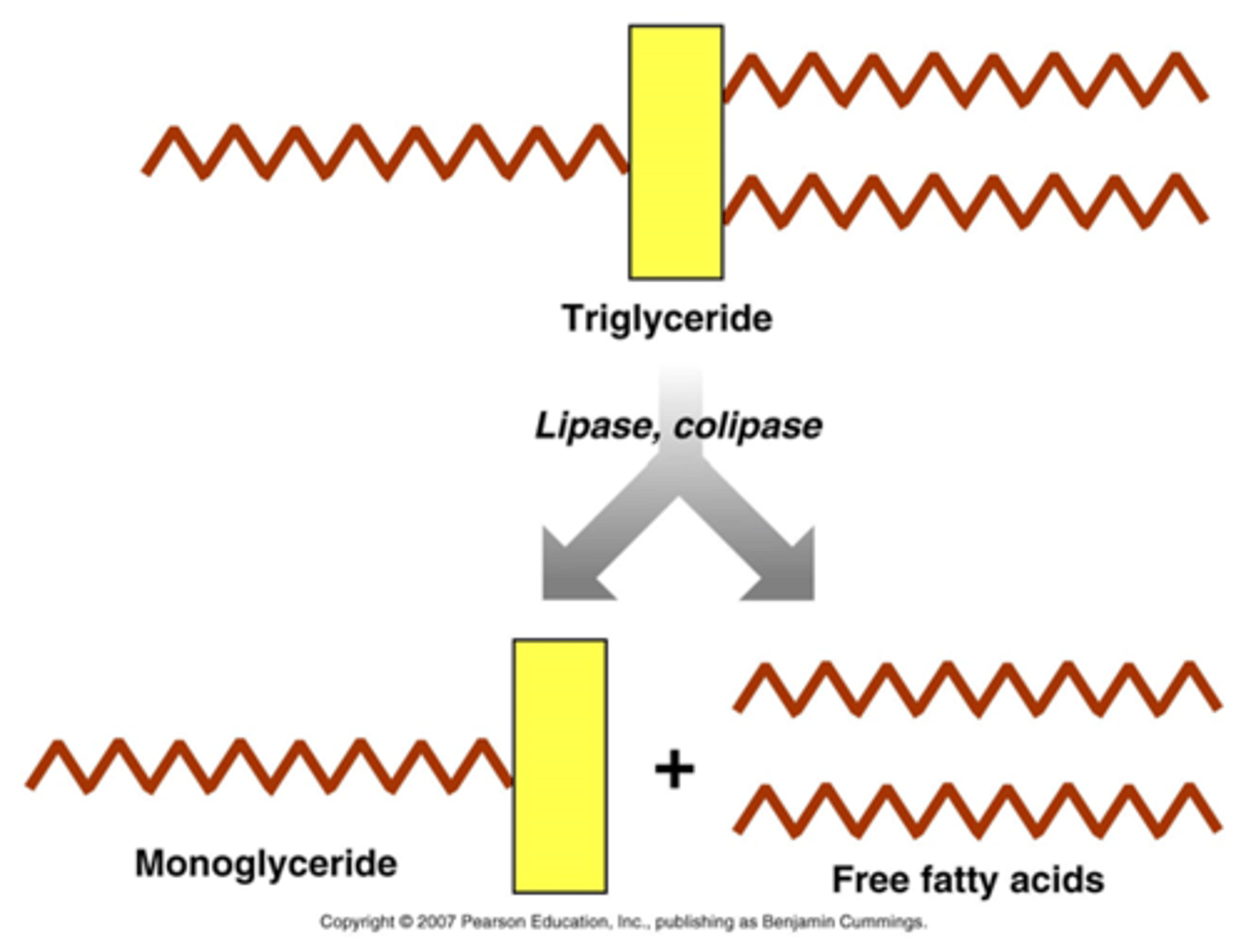
Digestion of Triglycerides
Monoglycerides + Free Fatty Acids
Bile salts are _________________ which allow emulsficcation
amphipathic
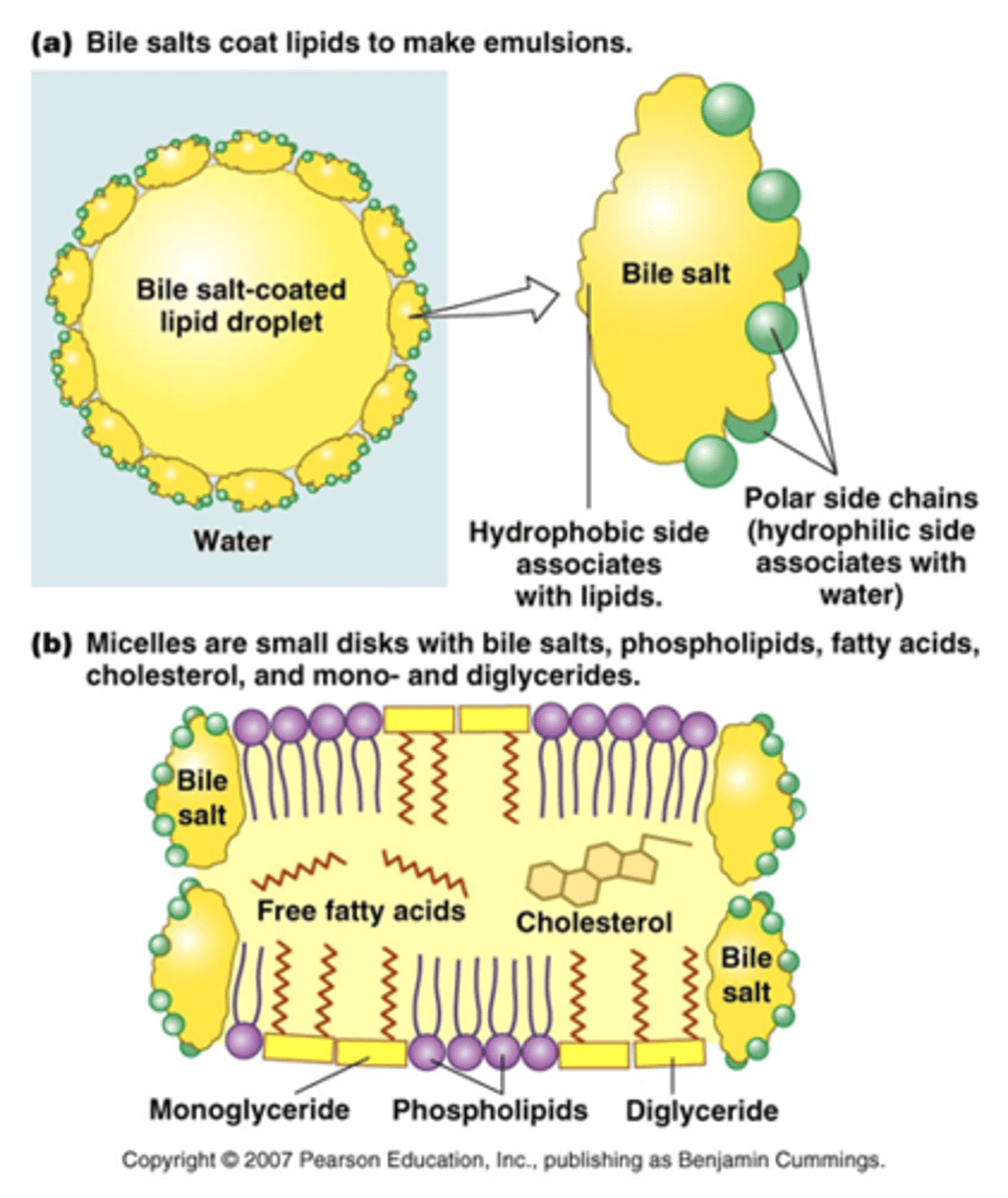
What are micelles made up of?
Bile Salts, phospholipids, mono- and di-glycerides, free fatty acids, cholesterol
In addition to nutrients, the intestines absorb......
Water
Ions
Vitamins
Minerals
What are the three phases of digestion?
cephalic, gastric, intestinal phase
What is the cephalic phase of digestion?
earliest phase of digestion in which the brain prepares the body in anticipation of food (via the thought, smell, or food in the mouth)
During the cephalic phase, the anticipation of food causes GI ___________ and GI _____________.
motility
secretions
During the Cephalic phase the mouth begins digestion ___________________ and _________________.
Mechanically
Chemically
How does the mouth exhibit mechanical and chemical digestion?
Mechanical: Grind, mix & liquefy
Chemical: water, lingual amylase, mucus, and lysozyme
What organ is involved in the gastric phase?
The Stomach
The Stomach has three elements which are involved in the gastric phase?
Storage
Digestion
Protect Walls
Describe the role of storage in the gastric phase?
It has to do with when food was not available so our body holds on to food all the time so you can tap into the nutrients later
Describe the role of digestion in the gastric phase?
Parietal cells - secrete HCl
Chief cells - secrete lipase and pepsin
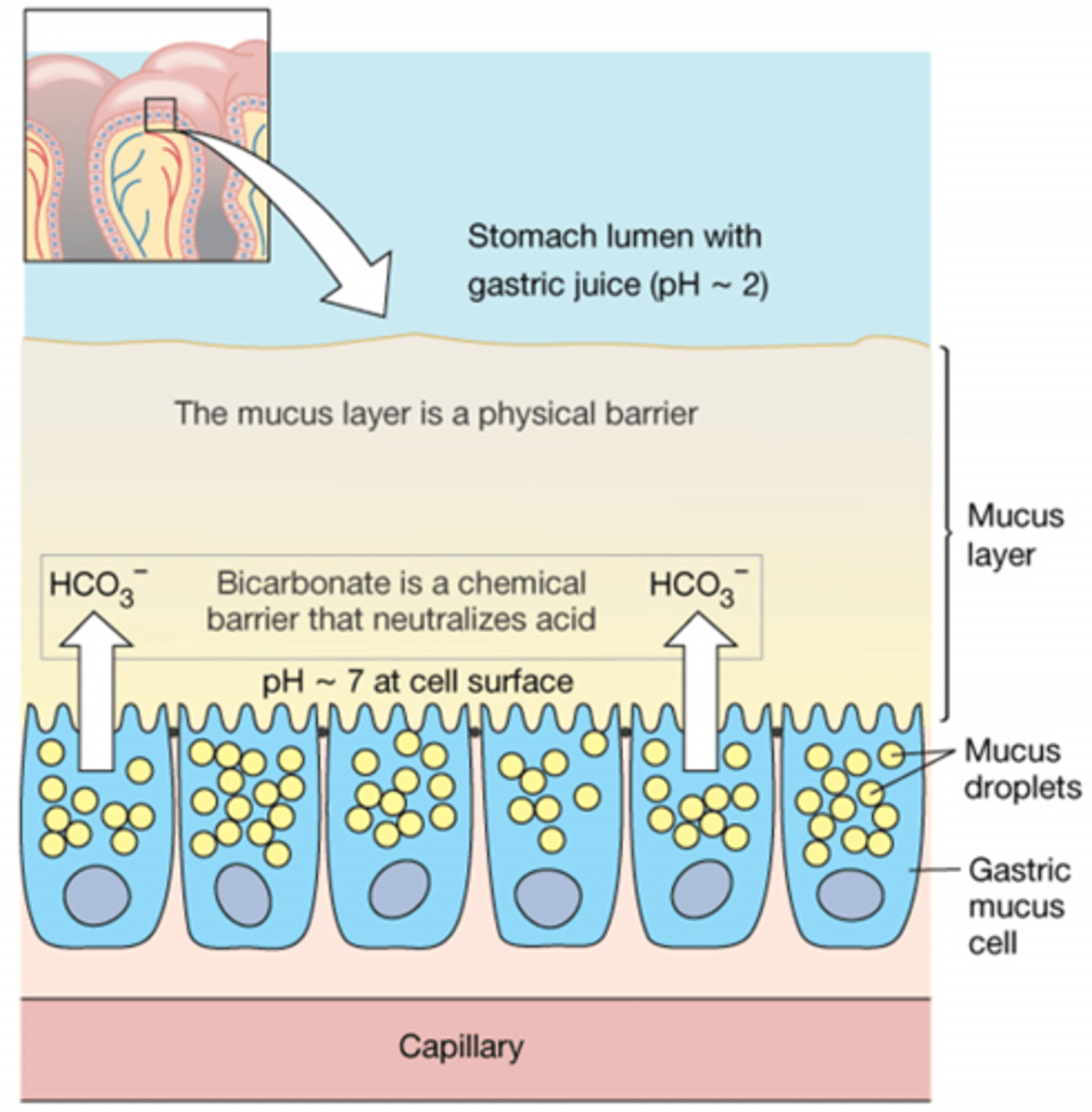
Describe the role of protecting walls in the gastric phase?
Mucus protects the stomach from digesting itself.
What factors are in place to ensure that your stomach doesn't digest itself?
Gastric Mucus cells secrete mucus, which develops a mucus layer.
The bicarbonate is released by the gastric mucus cells which gets trapped in the mucus, creating a gradient of the buffer which neutralizes the acidic pH of the stomach
What is the intestinal phase?
Where the bolus enters the duodenum
The cephalic input to the CNS leads to the activation of the _______________ ______________ system
Enteric Nervous
When the bolus enters the small intestine, it triggers the activation of the __________ ___________ system, which reduces GI __________ , slows gastric ____________, and causes the release of a mix of stuff from the sphincter ___________.
enteric nervous
motility
emptying - limited chyme entrance rate
Oddi
What is being released from the sphincter Oddi?
Sodium Bicarbonate (neutralizes HCl) - (pancreas)
Bile (gallbadder)
Enzymes (pancreas)
What happens to enzymes when they are released into the lumen of the small intestine?
The enzymes are anchored to the lumen, so that the chyme is broken down passes the enzymes.
Why are enzymes anchored to the small intestine?
Because if the body had to make new enzymes all the time, that would be a lot of wasted energy.
During the intestinal phase, what is the role of the liver?
Make bile to be secreted in the gallbladder and stored
Recycle bile salts (they aren't excreted)
Hepatic system (portal and vein)
What is the role of the Hepatic system?
Breaking down anything harmful before it enters the blood and can reach the lungs
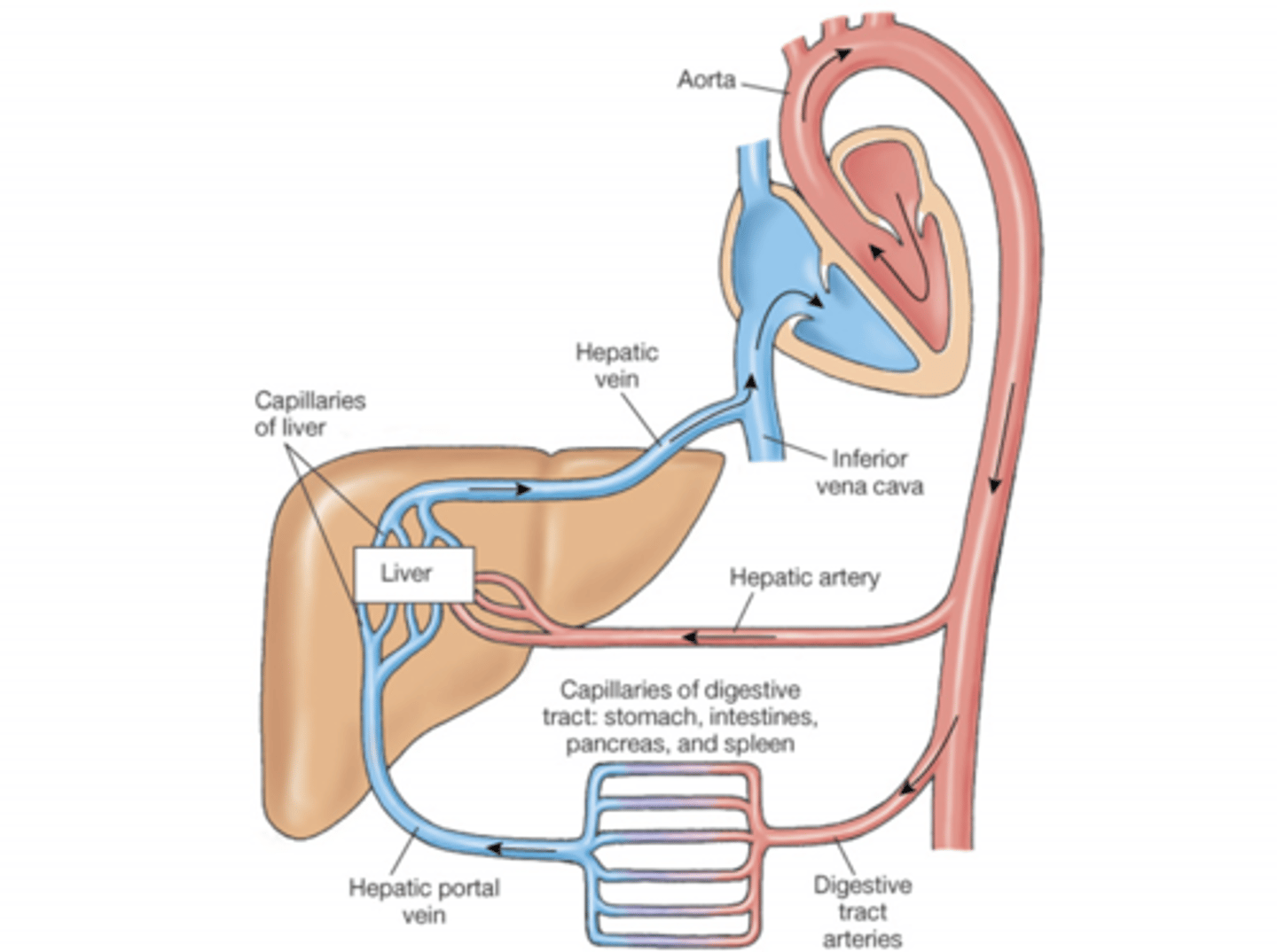
What is the role of the Hepatic portal system?
Direct absorbed nutrients (carbs, protein)
Blood from the left side of the heart is split between which 2 arteries?
Hepatic arteries
Digestive tract arteries
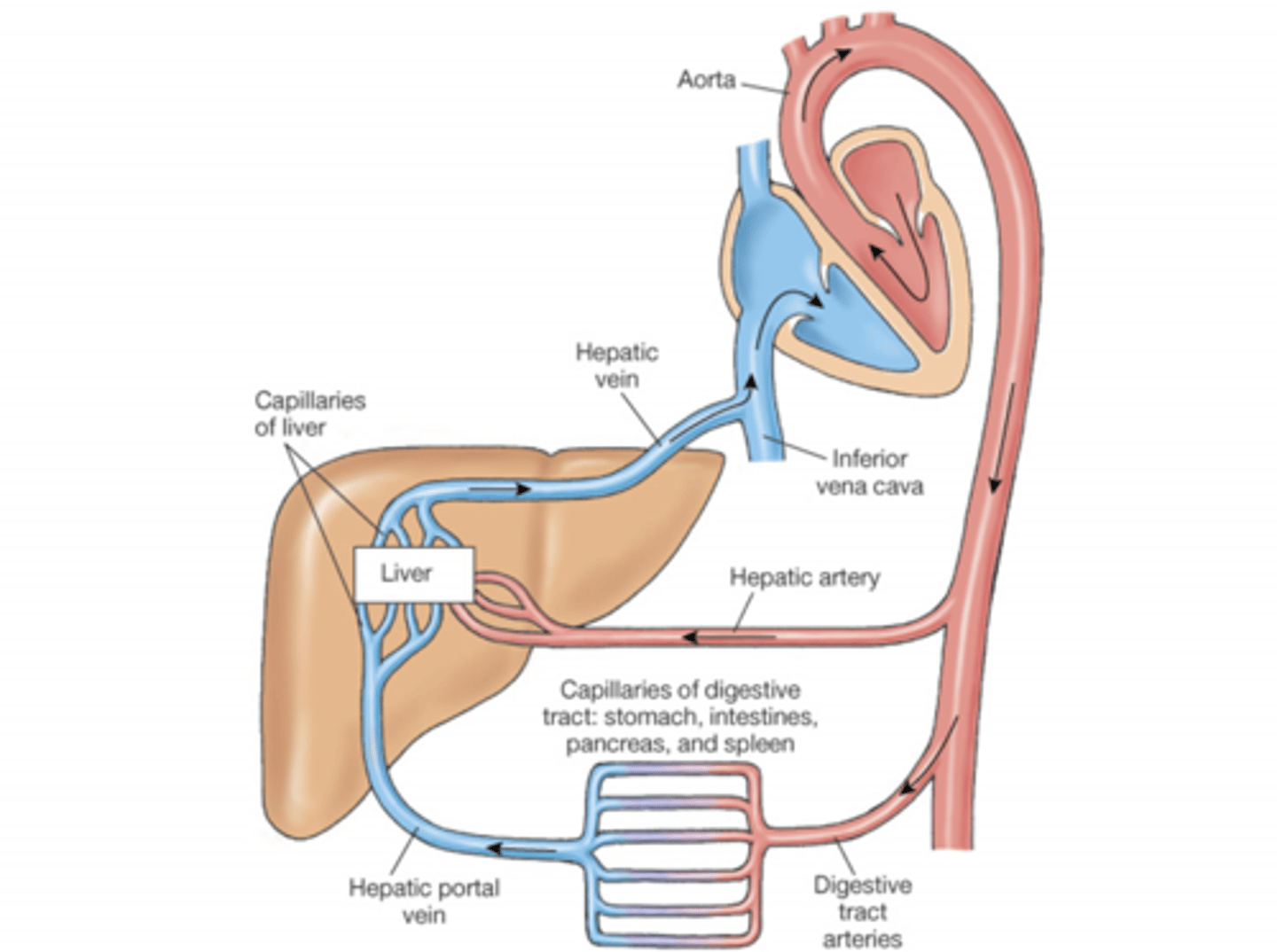
The blood from the liver all goes to the _____________
Right side of the heart.
How much water does the large intestine reabsorb, and how much water does the small intestine reabsorb?
SI - 7.5 L/day
LI - 1.5 L/day
The large intestine stores __________ and the ___________ within the LI make sure that they don't leave at an inappropriate time
feces
sphincter
What is the defecation reflex?
removes undigested feces from the body
defecation reflex is triggered by
It is triggered by the movement of fecal material into the normally empty rectum
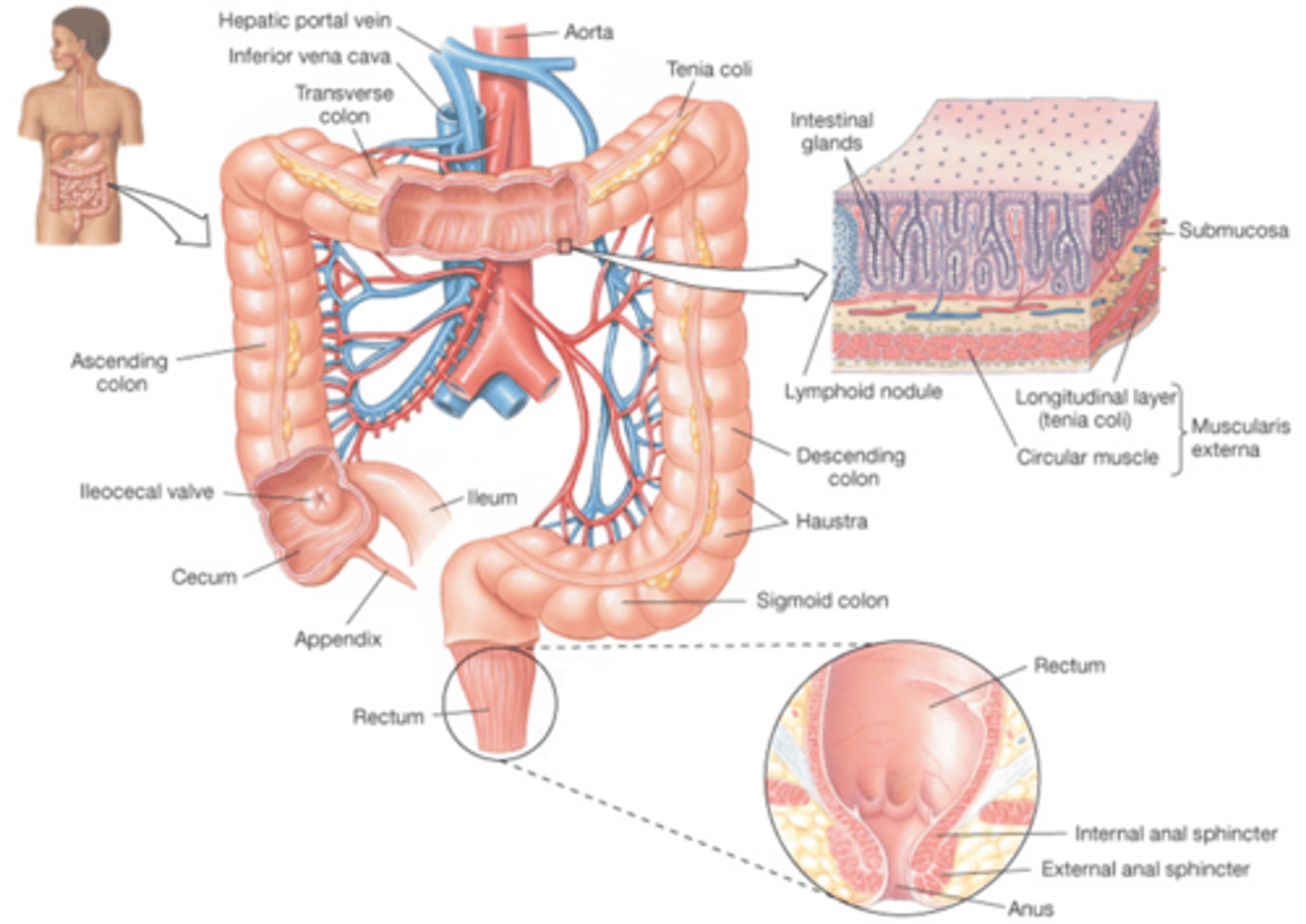
Describe the overall process of the defecation reflex?
internal anal sphincter (involuntary) relaxes and peristalsis contractions in the rectum push material toward her anus.
The external anal sphincter (voluntary) - is consciously relaxed if the situation is appropriate
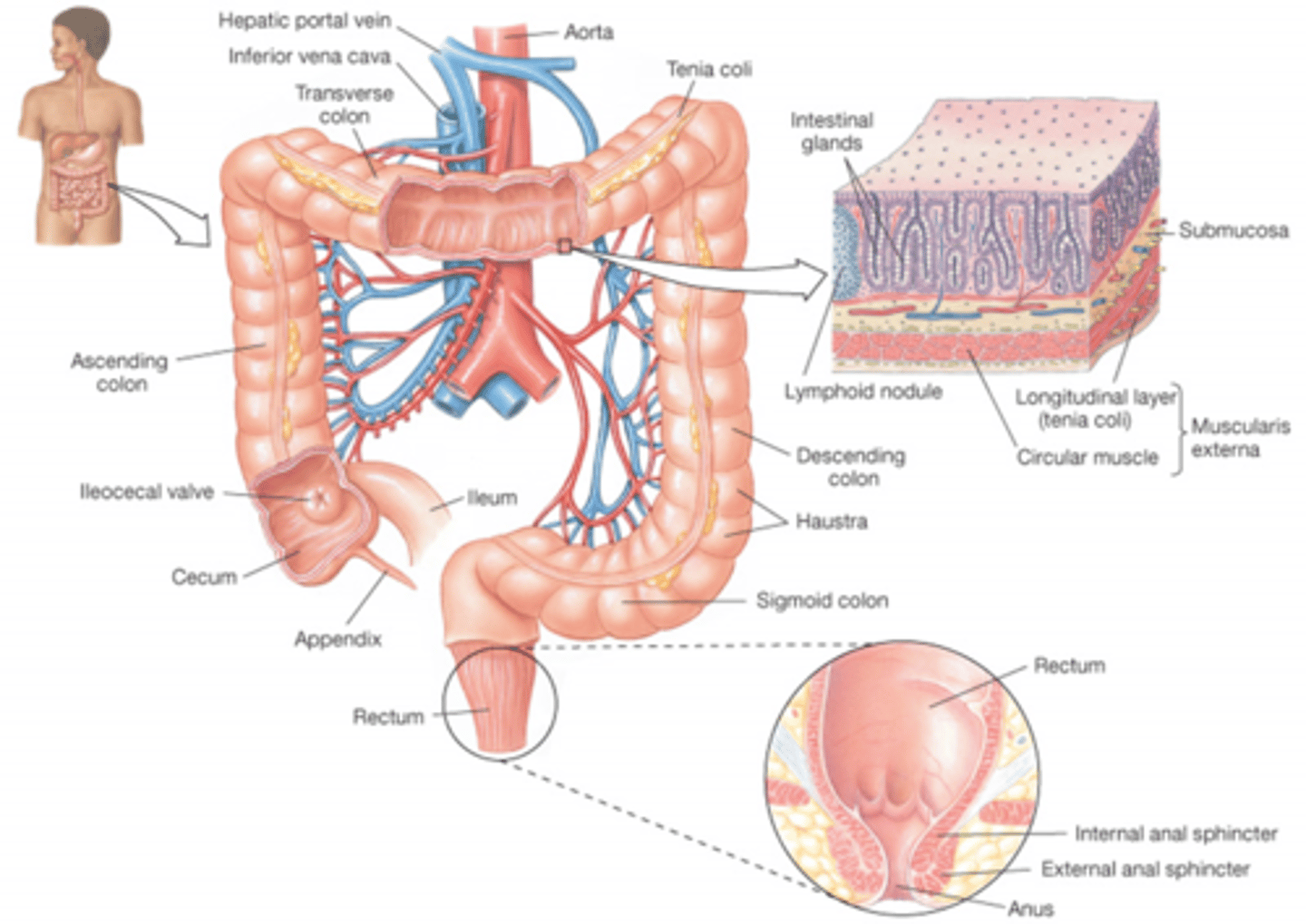
Describe H2O absorption in the Large instestine? (regulation)
Water is regulated in the collecting ducts by managing the number of aquaporins via vasopressin
Describe digestive health related to protection?
M cells
Peyer's patches
Lymphocytes (GALT)
Describe digestive health related problems?
Irritable bowl syndrome
Diarrhea
Vomiting
Ulcers
Heartburn
What is the state of having diarrhea?
The intestinal secretion of fluid is not balance by absorption. So you get watery stools
What are the two ways in which you get diarrhea?
The bacterial toxins cause either
1. disruption to water absorption
2. osmotically active solutes that "hold" water in the lumen
How do you treat diarrhea?
Salt solution via IV so that it draws the water into the cells and out of the lumen
What can prolonged vomiting lead to?
alkalosis - which activates the principle P cells
How are ulcers caused?
H. Pylori
What is the affect of an ulcer?
removing of mucus from protecting the stomach
Describe heartburn as it related to digestive health?
Acid Reflux disease
(the lower esophageal sphincter is too weak to keep acid in the stomach)