OVERVIEW OF PCR
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The first specific amplification method of any type. It is also the first and prototypical method for target nucleic acid amplification.
Kary Mullis
He discovered PCR in the mid-1980s, which he was granted a nobel prize for in 1993.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
It is a copy machine for DNA that revolutionized molecular biology.
False.
PCR is used to determine and confirm cellular or organismal presence by the detection of its genomic DNA or RNA (bacterial, viral, eukaryotic organisms).
Modified True or False.
PCR is used to determine and confirm cellular or organismal presence by the detection of its genomic RNA (bacterial, viral, eukaryotic organisms).
True
Modified True or False.
PCR is used to characterize cells or organisms by determining the DNA/RNA sequence of an amplified DNA/RNA target
Amplicons
These are the copies of a specific DNA sequence. It is formed after PCR.
In vitro
PCR is DNA replication ___ ___
DNA Polymerase
What is the main replication enzyme?
Base Pairing Rule (A-T, G-C)
DNA replication follows what rule?
False.
By amplifying the amount of nucleic acid materials obtained from clinical samples. Molecular techniques can effectively provide a quantitative representation of an individual's health
Modified True or False.
By amplifying the amount of nucleic acid materials obtained from clinical samples. Molecular techniques can effectively provide a qualitative representation of an individual's health
Water
Buffer
DNA Template
Thermostable Polymerase
Primer Pair
Magnesium (Mg2+)
Deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs)
What are the components of PCR?
Water
It is the medium for all other components.
Purified
Double distilled
Deionized
Autoclaved
Nuclease free
No detectable amounts of nucleic acid
Describe the water used for PCR.
Buffer
It stabilizes DNA polymerase, DNA, and nucleotides.
DNA Template
It contains the target region of interest.
Thermostable polymerase
Taq polymerase
It is used to catalyze DNA-dependent DNA synthesis.
Give an example
Thermus aquaticus
Taq polymerase comes from what thermophilic bacteria?
Primer Pair
These are oligodeoxynucleotides that flank the region of interest.
Forward Primer Pair
A type of primer pair that locates the replication start point along the template’s sense strand.
Reverse Primer Pair
A type of primer pair that marks a second replication start point along the antisense, downstream of its opposite primer.
18-30 base nucleotides
The length of a primer pair should be?
Magnesium
It acts as a cofactor for polymerase activity. It also stabilizes the DNA double helix.
Too little: Enzymes will not work
Too much: DNA will become extra stable and will cause non-specific priming
What are the consequence(s) if Magnesium is:
Too little
Too much
dNTPs
These are the equimolar building blocks of DNA.
Pre-PCR → PCR → Post-PCR
What is the typical PCR set-up in a laboratory?
Isolation of nucleic acid from samples
Preparation of PCR reaction components (mastermix)
Addition of nucleic acid template into the PCR Reaction Mastermix
Pre-PCR includes?
PCR
Denaturation, Annealing, Elongation
This PCR set-up includes Thermal Cycling
What is it composed of?
40
How many cycles can be done in thermal cycling?
Post-PCR
It includes the analysis of amplified DNA.
Pre-PCR
It is done prior to performing Molecular Biology techniques. It is the first step in PCR analysis.
Cellular lysis
DNA / RNA extraction
Sample treatment requires?
Heat denaturation
It refers to the high heat used to disrupt and separate DNA duplexes.
Heat
It breaks the hydrogen bonds of DNA template and separates into single strands.
94 C
DNA is heated to a minimum of (what temperature)?
Primer annealing
It refers to the attachment of primers to the template strand.
50 - 60 C
The DNA is cooled down to (what temperature)?
Individual ssDNA
DNA primers bind to ___ in annealing phase.
Primer extension
It refers to the elongation of daughter strand with DNA polymerase.
72 - 74 degrees C
What is the temperature in elongation?
Repetitively
Turnaround time
The PCR cycle would continue ___ in a predetermined ___.
Running the correct controls
It is essential for ensuring and maintaining the accuracy of the assay.
Positive controls
It ensures that the enzyme is active, the buffer is optimal, the primers are priming the right sequences, and the thermal cycler is cycling appropriately.
Negative control without DNA
It ensures that the reaction mix is not contaminated with template DNA or amplified products from a previous run.
Contamination control
Reagent blank
A negative control without DNA is also called?
Negative control with DNA
It lacks the target sequence (negative template control) and ensures that the primers are not annealing to nontarget sequences of DNA.
Gel electrophoresis
Capillary Electrophoresis
Nucleic acid hybridization
DNA sequencing
Real-time quantitative PCR
In Post-PCR, what are used to analyze PCR products?
False.
Depending on the application, the size, presence, or intensity of PCR products is observed after electrophoresis.
Modified True or False.
Depending on the application, the size, presence, or intensity of PCR products is observed before electrophoresis.
Reverse Transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR)
Multiplex PCR
Real-time Quantitative PCR
The modifications of traditional PCR
Reverse Transcriptase PCR
It refers to the conversion of the RNA template into its complementary DNA strand (cDNA), which is an essential step in the analysis of gene transcripts.
The cDNA is sequenced, cloned, and applied to estimate the copy number of specific genes in order to characterize and validate gene expression.
RNA virus
The enzyme reverse transcriptase comes from what organism?
Multiplex PCR
It is a powerful technique that enables amplification of two or more products in parallel in a single reaction tube. It typically employs different primer or probe pairs in the same reaction for simultaneous amplification of multiple targets.
Human Papilloma virus
What organism can be used in multiplex PCR?
Multiplex PCR
It is used widely in genotyping applications and multiple areas of DNA testing in research, forensic, and diagnostic laboratories.
Multiplex PCR
It is used for the detection of multiple pathogens using multiple primer sets in a single reaction.
Ladder
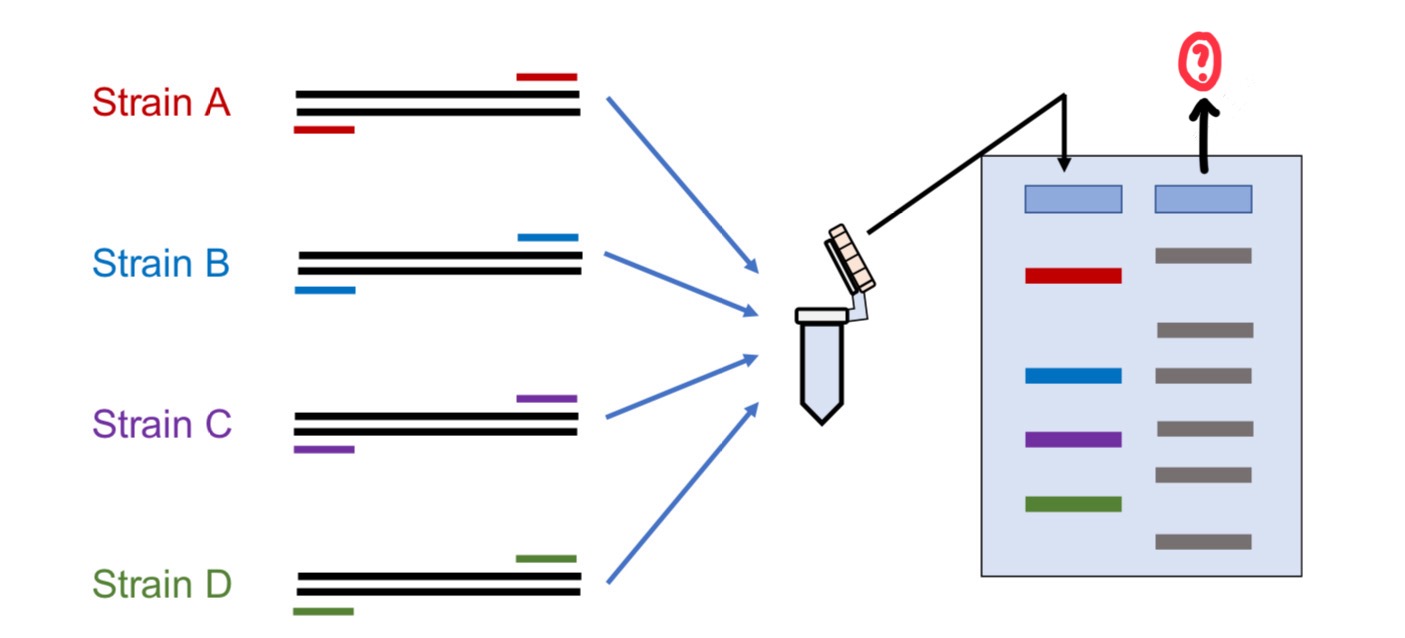
Ladder
It is used as a standard to compare the bands from the gel electrophoresis.
Real time / Quantitative PCR
In this PCR, the accumulation of amplification product is measured as the reaction progresses with product quantification after each cycle.
Real Time / Quantitative PCR
Viral load of Hepatitis B virus is acquired through?
Early: high amount of starting template
Late: low amount of starting template
In Real Time or Quantitative PCR:
The detectable fluorescence in earlier cycles of the amplification program indicates ____, while fluorescence in later cycles indicates ____.
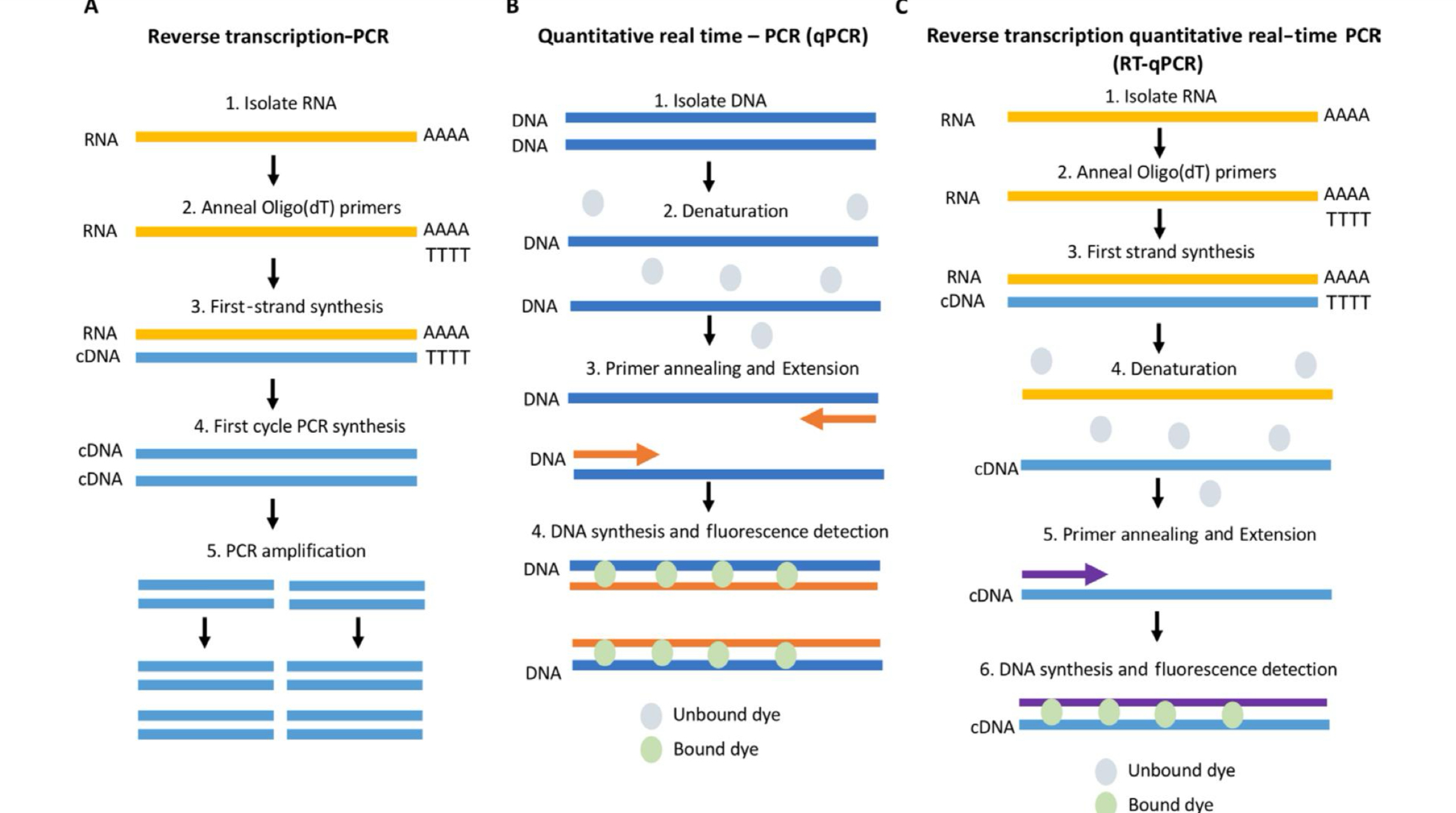
Isolate DNA
Quantitative real time PCR first step
Opaque
Fluorescent dye can be easily degraded in transparent PCR tube due to misdirection
What PCR tube is used for fluorescent dyes?
Why?
Centrifugation
A procedure that can remove bubbles.
Treshold cycle (CT)
The PCR cycle at which sample fluorescence crosses the threshold is the?
Fluorescent reporter molecule
Real-time detection of PCR products is enabled by the inclusion of a ____ ____ ____ in each reaction well that yields increased fluorescence with increasing of product DNA.
Ethidium bromide
The first approach in qPCR utilized ___, which is specific to double-stranded DNA. However, due to its toxicity, it was replaced.
SYBR Green
Specific, robust fluorescence, reduced toxicity
Ethidium bromide is replaced by ___. It is also specific with dsDNA.
What is its advantage?
Carcinogen
Ethidium bromide is a known?
Probe
Its purpose is to identify one or more sequences of interest within a large amount of nucleic acid.
False.
The probe should hybridize specifically with the target DNA or RNA that is to be analyzed.
Modified True or False.
The probe can either hybridize or neutralize the target DNA or RNA that is to be analyzed.
Taqman
Molecular Beacons
Scorpions
Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer
What are the common probes used in qPCR?
TaqMan
It was developed from one of the first probe-based systems for quantifying cDNA by qPCR.
Molecular Beacons
It measures the accumulation of product at the annealing step in the PCR cycle. It does not elongate or extend.
Scorpions
It is a target-specific primer which are tailed at the 5' end with a sequence complementary to part of the internal primer sequence, a quencher, a stem-loop structure, and a 5' fluorophore.
Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
It utilizes two specific probes, one with a 3' fluorophore (acceptor) and the other with a 5' catalyst for the fluorescence (donor).
Acceptor
The 3’ Fluorophore in FRET
Donor
The 5’ Catalyst of fluorescence in FRET
FRET
This PCR transfers energy.
True
Modified True or False.
Real-time PCR results can either be qualitative (the presence or absence of a sequence) or quantitative (copy number).
TaqMan probe
It hybridizes to the target sequences between the PCR primer-binding sites. The probe is covalently attached to a fluorescent reporter dye (R) at the 5' end and a quencher (Q) at the 3' end.
5’ end
At what end is Reporter Dye seen?
3’ end
At what end is Quencher seen?
True
Modified True or False.
In TaqMan, when the quencher and reporter dye are together, there will be no fluorescence signal.
Reporter Dye
This contains the fluorescence signal.
TaqMan signal fluorescence
It is generated when Taq polymerase extends the primers and digests the probe and releases the reporter from the vicinity of the quencher.
Molecular Beacon Probe
It contains target-specific sequences and a short, inverted repeat (~5 bp) that hybridizes into a hairpin structure. The 5' end of the probe has a reporter dye (R), and the 3' end has a quencher dye (Q).
True
Modified True or False.
In the presence of target sequences (Molecular Beacon), hybridization of the probe will open the hairpin, moving the quencher from the reporter and allowing signal fluorescence, which doubles with every doubling of target sequence.
Scorpion
An advantage of this system is the covalent attachment of fluorescent signal to the PCR product, which is useful for further analysis, such as size assessment by capillary electrophoresis.
False.
FRET probes are separate oligomers, one covalently attached to a donor fluor (D) and one to an acceptor or reporter fluor (R). The acceptor/reporter will fluoresce only when both probes are bound next to one another on the target sequences. As more target accumulates, more probes bind, and more fluorescence is emitted.
Modified True or False.
FRET probes are separate oligomers, one covalently attached to a donor fluor (D) and one to an acceptor or reporter fluor (R). The acceptor/reporter will fluoresce only when both probes are bound next to one another on the target sequences. As more target accumulates, less probes bind, and more fluorescence is emitted.
Sigmoidal curve
True amplification displays what curve?
Exponential phase
This phase refers to the increase of DNA copies.
Plateau phase
The enzymes increased are finished and there are no bases to be added, it has reached what phase?
Baseline
Low-level signals attributed to the background or the "noise" of the reaction.
Bubbles
Vibrations
Incorrect pipetting
PCR is sensitive. If there is noise, it means it is unstable. It can be caused by?
Treshold line
The minimum level of fluorescence to determine a CT value. It is above the baseline.
False.
CT is inverse to starting template amount.
Modified True or False.
CT is proportional to starting template amount.
CT value
When the fluorescence crosses the treshold line, it determines the?
Contamination
Late amplification without sigmoidal curve means?
Sigmoidal amplification
CT value
What are the 2 requirements to determine the result in qPCR?