Rad Tech unit 2 Exam
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Attenuation
The process by which a beam of x-ray photons is reduced as it passes through matter is known as:
Photostimulable phosphor plate (PSP)
Computed radiography uses which of the following as its image receptor:
125
What mAs value would result using the 500 mA setting at 0.25 secs:
130
A radiograph is made using 40 mAs at a 40 inch SID. If the image must be repeated at a 72 inch SID, what mAs value is necessary to maintain the same exposure?
kVp
The 15% rule helps explain the effect of ____ on exposure
X-ray Tube
The component of the radiographic system that produces radiation is the:
Operator control console
The control of exposure factors such as mAs and kVp is performed at the:
Anode and Cathode
The primary components of the x-ray tube are the:
Fluoroscopy
It permits “real time” imaging of dynamic patient functions
Modern-day fluoroscopy systems record images electronically rather than using cassettes
Dose reduction features such as last image hold (LIH), pulsed fluoroscopy, and electronic shuttering are essential.
What is necessary for x-rays to be produced
A source of electrons
Rapid particle acceleration
Instantaneous deceleration
Photoelectric interaction
The interaction of x-rays with matter that constitutes the greatest hazard to patients in diagnostic radiography is:
14 mR
The intensity of radiation from a radiographic tube was 35 mR at a distance of 2.5 m from the tube. What would the intensity be at a distance of 4 m from the tube, if all other factors remained the same?
200 rem
An exposure of 2 Sv is received. How many rem is this equivalent to?
The Photoelectric Effect
Lead absorbs x-rays through the process of ____.
X-Ray Production Requirements
1. X-ray tube with a vacuum inside
2. Source of electrons (from a filament)
· Cathode
3. Method to accelerate electrons to great speed
· Voltage (kVp)
4. Method to stop electrons
· Target
· Anode
<1%
What % of electrons hit the target are actually produced in to x-rays?
Primary radiation
is the first initial one out of the tube (air only)
Scatter radiation
went in a different direction
Absorbed radiation
in the patient’s body
Remnant radiaton
what is left after the patient has absorbed some/ goes to make image
Attenuation
is the loss of radiation energy as a result of passing through an absorbing material, such as the human body
radiopaque
High attenuation occurs in what kind of matter (whiter)
radiolucent
Low attenuation occurs in what kind of matter (able to go through easier, darker area)
Film-Screen radiography
· Uses x-rays to create a permanent image on a piece of polyester film
· Consists of x-rays directed at a radiographic cassette with an intensifying screen
· Intensifying screens convert the x-ray energy to light, and light energy creates chemical changes in film
· Needed to be processed in a dark room
Computed Radiology (CR)
· Still needs a reader to process the image
· Aka: Cassette-based DR
· Filmless
Digital Radiography (DR)
· Cassette-less system
· Direct capture
· Indirect Capture
· Most popular
Photographic Qualities
how good it looks
Geometric Qualities
should look a certain way
Photogenic Qualities: Image Density (Intensity)
· The overall darkness or blackness of an image
· Directly related to x-ray exposure hitting the receptor
· Primarily affected by milliamperage (mA), exposure time (S), source-to-image (SID)
mA is a Primary Factor of Density
· mA represents the quantity of x-ray production
· Direct relationship (if you turn the mass up, it gets darker)
· mAs is calculated by simple multiplication of mA and seconds
· Regardless of the mA and time combinations, the same mAs value will yield the same exposure
· mAs reciprocity law
Kilovoltage Peak (kVp)
· controls x-ray beam penetration
· Quality
· Direct relationship
· X-ray beam is polyenergetic or heterogenous
· 15% rule
Distance
· Displayed as source-to-image distance (SID)
· X-ray production is similar to a point light source (flashlight)
· Behaves according to the laws of light and intensity as a function of distance
· Inverse square law
Grids
· Used to reduce the amount of scatter radiation reaching the image receptor= Scatter Control
· Intercept a portion of the remnant radiation
· Improve image quality.
Exposure Index (EI)
· A numeric (quantity) representation of total x-ray exposure to the receptor
· Not an indicator of the patient’s absorbed dose
· Values can vary greatly among manufacturers= different results have different #s per brand
· S#
· In the future: Deviation Index (DI) will be used to measure patient exposure used by the radiographer
Geometric Qualities
· Contribute to image quality by affecting.
-image resolution (clarity), size, and shape
· Also known as recorded detail, sharpness of detail, and definition
· Complemented by visibility of detail, which is a photographic property
Factors Affecting Recorded Detail:
· Motion
· Object unsharpness
· Focal spot size
· SID
· Object-to-image distance (OID)
· Material unsharpness
· Distortion
Distortion
Any misrepresentation of the true size or shape of the patient’s anatomy as demonstrated on the radiographic image
Size distortion
· The image is always slightly larger than the actual object size
· Known as true size distortion, its minimized by using longer SIDS and minimum OIDS
· Magnification
· Reduce OID to avoid
Shape distortion
· Elongation
· Foreshortening
· Any misrepresentation of the true shape of the patient’s anatomy
· Also called true distortion
· Controlled it:
-Align central ray, patient’s anatomy and IR
· May be deliberate to deal with superimposed structures
Elongation
shape distortion resulting form improper alignment of the Image receptor
Foreshortening
shape distortion resulting from improper alignment of the part
Fluoroscopy
· Use of x-rays to create real-time images of patient anatomy and function
· Patient exposures are much MORE (higher) than radiographic exposures
· Requires a radiographic/fluoroscopic (R/F)
· Physicians can observe the body’s physiologic actions
Diagnostic Yield:
how much good quality info can be gained from the exam or test ordered
· Why one modality is chosen over the other
· Dictated by the ACR considerations
Diagnostic Efficacy
The accuracy of diagnostic info on a medical image is its
X-Ray machine design features
· X-ray and x-ray tube support
· Collimator assembly- holds the tube
· Radiographic table-
· X-ray generator and control
· Upright image receptor
X-ray tube design
· Tube is inside the lead- lined tube housing
· Made of Pyrex Glass with High vacuum
· Produces x-radiation when high-energy electricity passes through
Collimator Assembly
· Controls the size and shape of the x-ray field directed toward the patient
· Projects high intensity light field on the patient, which represents the area of the x-ray field exposure
· May be manual or automatic/positive beam limitation (PBL)
Radiographic Table
· May be fixed height or variable height
· Typically has a four way “floating” tabletop
· Tabletop is highly Radiolucent (doesn’t stop radiation)
· Some table designs permit a carriable- speed, tilting capability
Tilting Radiographic Table
· Utilized in Fluoroscopy
· These designs will tilt the table from horizontal position to vertical upright position to Trendelenburg
· Most tables have four-way tabletop travel
· These tables typically do not have variable height capabilities
Bucky Assembly
· Consists of a receptor tray and radiographic grid
· Used with Film Screen and computed radiography systems
· The grid spins to blur out the lead grid lines
Upright Bucky assembly
· Upright Bucky with lateral chest support arm
Generator Control (control console)
· Control console is the interface between the radiographer and the sophisticated electronics of the x-ray machine
· Set all the numbers, where all the info comes from
X-ray Tube supports
· Two basic designs
· Facilitate easy and efficient positioning of the x-ray tube assembly around the patient in any orientation
· Ergonomic (comfortable) Friendly
· Capable of various motions depending on need
· Detents (areas where it wants to lock into place) says you are in the right spot
Image receptors (IR):
· Cassette- based systems
· Film-screen
· Computed radiography (CR)
Digital Radiography (DR) systems
Referred to as flat panel technology
DR systems use thin-film transistors (TFTs)
· Indirect digital detector technology
· Direct digital detector technology
Fluoroscopy
· Dynamic imaging
· Provides live, real-time images of patients using x-rays
· Used for a wide array of diagnostic procedures
Mobile (C-Arm) Fluoroscopy system
· Used in surgery and interventional exams
· Uses a C-arm design
· Image receptor is at a fixed SID and centered to x-ray tube
Mobile X-ray imaging (Portables):
· Mobile radiographic units are used extensively in hospitals
· Bring into patient’s room
· Needs to be charged
· Easier on the patient
Incident (primary) X-ray
is the x-ray that comes from the x-ray tube
Coherent Scattering:
X-rays with energies BELOW 10 keV (low energy)
No ionization occurs due to no energy transfer
Called
Classical Scattering
Thompson (J.J Thompson)
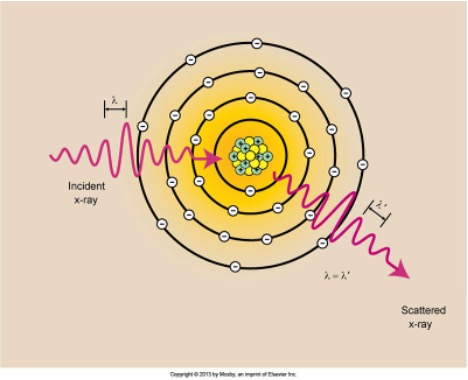
Scattered x-rays:
o Wavelength is equal to the incident x-ray
o Equal Energy to the incident x-ray
o Direction Changes
Compton Scattering:
· X-rays that occur throughout the diagnostic range
· Outer-shell electron interaction
o Ejects it from the atom
Scatters x-ray in a different direction
X-ray loses energy
Ionizes the atom
· Causes Scatter radiation to show on the image
· Tighter the ray, the more energy
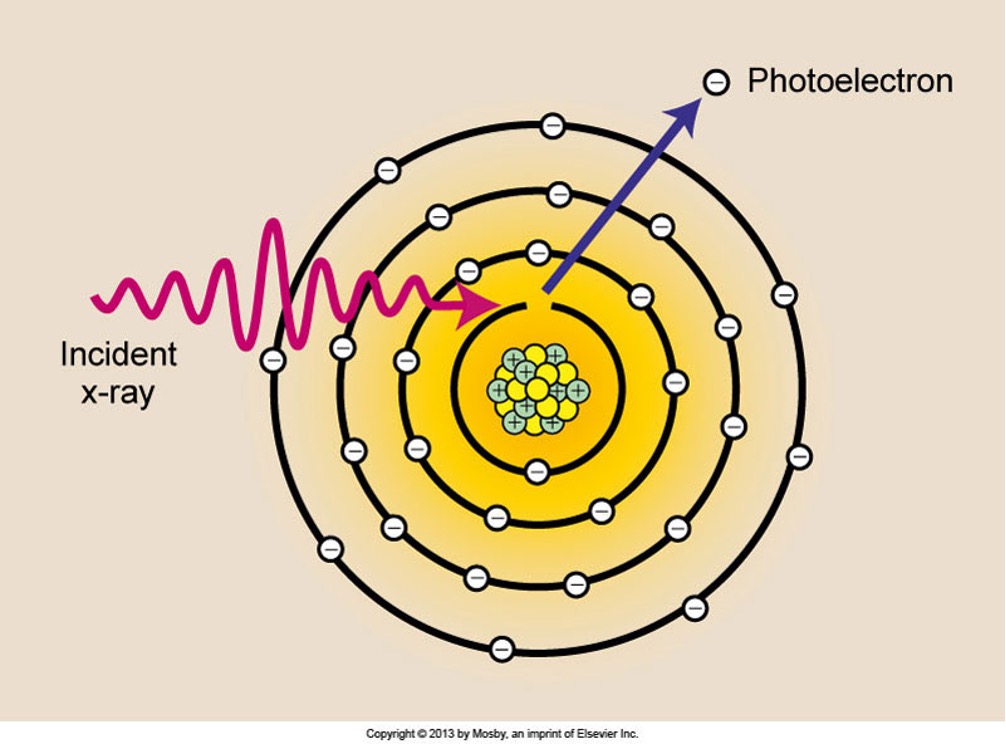
Photoelectric Effect:
· X-rays in diagnostic range
· Ionizing interactions with inner-shell electrons
· No scattering= totally absorbed
· Albert Einstein= Nobel Prize in 1921
· Photoelectron- electron that is removed from the atom
· Energy is equal to the incident x-ray and the binding energy of the electron
· Characteristic X-rays are produced after a photoelectric interaction
· Vacant k Shell
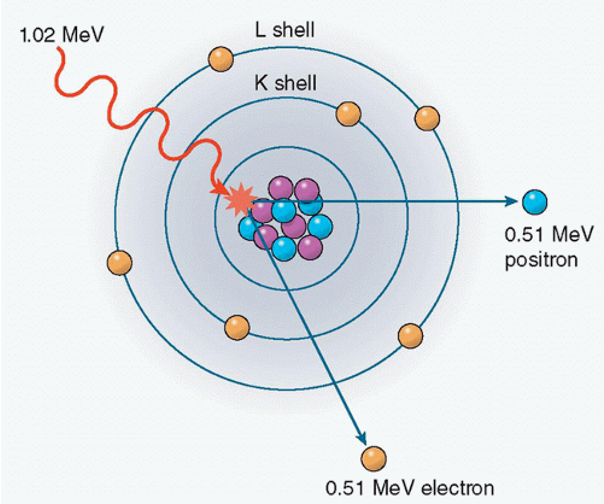
Pair Production:
· Doesn’t occur within x-rays
o Only in PET scans
· Incident x-ray has sufficient energy that comes close to the nucleus of the atom (a nuclear field)
· Causes x-ray to disappear.
o Positive charged electron (positron)
o Negative charged electron
· Annihilation Radiation: When the positron unites with a free electron and mass of both particles is converted to energy
· PET Scan: Positron Emission Tomography
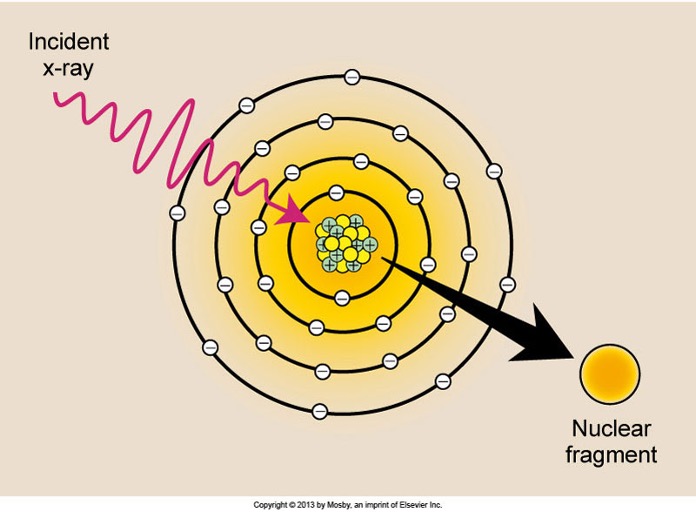
Photodisintegration:
· X-rays with energy above 10 MeV (high energy)
· Energy absorbed by the nucleus
· Doesn’t occur in diagnostic imaging
· Nucleus raised to an excited state and instantly emits a Nuclear Fragment
Roentgen
· Measures exposure in air and is not used to express absorbed dose to individuals
· A measure of ionization in air as a result of exposure to x-rays or gamma rays
Radiation Absorbed Dose
· Expressed as rad
· Measures amount of energy absorbed in any
· 1 Gy= 100 rad
· Rad has been replaced by the gray (Gy)
· Patient
Radiation Equivalent Man
· Measured as rem
· Unit of dose equivalence (dose to you as the Tech)
· 1 Sv=100 rem
Curie
· Measures the activity of a radioactive material (radionuclide)
· Used in nuclear medicine and radiation therapy
Standards of Exposure
· Standards are regulated by the FDA and its center for Devices and Radiologic Health (CDRH)
· The annual whole-body effective dose limit for the occupational worker is 50 mSv (5 rem) (5000 mrem)
· Use the Cardinal rules: time, distance, and shielding
Radiation Monitoring
· Any occupational worker is regularly exposed to ionizing radiation must be monitored to determine estimated exposure
· Any worker who is likely to receive more than one tenth of the recommended dose-equivalent limit should be monitored
Occupational Personnel Monitoring
· Monitors/measures the quantity of radiation received on the basis of conditions in which the radiographer was placed
· Worn at the collar level
· Worn outside of lead apron
· Decide should face forward
· Pregnant radiographers may have a second device worn at waist level and under the apron
Coherent Scattering:
Compton Scattering:

Photoelectric Effect:
Pair Production:
Photodisintegration:
PACS (picture archiving and communication system)
used to securely store and digitally transport electronic images and clinically reverent reports
eliminates the need to manually file and store things
HIS (hospital Info system)
improves efficiency and effectiveness of patient care
stores, manages and captures info related to activities of patients and statistical data
RIS (radiology info system)
networked software system for managing medical imagery and associated data
tracks imaging order and billing info
PBL (positive beam limitation)
the automatic or semiautomatic adjustment of an x-ray beam to the size the selected image receptor, whereby exposures can’t be made without such adjustment
OTC (overhead tube crane motions)
transverse, vertebral, longitudinal movements
AEC ( Automatic Exposure control)
density control decide that terminates the exposure when a predetermined amount of radiation has been reached
ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable)
competent imaging professionals will strive to maximize diagnosis yield using a minimum of output factors
Bq (becquerel)
SI unit of activity
Ci (curie)
measures the activity of radioactive material
Gy (gray)
1Gy=100rad
R (roentgen)
unit measures radiation exposure
Sievert
1sv=100rem
rad (radiation absorbed dose)
measures the amount of energy in the patient