IPS1 - A1 - Physical Pharmacy Principles
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Physical Pharmacy
___-
is the application of physical, chemical, and biological principles in the formulation of a drug product
To understand and develop dosage forms and drug delivery systems
Drug
___- is an agent or substance intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment and prevention of disease
Drug
____- is the pure form of the drug
Dosage form
____ - is a form suited for the administration of the patient
Dosage form
____ - is the form suited for administration of drugs
Drug product
____ - is a finished dosage form that contains an active drug ingredient (palatable, convenient, safe, and effective)
Drug product
drug + dosage form = ____ ?
Physical Pharmacy
____- is the study of physical and chemical properties of drugs
Physical Pharmacy
____ - deals with the physicochemical principles underlying the development of a successful dosage form
Theoretical approach
Quantitative approach
Physical Pharmacy have two approaches such as ___[2]
Pharmaceutics
____- is a branch of pharmaceutical sciences that is all about the FORMULATION
Pharmaceutics
____-is a branch of pharmaceutical sciences that deals with Investigations of physical and chemical properties of drug molecules
Pharmaceutics
____-is a branch of pharmaceutical sciences that deals with Design, fabrication and evaluation of drug delivery systems
Pharmaceutics
___-is a branch of pharmaceutical sciences that deals with Monitoring how drug products are absorbed, distributed, metabolized and excreted in the body
Pharmacokinetic
ADME principle is under ___ [Pharmacodynamic/Pharmacokinetic]
Pharmacodynamic
Mechanism of drug action is under ______ [Pharmacodynamic/Pharmacokinetic]
Pharmacology
PK + PD = _____ ?
Pharmaceutics
____- is a branch of pharmaceutical sciences that deals with Mechanism of drug action
Intramolecular Forces
Intermolecular Forces
Types of General Forces [2]
Intramolecular Forces
[Types of General Forces]
____ - within molecules
Ionic Bonds (transfer of e-)
Covalent Bonds (sharing of e-)
Metallic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Type of Bonds in Intramolecular Forces [4]
Pure Covalent
Polar Covalent
Ionic
[Bond Type] — Electronegativity (EN) Difference
EN Difference : < 0.4 = _____ ?
EN Difference : 0.4 – 1.7 (2.0) = ____ ?
EN Difference: > 1.7 (2.0) = ____ ?
Intermolecular Forces
[Types of General Forces]
____- between molecules
Van der Waals Forces
Ion–Dipole
Ion–Induced Dipole Interaction
Hydrogen Bonds
Types of Intermolecular Forces [4]
Higher EN difference = higher polarity
Dipole moment
Requirements for Polarity [2]
High Polarity
Higher EN difference = ___[high/low] Polarity
Polar
If a compounds have a Dipole moment it is considered as ____[polar/nonpolar]
high polarity
High EN difference =___ [high/low] polarity
UNDERSTAND 🙃
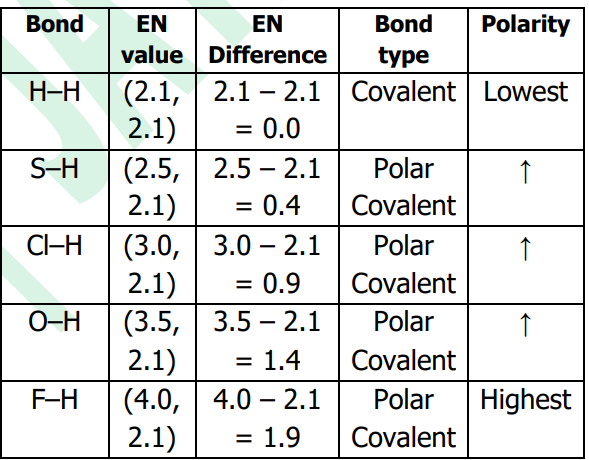
Order of increasing polarity:
H–H < S–H < Cl–H < O–H < F–H
Non-polar
[Polar/Non-polar]
____- Perfect symmetry
zero dipole moment
____- means that a molecule has no overall separation of positive and negative charges.
Polar
[Polar/Non-polar]
Asymmetric
have nonzero dipole moments
Non-polar
[Polar/Non-polar]
CO₂
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄)
Polar
[Polar/Non-polar]
HCl (Hydrogen chloride)
H₂O (Water)
NH₃ (Ammonia)
Polar
[Polar/Non-polar]
NH3 (Ammonia)
Polar
[Polar/Non-polar]
HCl (Hydrogen chloride)
Polar
[Polar/Non-polar]
H₂O (Water)
Attractive Forces
Repulsive Forces
Manifestations of Intermolecular Forces can be __[2]
Attractive Forces (“together”)
Repulsive Forces (“apart”)
Attractive Forces = ___ [together/apart]
Repulsive Forces = ___ [together/apart]
Cohesive forces
Adhesive forces
Types of Attractive Forces [2]
Cohesive forces
[Types of Attractive Forces]
_____-
like molecules
between same molecule
Adhesive forces
[Types of Attractive Forces]
____-
unlike molecules
between different molecule
3−4×10−8cm
At ______ cm distance, the attractive and repulsive forces are equal.
Van der Waals Forces
Ion-Dipole Forces
Ion-Induced Dipole
Hydrogen Bonds
Type of Intermolecular Forces [4]
Keesom Forces
Debye Forces
London Forces
Types of Van der Waals Forces [from strongest to weakest] [3]
polar
non polar
►Dipole = ____[polar/non polar]
►Induced dipole = ___ [polar/non polar]
Keesom Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
____-
have Orientation / Alignment effect
Dipole–Dipole Forces
Keesom Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
Polar molecule + Polar molecule
Example: water, alcohols, acetone
Keesom Forces
Water ,alcohol , acetone is an example of what Van der Waals Forces __ ?
Keesom Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
___-
Strength: 1–7 kcal/mole
Debye Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
have Induction effect
Dipole–Induced Dipole Forces
Debye Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
Polar molecule + Nonpolar molecule
Example: ether, ethyl acetate
Debye Forces
Ether, ethyl acetate is an example of what Van der Waals Forces __ ?
Debye Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
___-
Strength: 1–3 kcal/mole
London Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
____-
Dispersion effect
Induced Dipole–Induced Dipole
London Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
____-
Originate from molecular vibrations
London Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
Nonpolar + Nonpolar
Example: hexane, Carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄)
London Forces
hexane, Carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄) is an example of what Van der Waals Forces __ ?
London Forces
[Types of Van der Waals Forces]
_____-
Strength: 0.5–1 kcal/mole
Ion–Dipole Forces
(+/–) charged ion + polar molecule
Example: quaternary ammonium + tertiary amine, solubility of salts in water
Ion-Dipole Forces
quaternary ammonium + tertiary amine
solubility of salts in water
The following are example of what Type of Intermolecular Forces ?
Ion–Induced Dipole
[Type of Intermolecular Forces]
(+/–) charged ion + nonpolar molecule
Example: iodine + KI (formation of tri-iodide complex)
Ion-Induced Dipole
Iodine + KI (formation of tri-iodide complex) is an example of what Type of Intermolecular Forces ?
Hydrogen Bonds
[Type of Intermolecular Forces]
____-
Interaction between molecules containing H and highly electronegative atom (F, S, O, N)
Hydrogen Bonds
[Type of Intermolecular Forces]
_____-
Special type of dipole–dipole interaction
Strength: 2–8 kcal/mole
a.)Hydrogen Bonds
Examples:
Water
Alcohol
Carboxylic acids
Esters
Aldehyde
NOT ethers and ketones
a.)Hydrogen Bonds
b.) Ion–Induced Dipole
c.) Ion–Dipole Forces
ether
ketones
All functional groups have H-bond except ___[2]
High dielectric constant (universal solvent)\
High boiling point
Abnormally low vapor pressure
Responsible for unusual properties of water:[3]
High dielectric constant
Our universal solvent have ___[high/low] dielectric constant
In proteins: α-helices, β-sheets
In nucleic acids: DNA (A–T and G–C bonds)
Hydrogen Bonds can also exist intramolecularly in our ___[2]
Guanine (G) -Cytosine (C)
In our DNA what nitrogenous bases have 2 hydrogen bond ?
Adenine(A) - Thymine(T)
In our DNA what nitrogenous what nitrogenous bases have 3 hydrogen bond ?
strength of attractive forces
The _____ of the attractive forces governs the physical and chemical properties of substances.
True
[T/F] The strength of the attractive forces governs the physical and chemical properties of substances
strong interaction
Stronger IMFA = ____ [strong/weak] interaction
high BP, MP, viscosity, surface tension.
Stronger IMFA = ____ [high/low] BP, MP, viscosity, surface tension.
Trend: [strongest to weakest]
Hydrogen bonding
Dipole-dipole
London Dispersion
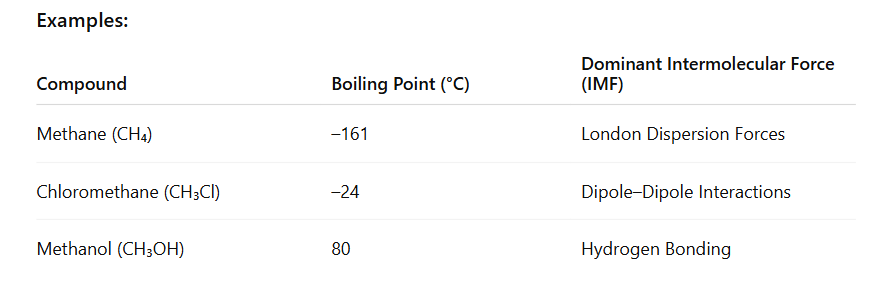
Increasing Boiling Point: [low to high]
Methane (CH₄) → weakest IMFA
Chloromethane (CH₃Cl) → Moderate IMFA
Methanol (CH₃OH) → Strongest IMFA
EXAMPLE
Stronger IMFA = stronger interaction = higher BP, MP, viscosity, surface tension.
Additive
Constitutive
Colligative
Physical Properties of Drug Molecule [3]
Additive
[Physical Properties of Drug Molecule]
___-
Derived from the sum of individual properties of atoms or functional groups present in molecules
depends on the amount
EXAMPLE: mass, molecular weight, volume
a.) Additive
mass, molecular weight, volume is an example of what Physical Properties of Drug Molecule ?
a.) Additive
b.) Constitutive
Constitutive
[Physical Properties of Drug Molecule]
____-
Dependent on the structural arrangement of the atoms within the molecule
EXAMPLE: optical activity, surface tension, viscosity and refraction of water
b.) Constitutive
optical activity, surface tension, viscosity and refraction of water is an example of what Physical Properties of Drug Molecule ?
a.) Additive
b.) Constitutive
c.) Colligative
vapor pressure lowering, BP elevation, FP depression, osmotic pressure is an example of what Physical Properties of Drug Molecule ?
a.) Additive
b.) Constitutive
c.) Colligative
Colligative
[Physical Properties of Drug Molecule]
_____ -
Dependent upon the total number of nonvolatile solute particles present in the solution
depends on the structural arrangement
EXAMPLE: vapor pressure lowering, BP elevation, FP depression, osmotic pressure
Molar refraction
____ -
is an example of a combined additive–constitutive property
measure in moles / substance