Musculoskeletal 2
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
The Stomatognathic System is made up of….
Bones (skull, mandible, hyoid, teeth, clavicle, sternum), joints (dentoalveolar, TMJs, ligs/discs), muscles, vascular system, lymphatics, palate/gums/glands
Integrated functional unit of the mouth, jaws, and associated structures
What are the 2 cavities of the articular disc of the TMJ?
Upper cavity - mandibular translation
Lower cavity - mandibular rotation
Ant. - Lateral pterygoid muscle
Post. - Retrodiscal pad
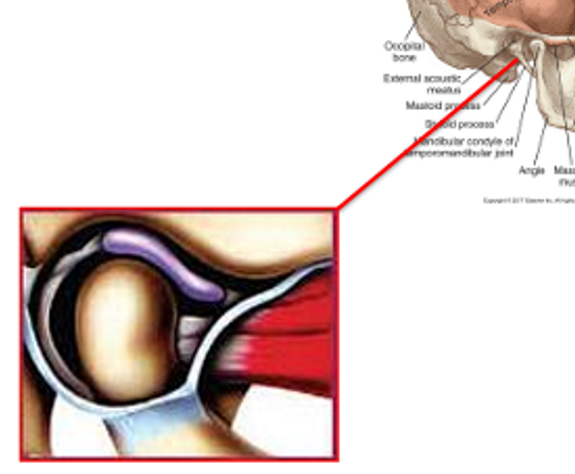
What is the Retro discal Pad?
Bilaminar
positioned posterior to the articular disc
Superior portion - Elastic
Inferior portion - Non-elastic
Vascular, richly innervated and potential source of pain
Located between the posterior border of the articular disc and the posterior capsule of the TMJ
Nerve Supply of the TMJ area?
Primary trigeminal nerve (particularly mandibular V3)
Upper 3 cervical nerve roots (Opthalmic, maxillary, mandibular)
Muscles of Mastication - Temporalis & Masseter
Primary function = elevate mandible (close mouth)
Innervation: V3
Muscle of Mastication - Lateral Pterygoid
2 distinct portions - superior & inferior bellies
Action
bilateral contraction = protrusion
unilateral contraction = contralateral laterotrusion
Innervation V3
Muscle of Mastication - Medial Pterygoid
Attach onto ramus of mandible
Action
bilateral contraction = elevate mandible
unilateral contraction = laterotrusion
Innervation V3
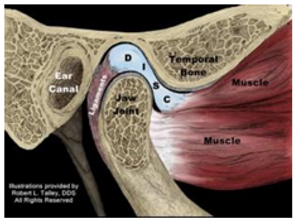
Is this the Open or Closed position of the TMJ?
Closed Position
ant translation, ant rotation
disc pulled back by elastic fibers of retro discal pad, controlled eccentrically by lateral pterygoid
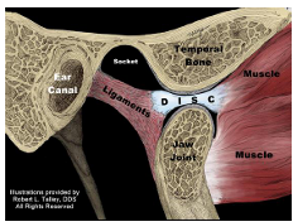
Is this the Open or Closed position of the TMJ?
Open position
40-55mm
Ant rotation, ant translation
What are some red flags for TMJ disorders?
Worsening pain
fever, weight loss, aches, pains
night pain
facial/neck masses
unilateral hearing loss
pain with exertion
How many cervical nerves are there?
8 nerves
1st 7 exit above the corresponding vertebrae
C8 exits below the 7th Cervical vertebrae
What are the 5D’s and 3N’s for VBI symptoms?
Dizziness (vertigo or lightheadedness)
Diplopia (double vision)
Dysarthria (slurred or impaired speech)
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Drop attacks (sudden loss of postural control without loss of consciousness)
Nausea (or vomiting)
Nystagmus (involuntary eye movements)
Numbness (especially facial or perioral paresthesia)
______: Grade 1 → compression, traction, ischemia
______: Grade 2, 3, 4 → Nerve crush
______: Grade 5 → Nerve laceration, Grade 6 → gunshot, stab etc
Neuropraxia
Axonotmesis
Neurotmesis
5 nerves and their roots of the Brachial Plexus
Musculocutaneous (C5-7)
Axillary (C5-6)
Radial (C5-T1)
Median (C5-T1)
Ulnar (C7-T1)
Compression injury to the nervous system
disruption of blood supply and axonal transport
reversible after short duration
total conduction loss within 60-90mins
rapid recovery still occurs if duration <6hrs
Tension injury to the nervous system
conduction impaired if held >1 hour
complete loss of conduction at ~15% elongation
What is Myelopathy?
Compression of the spinal cord
4 Diagnostic Criteria of Neuropathic Pain
Criterion 1: pain descriptors
Criterion 2: pain distribution
Criterion 3: pain with signs/ sensation
Criterion 4: objective diagnostic tests
Indications for Neurodynamic Tests
minor neurological symptoms
stable and not rapidly deteriorating
pain isn’t severe at time of examination
Contraindications for Neurodynamic Tests
physical exam is inappropriate
severe pain could be provoked
unstable, irritable, hypertensive
Mobility depends on the relationship between _____ and cross-sectional area of _____ and ____ ____ _________.
Mobility depends on the relationship between height and cross-sectional area of discs and facet joint orientation.
Global Normal ROM for Thoracic Spine (Flx, Ext, LatFlx, Rot)
Flexion = 30-40deg
Extension = 15-20deg
Lateral Flexion + rotation = both 25-30deg
Subjective Exam for Thoracic
Innervation:
Pain Sources:
Referral Patterns:
Cervical into Thoracic pain:
Innervation: Dorsal rami or sinuvertebral nerve
Pain Sources: IVD, facet, muscles (traps/scalenes), ganglion
Referral Patterns: inconsistent location (intersegmental stimulation), visceral (esophagus, pancreas, spleen, heart), dermatomes (T5, T7-8, T10-11, T12)
Cervical into Thoracic pain: C 6/7 referral
Thoracic Objective Exam - 3 functional regions to test
Upper Thoracic - cervical AROM + shoulder elevation
Middle Thoracic - Flexion, Extension, Rotation, Lateral flexion
Lower Thoracic -Lumbar AROM
4 General Managements of Thoracic Spine Pain Disorders
Improve Posture
Improve spinal mobility
Optimise muscle function
Address contributing impairments
Manual therapy: PAIVMs, SNAGs, neutral mobilisations and manipulations
Upper cervical referral area →
Lower Cervical referral area →
Mid thoracic referral area →
Lower thoracic a& thoracolumbar referral area →
Upper cervical referral area → upper thoracic region
Lower Cervical referral area → anterior chest wall
Mid thoracic referral area → mimics visceral pain
Lower thoracic a& thoracolumbar referral area → lumbar region (iliac crest)
Shoulder Pain Subjective Assessment Findings
Body Chart:
Dull, aching, poorly localized, less traumatic, impingements, instability
History
Atraumatic: insidious, progressive worsening of pain
Traumatic: Sudden, intense sharp pain, major loss of ROM
Agg Factors
Reaching hand behind back/head, should elevation, reaching across body
Easing Factors
rest, unloading, support
Night Symptoms
Visceral, red flags, agg by ipsilateral side lying
Patient Reported Outcome Measures
Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire (DASH)
Simple shoulder test
Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI)
Quiz: Does Physiotherapy have a large role to play in the management of cluster headaches?
No
Quiz: At what degree can operative intervention for scoliosis be indicated?
More than 60 degrees of curvature
Quiz: Features of craniovertebral instability
Excessive movement at C1-2
Neurological symptoms
wry neck posture
acute trauma/ degeneration/ congenital conditions
Quiz: Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Positive HLA-B27
age 16-25
hip and buttock pain
worse after activity
AM stiffness
limited chest wall excursion
Quiz: What are some questions to ask about TMJ “clicking”
Hard vs soft
timing of clicking
consistency of clicking
is there locking and/or catching present
associated pain
Quiz: What is not considered a “high risk feature” in the Canadian c-spine rule?
Delayed onset of neck pain
Quiz: What is the most specific orthopedic test for a tear in the infraspinatus tendon?
External rotation lag sign
Quiz: Common clinical feature of cervicogenic headache?
Tenderness in the region of C1-3
Quiz: What is not a sign of Cervical myelopathy?
Upper limb HYPOreflexia
Quiz: What 3 tests make up the Cluster of Wainner?
Upper limb tension test (ULNTT1)
Spurlings test
Cervical axial distraction
Quiz: Percentage of scoliosis patients report back pain present?
25%
Quiz: What is not a source of subacromial impingement syndrome?
Subscapularis tendon
Quiz: Thoracic spine is the most common site of metastases for which type of cancer?
Breast cancer
Quiz: 3 Upper motor neuron integrity tests
Babinski sign, inverted supinator sign and Hoffmans sign
Quiz: List 4 clinical features of cervicogenic headache you could use to differentiate it from migraine?
Uni
head mov
restr
tender
- unilateral headache
- pain provoked by certain head movements
- restricted ROM
- tenderness over cervical region
Quiz: What are the 4 key features of the Canadian C-spine rules?
UEP
AL
Age
RH45LR
Upper extremity paresthesia
Axial loading to the head
Age >65
can rotate head 45deg left and right
What are some symptoms of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalgias?
Ipsilateral pain
lacrimation
rhinorrhea
nasal congestion
sweating
restlessness
What are some symptoms of Cervical Arterial Dissection?
Horners syndrome
constricted pupils
droopy eyelids
inability to sweat)
Neuro exam findings
What are the 4 sub-SLAP types
Degeneration
SL + LHB detachment
SL detached, LHB intact
SL + LHB teat + displacement
4 stages of Migraine
Prodrome
Aura
Migraine
Postdrome
What 6 pathologies are considered in the “Big 6?”
Rotator cuff pathology
Biceps tendon pathology
Glenohumeral instability
Scapular dyskinesia
Glenohumeral rotation deficit (GIRD)
Impingemenet-related shoulder pain
Grading System of Shoulder Pathologies
Grade 1: Tear of capsule & AC ligaments (‘Sprain’)
Grade 2: Rupture AC ligaments & tear to the CC ligament (‘sprain’)
Grade 3: Rupture AC ligament & CC ligament (‘dislocation’)
Grade 4: Post-displacement of clavicle (‘dislocation’)
Grade 5: Similar to Grade 3 + greater ST damage (‘dislocation’)
Grade 6: Inferior displacement to subacromial/sub coracoid space (‘dislocation’)
Dynatome vs Dermatome
Dynatome: resemble dermatome maps, but frequently fell outside the classic distribution
Dermatome: area off skin innervated by a single nerve root
Cervical Red Flags and Categories
Category 1: immediate medical attention
head injury, cervical spine #, UCx spine instability
Category 2: Further Q’s and precautions
VBI, congenital/hereditary (RA, Down Syndrome, Marfans Syndrome), gait dysfunction/balance
Category 3: Further testing and differentiation
Myelopathy or visceral pain
Thoracic Red Flags and Categories
Category 1: Immediate medical attention
viscerosomatic pain, tumours, fractures
Category 2: Further Q’s and precautions
metabolic disorders, corticosteroid use, age over 50, spondylodiscitis
Category 3: further testing and differentiation
thoracic disc lesions (T6), Spinal cord compression disorders
Objective Assessment for Shoulder, Cx and Tx → Look for….?
Muscle Bulk
SS atrophy in chronic RC tendinopathy, atrophy of infraspinatus & lwoer traps, biceps atrophy, muscle bulging over distal humerus may be LHBB rupture
Posture
Cervical posture away from painful side, arms supported/held overhead, shoulder supported in 30deg scaption for comfort
Slumped posture, scapular protraction + down rotation, elevated medial scap border indicated pec minor shortening
AROM
Cx→ large loss of AROM in multiple planes, loss of EOR motion an low Cx pain
Tx → upper Tx pain requires strucutual differentiation, Mid Tx pain best reproduced with combined AROM
Shoulder → loss of ER, defined painful arc
PROM
Cx→ hypomobility, pain with Ext+Rot and PAIVMs
Tx→ reproduction of pain & hypermobility of PAIVMs
Shoulder → global ross of ROM, pain preproduced with ACJ PAMs
Special Tests
Key Indication Cx as the Primary Source
Subjective Examination
Pain in upper Cx and head most likely Cx (or TMJ or non-MSK)
Neck-spinal pain extending below elbow
Pain and sensory changes (p&n/n) in roughly dermatomal distribution
Other symptoms (dizziness, lightheaded etc) common in Cx headaches, WAD etc
MOIandaggs/ease can be useful– but break them down!
C5-6 commonly presents as pain into shoulder girdle, esp discogenic and CR
Objective Examination
* Forward head posture
Abnormal CxAROM, esp. loss of flexion and rotation
+vesegmental signs (palpation, PAIVMs, PPIVMs) and quadrant (Ext+ROT) test •-ve shoulder impingement tests
-ve segmental signs in Tx
+veneurological exam (high spec) and Spurlings test (high spec) = CxR
Key indication Tx as the Primary Source
Subjective Examination
Pain inferior to scapula, along ribs, anterior chest or iliac crest most likely Tx
Pain often well defined (+/- 1-2 segments) and more sharp than Cx referral
Rarely extends past shoulder point and into neck
Pain with inspiration or coughing
Hx of prolonged slumped sitting
Twisting/lifting MOI that triggers immediate onset Tx pain
Objective Examination
* Pain with combined Tx movements - often requires structural differentiation
+vesegmental signs (palpation, PAIVMs, PPIVMs)
-ve Sh impingement tests •-ve Cx segmental findings
Key Indications Shoulder as the Primary Source
Subjective Examination
Location of pain most commonly antero-supero-lateral shoulder region
Rarely into neck or below elbow
Usually recall some MOI – either overuse or sudden lifting related pain
Unable to sleep on affected side
Joint signs (clicking, catching, unstable, weak) common
Objective Examination •
SS atrophy and abnormal scapular positioning – protracted+down-rotated
+ve impingement tests – H-K, Neers and quadrant
Limited active-passive ER and pure GHJ abduction • TOP over AC
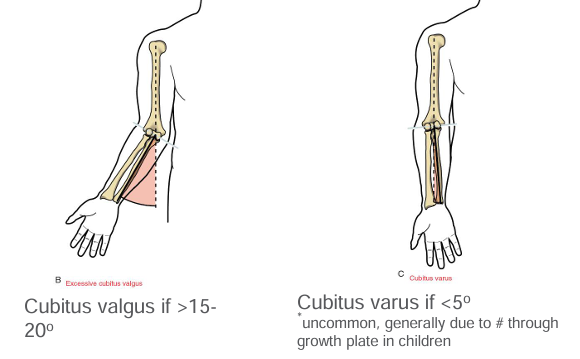
Normal Elbow Carrying Angle
Normal – approx 15o
Males = 5-10 deg
Females = 10-15deg
Cubitus Valgus vs Cubitus Varus
3 Ligaments of the Elbow
Medial (Ulnar) collateral ligament (ant, post, transverse)
Lateral (Radial) collateral ligament
Annular ligament
4 Criterions for the Pathologies of Neuropathic pain diagnosis
Criterion 1 & 2: Subjective Examination
Criterion 3: physical tests (sensation, motor as required)
Criterion 4: Objective tests (nerve conduction)
Peripheral Neuropathies Common Area
Entrapment/compression or tension/elongation of:
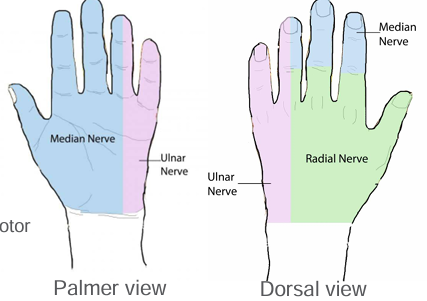
Median nerve
Ulnar Nerve
Radial nerve
Stingers and Burners (Cx)