Bio Unit 2: Molecules of Life
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
Organic chemistry
The study of compounds that contain carbon atoms
What is SCHNOP’s
Sulfur, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphate
What element is hydrocarbons?
Carbon
What element is carbohydrates and lipids?
Oxygen
What element/s is amino acids and proteins?
Nitrogen & sulfur
What element is nucleic acids, rna, and dna?
Phosphate
What single element atoms might be in some proteins?
Iron, copper, magnesium
What are almost all molecules a cell makes composed of?
Carbon atoms bonded to one another and also to atoms of other elements
What atoms are very versatile?
Carbon atoms
Why are carbon atoms very versatile?
They form backbones of most organic molecules, they can bond to other carbon atoms, and bond up to four other atoms
Why can a carbon atom bond up to 4 other atoms?
They only have 4 valence electrons
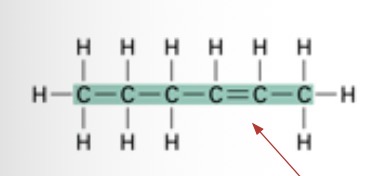
What kinds of chain is this?
Straight chain

What kind of chain is this?
Branched chain
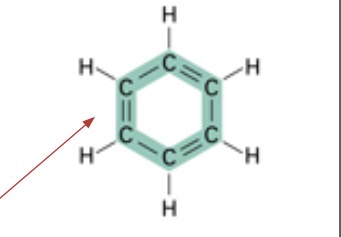
What kind of chain is this?
Ring
Organic molecules
Carbon based molecules
Inorganic molecules
Non-carbon based molecules
What do the properties of an organic compound depend on?
Size and shape of its carbon backbone, and atoms attached to that skeleton
Functional groups
Groups of atoms within a molecule that interacts in predictable ways with other molecules in chemical reactions
What type of molecules are functional groups?
Polar molecules
Why are functional groups polar molecules?
O or N atoms exert a strong pull on shared electrons
Hydrophilic
Water loving
Macromolecules
Giant molecules
Monomers
Smaller units that are building blocks of larger molecules
Polymers
Long chains of molecules formed by linking monomers together
Polymerization
A monomer linking to other monomers to create a polymer
Dehydration reaction
Building macromolecules
What happens each time a monomer is added to a chain to create a polymer?
A water molecule is released
What does a dehydration reaction require assistance from?
An enzyme
Hydrolysis reaction
Breaking down a macromolecule
What happens each time water is added to a polymer?
It breaks down into monomers
What does a hydrolysis reaction require the assistance of?
Enzyme
What type of reaction is digestion?
Hydrolysis reaction
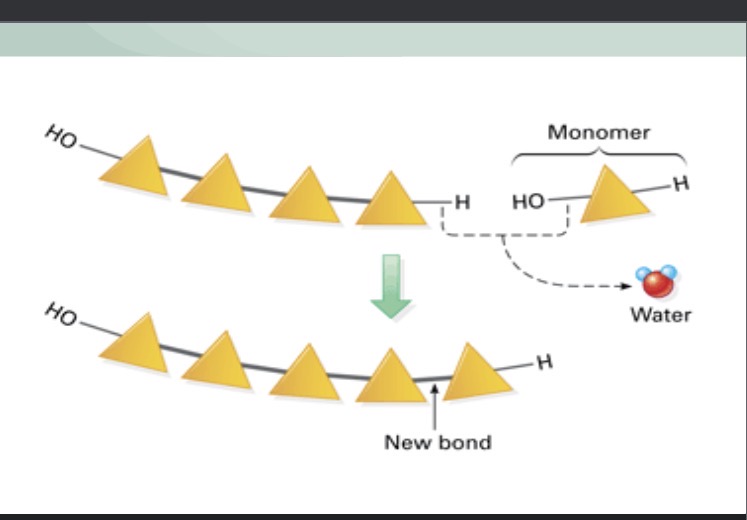
What type of reaction is this?
Dehydration reaction
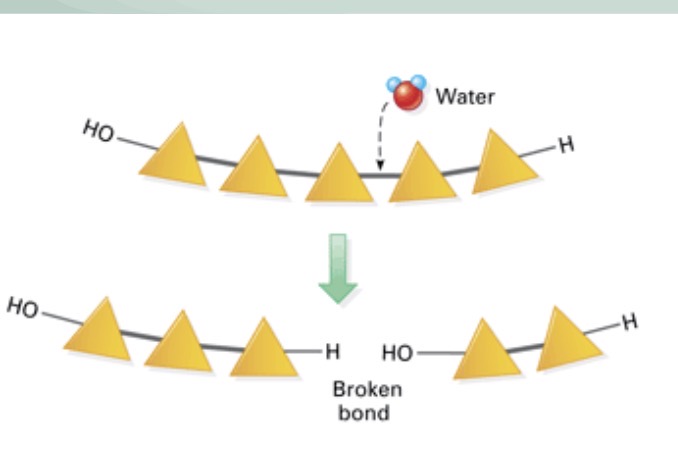
What type of reaction is this?
Hydrolysis reaction
Carbohydrates
Group macromolecules that are made up of sugar molecules
What are carbohydrates composed of?
Carbon, hydrogen,oxygen
What is the ratio of carbohydrates?
1:2:1
What is example of a carbonohydrates?
C6H12O6 (glucose)
What is the main function of carbohydrates in animals?
Source of energy for organisms
Whats the main function of carbohydrates for plants?
Structural purposes
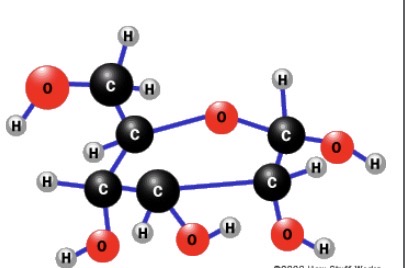
What is this?
Glucose
Monosaccharides?
Monomers of carbohydrates
What is a simple sugar?
Monosaccharide, made of one sugar unit
Disaccharide
Double sugar; constructed of two monosaccharides by dehydration
Whats a example of monosaccharides?
Glucose and fructose
Whats an example of disaccharides?
Sucrose
What are glucose and fructose?
Isomers
Isomers
Same chemical formula, but different in how atoms are arranged
Whats the difference between fructose and glucose?
They react differently and fructose is sweeter
Do isomers react differently with other molecules?
Yes
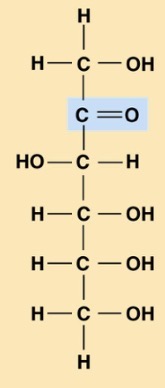
What is this?
Fructose
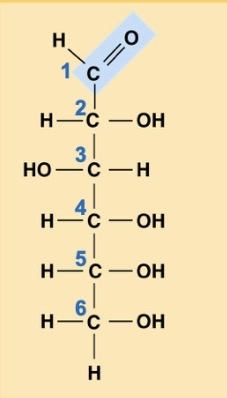
What is this?
Glucose
How are disaccharides formed?
By joined two monosaccharides together through a dehydration reaction
Polysaccharides
Complex carbs; a long polymer chain made up of many monosaccharides
How is a polysaccharide formed?
Dehydration synthesis
Example of polysaccharides?
Cellulose, starch, glycogen
Starch
Made entirely of glucose monomers linked in a straight chain
What does starch serve?
Sugar stockpiles for plants to break down for energy
What is starch only found in?
Plants

What is this?
Glucose
What is starch made up of?
Glucose
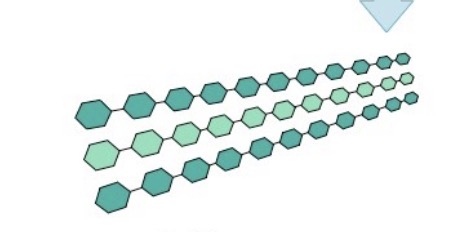
Glycogen
Made entirely of glucose monomers; more highly branched than a starch polymer
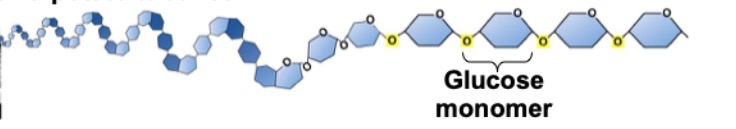
What is this?
Starch
Where is glycogen found?
The liver and muscle cells
Where is glycogen only in?
Animals
What does glycogen do?
How sugars are stored in animal cells
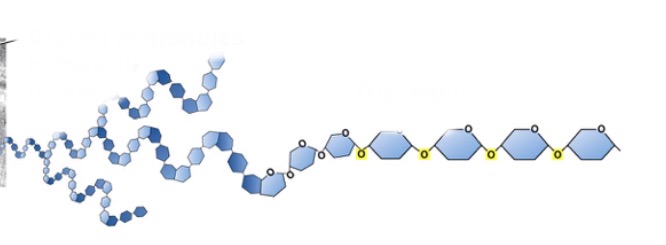
What is this?
Glycogen
Cellulose
Made entirely of glucose monomers linked- multiple chains are linked together forming a cable like structure
What does cellulose serve?
Building materials to protect the cell and stiffen the plant
What is cellulose found in?
Plants
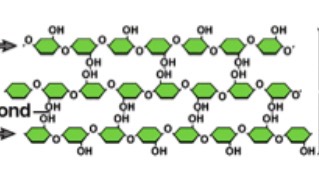
What is this?
Cellulose
Chitin
Important component of arthropod exoskeletons and fungal cell walls
Why cant most animals not digest cellulose (fiber)?
It passes right through their digestive system
What do microorganism inhabiting your digestive tracts help do?
Break down cellulose
How many sugar molecules does a monosaccharide have?
One
How many sugar molecules does a disaccharide have?
Two
How many sugar molecules does a polysaccharide have?
Many
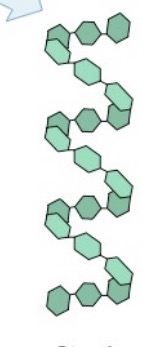
What is this?
Starch
What is this?
Cellulose
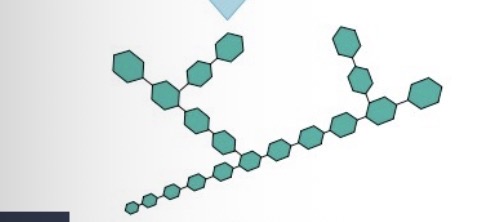
What is this?
Glycogen
Where is glycogen?
Granules
Where is cellulose?
Cell wall
Where is starch?
Granule

What is this?
Cellulose
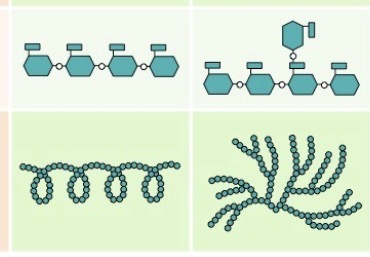
What is this?
Starch
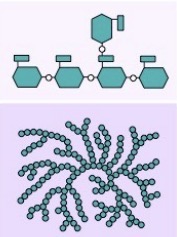
What is this?
Glycogen
Lipids
Groups of macromolecules that are known as fats
What are lipids mainly composed of?
Carbon and hydrogen and sometimes oxygen
Hydrophobic
In nature - not soluble in since they are nonpolar molecules
What is phospholipids structure?
A hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
What are lipids functions?
Storing energy, water proofing surfaces and important parts of biological membranes
What is a larger lipid molecule?
Fats
What is the building block of fats?
3 carbon backbone (glycerol) and 3 fatty acids
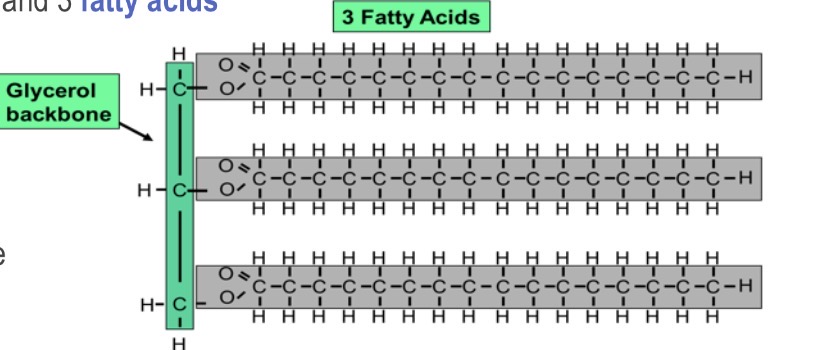
What is this?
Triglyceride
What is a triglyceride?
Major form of fat storage in the body
What links a fatty acid to a glycerol?
Dehydration reaction
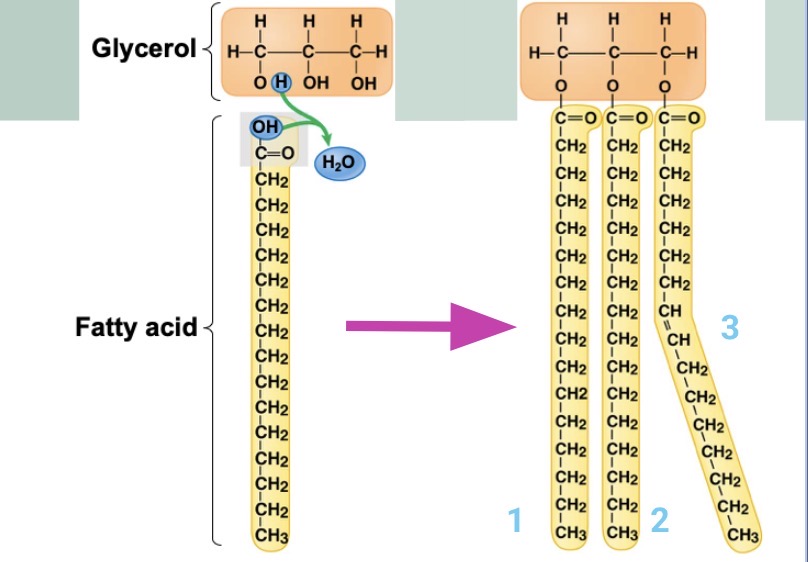
What is this?
How triglyceride is formed

What is this?
How triglyceride is formed
Unsaturated fatty acid
Structure contains one or more double bond; liquid at room temperature
Example of unsaturated fatty acid?
Olive oil, vegetable oil