Defects, Deterioration and Shrinkage of Wood
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
codes and specs 3434
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Defects
Pattern in the surface
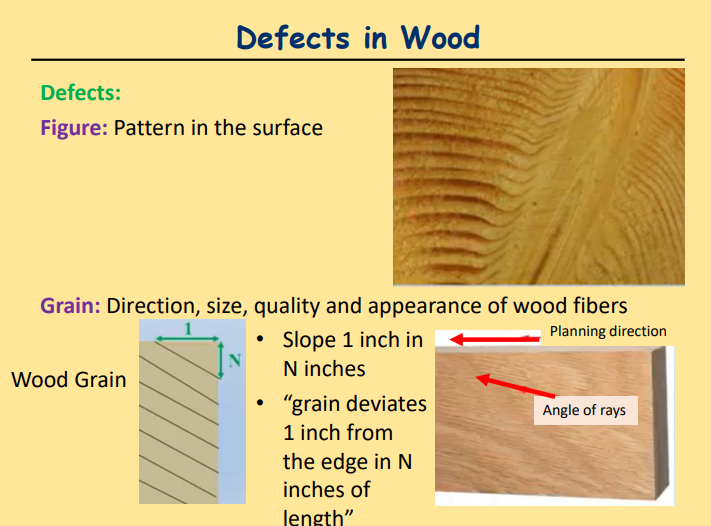
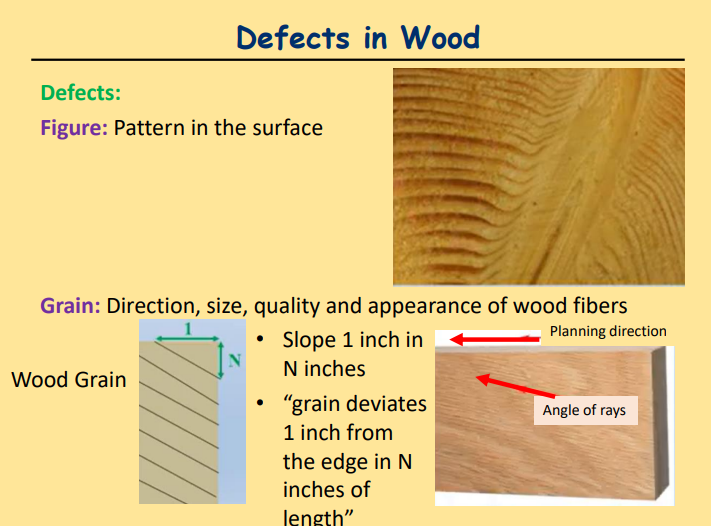
Grain
Direction, size, quality and appearance of wood fibers
Defects in Wood 1
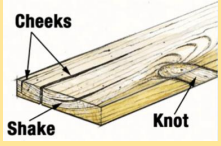
Knot: Branch or limb embedded in a tree
and exposed in sawing
• Effects tensile strength and flexural
strength

Shake
Separation of wood between and parallel to the grain
Check
Lengthwise separation of wood
Wane
Lack of wood in the corners
Dry Shrinkage
Uneven drying creates cracks
Warping
bow, warping, cup, crook, twist, kink

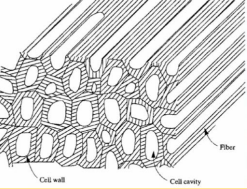
Shrinkage
• Wood absorbs moisture when it contacts water: Volume
increases until it reaches FSP
• FSP: Moisture content when the cell walls are saturated and
the cell cavities are empty
• As water is lost in the cell cavity: No dimensional change
• As water is lost in the cell wall: Dimensions of wood will
decrease causing shrinkage
• Moisture content below FSP
• On average there is a 12% decrease in volume when going
from FSP to a moisture content of 0%
Shrinkage
• Wood absorbs moisture when it
contacts water: Volume increases
until it reaches FSP
• FSP: Moisture content when
the cell walls are saturated and
the cell cavities are empty
Factors Influencing Shrinkage
• Species
• Cell wall thickness
• Cell arrangement
• Sapwood/Heartwood
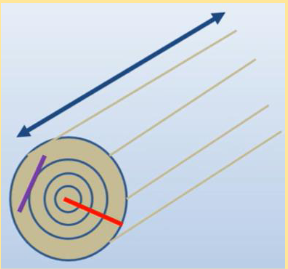
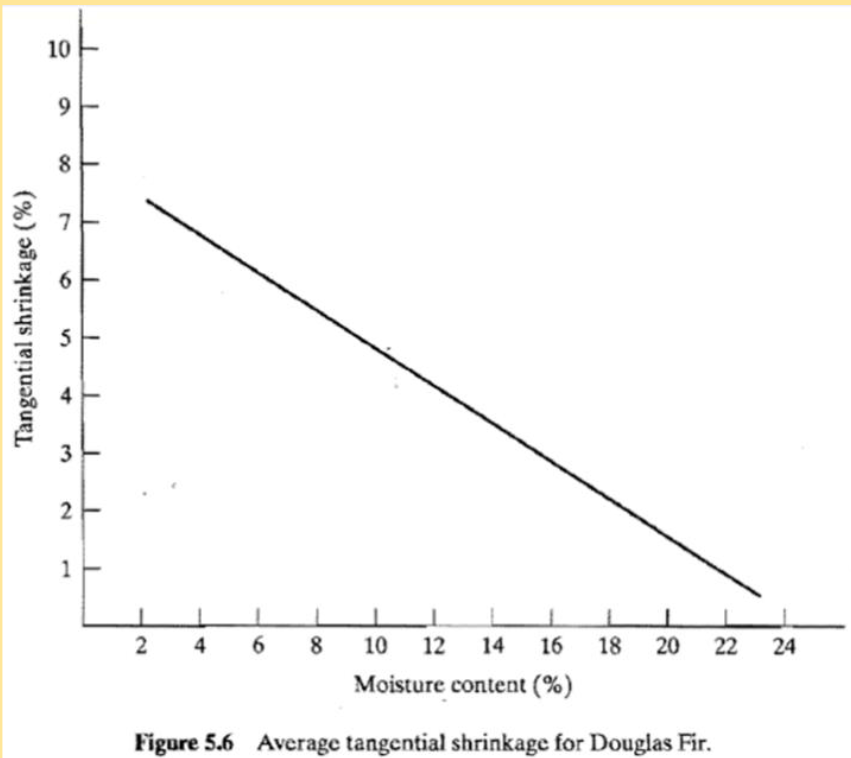
Tangential Shrinkage
Plane tangent to the
growth rings
• Highest amount of shrinkage occurs on
this plane
• Approximately 1% volume decrease per
4% decrease in MC below the FSP
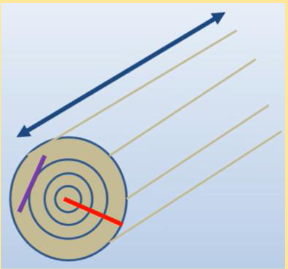
Radial Shrinkage
Occurs on the plane that
goes with the radius of the log
• = ½ x Tangential Shrinkage
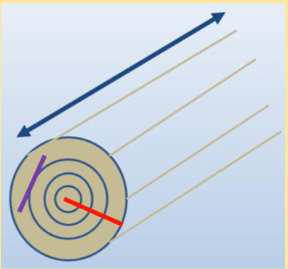
Longitudinal Shrinkage
Occurs along the
longitudinal axis of the log
• Negligible
Shrinkage of Wood
• When differential shrinkage occurs between building parts
and aren’t accounted for properly:
• Affects plumbing, electrical, HVAC, finished surfaces
• Causes cracks in the wall
Seasoning:
The controlled drying of lumber
Methods:
• Air drying
• Kiln drying
Why?
• Increase strength
• Lower shrinkage in service
• Improve decay resistance
• Reduce the weight
• Needed to apply
preservative treatment


Treatment and Durability
Influential factors:
• Species
• Environment
• Seasoning
• Part of tree
• Sapwood: More susceptible to decay
• Heartwood: More durable
Use chemical treatments, coatings, seasoning, water proofing
Why? Wood decays if unprotected
Why? Insect/fungal attack
Ease of chemical treatment depends on:
• Density
• Wood structure
• Moisture content
• Dimensions
• Cell wall composition

Decay:
Fungal attack
• Grows in cells
destroying lignin and
feeds on cell material
• Brittle failure
• Weakens wood
To grow, fungi need:
• Proper temperature
• MC > 19%
• Oxygen
• Food
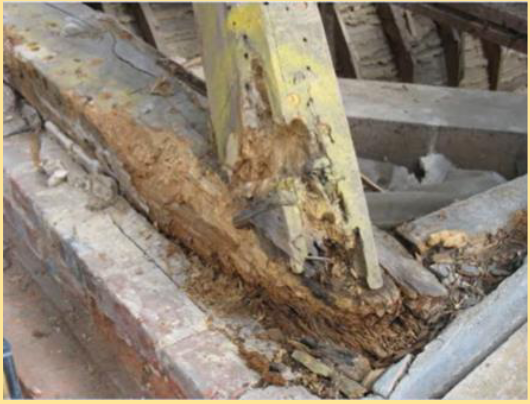

Brown Rot
Fungus attacks cellulose
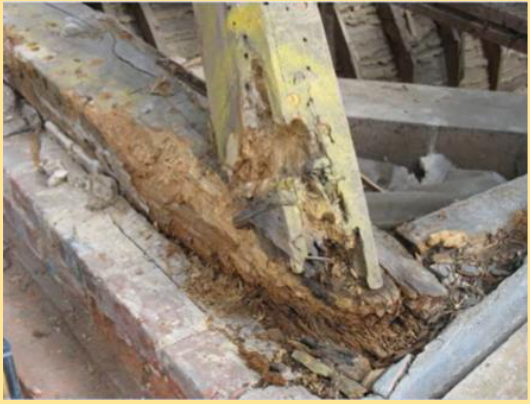

White Rot
Rot from cellulose and
lignin
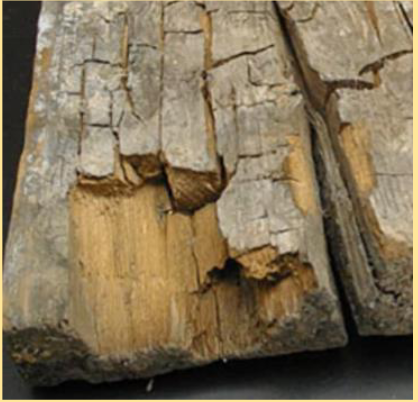

Dry Rot
Attack part of wood which
gives it strength and stiffness
(spreads fast)

Wet Rot
Rot of wet lumber

Destruction
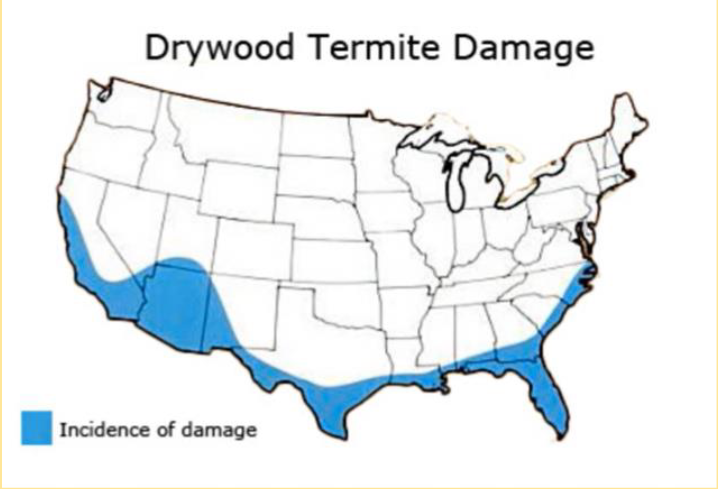
• Insects (Termites)
• Termites are the most common wood
eating insect
• Live in cellulose
• Dry wood (mostly in the south)
Use chemicals or
concrete foundation to
help reduce termites