Cornea
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is epithelial tissue?
A sheet of cells on a basement membrane, the basement membrane overlays connective tissue
What is shape of the endothelium?
a special simple, squamous epithelium
How is the phospholipid bilayer formed?
a polar (water loving) head and nonpolar fatty acid (hydrophobic) tail that faces inward
What are extrinsic/ peripheral proteins?
outer or inner surface of the bilipid membrane wall
What forms a meshwork outside of the epithelial cells?
carbohydrates which are glycocalyx “sugar coating” of cell membranes
What are desmosomes?
small plaques with tonofibrils tying one plaque and cell to another
tight (macula occludens) or looser (macula adherans)
What is tighter? macula occludens or macula adherans
macula occludens
What do gap junctions do?
allow two-way communication of small molecules and ions between two adjoining cells through channels called connexins
What are hemidesmosomes purpose?
to anchor cells to the basement floor
they have one plaque on the floor of basal cells
What is the terminal bar and its formula?
refers to the tight junctions between cells that help to form the blood-retina barrier.
Terminal Bar = ZO + ZA
Zonula occludens
Tight junction "occludes"; impervious, cell membranes 1-2 nm apart
Zonula adherans
Intercellular space filled with glycoprotein “glue” + microfilaments into the cell cytoplasm. "Adheres" one cell to the other. Not completely tight. Cell membranes about 15-25 nm apart.
What is the principle refracting component of the eye?
the cornea
What is the cornea?
a transparent, avascular tissue covering the front of the globe
What are some facts about the cornea?
its bathed in fluids they provide the cornea with O2, glucose, and amino acids.
made up of 5 layers
its continuous with the conjunctiva and sclera
The cornea is aspheric in shape, what does that mean and what does it do?
aspheric: flattens toward the periphery
the shape reduces optical spherical aberration
What is the thickness of the cornea?
hint: Dr. Sarah’s birthday
~530 um centrally and about 710 in the periphery
What is the thinnest layer of the cornea?
the endothelium (5 um)
What are the layers of the cornea epithelium?
the epithelium is 5-7 layers thick (~50 um)
2 layers are squamous cells
2-3 layers are wing cells
1 cell layer of columnar basal cells
At the __________ you have squamous cells which are 2 to 3 layers thick.
surface
Where are squamous cells from?
wing cells and they slough off into the tear layer eventally
Wing cells are also 2 to 3 layers thick, why are they called wing cells?
They are cuboidal with a wing appendages that go around the apex of basal cells
Where are wing cells descendants of?
basal cells
What are basal cells descendants of?
stem cells located in the limbus
What is the germinal layer of the epithelium?
basal cells which have a high metaabolic activity with a lot of mitochondria and golgi bodies
Gap junctions are only in basal cells, what do they do?
allow the flow of molecules and ions between cells
What is the epithelial life cycle?
basal cells → wing cells → surface squamous cells
the only layer to divide is the basal layer which come from stem cells in the limbus or from mitosis of other basal cells
How long does it take for new basal cells to slough off squamouns cells?
7-10 days
Corneal Epithelial Healing
Mitotic activity temporarily halts at the start of corneal epithelial healing.
Basal cells lose hemidesmosomes and spread across Bowman’s layer through ameboid movement at a fast rate (~60-100 µm per hour).
Initially, only one layer of flattened basal cells forms; once the stroma is covered, a new basement membrane is created, and mitotic activity resumes.
Healing is rapid: a 6 mm abrasion can heal in 48 hours, with smaller abrasions sometimes healing overnight.
Recurrent Corneal Erosion
a result of the epithelium not being firmly anchored to Bowman’s layer
often follows trauma
common in diabetics/elderlu
Bowman’s Layer is a
transitional layer of modified stroma
random, non-bundled collagen fibers in mucoprotein ground substance
acellular
does not regenerate but will be replaced by stroma-like tissue
made up of two types of collagen: Type 1 and 7
The stroma is ____% of the corneal thickness and consists of
90%
collagen lamellae
ECM
keratocytes
Collagen is most common of all proteins in the body
its extracellular, insoluble, fibrous protein w a variety of morphological roles
What is the backbone of collagen?
glycine which combines other amino acids to form over 10 different types of collagen
What is tropocollagen?
3 minor helicies form a major helix to make this collagen molecule
tropocollagen→ microfibril → fibril → collagen fiber → lamellae
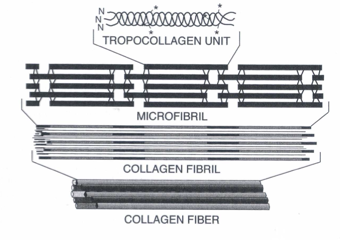
Collagen fibers form 200 to 300 ribbons or a lamellae, what is it
stromal lamellae is at the limbus and has a structural effect that controls corneal curvature and can alter the refractive error if damaged
What is the structure of lamellae?
amino acids → collagen alpha chains → tropocollagen molecules → collagen microfibrils → collagen fibrils → collagen fibers → stromal lamellae
What is the ECM?
extracellular matrix that is also called ground substance
functions like glue and made of proteoglycans
What are gags (
glycosaminoglycans
keratan sulfate and dermatan sulfate
hydrophilic
forms a gel