4. mutations + polymorphisms
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Locus (loci)
DNA segment that occupies a specific position on a chromosome
Alleles
alternative versions of DNA sequence at a specific locus
2 alleles for each locus: maternal & paternal
wild-type/common allele vs variants/mutants
Most genes have one prevailing allele = wild-type/common allele
All other versions = variants/mutants
polymorphic
A locus with >2 common alleles
“private” alleles
Rare variants confined to families
Zygosity
degree of allele similarity at one locus in an organism
Homozygous
2 copies of same allele at one locus
Heterozygous
2 different alleles at same locus
Genotype
genetic information at a locus
Phenotype
appearance of an organism based on genotype
source of genetic diversity
Mutations
how much sequence identity among individuals
Approx. 99.9% sequence identity among individuals
0.1% = genetically determined variability
reference sequence
NO standard genomic sequence!
The most common sequence in a population
Mutation Classifications
Classification by:
size (chromosome, subchromosomal + DNA mutations)
function (from non-functional to lethal)
heritability (germline vs somatic)
Chromosome mutations
intact structure, change in chromosome number
Euploidy + Aneuploidy
Euploidy
multiplication of a chromosome set (tetraploidy)
Aneuploidy
additional chromosomes (trisomy, monosomy)
Subchromosomal mutations
changes in portions of the chromosomes
copy number variations, structural rearrangements
DNA mutations
substitutions, deletions, insertions up to 100bp
Mutation frequency
number of mutations/locus/cell division
what is mutation frequency dependent on?
Frequency of spontaneous and induced nucleotide changes
Probability of repair
Probability of detection
mutation rates very by:
species + genes
areas of DNA mutate differently (hot spots)
Rate of disease-causing mutations
incidence of new cases of genetic disease NOT present in parents and caused by a single mutation
Chromosome mutations
Result of chromosome mis-segregation during meiosis
Generally severe, resulting in spontaneously aborted fetuses
Regional mutations
Result of homologous recombination between fragments with high homology at different sites or following repair of double-strand breaks
Gene mutations
Replication errors <1 mutation/genome/cell division
DNA repair errors
Frequently from spontaneous mutations that evade the repair machinery
nucleotide substitutions
synonymous
missense
nonsense
mutation affecting mRNA processing
dynamic mutations
Synonymous mutations
nucleotide change that specifies the same amino acid (AA)
Missense mutations
single nucleotide change that specifies a new AA
Transitions + Transversions
transition
purine → purine
pyrimidine → pyrimidine
transversion
purine → pyrimidine
pyrimidine → purine
Nonsense mutation
point mutations resulting in replacement of coding codon by a “stop” codon
Mutation affecting mRNA processing
mutations that abolish or create alternative intron-exon junctions
causes alterations of the splicing pattern
Dynamic mutations
amplifications of simple trinucleotide repeats in the coding region or untranslated regions
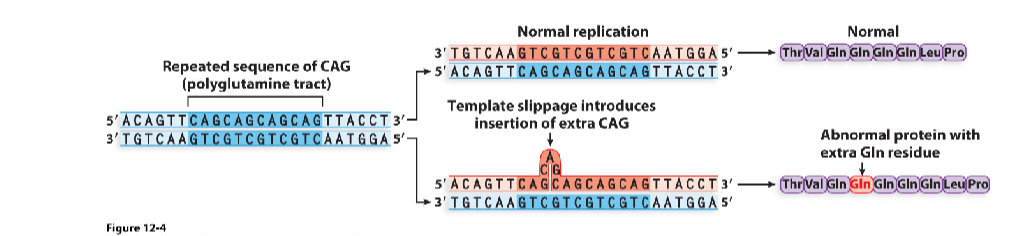
deletion, insertions, rearrangement mutations (frameshift)
rearrangement of small nr. of nucleotides (not a multiple of 3) resulting in altered reading frame → functionally altered protein
consequences of mutations
gain/ lose function, lethality, domitive negative
gain of function
Overproduction/ inappropriate production of protein
loss of function
Reduced production of protein
The product of the normal allele is generally sufficient for function
haploinsufficiency
50% of protein is insufficient for function
dominant negative
a mutated protein interferes with the function of the normal protein, so even though a healthy allele is present, the overall function is disrupted.
heredity of mutations: germline mutations
Mutations inherited from parents or de novo (spontaneous, not from parent) mutations that are transmitted to offspring
De novo mutations are very rare
heredity of mutations: somatic mutations
Are not transmitted to the next generations
Genomic heterogeneity specific to highly proliferative tissues (eg., epithelial,
hematopoietic cells)
Typically undetected
what mutation type is frequent in cancers?
Somatic mutations
Genetic polymorphisms
Mutations with a frequency exceeding 1% of all alleles in a population
(regardless of the type, size, effect, or location of mutation)
1. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
change of 1bp
Average 1 for every 1000bp (approx. 5-10 million SNPs/genome)
Generally, do not produce phenotypic differences
where are SNP hotspots? whats the rate?
25x higher rate at adjacent CG (CpG)
how many SNPs in protein-coding genes?
approx 100,000
nonsynonymous → protein variants
2. Insertion-deletion polymorphisms (indels)
up to 1000bp
Simple or Microsatellites
Simple Indels
presence or absence of a short fragment → 2 alleles
Microsatellites (short tandem repeat polymorphisms STR)
variable number of repeated short segments (2, 3, or 4 nt) → multiple alleles
Infer familial relationships by DNA fingerprinting (study of alleles at 13 loci)
3. Copy number variants (CNVs)
up to hundreds of kb
Can include dozens of genes → altered gene dosage
4. Inversion polymorphisms
few bp – mb
Sequence homology at edges (homologous recombination)
Balanced – no loss/gain of DNA
detection of mutations process
discovery
validation
screening
Discovery
–
Initial identification
Whole genome/exome sequencing + comparison to reference sequence
Validation
Replication assay to exclude sequencing errors
Larger population to get statistical occurrence
Screening
Sequencing/analysis of thousands of SNPs from same individual and multiple individuals
High-density DNA arrays (SNP arrays)
Genetic analysis
Establish a catalogue of all known human genes and variants and their location
On-going list of tens of millions of variants in different populations
Methods for mapping human disease variants
Linkage analysis (family-based)
Association analysis (population-based)
Genome sequencing
genome-wide association studies
Molecular technique that analyses simultaneously hundreds of thousands of variations in genomic DNA to determine if a genetic locus is associated with a certain phenotype
Candidate gene associations have greater power, but rely on previous knowledge
GWAS find unbiased susceptibility variants for complex traits, without a prior hypothesis of gene function
Study design
Standard case-control (matched or unmatched)
SNP imputation
Genotyped SNPs allow for determining possible variants on neighboring SNPs based on reference genomes (HapMap)
Linkage disequilibrium
non-random association of alleles at linked loci
Measure of tendency of some alleles to be inherited together as haplotypes
Haplotypes
sets of closely linked SNPs present on the same chromosome, which tend to be inherited together
Manhattan plot
scatter plot of association between statistical significance as p-value on the y-axis against chromosomes on the x-axis
Association of hundreds of thousands of markers → traditional statistical significance thresholds (eg. p<0.05) not appropriate; association
considered statistically significant if p=5x10-8
If a SNP is significantly associated with the phenotype
Causal relationship between SNP and disease
Marker in linkage disequilibrium with causal locus
False positive
Clinically functional variants: Risk variants
increase risk of disease
Clinically functional variants: Protective variants
lower risk of disease
Clinically functional variants: Risk of disease
diagnosis of disease
23andme
testing of genome-wide polymorphisms
Problems : privacy, lack of regulation
Traits: cilantro aversion, hairline, photic sneeze reflex, caffeine metabolism, hair curliness, bitter taste, newborn hair amount, earlobe type, muscle composition, eye color, dimples, sweet taste preference
Carrier status: cystic fibrosis, BRCA1, sickle cell anemia, glycogen storage disease, maple syrup urine disease, Sjorgen’s syndrome
Ancestry: ancestral composition, maternal/paternal lineage
Drug response
Clinical utility/ limitations
Gene-disease associations not relevant for all patients
Environmental role unknown and hard to predict and estimate
Relevance only for prognosis (confounding factors can change risk)
Combined risk from multiple SNPs is hard to calculate