Demonstrate how conditions affect chemical reactions.
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
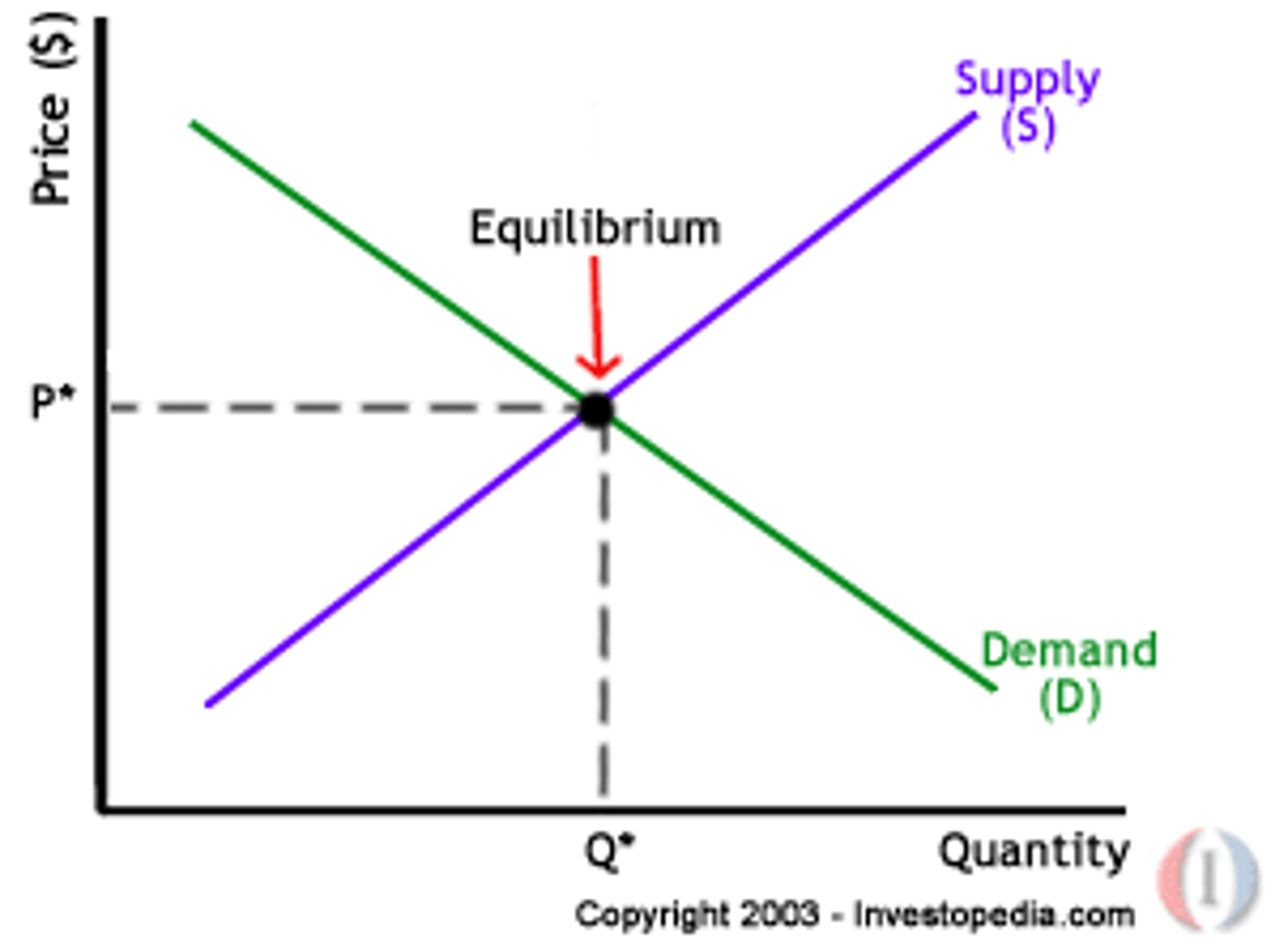
equilibrium
the stage of a chemical reaction in which both reactants and products are present and their concentrations no longer change.
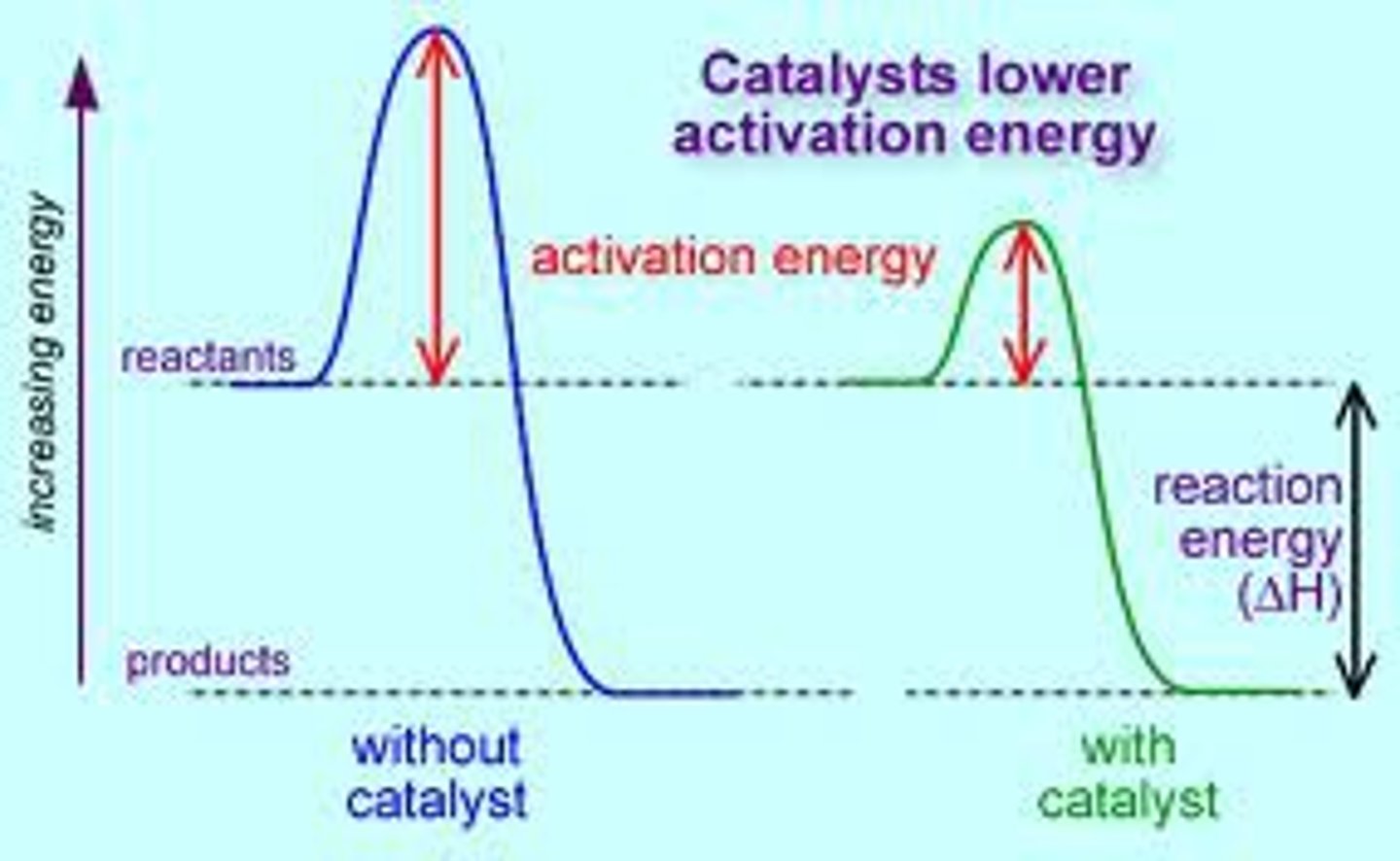
catalyst
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing permanent chemical change by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
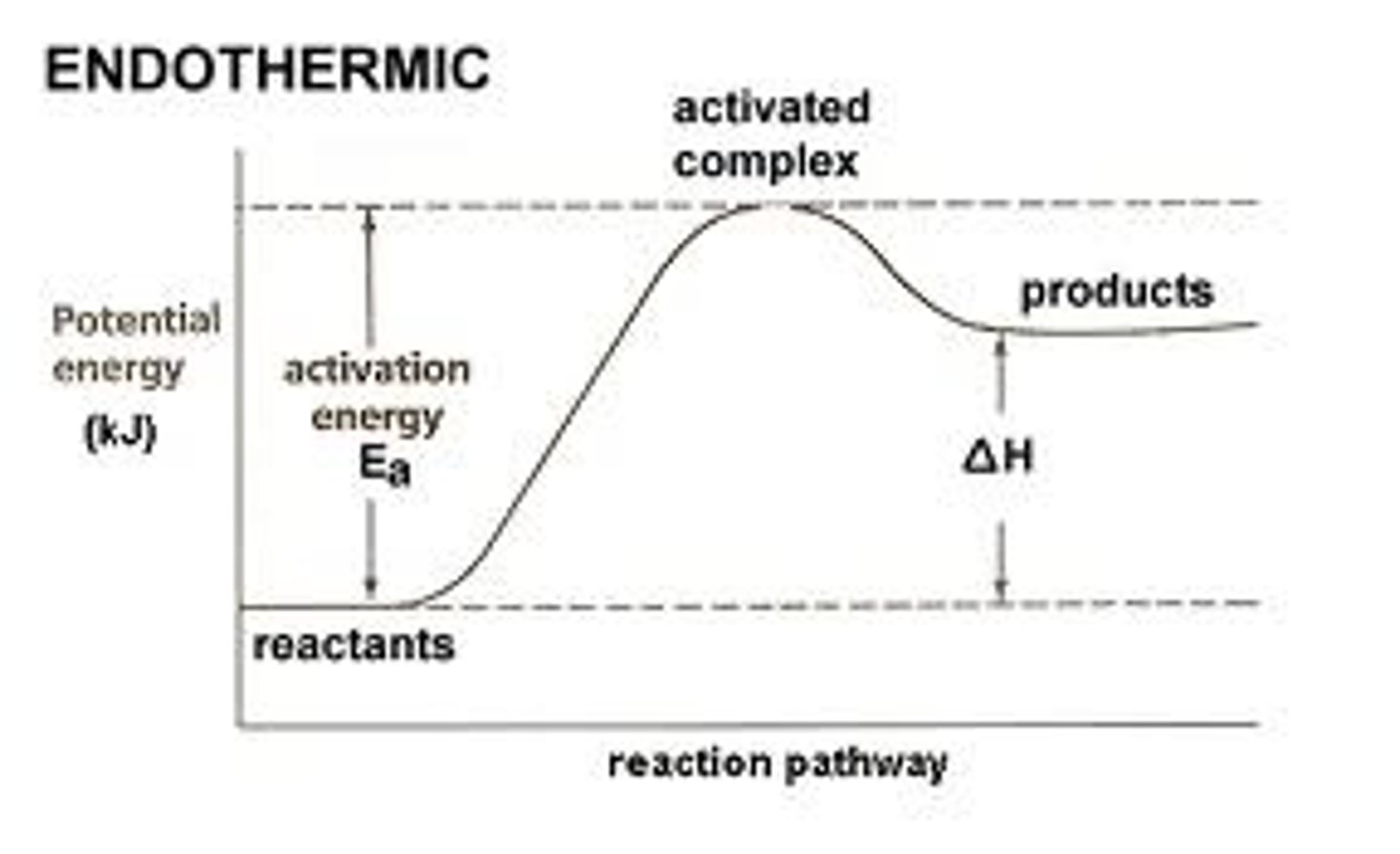
endothermic
involving absorption of heat.
exothermic
involving release of heat.
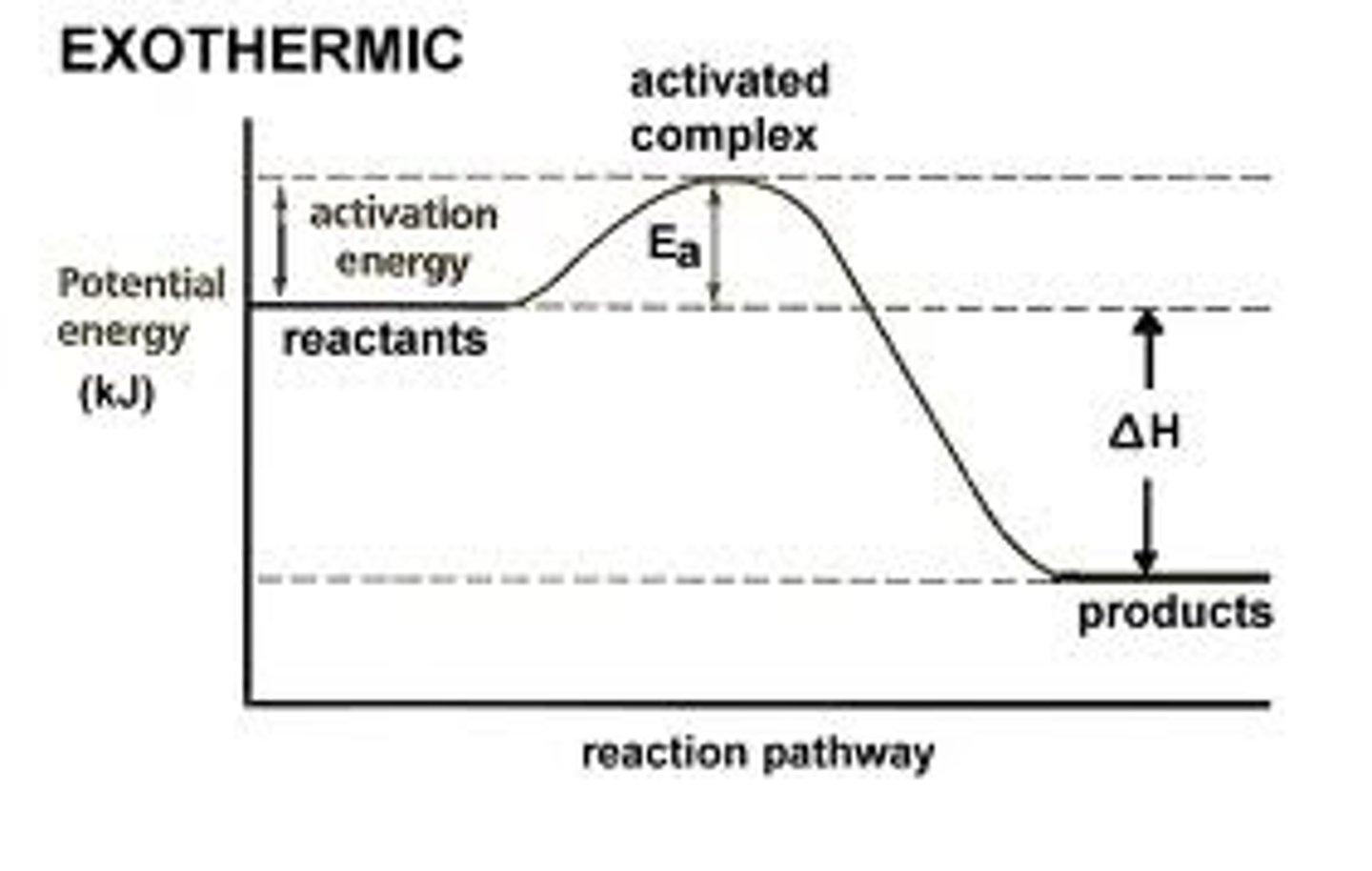
changing factors such as
pressure, concentrations of reactants and products, temperature, and the presence of catalysts, will change the speed of a reaction
when temperature rises,
the rate of an ENDOTHERMIC reaction (where heat is required) will increase. However, when temperature rises, an EXOTHERMIC reaction (where heat is released) will slow down.
increasing the pressure surrounding a gas phase reaction
increases the chance of collisions between atoms and molecules.
-this will increase the rate.
Increasing concentration of reactants
increases the probability that reactants will come in contact with each other, thus increasing the likelihood of breaking or creating a bond.
-concentration increased, the reactions will slow down.
YOUTUBE CHEMICAL EQUILBIRIAL REACTIONS
PRACTICE CHEMICAL EQUILBIRIAL REACTIONS.
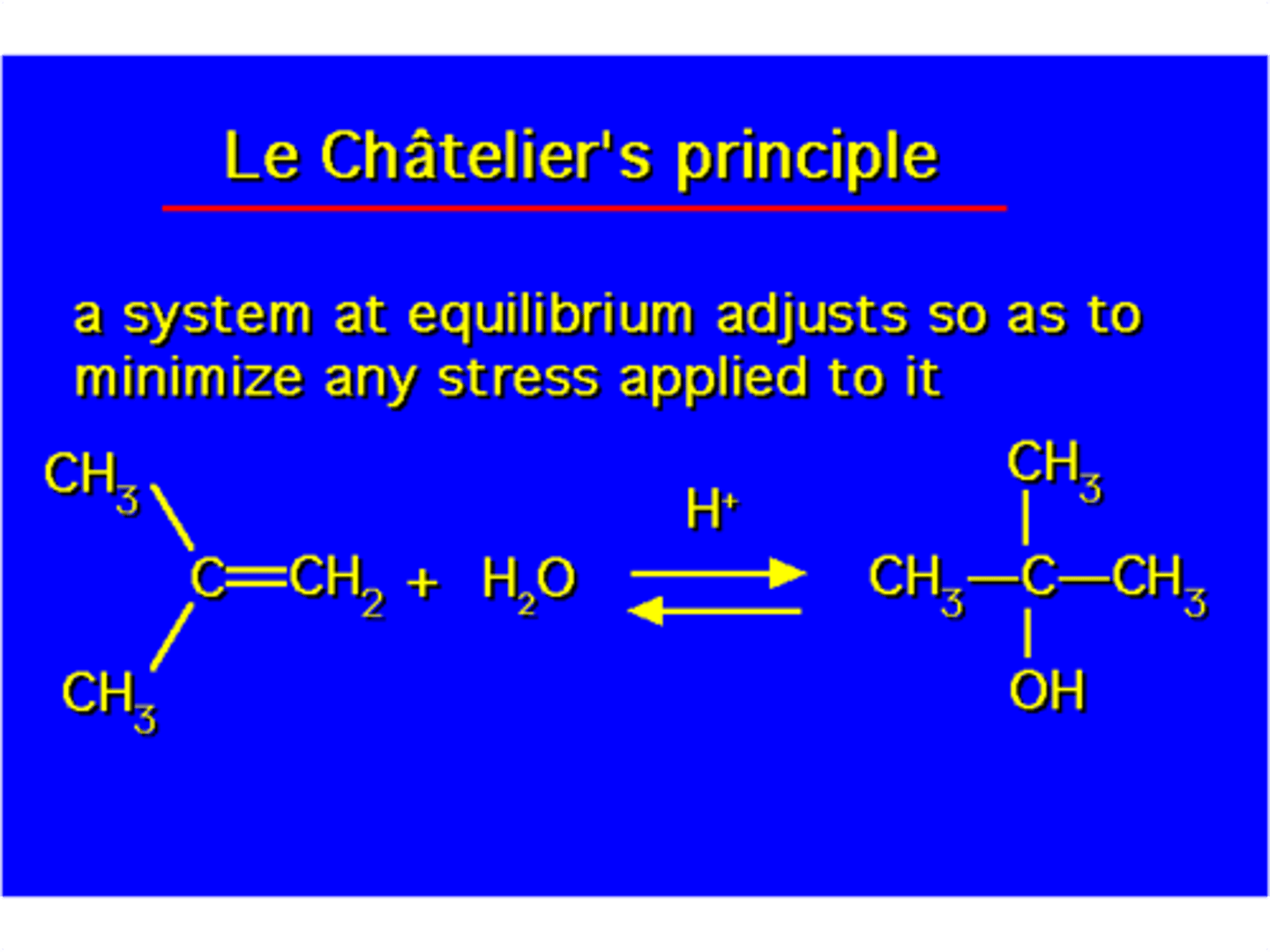
Le Chatelier's Principle
a principle stating that when a chemical reaction at equilibrium is perturbed, it responds by proceeding in a direction that will restore the equilibrium.
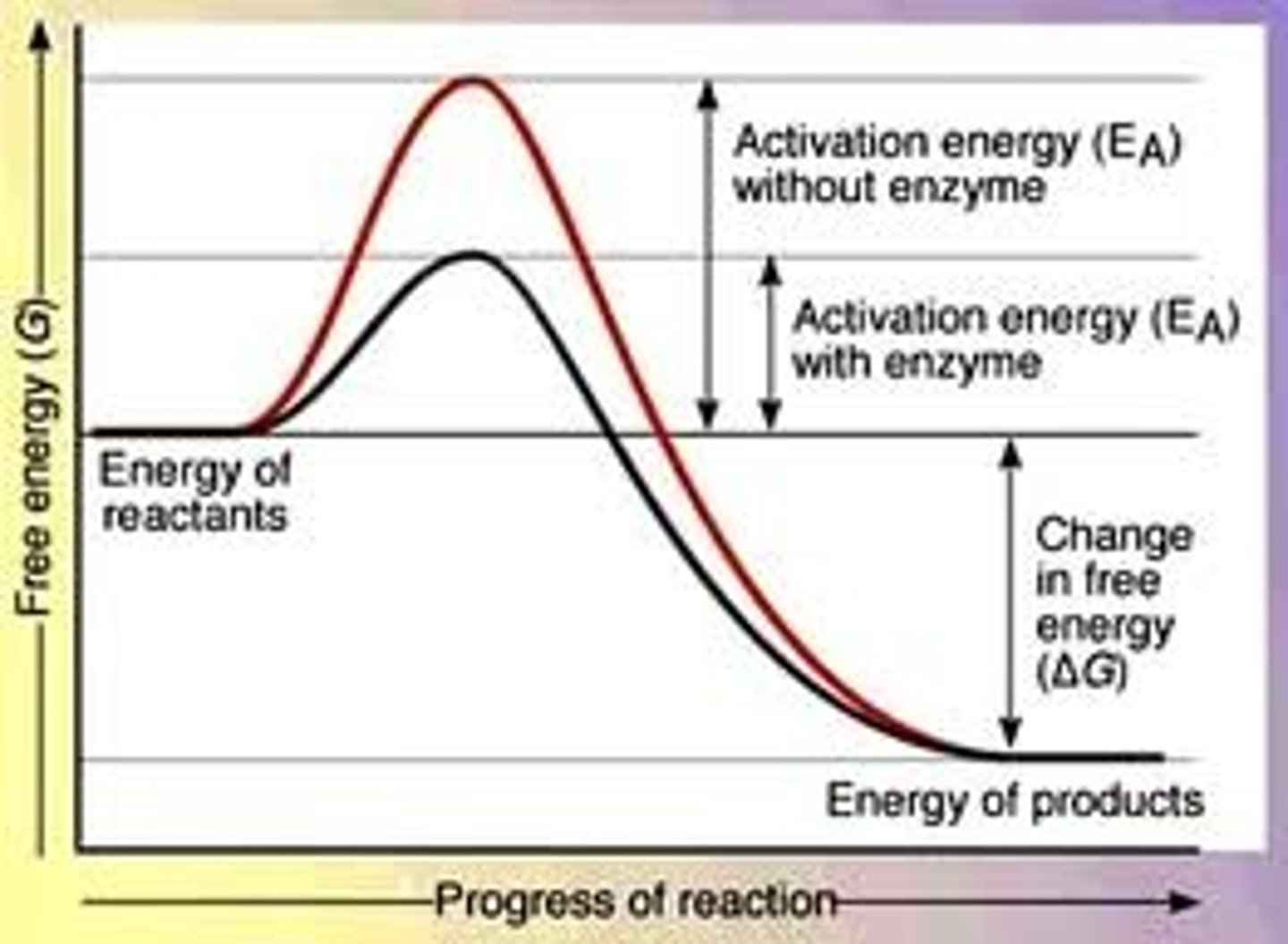
activation energy
the minimum energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction.