AP Biology Chapter 1.1 Quiz (Water, pH, Acid/Bases)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorus Sulfur (CHNOPS)
What are the elements that make up 96% of life?
96%
How much of life does CHNOPS make up?
Trace elements, like zinc, cobalt, or copper.
What other types of elements are in our bodies to make up life?
Hydrogen and Carbon
What two main elements are used to look for life?
There are 2 hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. (It almost looks like a mickey mouse shape)
What is the structure of water?
Water
Without ______, life doesn't exist.
This means that the oxygen atom is more negative and the water is more positive. This is because oxygen is more electronegative than water, so it hogs the electrons more often, creating a more negative charge. This makes the water more positive, so even though they have a covalent bond and should just be sharing molecules, the oxygen takes the electrons more often, making the type of charge different. Oxygen is the negative region, hydrogen is the positive region.
How is water a polar molecule?
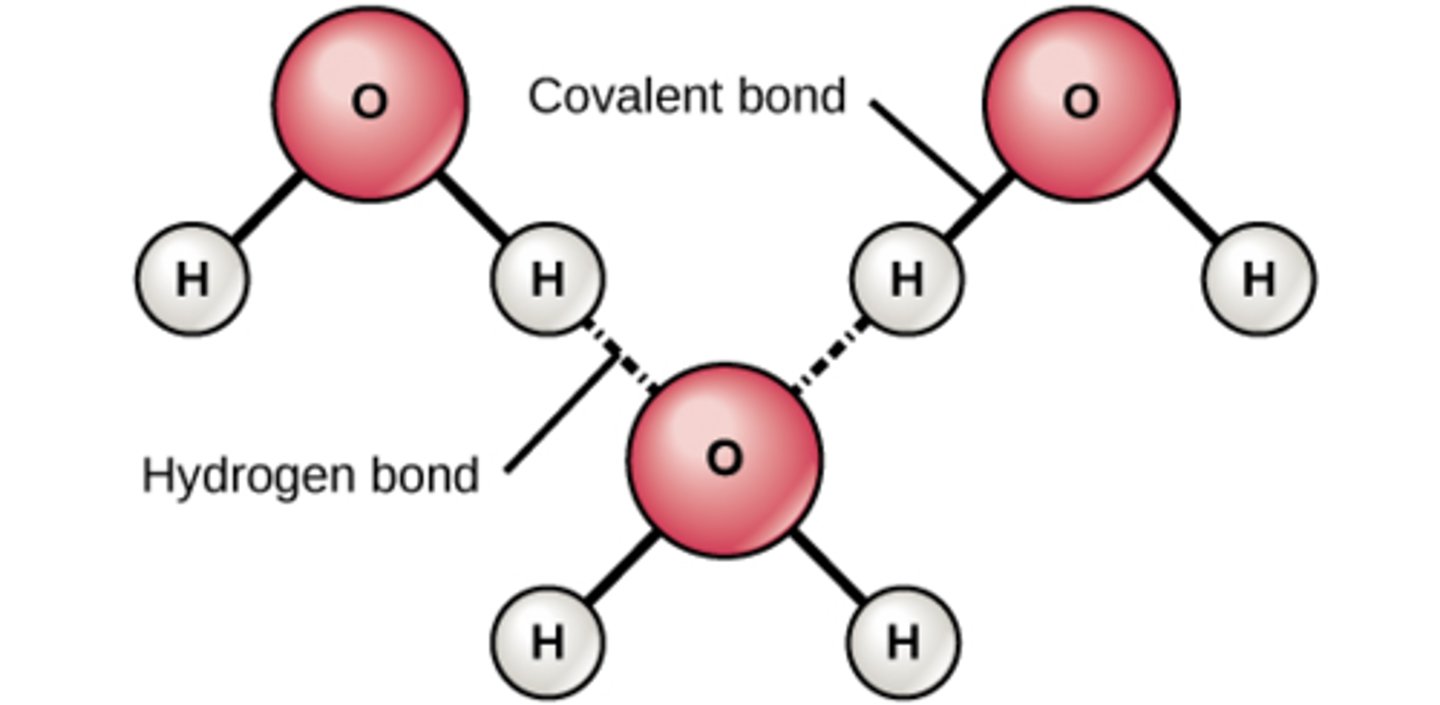
Polar molecule
Chemical species in which the distribution of electrons between the covalently bonded atoms is not even
Electronegativity
Measures the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons.
This is due to the electronegativity of oxygen creating semi-positive regions and semi-negative regions of the molecule. Because water is more positive, it can attach to other oxygen atoms from water creating weak hydrogen bonds. The same can be said for oxygen it can attach to the positive hydrogen with weak hydrogen bonds. If oxygen wasn't electronegative this couldn't happen.
Why are there hydrogen bonds between water molecules?
Cohesion is when water molecules can stick to one another because of their hydrogen bonds. The positive hydrogen attaches to the negative oxygen or the negative hydrogen attaches to the positive hydrogen. This allows them to stick to one another and is the basis for other properties.
Explain the property of cohesion.
Cohesion
Water molecules can stick to one another because of their hydrogen bonds. The positive hydrogen attaches to the negative oxygen or the negative hydrogen attaches to the positive hydrogen. This allows them to stick to one another and is the basis for other properties.
Water molecules can stick to other hydrophilic things because of the charges of hydrogen and oxygen. The positive part of hydrogen can stick to the negative of another charged molecule and vice versa.
Explain the property of adhesion.
Adhesion
Water molecules can stick to other hydrophilic things because of the charges of hydrogen and oxygen. The positive part of hydrogen can stick to the negative of another charged molecule and vice versa.
4.184J or 1C per gram/1 degree Celsius.
What is the high specific heat of water?
Water temperature changes slowly and holds temperature well. Hydrogen bonds require an input of energy to break therefore requiring more energy for water to change states of matter than non-polar or non-charged molecules
Explain the high specific heat of water.
High specific heat of water
Water temperature changes slowly and holds temperature well. Hydrogen bonds require an input of energy to break therefore requiring more energy for water to change states of matter than non-polar or non-charged molecules
Water is less dense in solid form - Solid water molecules form a lattice that is less dense than liquid water and therefore floats. The partial positive hydrogens must face the partial negative oxygens of adjacent water molecules for the most stable structure since molecules are not sliding past one another in a solid. This lattice form is less dense than the water's structure at a warm temperature.
Explain the density of water when it freezes.
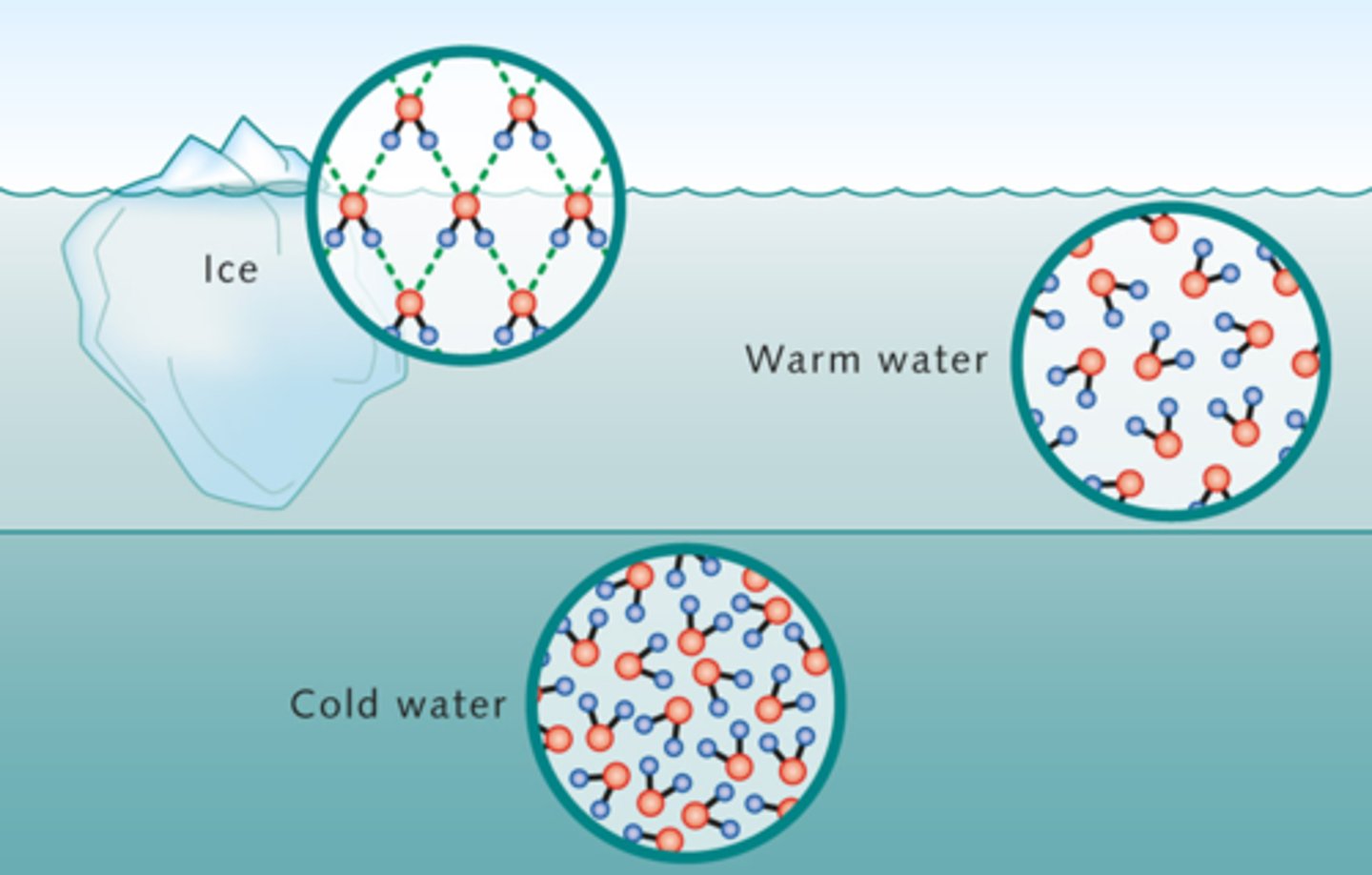
Expansion upon freezing
Water is less dense in solid form - Solid water molecules form a lattice that is less dense than liquid water and therefore floats. The partial positive hydrogens must face the partial negative oxygens of adjacent water molecules for the most stable structure since molecules are not sliding past one another in a solid. This lattice form is less dense than the water's structure at a warm temperature.
Water becomes most dense just before it freezes. The molecules stop moving and come in very close together, making it super dense. This causes it to sink to the bottom, warm water is less dense than this but because of the lattice structure of ice it floats to the top of the ocean.
If ice floats, why does it get colder as you go deeper and deeper into the ocean?
It allows all of the wildlife under the surface to continue to live in a mostly stable environment, if entire lakes froze from top to bottom that would kill all of the animals in it, since only the top freezes those animals can continue to thrive.
Why is expansion upon freezing so important for wild life?
4 degrees celsius/right before it freezes
When is water most dense?
Hydrophilic
Molecules that are polar/have a charge and; therefore, attracted to water

Hydrophobic
Molecules that are nonpolar/don't possess a charge and; therefore, are not attracted to water
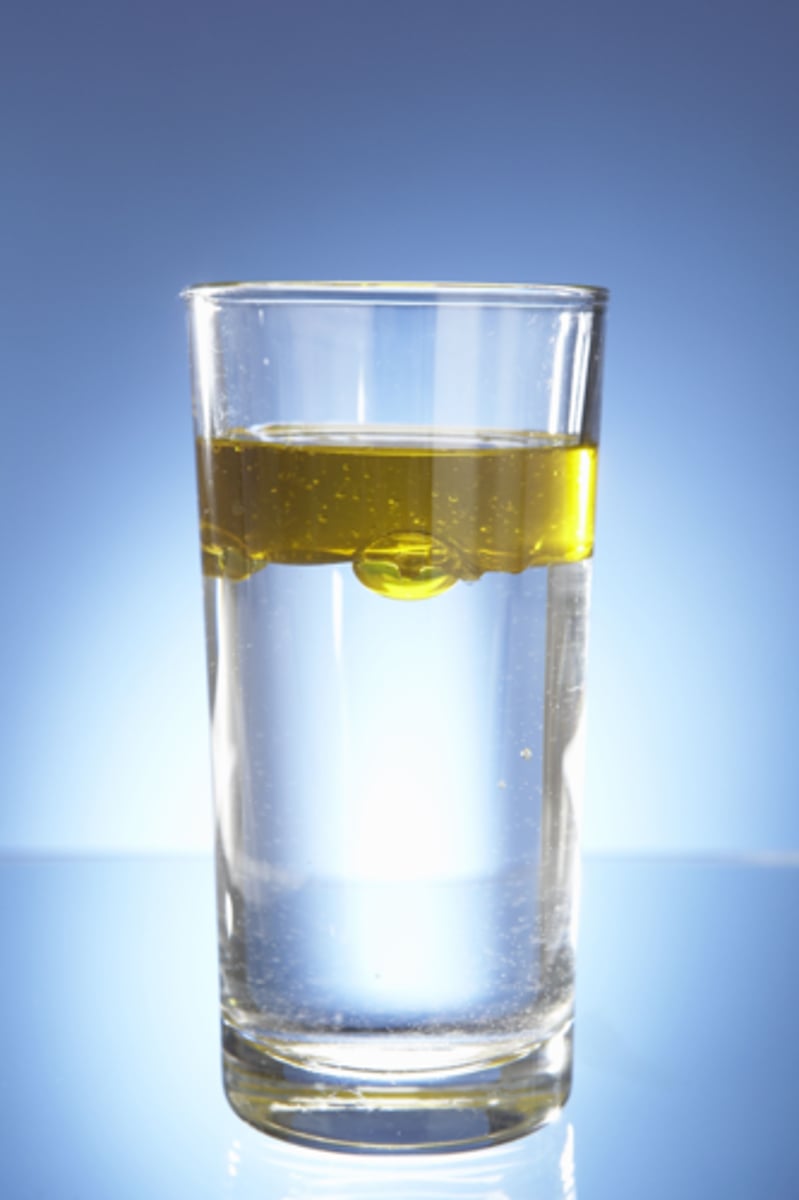

Water is able to dissolve anything that is hydrophilic, this is due to hydrogen bonds which is due to the electronegativity of oxygen. With the hydrogen bonds, water can grab onto any other molecule that is hydrophilic and break it down. However, it cannot do this with hydrophobic molecules.
Explain why water is the most versatile solvent.
Water is the most versatile solvent.
Water is able to dissolve anything that is hydrophilic, this is due to hydrogen bonds which is due to the electronegativity of oxygen. With the hydrogen bonds, water can grab onto any other molecule that is hydrophilic and break it down. However, it cannot do this with hydrophobic molecules.
Water can't dissolve absolutely everything, it can't dissolve hydrophobic molecules. This is why when we take a shower our skin doesn't melt off. Or when oil and water mix, the oil rises to the top rather than combining with the water.
Why isn't water a universal solvent?
1. Cohesive/Adhesive Behavior
2. Ability to moderate temperature (High specific heat)
3. Expansion upon freezing
4. Versatility as a solvent
What are the 4 essential properties of water?
Water has a high specific heat capacity because it's more difficult to break hydrogen bonds, it takes more energy to so water can hold heat for longer and it takes a lot to change the temperature of water. This makes it so fish who live in lakes or animals in the oceans experience a relatively constant temperature and don't have to adapt to constantly changing temperatures. If they did experience very low and very high temperatures randomly, they probably wouldn't be able to adapt and they would die.
Why is the high specific heat capacity of water also very good for animals in water and the environment?
Polarity, dissociate
________of the water molecule means that it can attract other molecules that are charged or polar. Water can also ______ ionic bonds.
Surface tension occurs due to cohesion. In a large body of water like a lake or pool, all of the H2O molecules stick together creating a large web of molecules. This web creates a give when you slap the water or cannonball into it, which can be painful.
Why does surface tension occur?
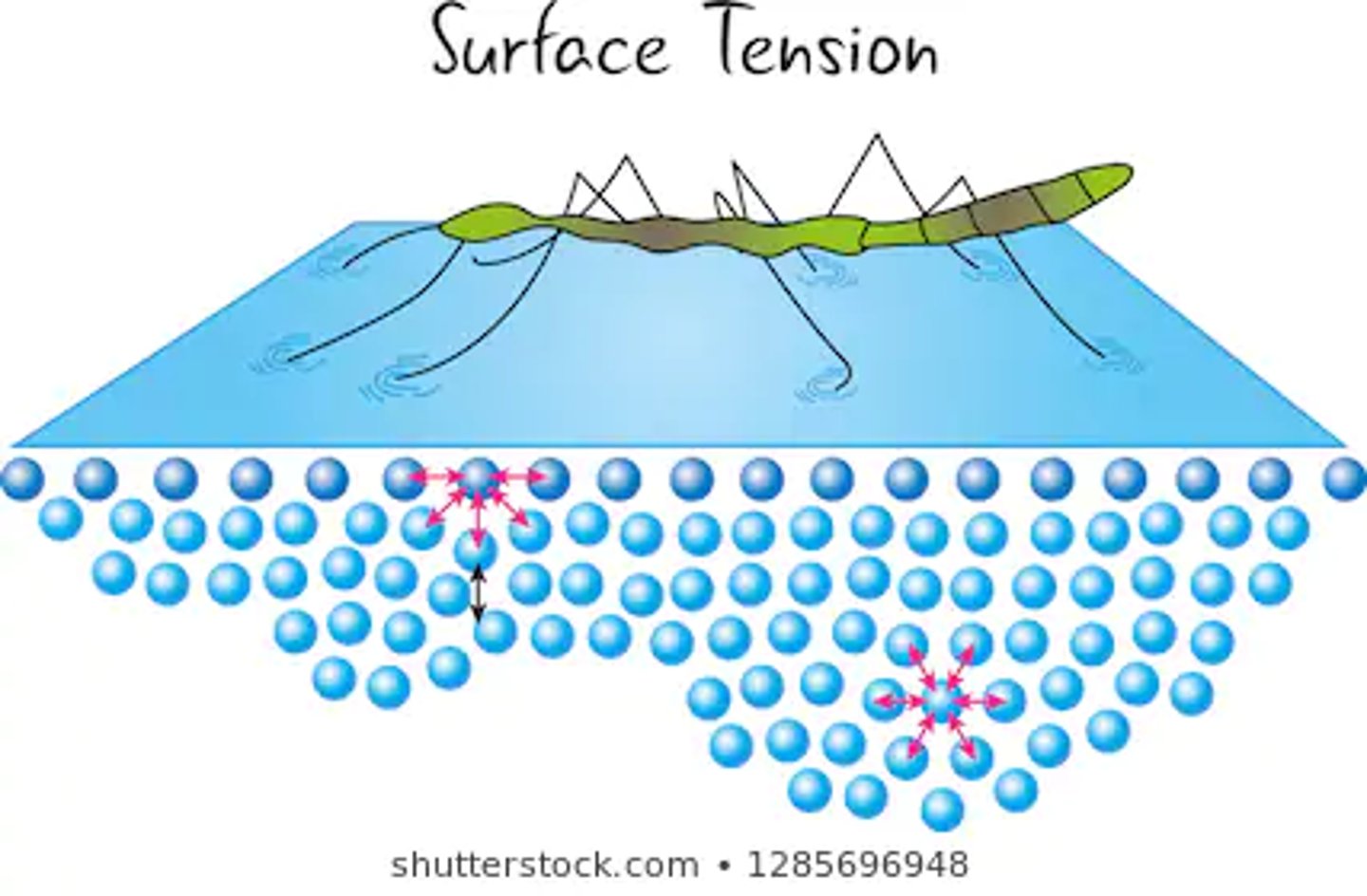
Some insects can walk on water due to surface tension.
What does surface tension allow some animals to do?
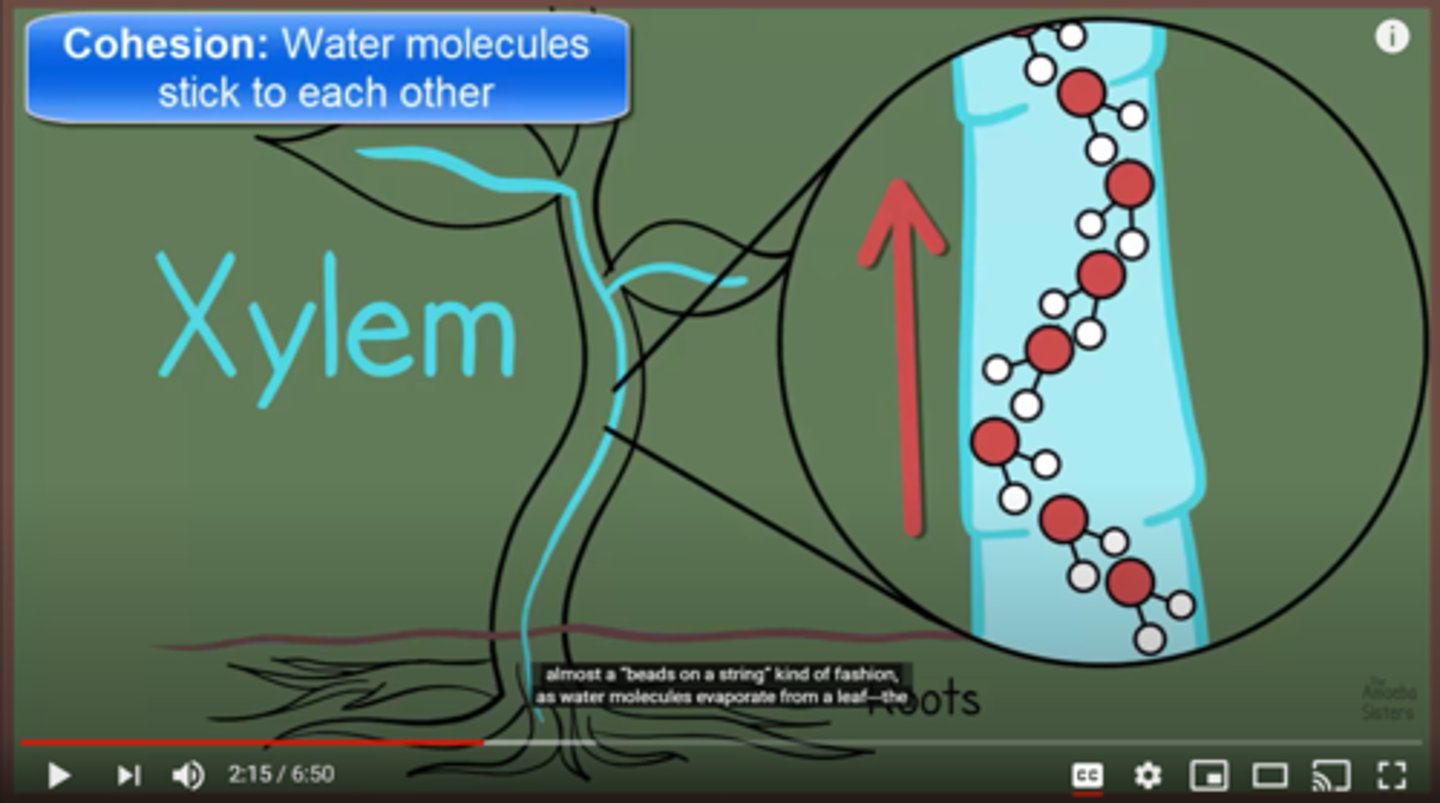
Capillary action is another feature of water. This is when water can move through narrow spaces without external forces like gravity. It can do this because of cohesion and adhesion. The water sticks to itself and then sticks to the material that it's in. This allows the water to move in a zig zag motion up a certain area, like the xylem of trees to get them water.
How does capillary action work?
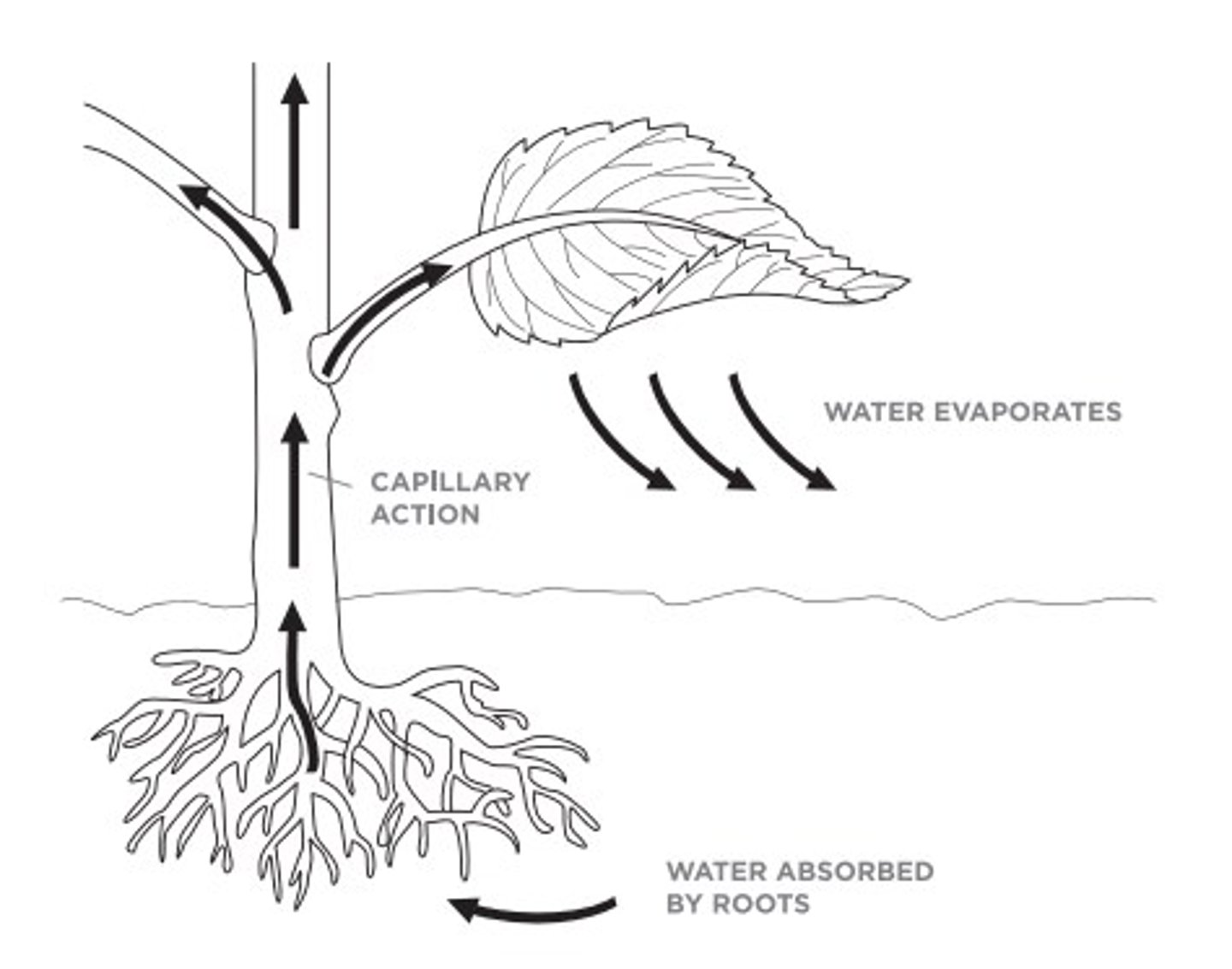
Capillary Action
This is when water can move through narrow spaces without external forces like gravity. It can do this because of cohesion and adhesion.
Water is absorbed through the roots of the tree. After that, the water goes up through the xylem, through cohesion and adhesion the molecules move up the tree in a zig zag form. After this , the water moves through the leaves and through evaporation disappears, the process then starts over again.
Explain transpiration and how this is an example of capillary action.
Most animals sweat when they get too hot. This is because when as water molecules get hotter on the skin they are more likely to make the phase change to gas, rather than cooler molecules. When they leave the skin, they evaporate and their heat is no longer on your skin.
How do some animals rely on evaporation to cool them?
Acid
A substance that causes an increase in the relative number of H+ ions in solution, it increases the proportion of H+ ions in a solution.
It means it can break apart molecules and either increase the proportion of OH- molecules or H+ molecules.
What does it mean when water dissociates something?
Base
Substance that causes an increase in the relative number of OH- ions in solution/ increases the proportion of OH- ions in a solution.
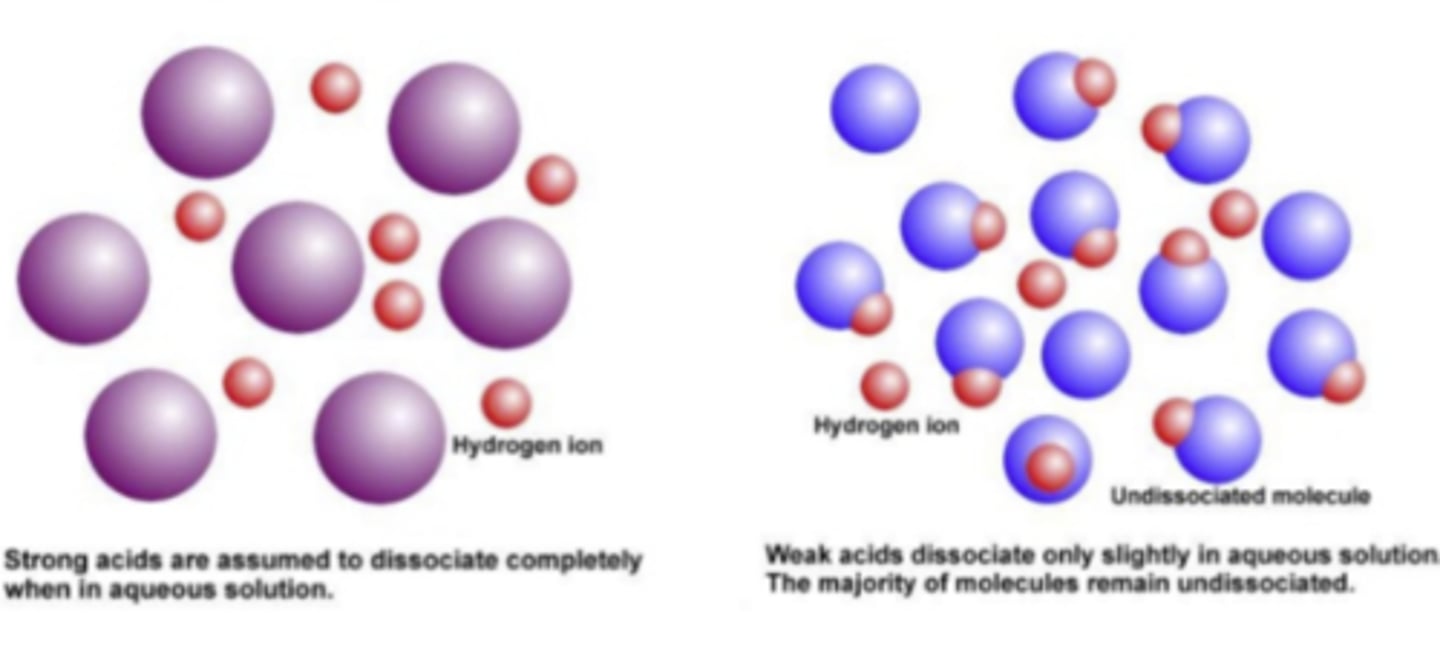
A strong acid or base means that the molecules completely disassociate. In a chemical equation, it would show an arrow going in one direction. Once they disassociate, they can never go back to the way they were again (or reassociate). (In the image, you see strong acids/bases are completely separated from the molecules, while weak ones are still pretty close together. )
What does a strong acid/base mean?
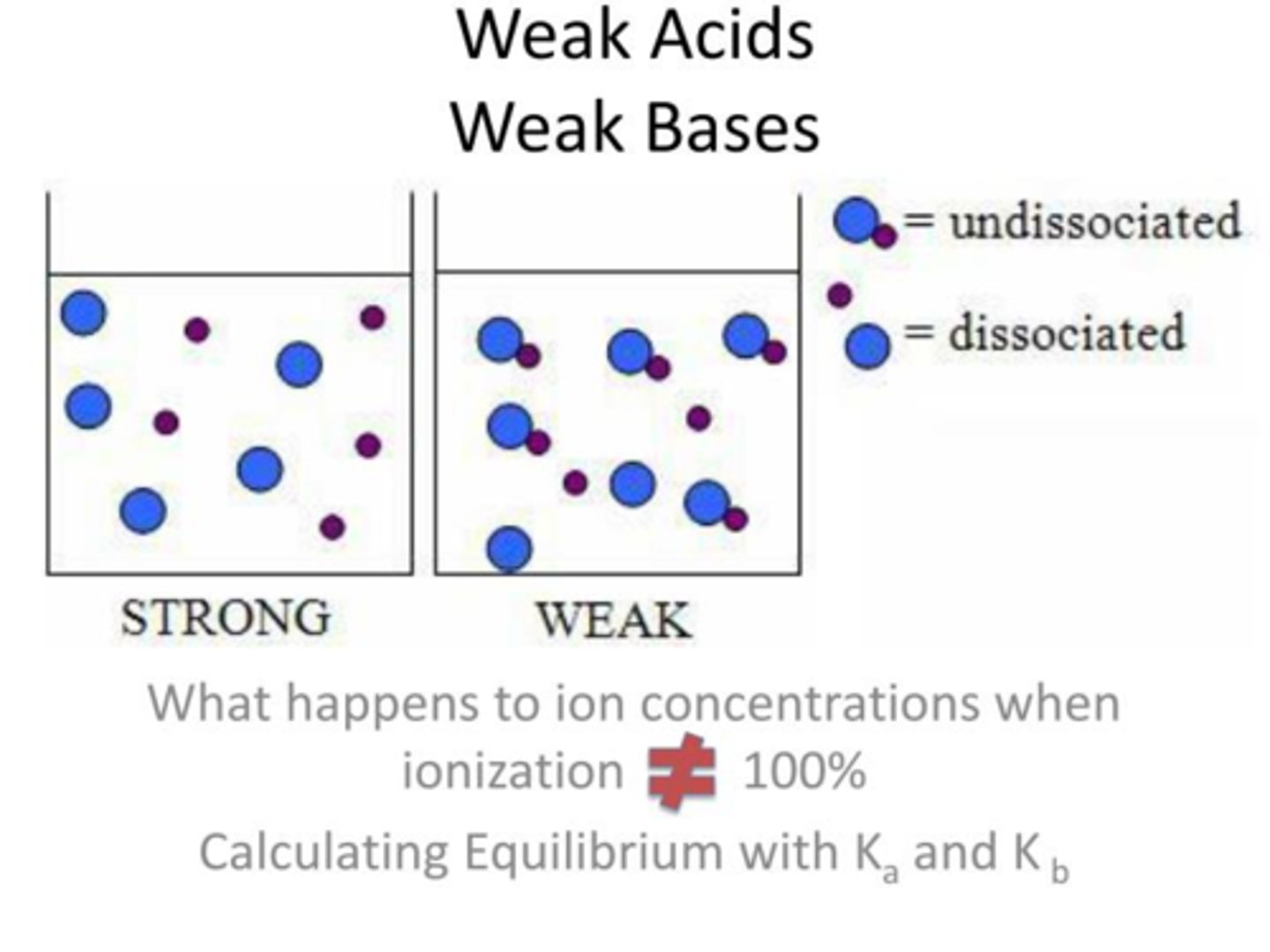
A weak acid or base means the molecules have not completely disassociated. In a chemical equation, the arrow would go in both directions. Once they dissociate, they can easily go back to the way they once were. (In the picture, you see that weak acids/bases remain close together to easily reassociate while strong ones do not)
What does a weak acid/base mean?
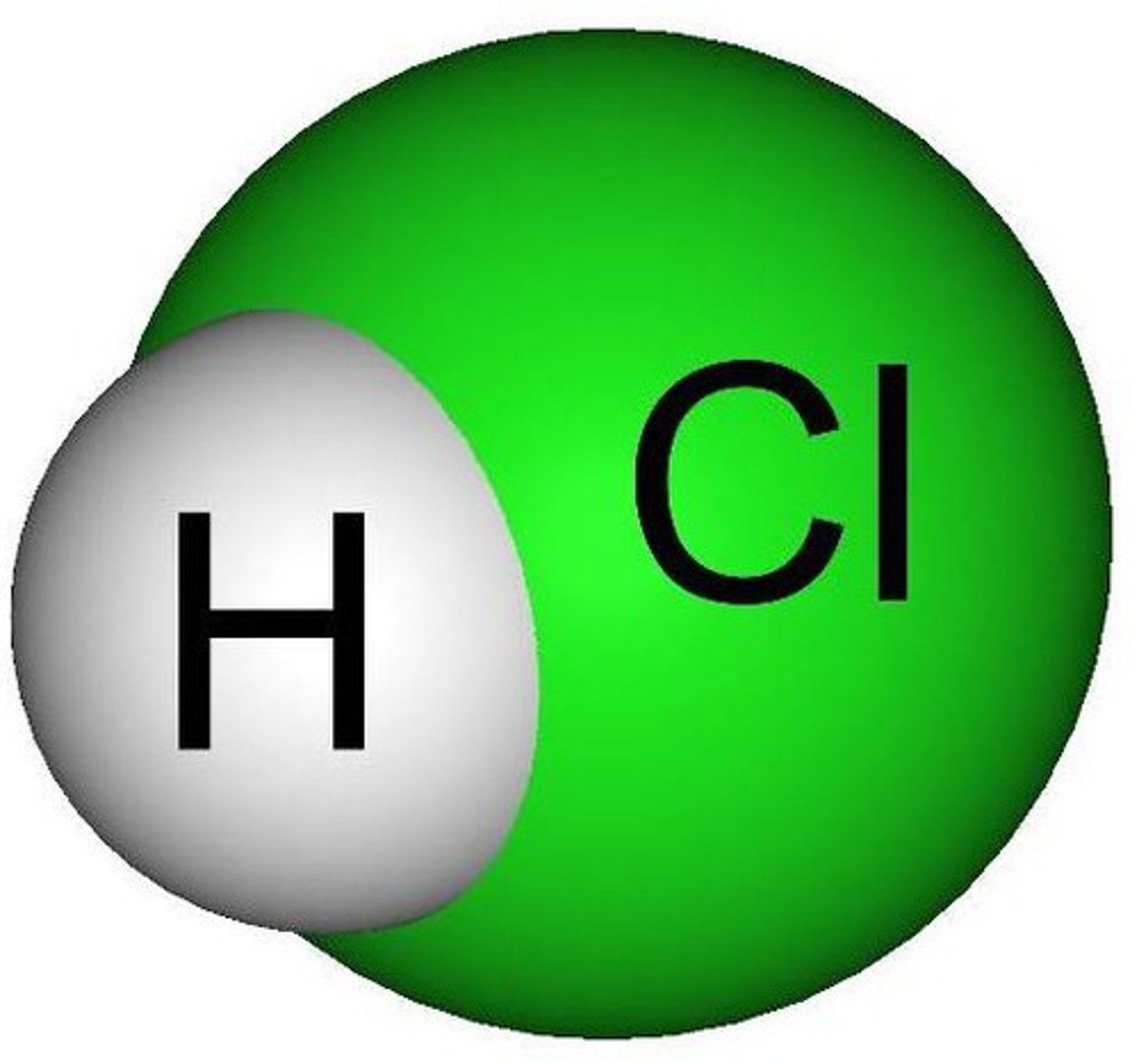
Strong
Is this a strong or weak acid/base?
Hydrogen Chloride
Weak
Is this a strong or weak acid/base?
Acetic Acid
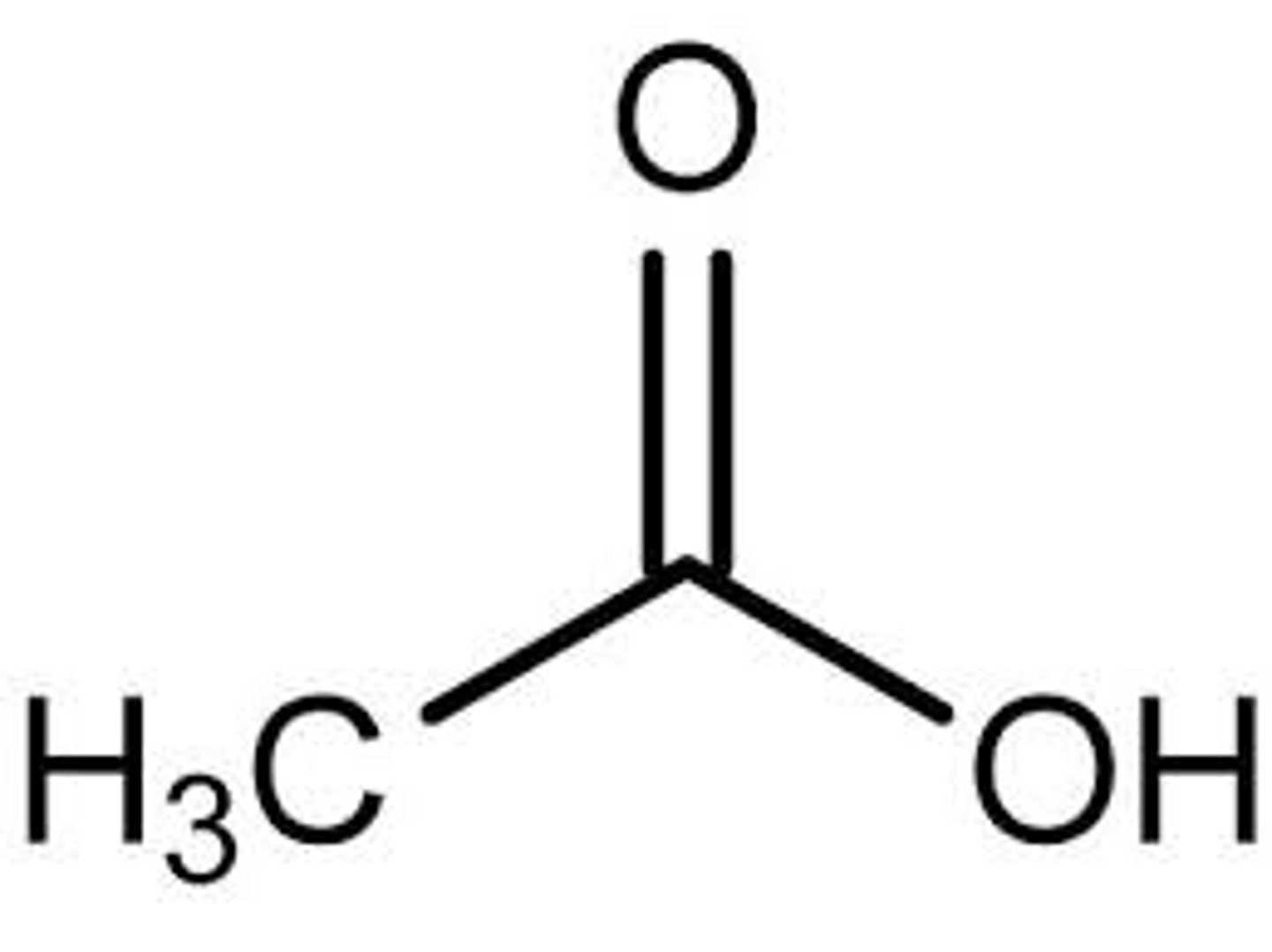
Strong
Is this a strong or weak acid/base?
Sodium Hydroxide
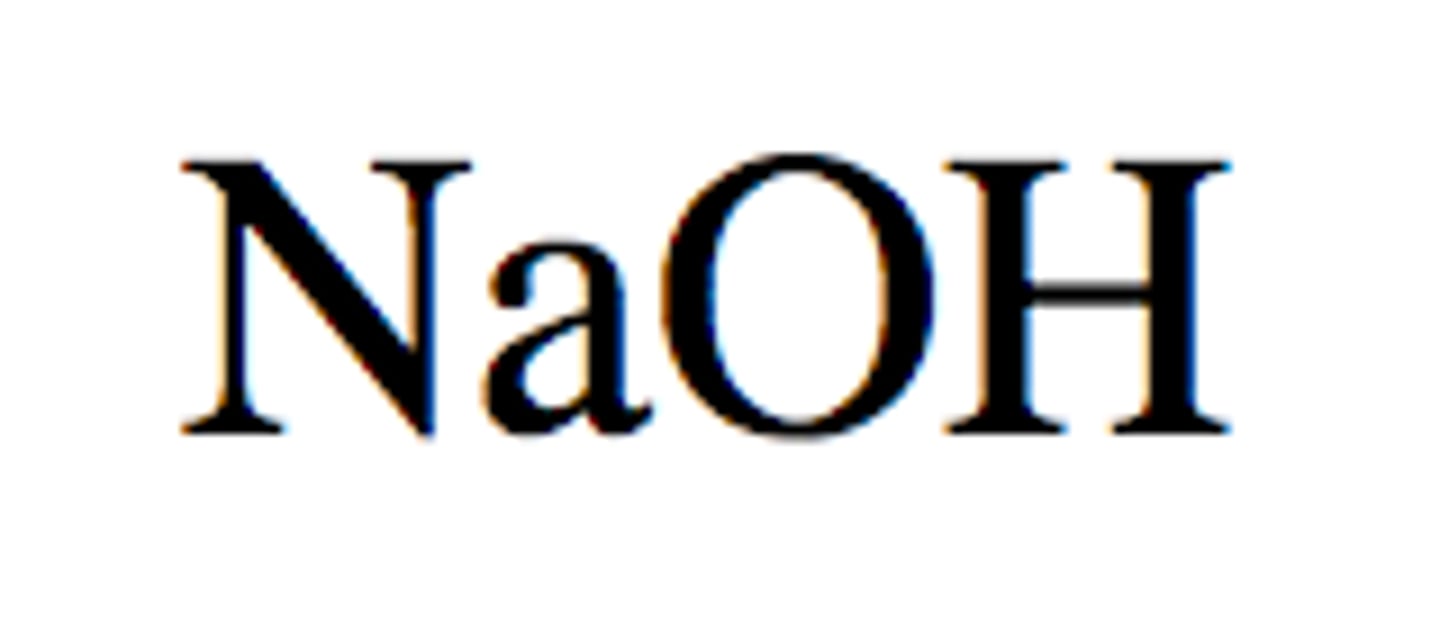
Weak
Is this a strong or weak acid/base?
Ammonia
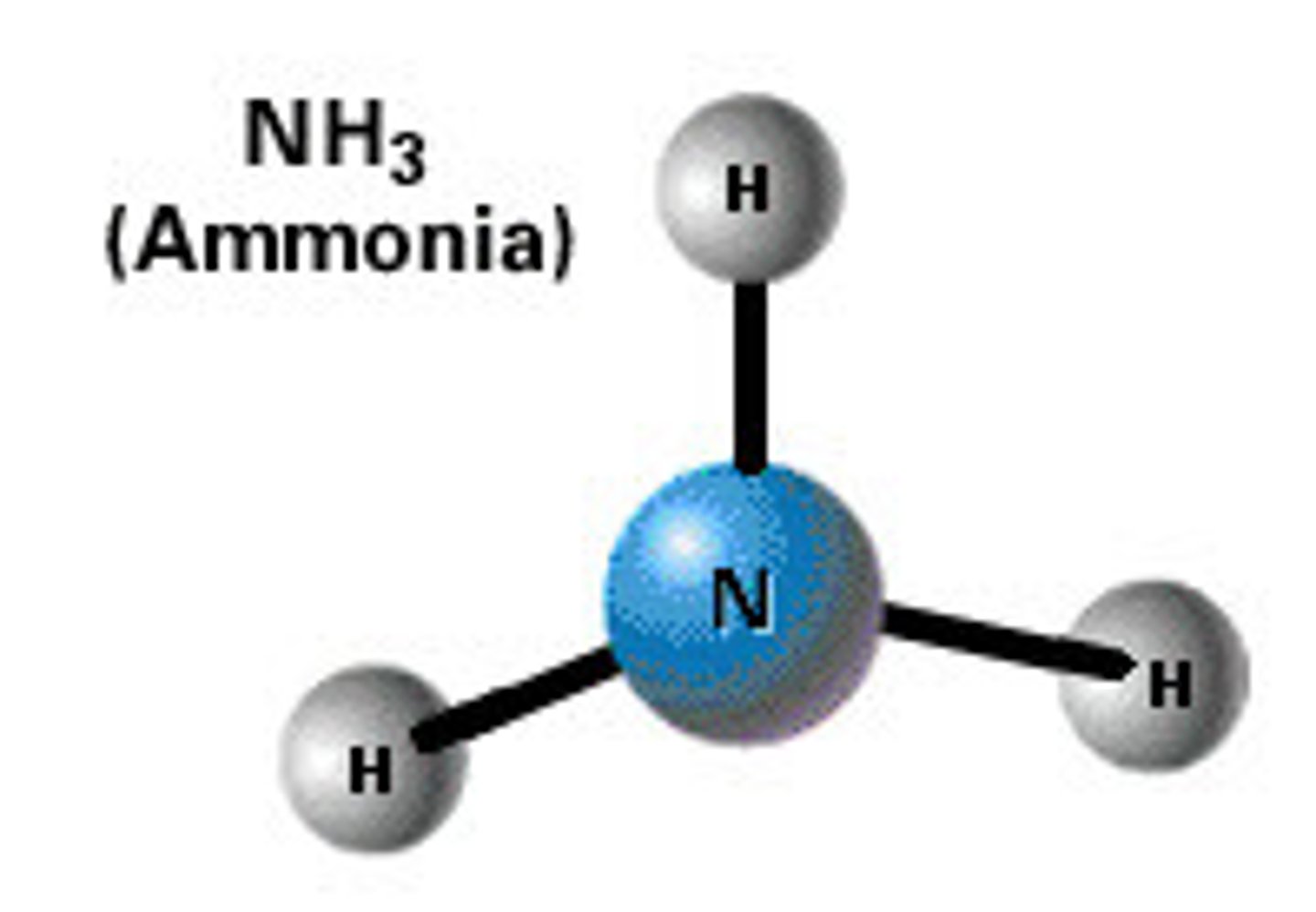
Power of hydrogen
What does pH stand for?
the negative logarithm of the concentration of hydrogen ions in moles/liter
How is pH calculated?
The level of acidity or basicness of water. They do this by measuring the proportion of hydrogen in the solution.
What does pH measure?
pure water = 1/10,000,000 moles of hydrogen ions
0.0000001 mole per liter
10^-7 mole per liter
What is the equation for pH?
7 (pure water)
What is neutral on the pH scale?
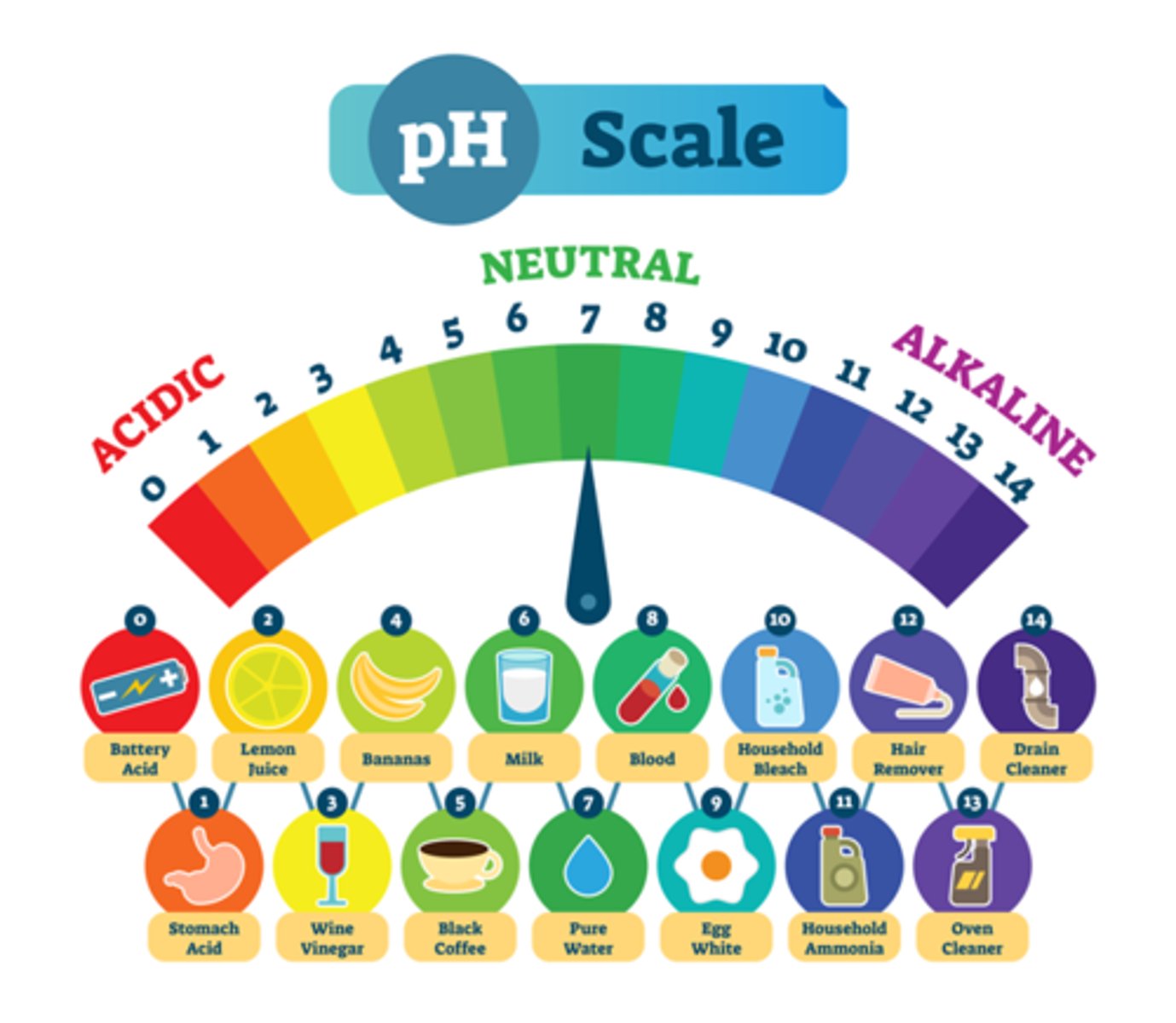
Lower
The more acidic something it is the ______ it is on the pH scale.
Higher
The more basic something is the ______ it is on the pH scale.
pH is based on a negative powers scale. The lower a number gets the closer it is to 10^0 (1). This means as you get lower on the pH scale, the proportion of H+ to OH- is very high. As you get higher, you are further away from 10^0, so the proportion of OH- to H+ is very high.
Why does it make sense that as you get lower on the pH scale the more acidic the solution is?
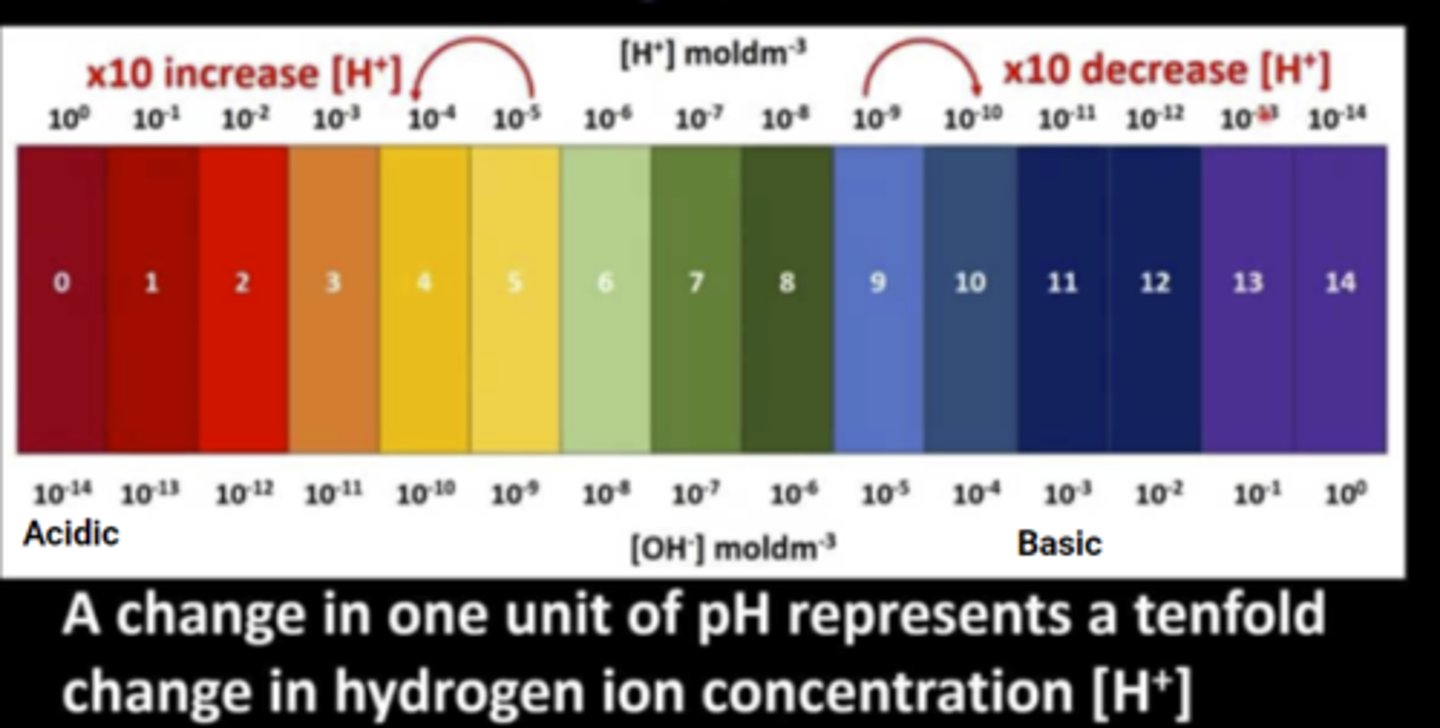
If you have 10^-10 H+ ions, then there are 10^-4 OH- ions. Subtract the power (without the negative) from 14 and that gives the proportion of OH- ions.
How do you figure out how many OH- ions are in a solution from the pH scale?
Buffers
combinations of H+ donor and H+ acceptor forms of weak acids/bases
stabilize the pH of a solution
What do buffers do?
When water and CO2 combine they create carbonic acid. Carbonic acid is released if the blood is becoming too basic and needs to come back down to somewhere close to 7. They give out H+ ions to cancel out the influx of OH- ions.
What does carbonic acid to act as a buffer system?
If the blood is way too acidic then bicarbonate is used to make it more basic and bring it down to around 7. This can negatively impact body function so bicarbonate is used to make the blood more basic and get it down to the right levels or use OH- to make it more basic.
What does bicarbonate do to act as a buffer system?
They are typically weak acids and bases because weak acids and bases don't completely disassociate, so they can go back and forth as much as they want. Strong acids and bases are completely disassociated and can never go back to their original form. We want the weak acids and bases because they can go back and forth as much as they need to, to keep the pH levels in check and aren't restricted by being completely dissociated, so they can use H+ ions or OH- ions.
Why are weak acids and bases typically used as buffer systems?
To make something more acidic, donating means give out.
When we say donate H+ ions what does this mean?
To make something more basic, to take it in, in order to make OH- ions.
When we say accept H+ ions, what does this mean?
10 -4 M
Measurements show the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of this lake?
10 -10 M
Measurements show the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydroxide ion concentration of this lake?
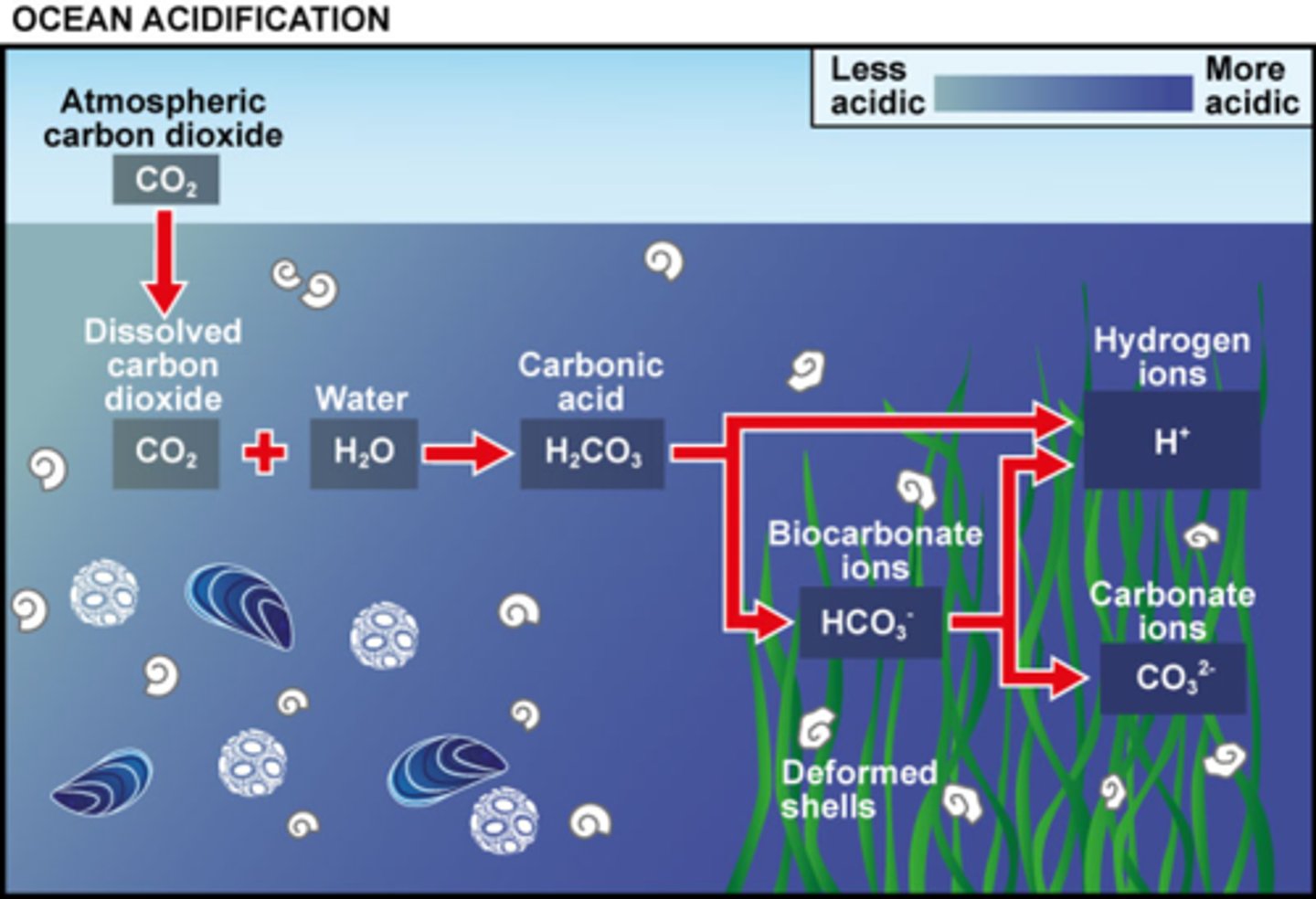
There is more CO2 in the atmosphere, when it is dissolved in the water it creates carbonic acid. When carbonic acid is formed it releases more H+ ions. Coral relies on a molecule called carbonate, coral uses the carbonate in order to make their shells. These excess hydrogen ions (created from carbonic acid) react with the carbonate ions, they then form bicarbonate. There is then no more carbonate for the coral to produce their shells, killing the coral reefs.
Explain ocean acidification and what it does to coral reefs.
There are 10^-6 H+ ions and 10^-8 OH- ions.
Exactly define the number of hydrogen and hydroxide ions at pH 6.
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Dissolve 90 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
The molar mass of glucose (C6H12O6) is 180 g/mol. Which of the following procedures should you carry out to make a 0.5 M solution of glucose?
concentration of H+ has increased tenfold (10X) and the concentration of OH- has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what they were at pH 9.
If the pH of a solution is decreased from 9 to 8, it means that the....
Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will decrease.
Increased atmospheric CO2 concentrations might have what effect on seawater?
polar covalent bonds
In a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by.....
the electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus.
The partial negative charge in a molecule of water occurs because....
10.0
The nutritional information on a cereal box shows that one serving of a dry cereal has 200 kilocalories. If one were to burn one serving of the cereal, the amount of heat given off would be sufficient to raise the temperature of 20 kg of water how many degrees Celsius?
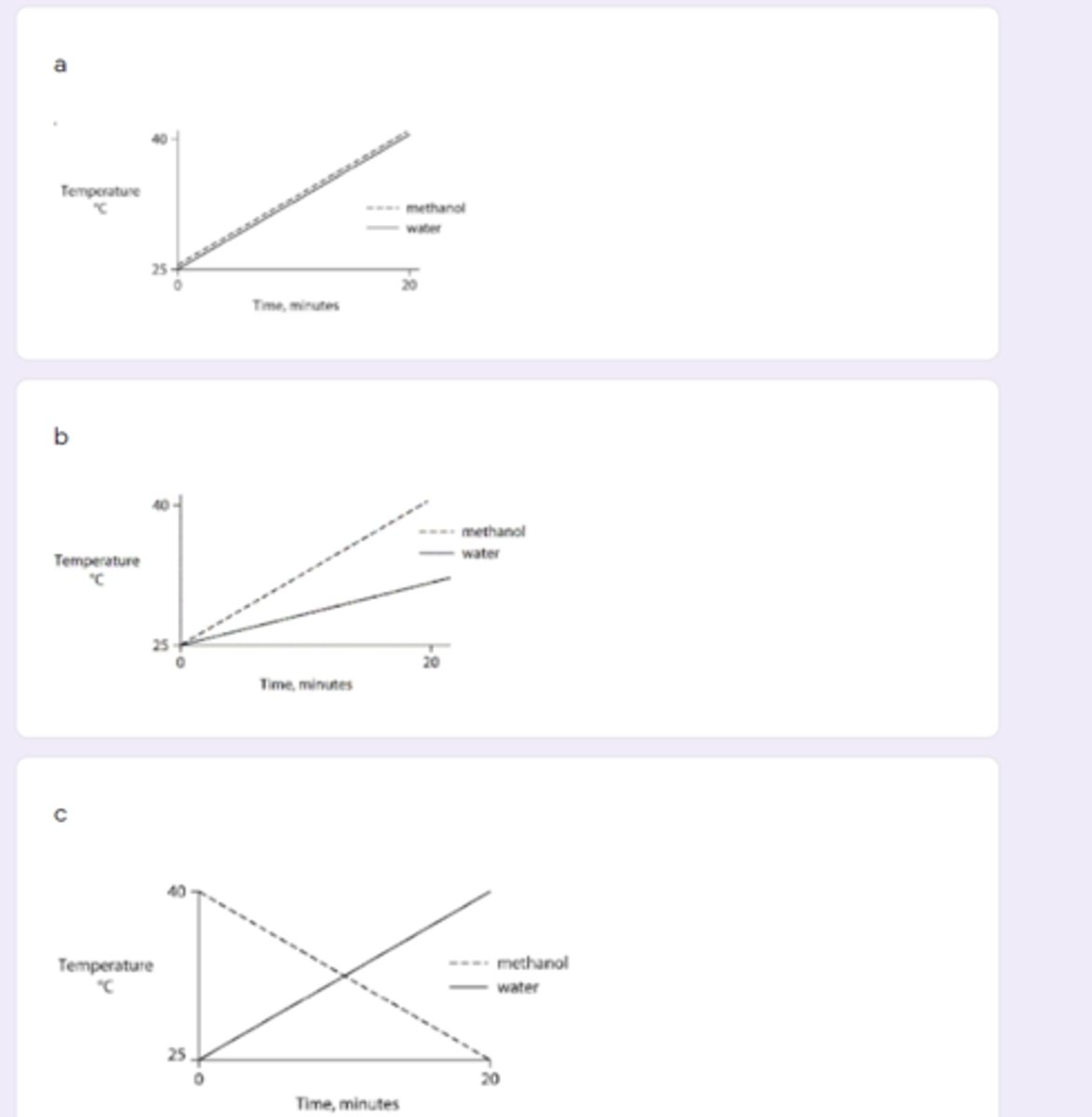
B
Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on identical containers of water and methanol (wood alcohol), so that each liquid absorbs the same amount of energy minute by minute. The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will happen to the temperature of the water and the methanol?
Evaporative cooling
process of removing heat from a surface due to the evaporation of water. Water can absorb a lot of heat without changing phases, allowing it to remove heat from the surface it is on. ... Since the heat is going from the surface into the water, the temperature of the surface decreases.
High heat of vaporization
It also takes an unusual amount of heat to vaporize a given amount of water, because hydrogen bonds must be broken in order for the molecules to fly off as gas.