Structural Kinesiology Quiz 5 Part 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
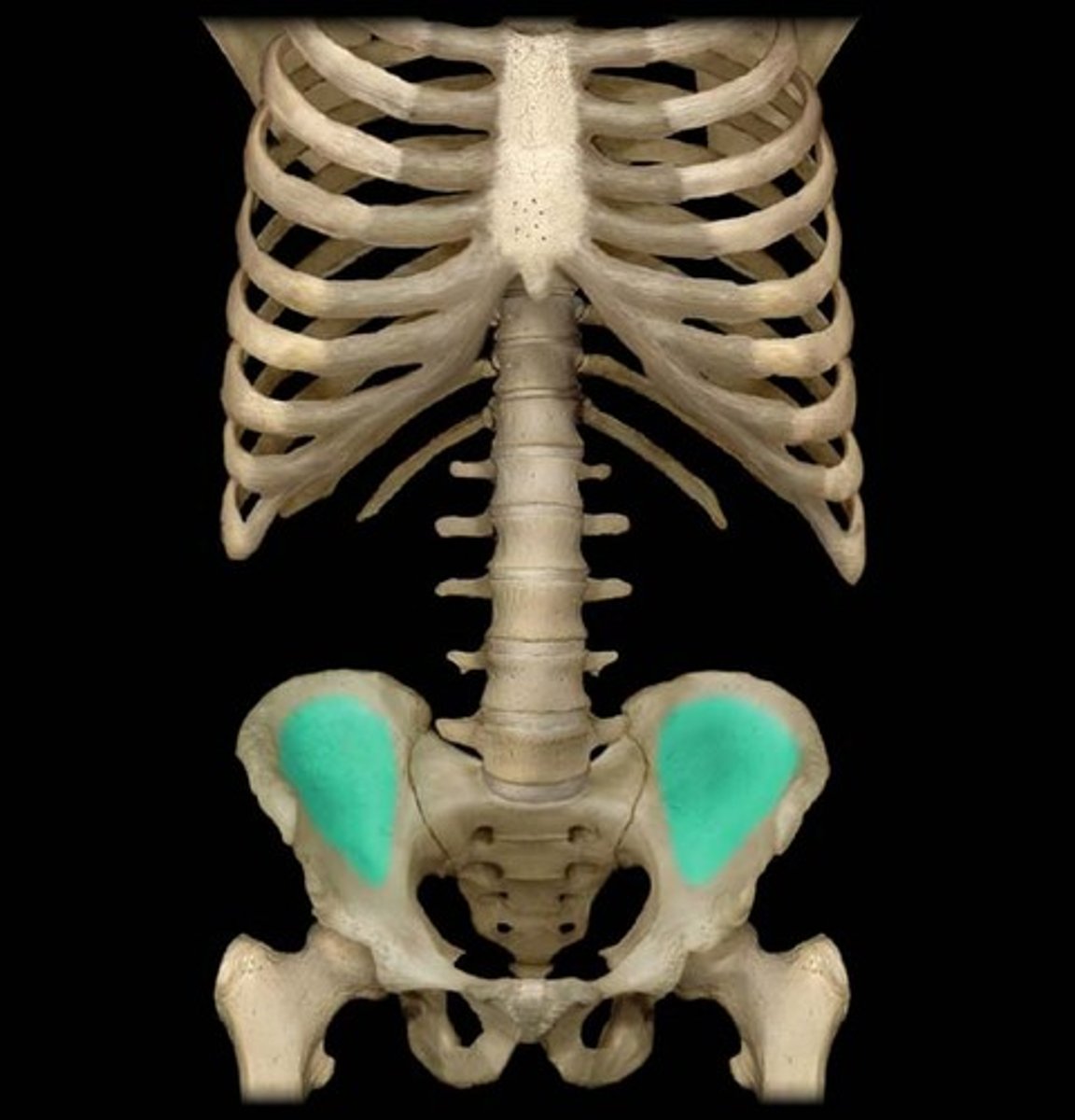
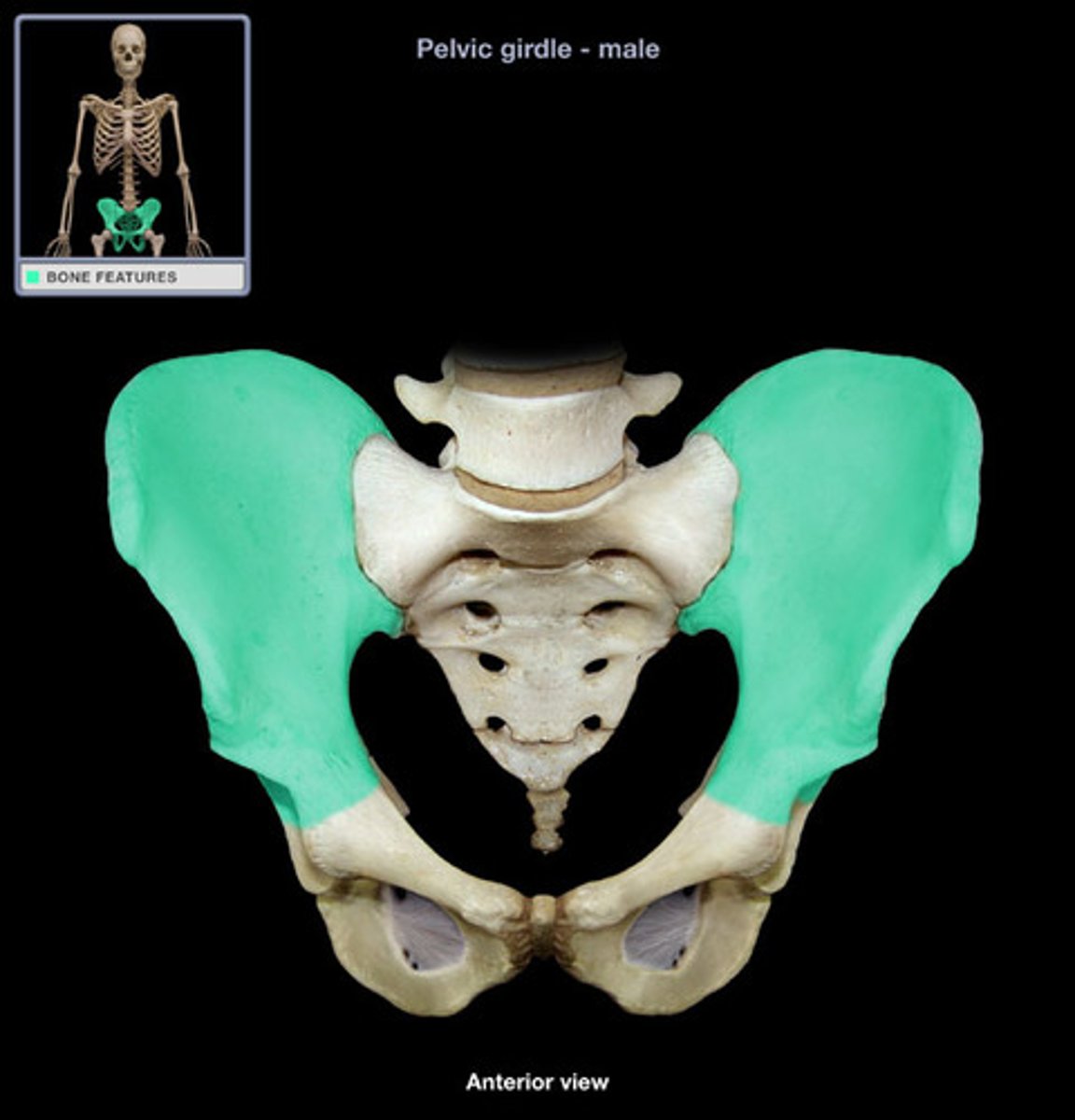
iliac crest
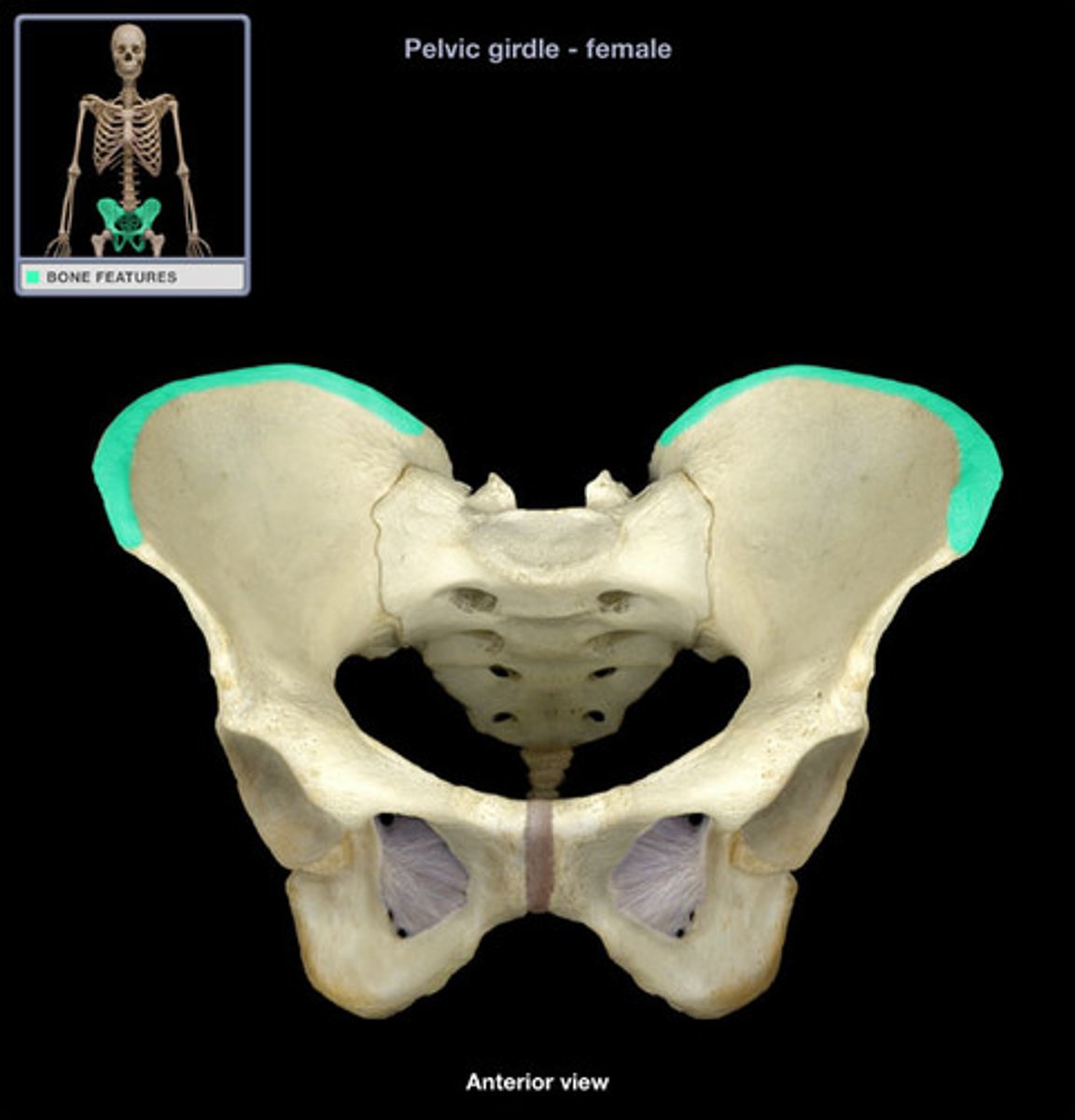
iliac fossa
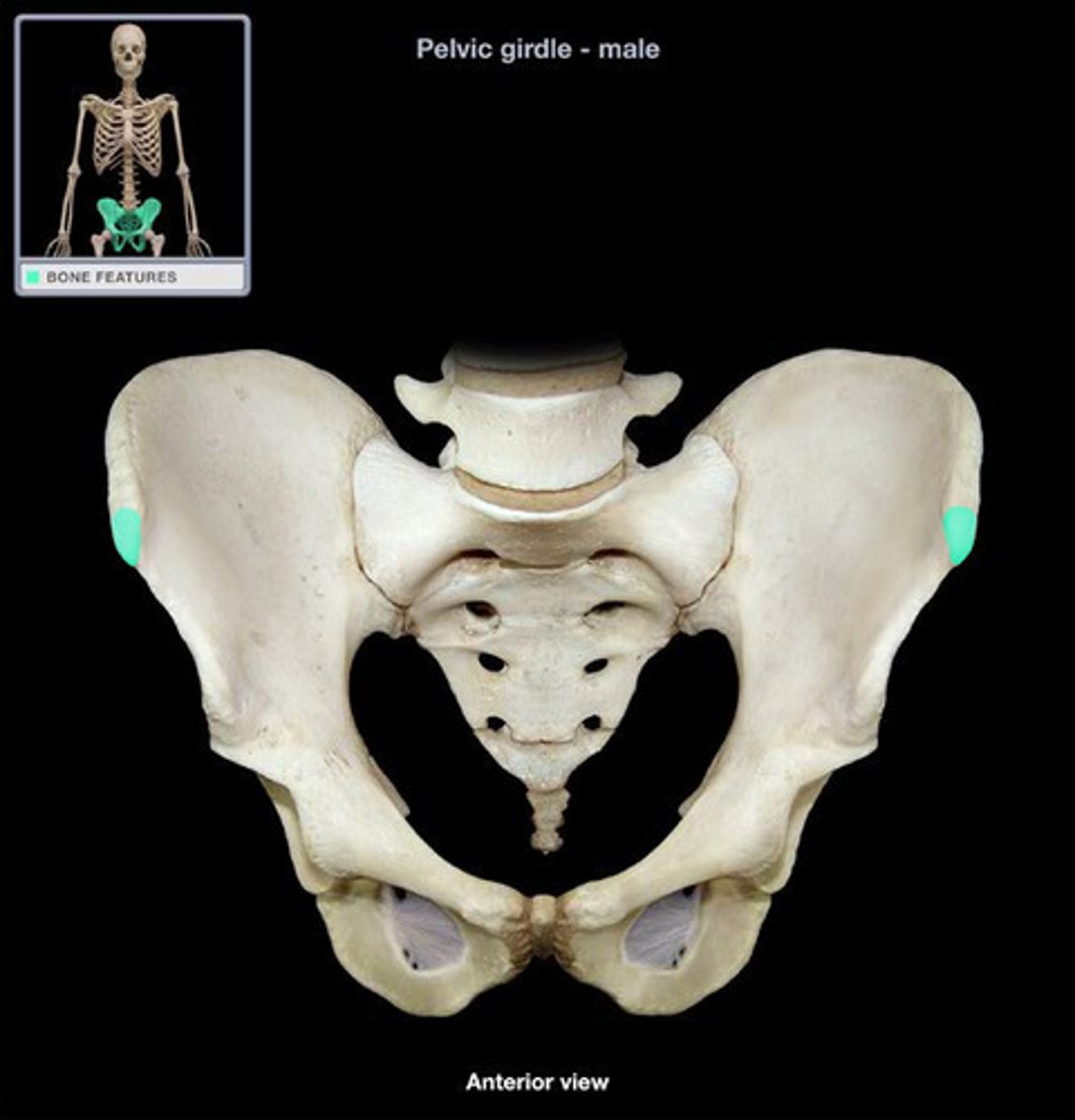
anterior superior iliac spine ASIS
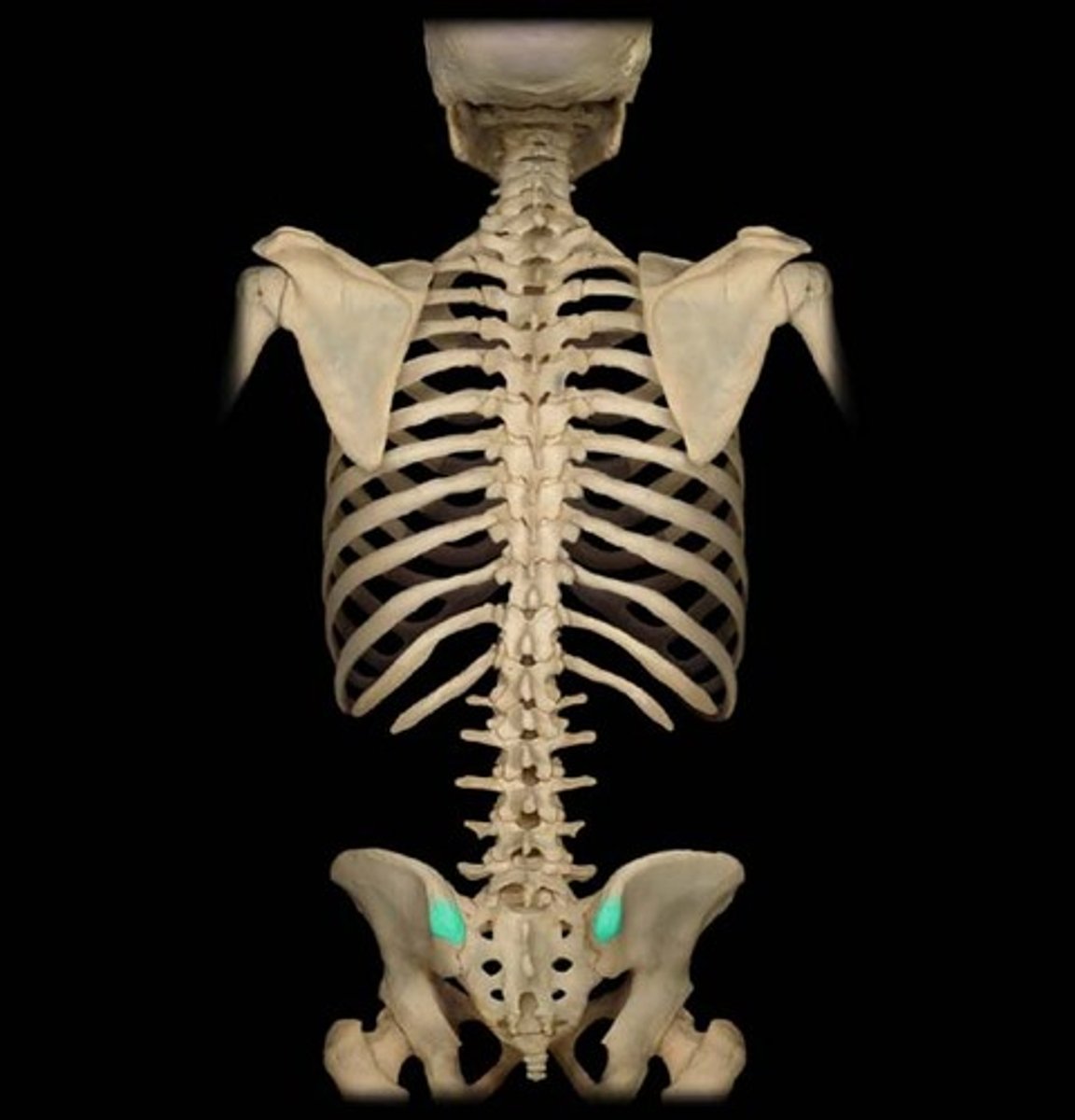
Posterior superior iliac spine PSIS
Anterior Inferior Iliac spine AIIS
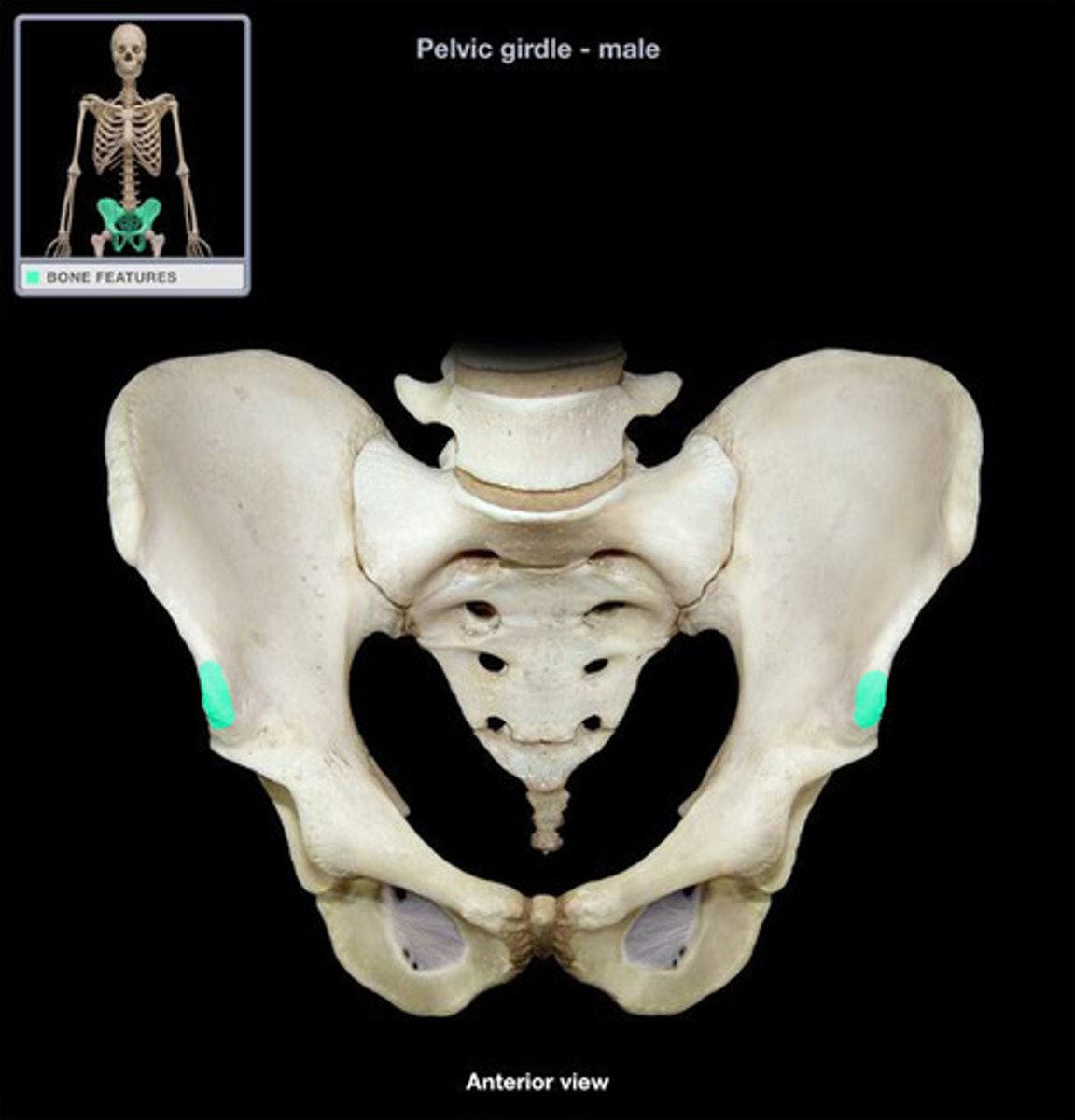
Posterior inferior iliac spine PIIS
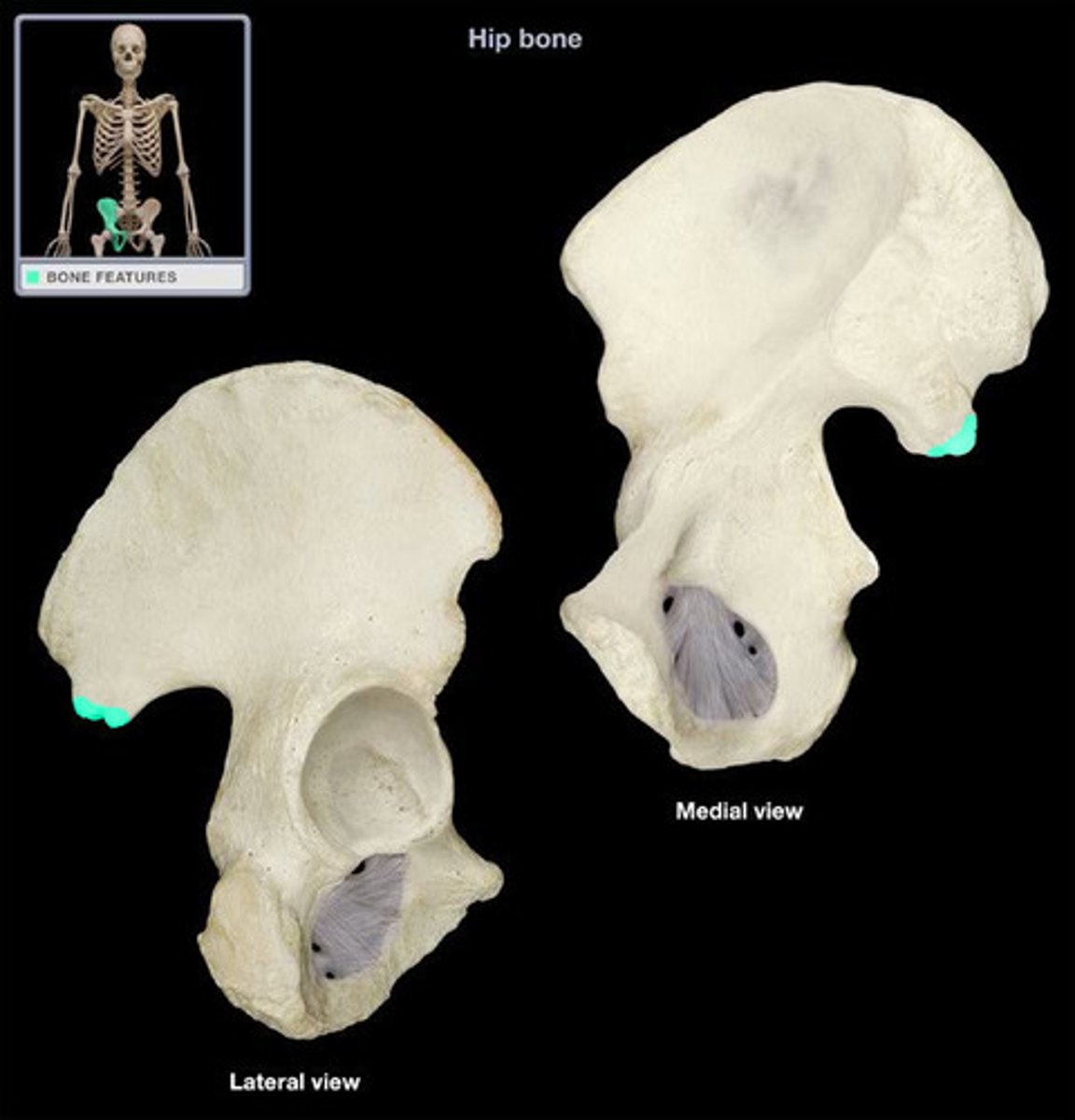
ilium
ischium
pubis
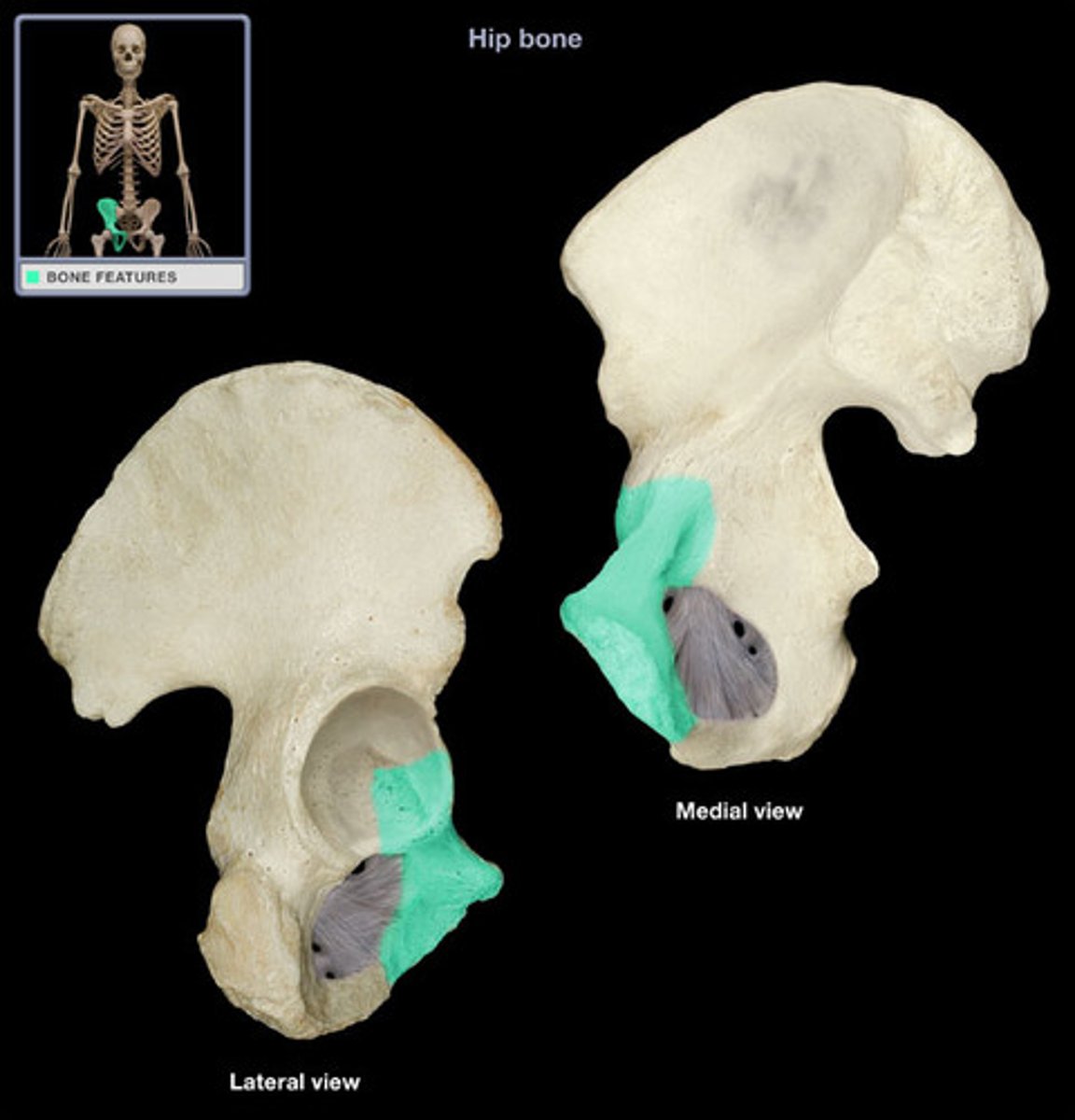
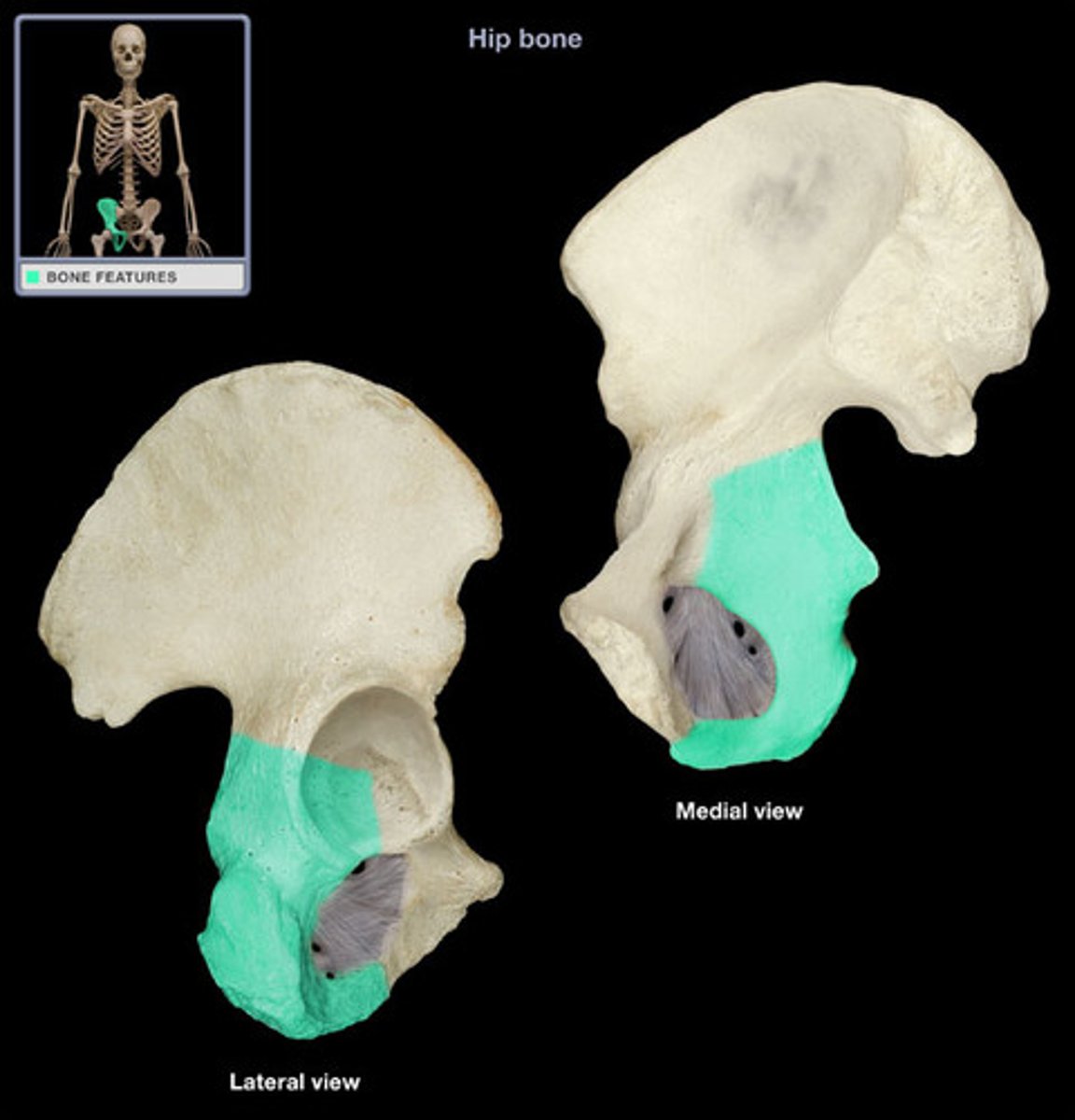
acetabulum
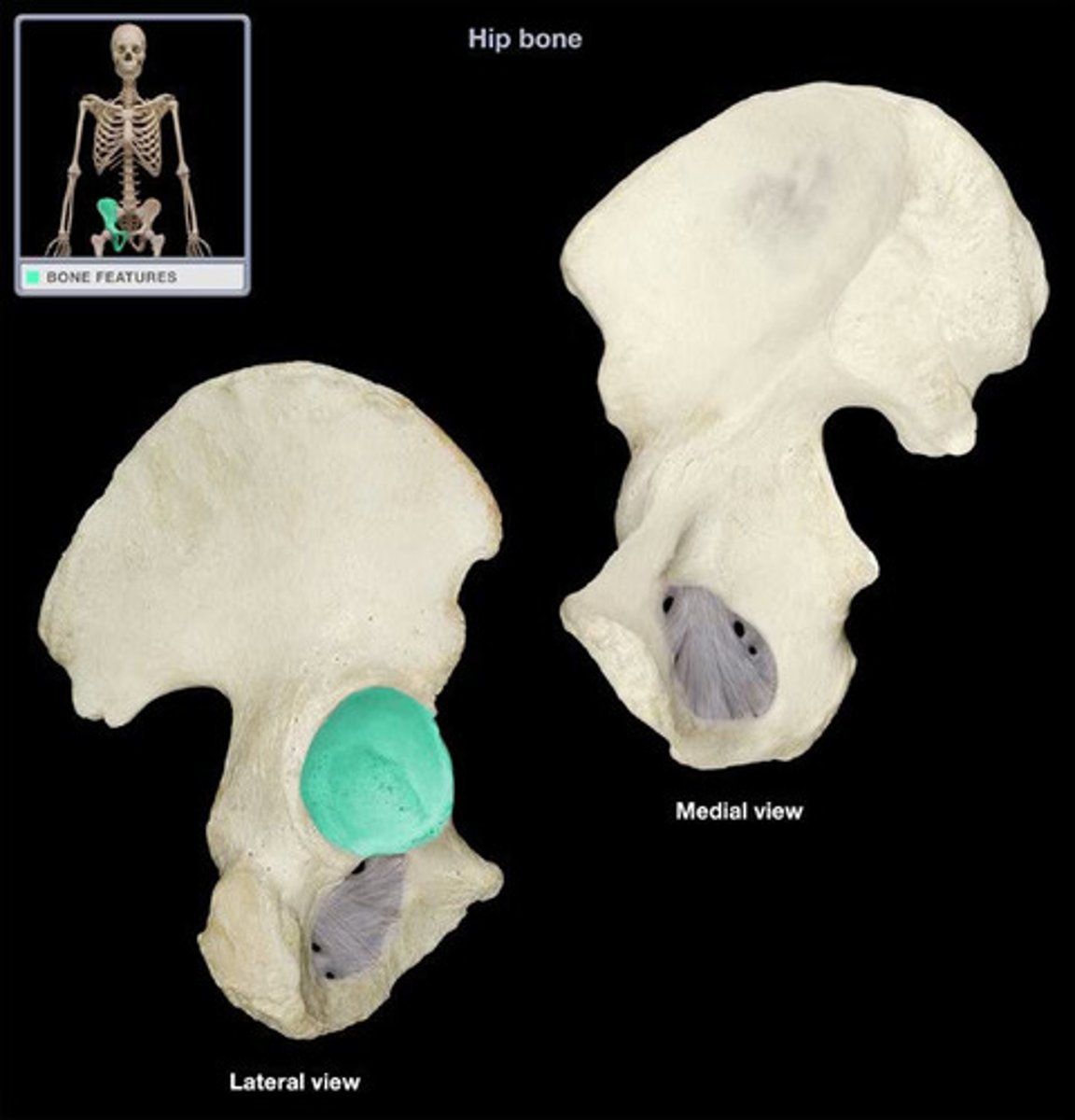
ischial tuberosity
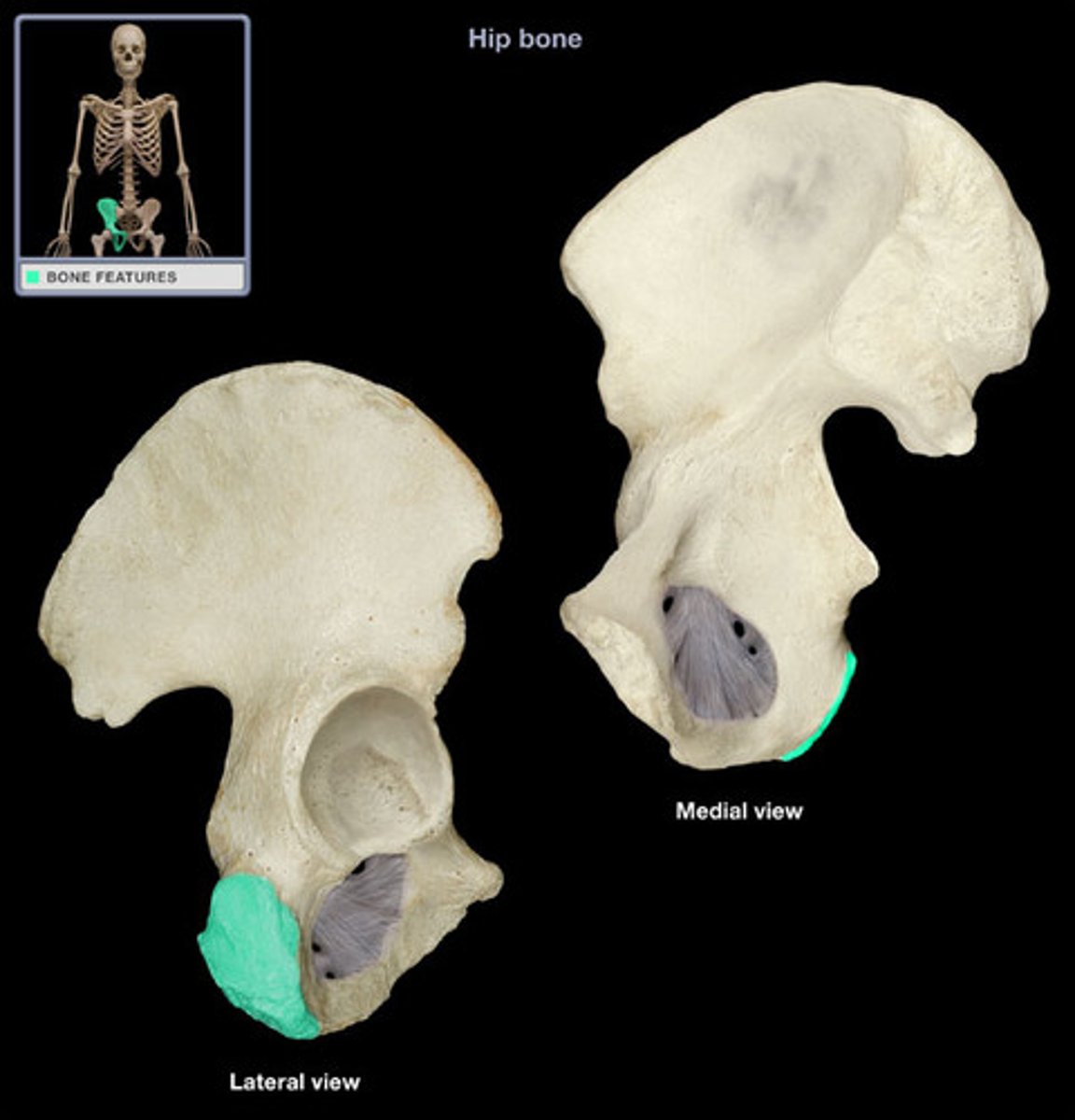
ischial spine
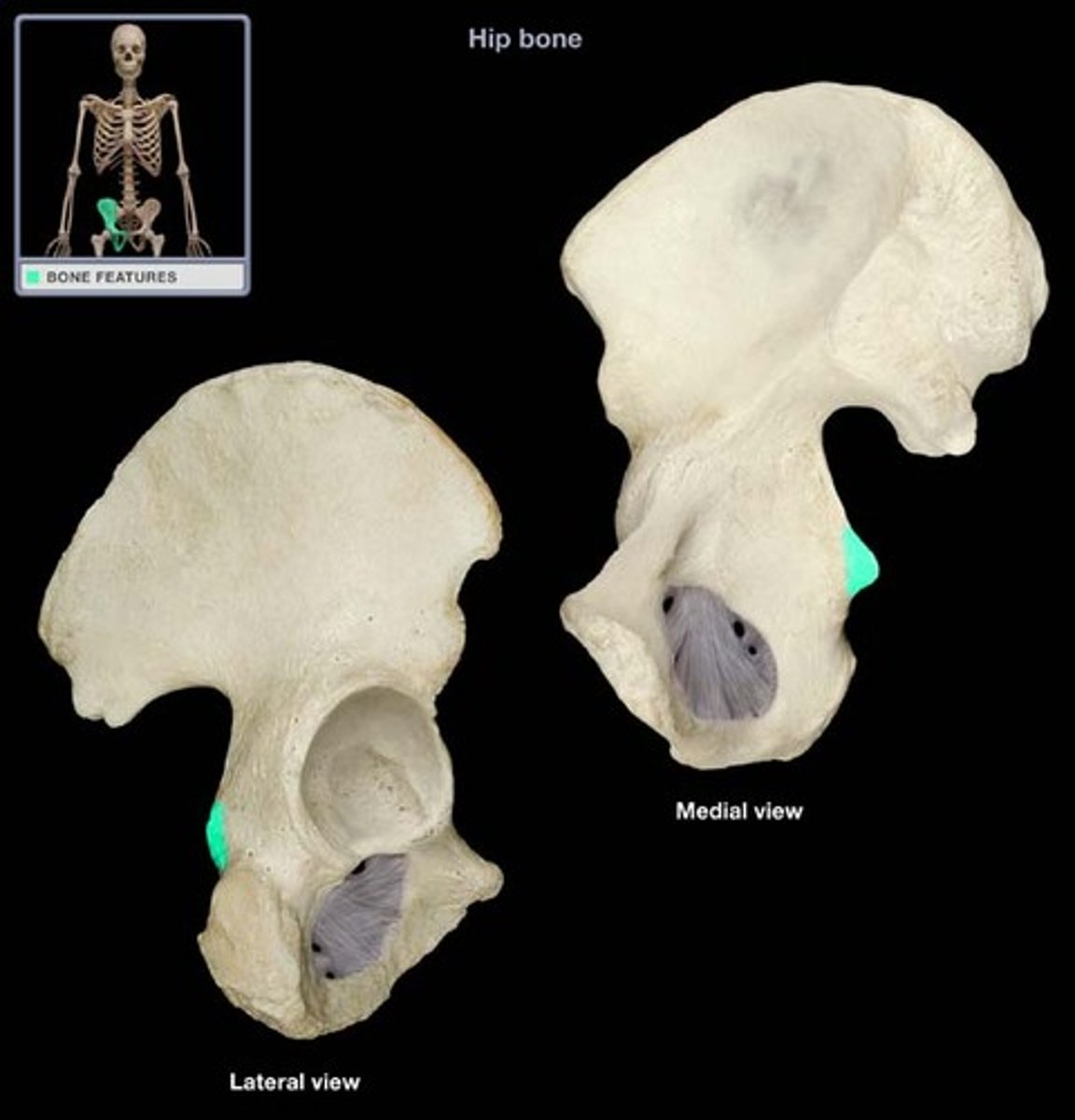
pubis inferior ramus
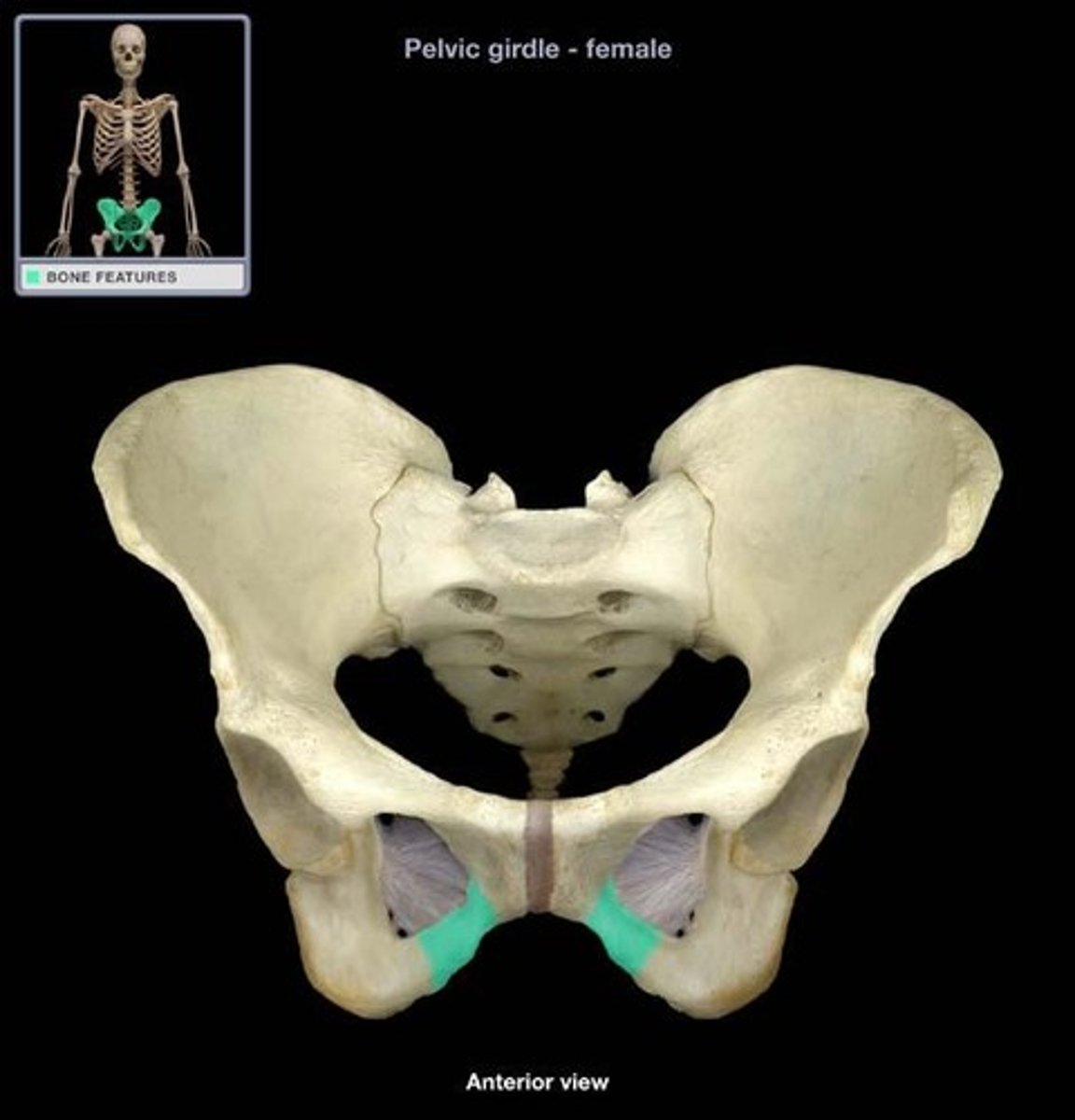
pubis superior ramus
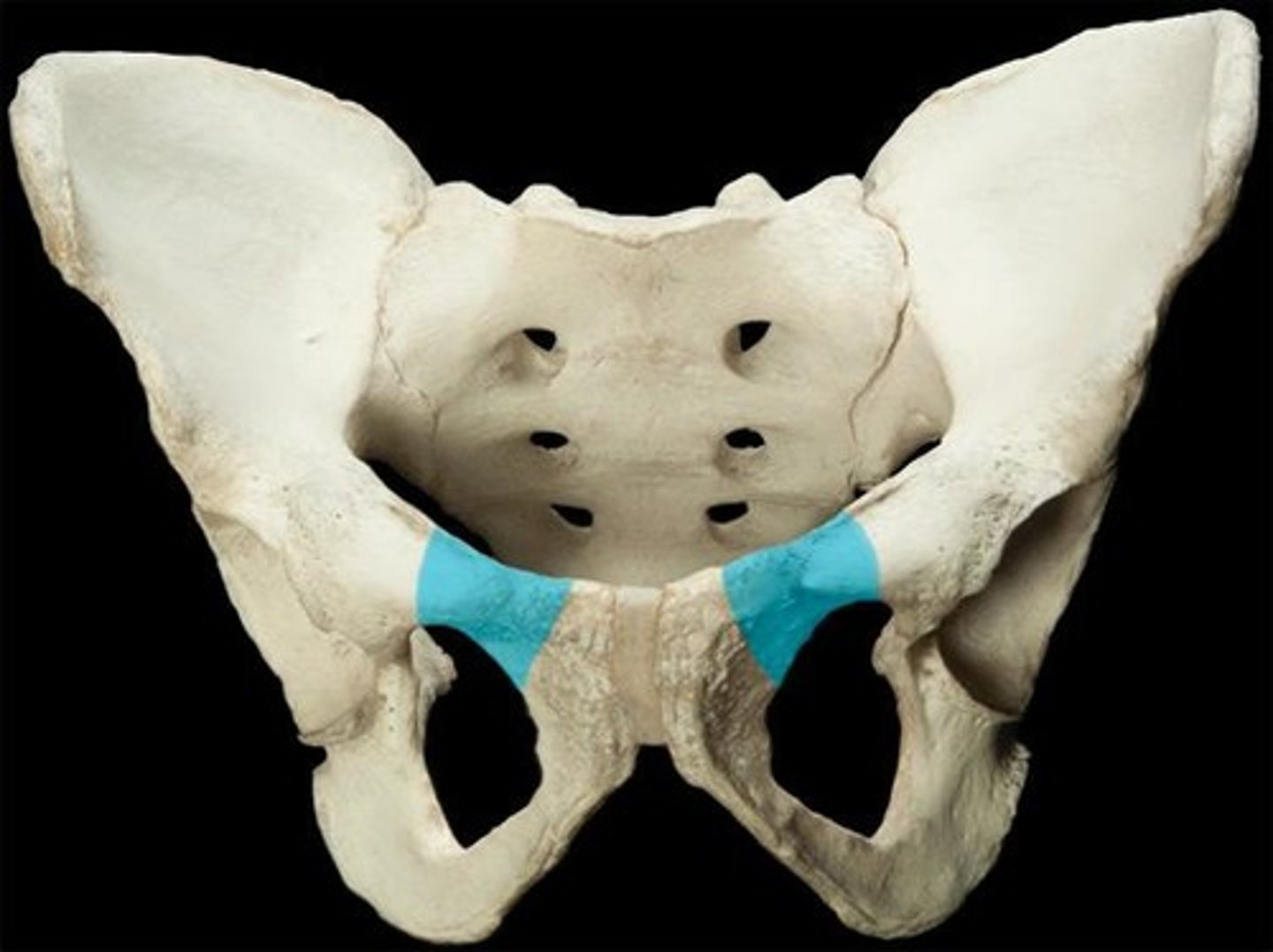
Obturator nerve
What nerve passes through the obturator foramen?
auricular surface of ilium
tuberosity of ilium
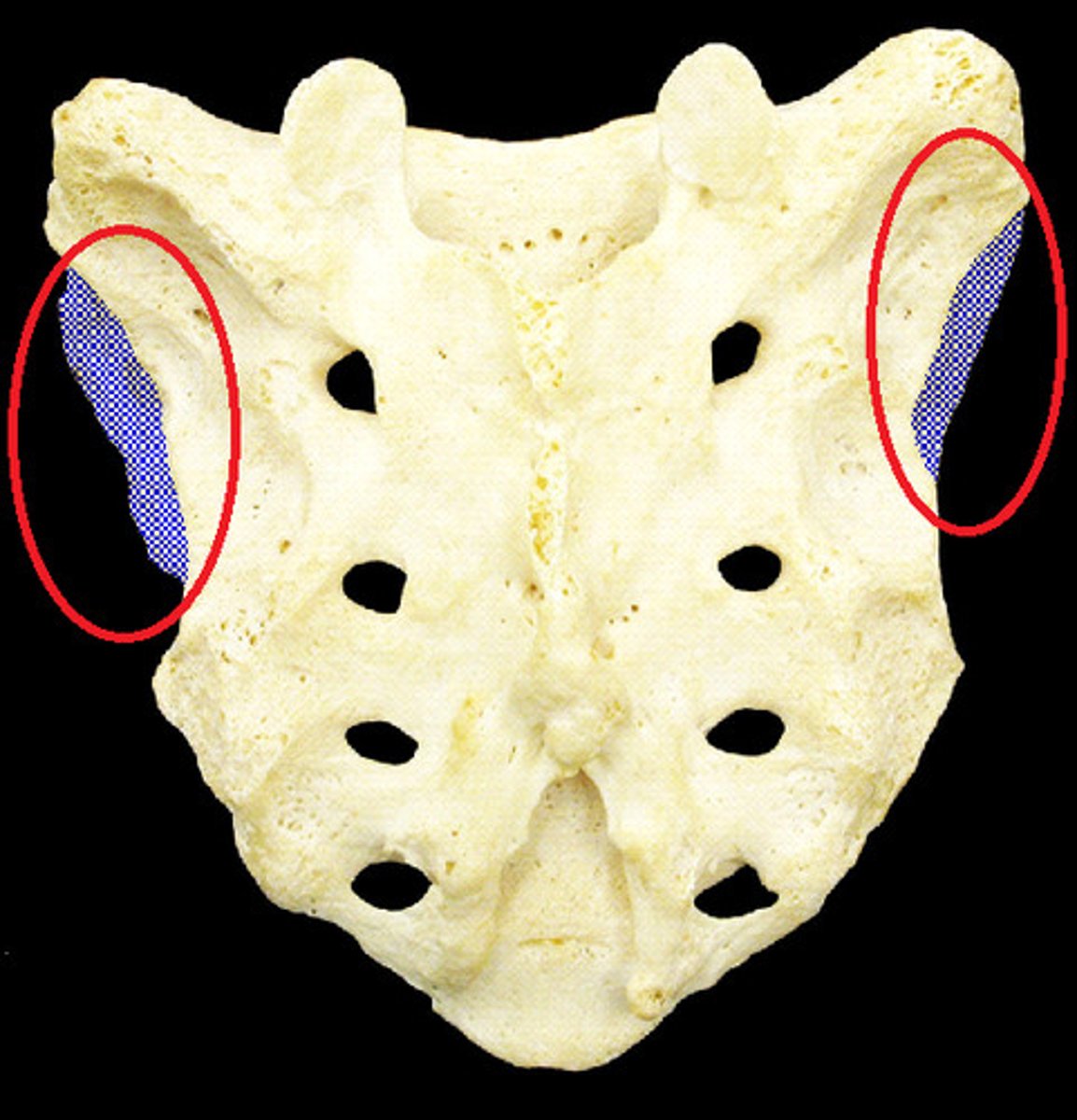
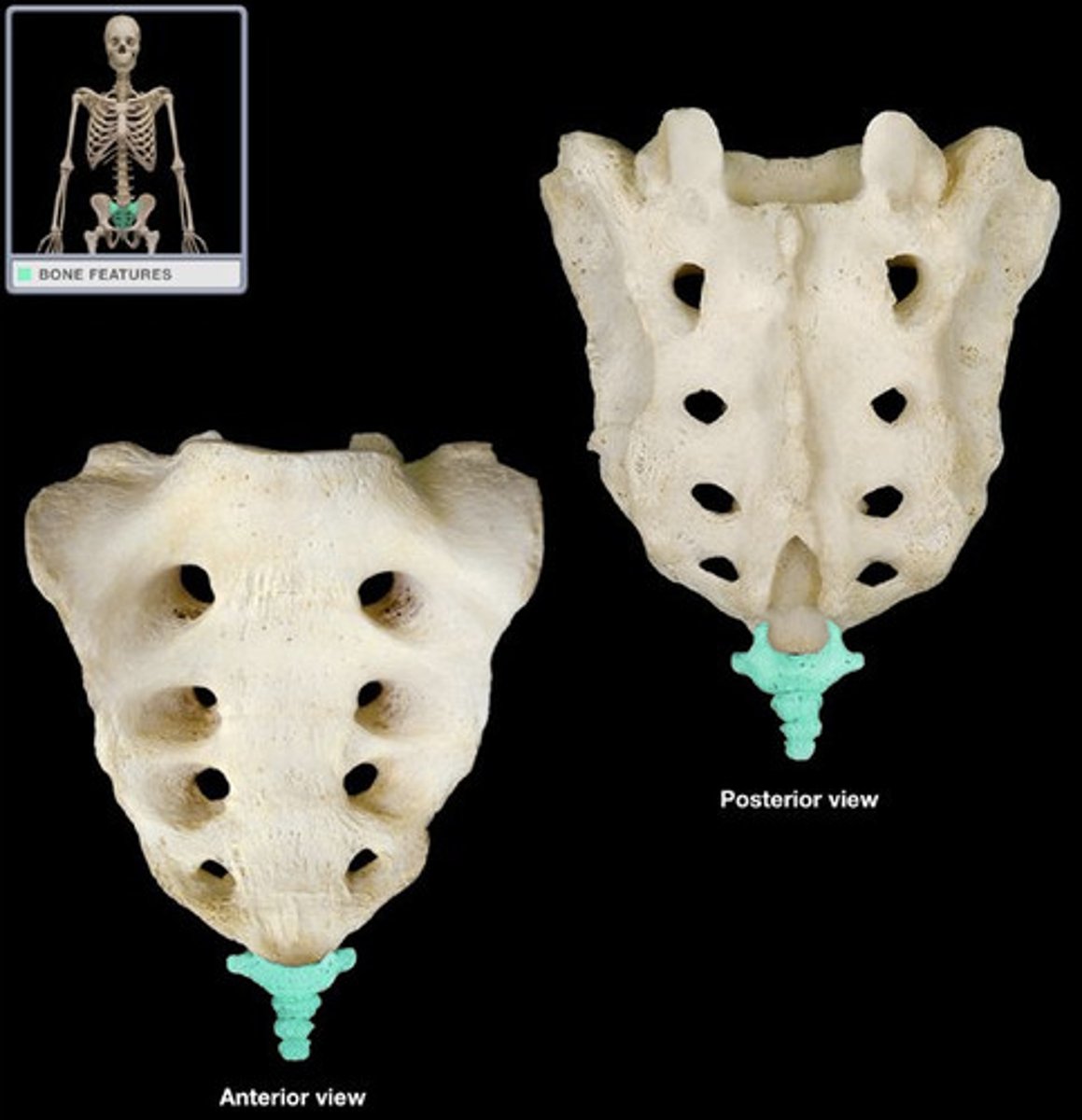
What parts of the pelivc bone articulate with the sacrum?
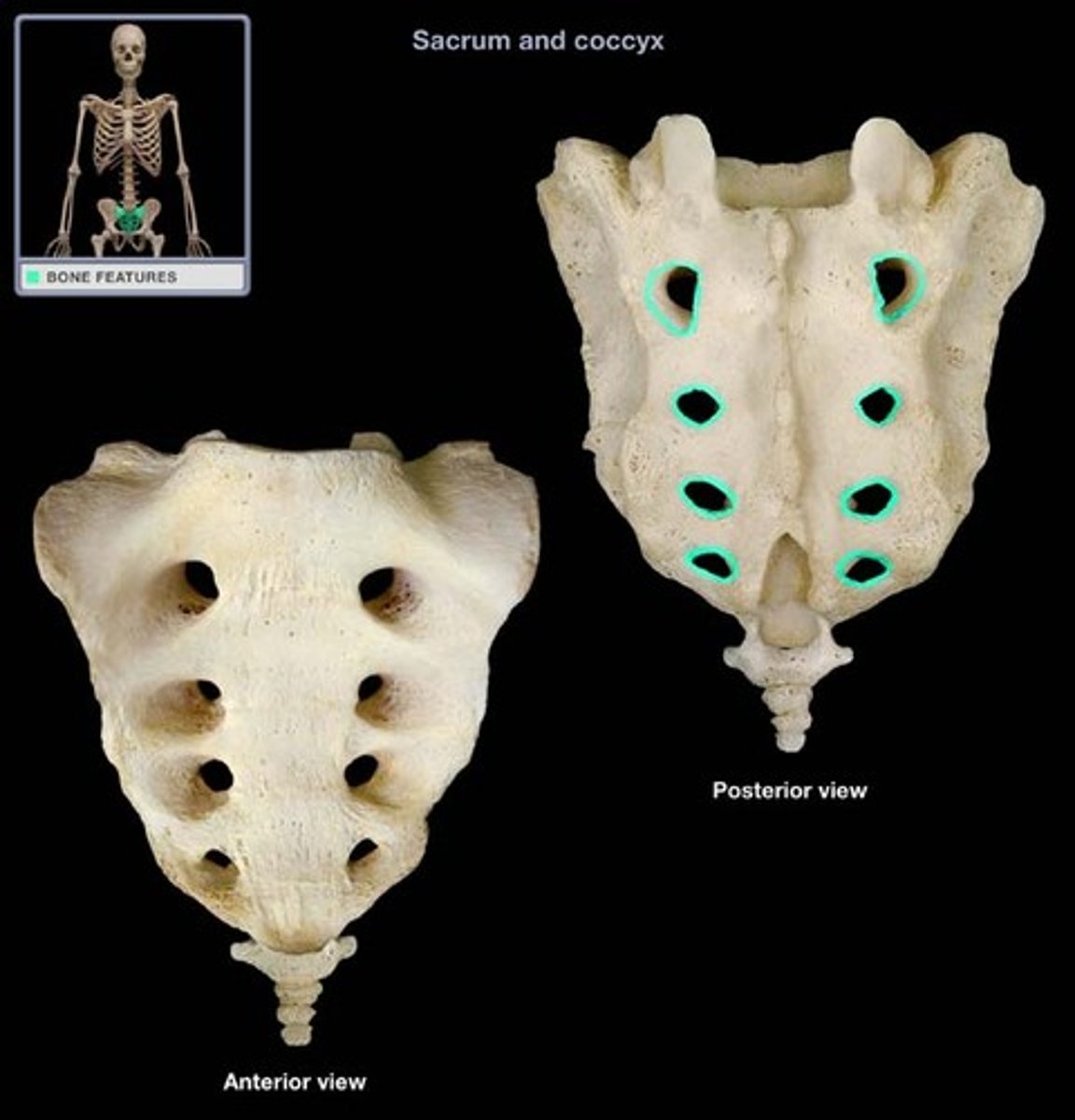
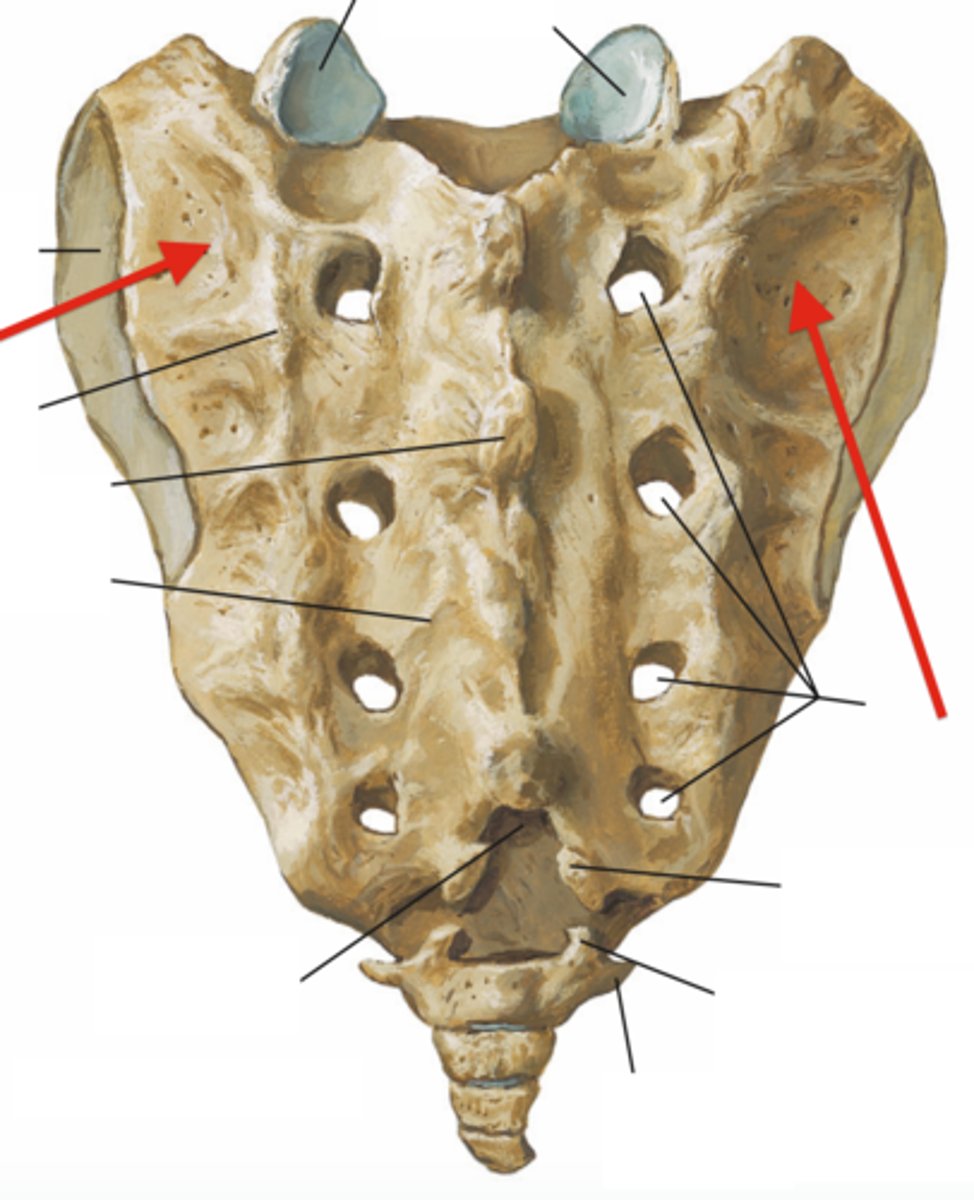
sacral foramina
ala of sacrum
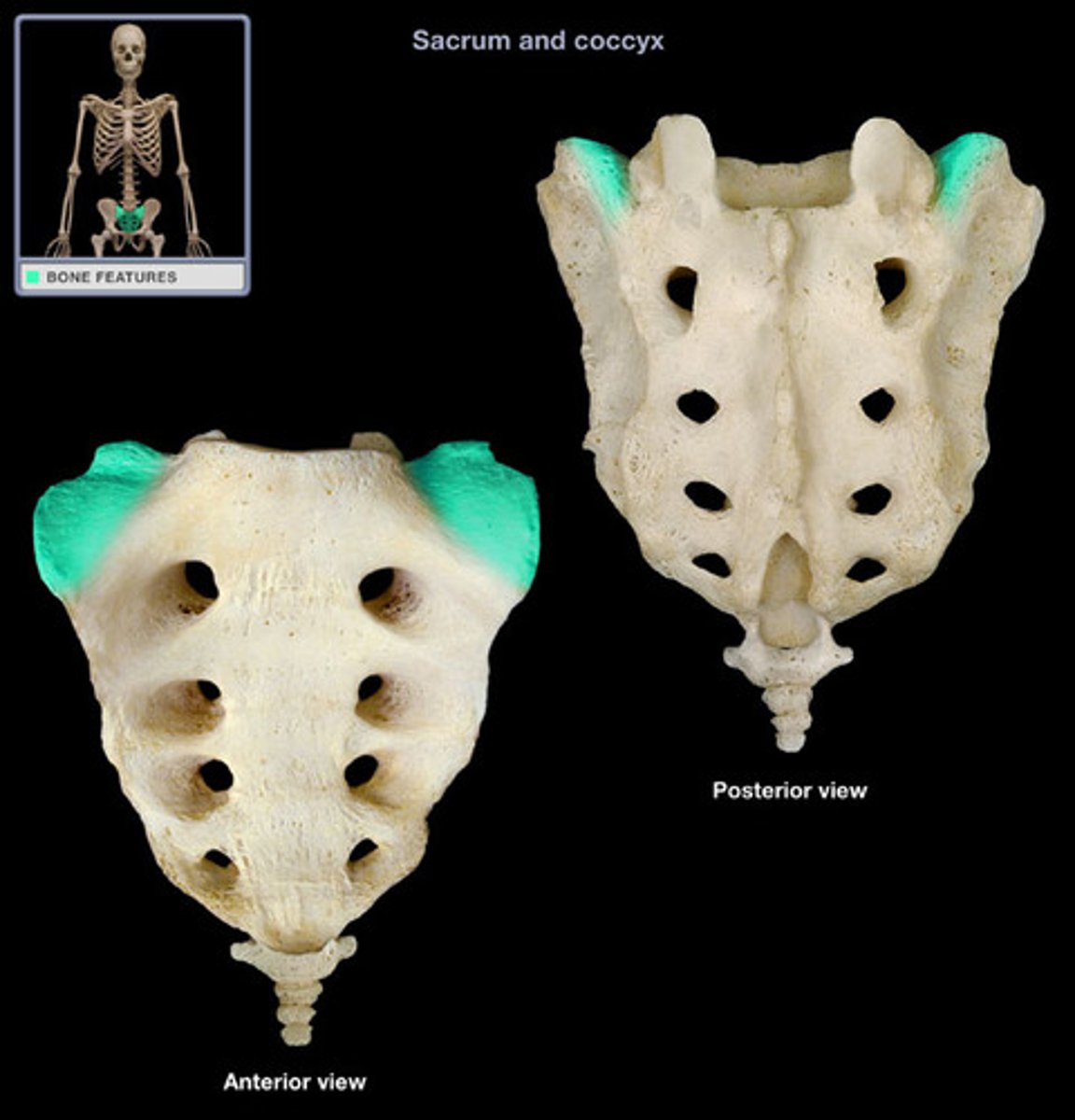
base of the sacrum
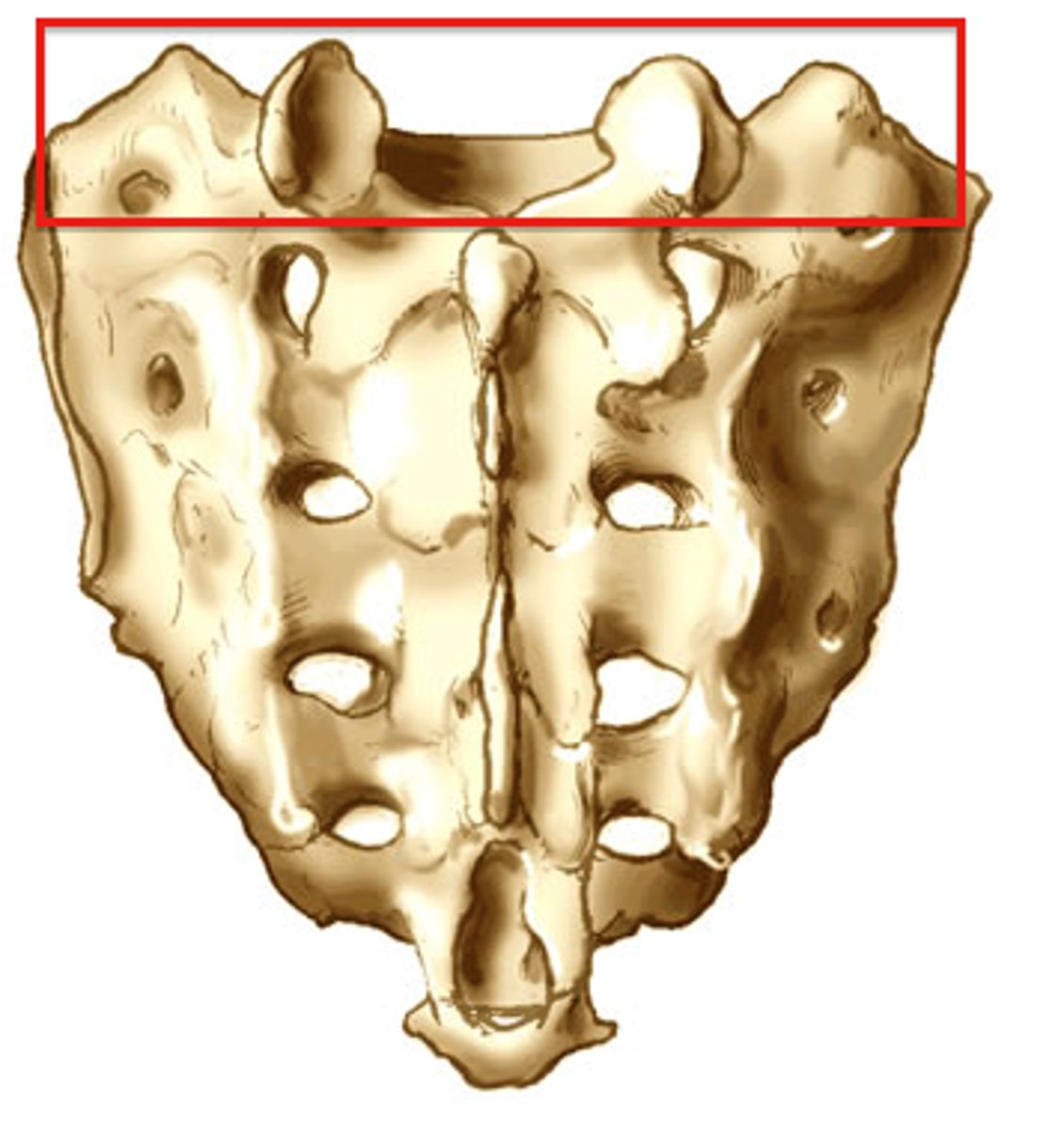
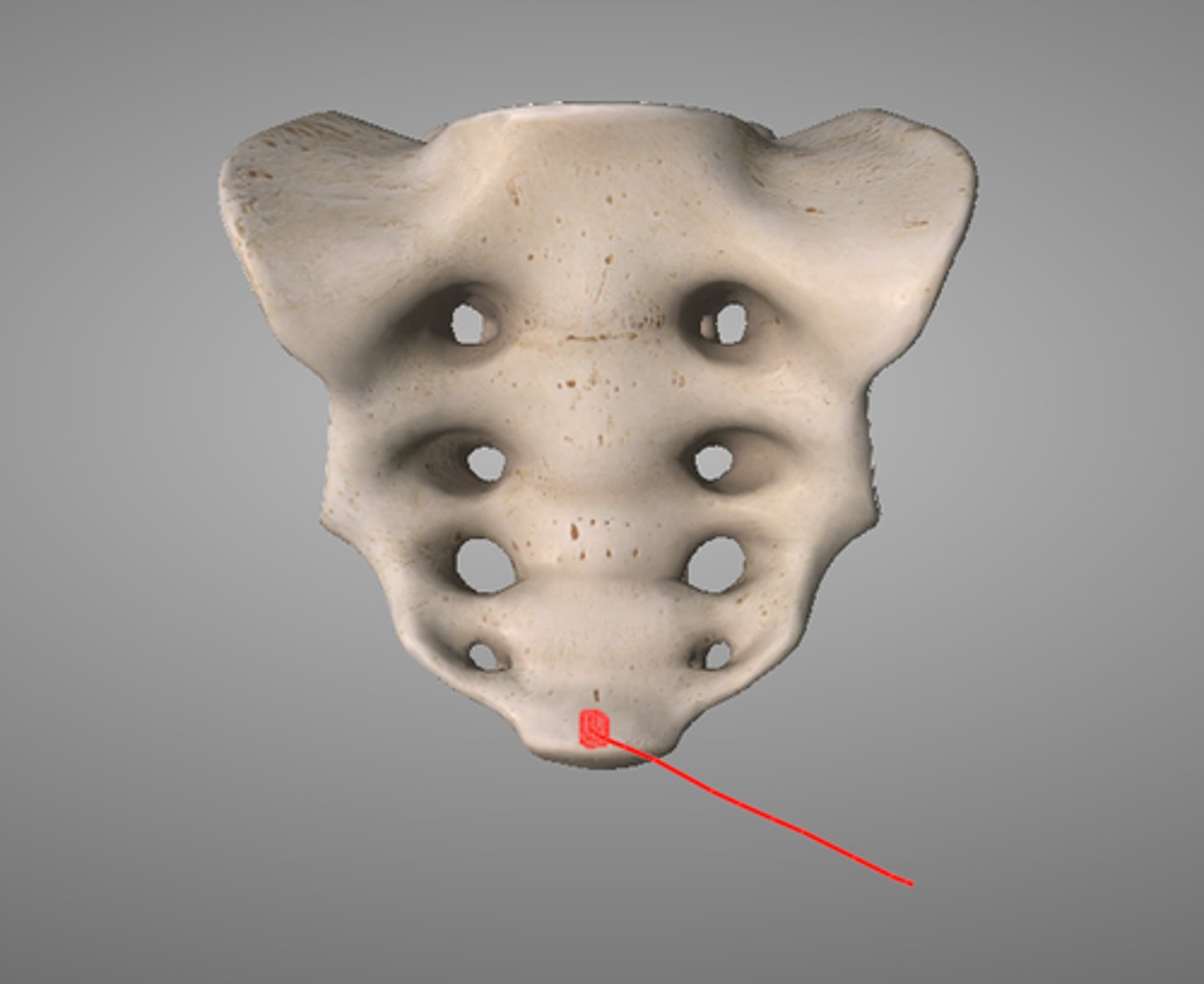
apex of the sacrum
auricular surface of the sacrum
sacral tuberosity
transmission of weightbearing load from above
protection and support of the contents of the pelvis
attachment sites for muscles of the trunk and lower limbs
What are the functions of the pelvic bone and sacrum?
ilium, ischium, and pubis
horseshoe shape
What forms the acetabulum and what shape does the articular cartilage look like?
four fused vertebrae of the base of your spinal cord
What is the coccyx?
attachment site for muscles and ligaments (especially pelvic floor muscles)
what is the function of the coccyx?
coccyx
head of the femur
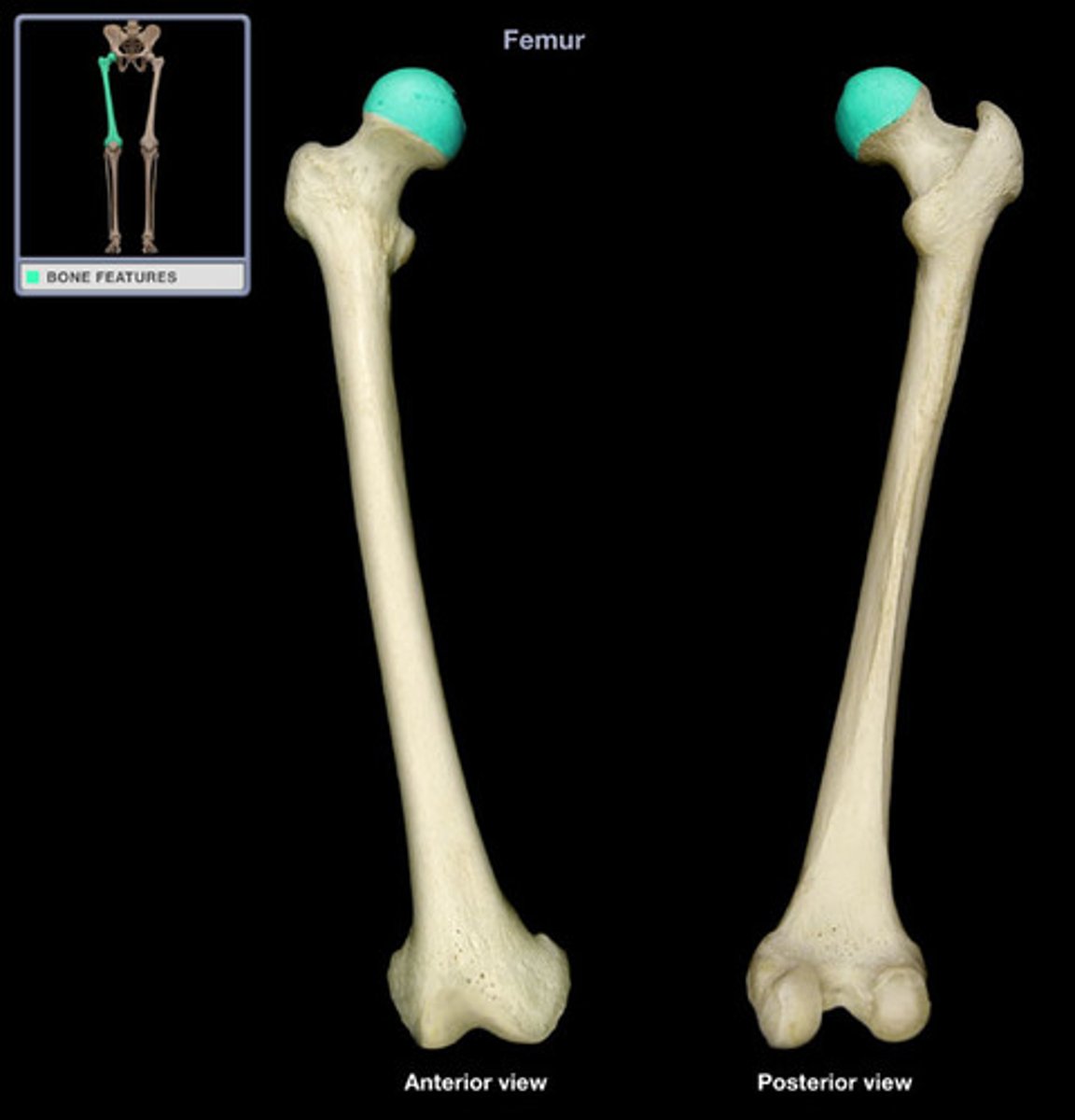
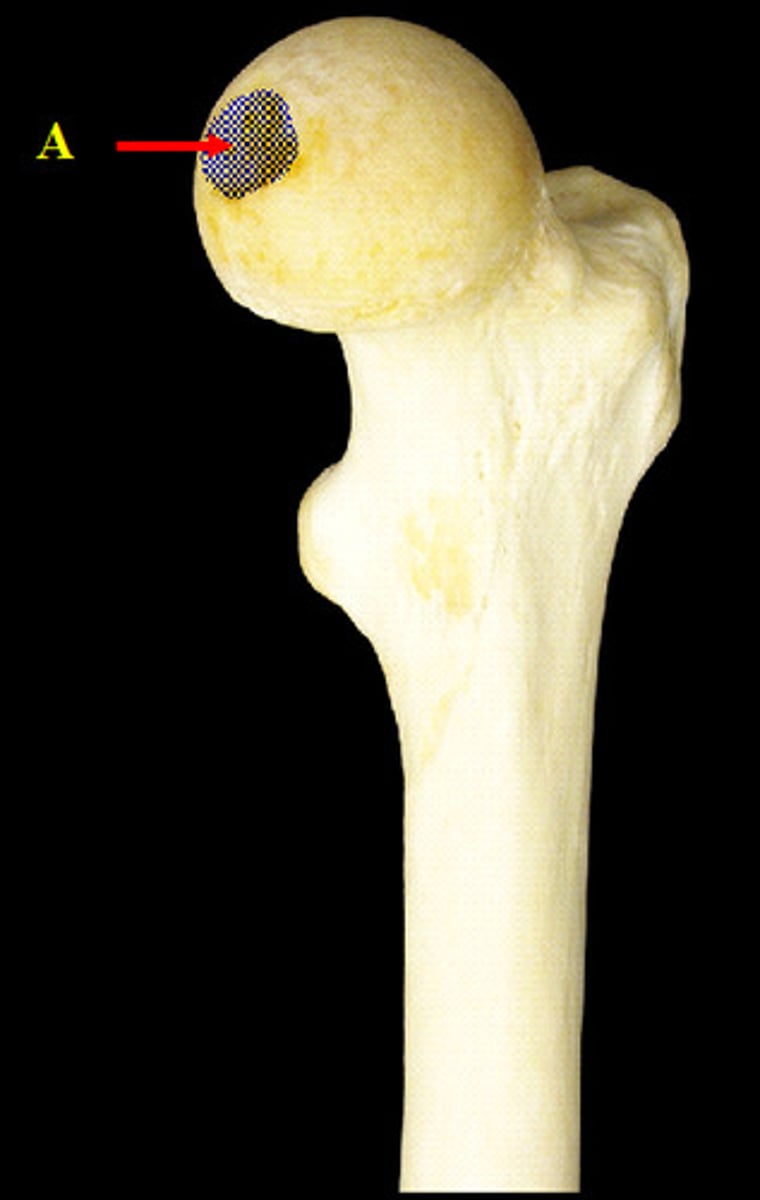
fovea of the femur
greater trochanter
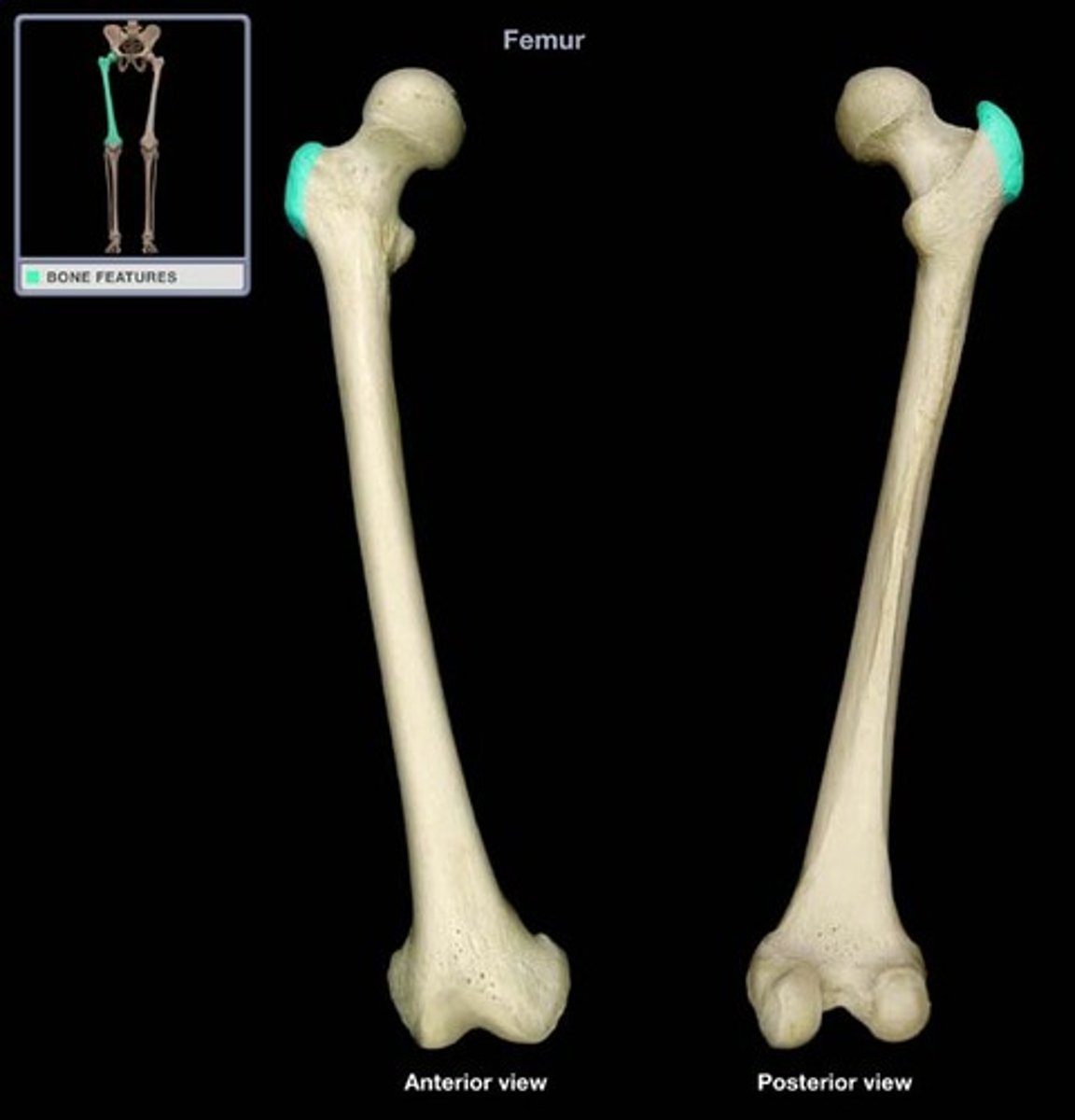
lesser trochanter
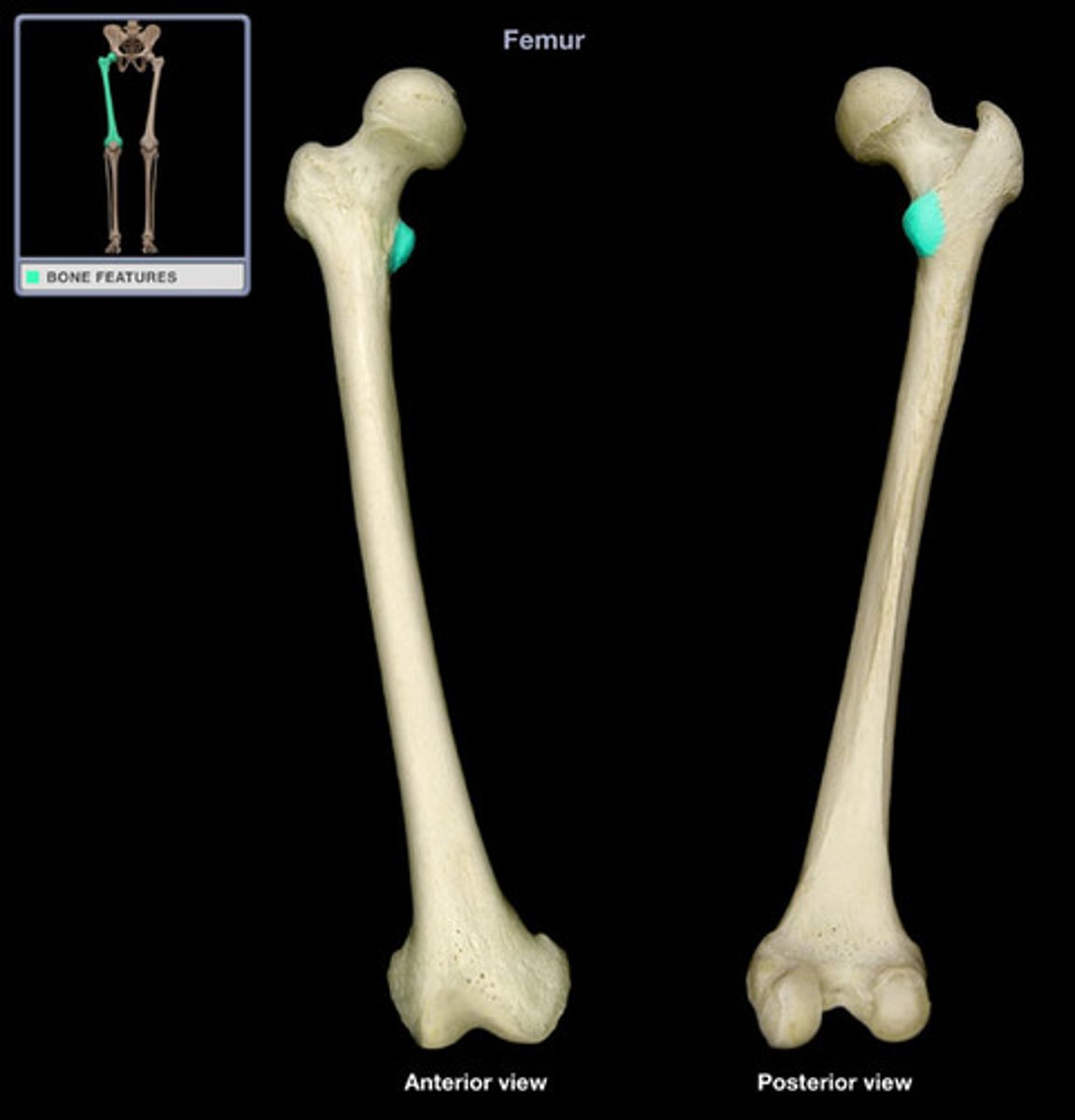
intertrochanteric line (anterior)
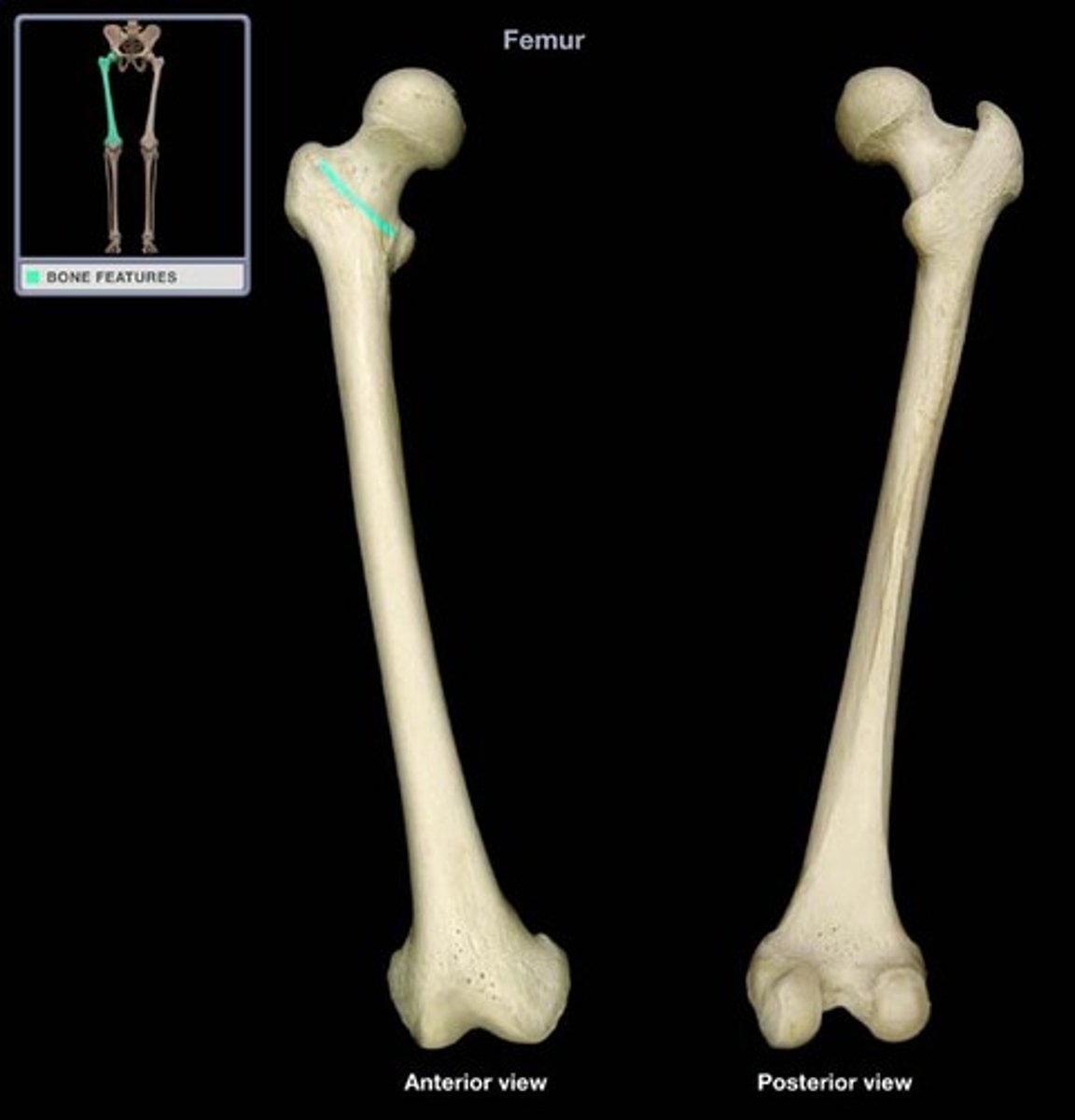
intertrochanteric crest (posterior)
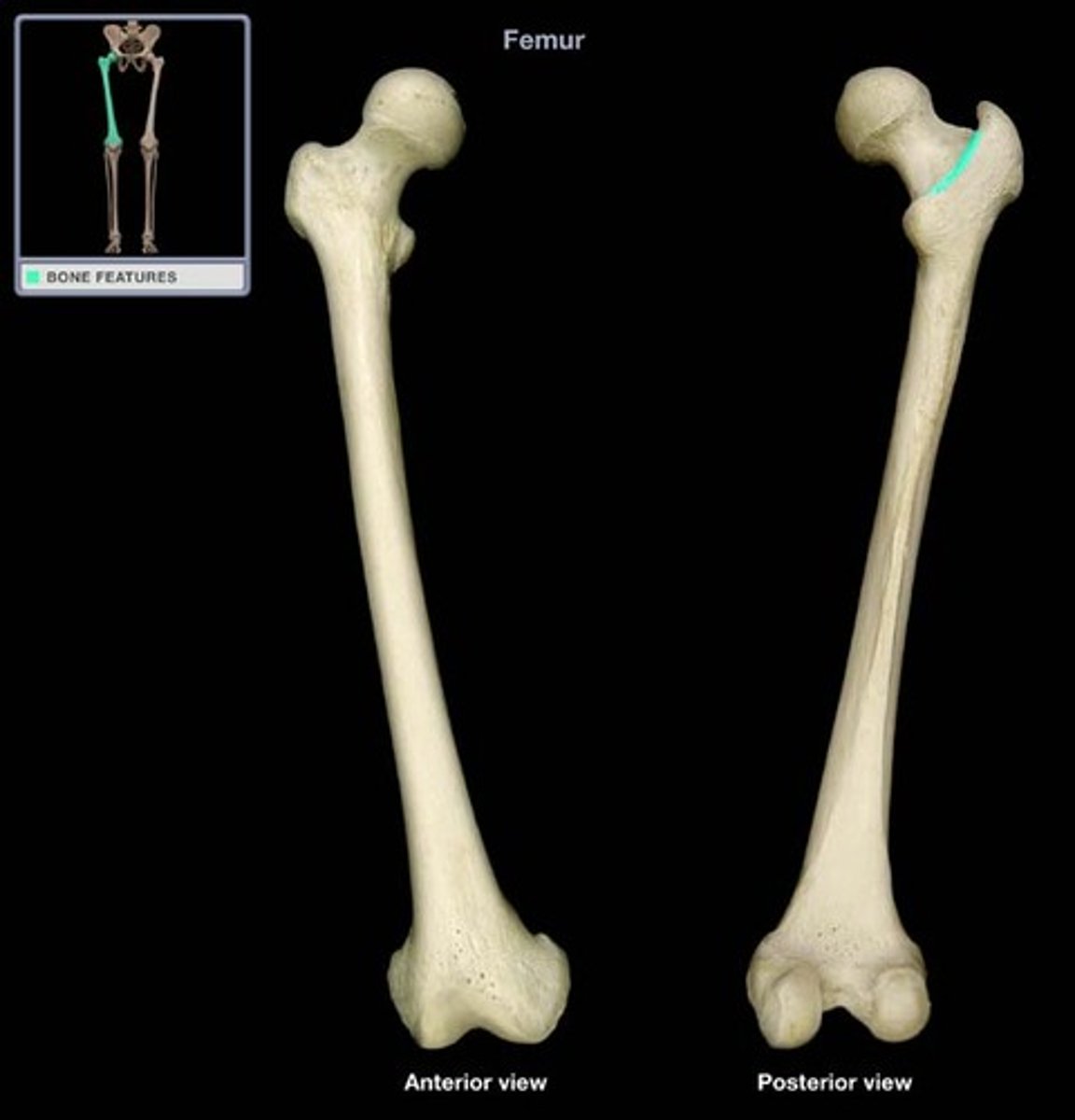
gluteal tuberosity
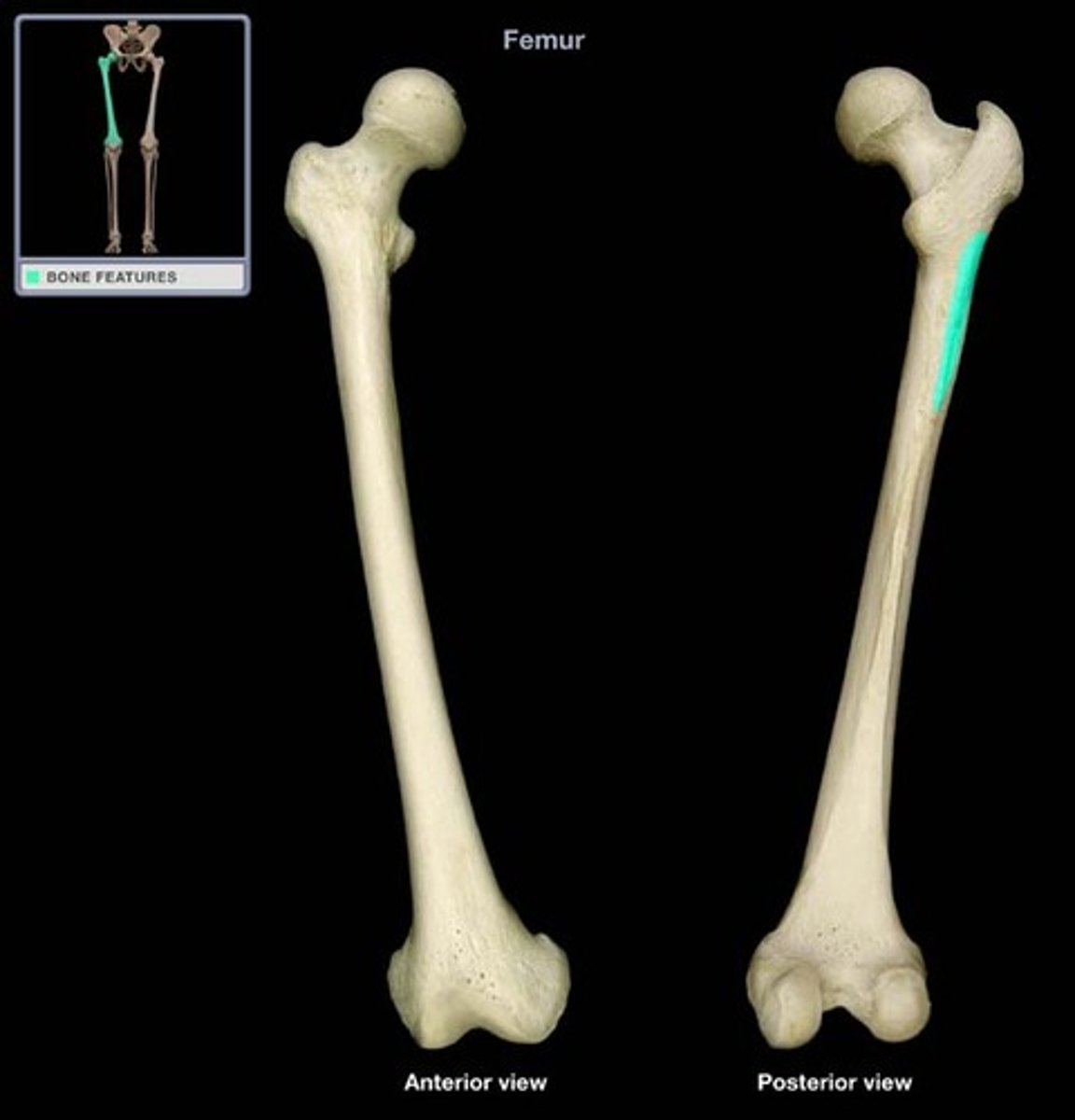
linea aspera
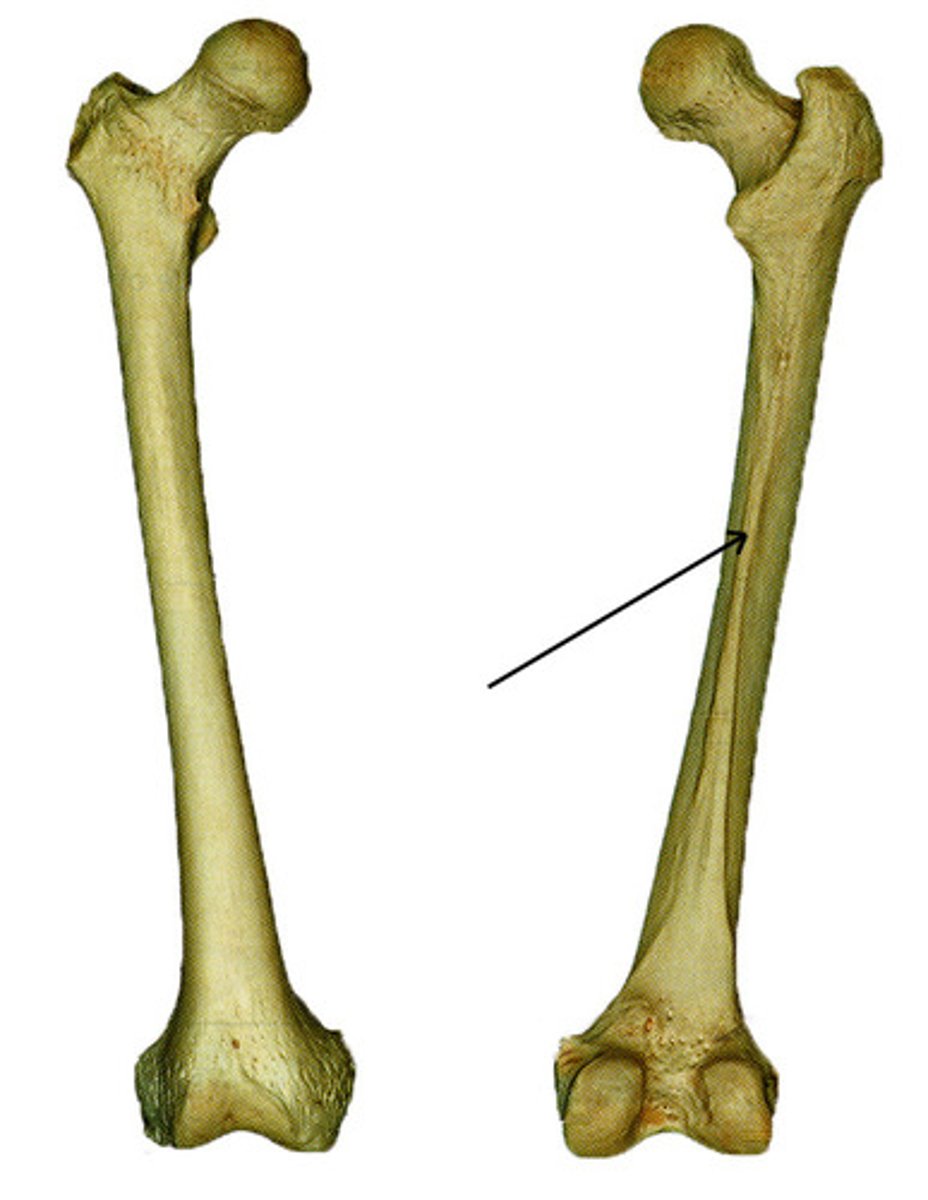
gluteus minimus and medius
Identify a muscle that has an attachment on the greater trochanter?
iliopsoas
Identify a muscle that has an attachment on the lesser trochanter?
gluteus maximus
identify a muscle that attaches on the gluteal tuberosity
Adductors and vastus muscles
identify a muscle that attaches on the linea aspera
Surfaces: bodies of two pubic bones
Joint: cartilaginous; symphysis (fibrocartilage pad)
What are the articulating surfaces of the pubic symphysis and what is the joint classification?
Ligaments: Superior and inferior pubic ligament
Muscles: rectus abdominis, adductor longus
What are the stabilizing ligaments and muscles of the pubic symphysis?
Anterior: auricular surfaces of the ilium and sacrum
Posterior: tuberosities of the ilium and sacrum
What are the anterior and posterior articulating surfaces of the sacroiliac joint?
Anterior: synovial plane(gliding) joint
Posterior: Fibrous Syndesmosis Joint
What is the joint classification of the sacroiliac joint?
interosseous sacroiliac ligament
anterior/posterior sacroiliac ligament
sacrospinous ligament
sacrotuberous ligament
What are the stabilizing ligaments of the sacroiliac joint?
Surfaces: acetabulum and femoral head
Joint: synovial, ball and socket
What are the articulating surfaces and joint classification of the hip joint?
labrum, capsule, and ligaments
What are some of the structures that stabilize the hip joint?
fibrocartilage ring surrounding the acetabulum
functions to increase the congruency/ stability of the joint and it provides shock absorption
What is the labrum of the hip joint and what does it do?
reinforces the hip joint by its strong dense fibrous nature
attaches at the edge of the acetabulum and the intertrochanteric line and crest
What does the joint capsule do at the hip joint and where does it attach?
iliofemoral ligament
anterior, shaped like an inverted Y; from the iliac portion of the acetabular rim to the intertrochanteric line and limits excessive hip extension and external rotation
ischiofemoral ligament
posterior; from the ischial portion of the acetabular rim to the greater trochanter and limits excessive hip extenison and internal rotation
pubofemoral ligament
anterior and inferior; from the pubic portion of the acetabular rim to blend with the joint capsule; limits excessive hip extension, abduction, and external rotation
Teres ligament
attaches from deep in the acetabulum to the fovea in the head of the femur, and it functions to stabilize the internally and to supply blood
become tight/taunt, which draws the head of the femur into the acetabulum, limiting hip extension ROM
the ligaments unwind which allows for a good amount of ROM
In general what do the hip ligaments do during hip extension? During hip flexion?
trochanteric bursa, gluteus medius bursa, iliopsoas bursa, ischial bursa
What are the different bursa found at the hip joint?
Flexion/extension, adduction/abduction, internal/external rotation, diagonal abduction and adduction, horizontal abduction and adduction, circumduction