Biology ✿ Ecology
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
ecosystem
the interaction of living with the non-living organisms
what are 3 things plants compete for?
space
sunlight
water/ minerals from soil
what are 3 things animals compete for?
food
mates
territory
interdependence
when organisms within a community depend on each other for survival
what makes a community stable?
when all the living and non-living organisms are in balance so that population sizes are constant
abiotic factors
give 3 examples
non-living factors
temperature
soil pH
light
biotic factors
give 3 examples
living factors
food availability
new predators
new pathogens
explain how to do random sampling using a quadrat
place quadrat in a random area
record number of organisms (flowers) in the quadrat
repeat atleast 10 times in random areas each time
use equation:
total population = total area / area sampled x no of organisms counted
extremophiles
organisms which live in extreme conditions
structural adaptation
features of an organisms body
e.g. thick fur
functional adaptation
features inside an organism
e.g. hibernation to slow metabolism
behavioural adaptation
the way an organism behaves
e.g. migration

Which two improvements would increase the validity of this method?
repeat atleast 10 times
use a random method to place the quadrats
what do food chains show?
feeding relationships in a community
the transfer of biomass
state the food chain order
producer → primary producer → secondary consumers → tertiary consumer → apex predator
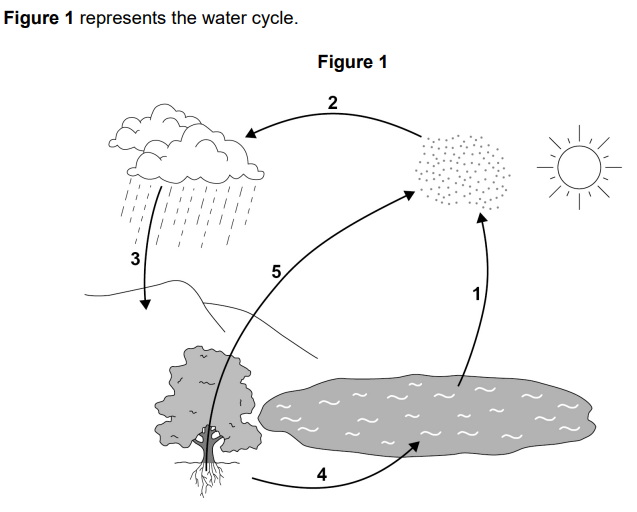
Name the processes 1 to 5 shown on Figure 1
evaporation
condensation
precipitation
draining
transpiration
describe how the carbon cycle works
CO2 is removed by photosynthesis of plants
CO2 returns to the atmosphere when animals respire
decomposers respire and return mineral ions by breaking down dead organisms
CO2 also returns to the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burnt (combustion)
why is high biodiversity important?
it ensures ecosystems are stable by reducing interdependence
state 5 ways humans are reducing biodiversity
polluting waters by using chemical fertilisers
taking up land for quarrying and building, reducing land for animals to stay in
deforestation
burning of peat bogs releases CO2, increasing global warming
destruction of peat bogs for compost reduces the area of habitat
Describe two ways to increase biodiversity in the UK.
planting trees
breeding programmes
what are 2 uses of peat bog
used as fuel
used for compost
what are decomposers? why are they important?
microorganisms that breakdown dead matter which releases nutrients back into the environment to be reused
explain how to do random sampling to estimate the number of dandelion plants in a field. [4]
use a random number generator to generate co-ordinates
place quadrats in the random co-ordinates and count the number of organisms in quadrat
repeat this 10 times
use equation (total area / quadrat area) x total no of organism counted
equation for total population size
(total area / quadrat area) x total no of organism counted
explain how to do random sampling using a transect line and quadrat to see how the factor of light intensity effects the distribution [6]
place a tape measure on the ground perpendicular to tree/ river (transect line)
place a quadrat at the start of the transect line
record number of organisms in quadrat
record the light intensity using a light meter
move quadrat 1 metre along the transect line
repeat along another transect
why might random sampling be unreliable?
number of samples may not represent the entire field
it is an estimate
biodiversity
the variety of different species
population
the number of species in a habitat
community
populations of different species in a habitat
producer
an organism which makes glucose by photosynthesising