Spatial and Central Visual Pathways: Vision, Edges, and Fourier Analysis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What defines an object in spatial vision?
Edges define objects.
What is spatial frequency in visual perception?
Spatial frequency refers to the number of light/dark bars per unit of visual space, measured in cycles per degree.
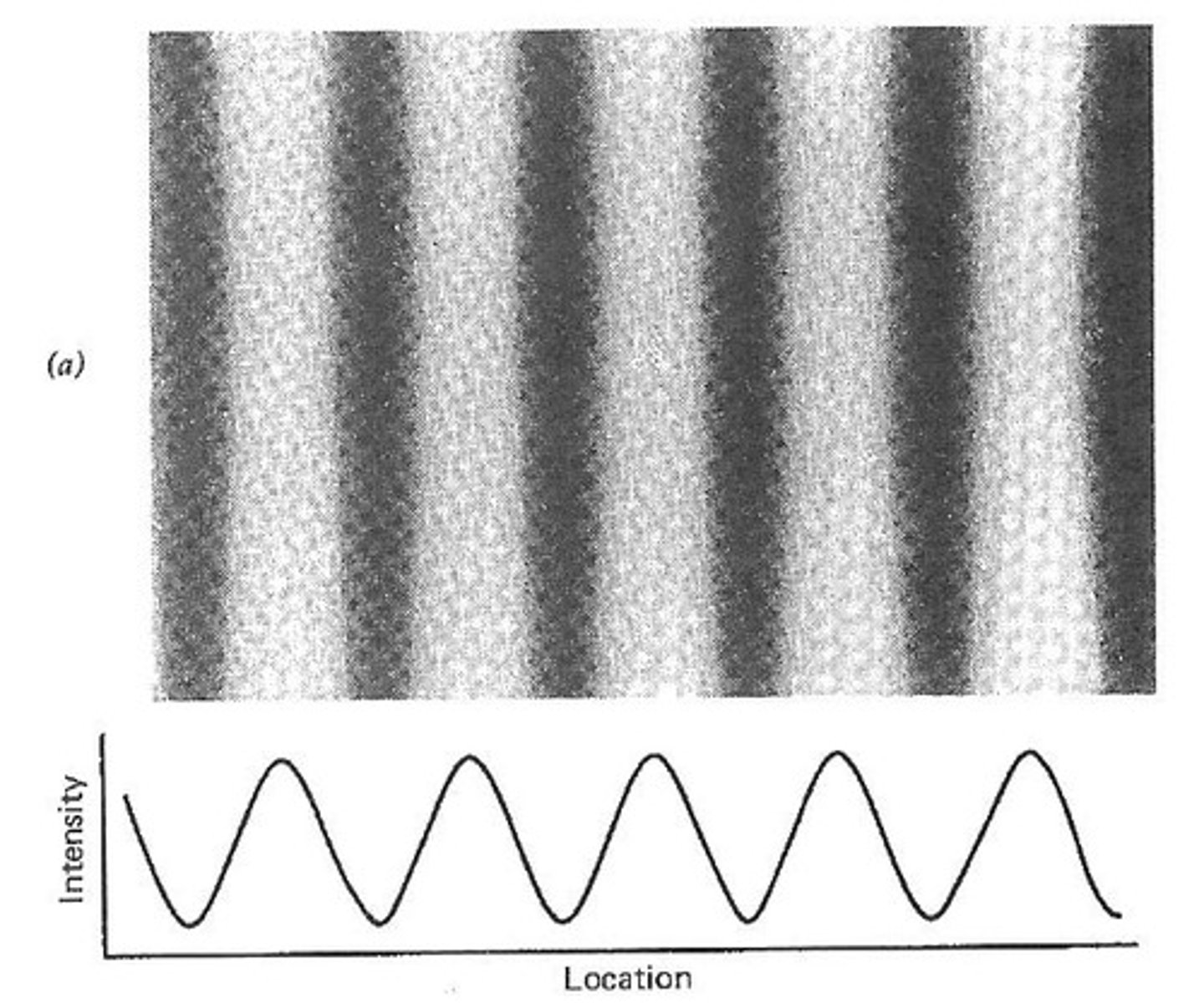
What is the role of contrast in visual perception?
Contrast is the intensity difference between light and dark areas in a visual image.
What is the significance of orientation in spatial vision?
Orientation refers to the axis of the bars in visual images, which affects how we perceive them.
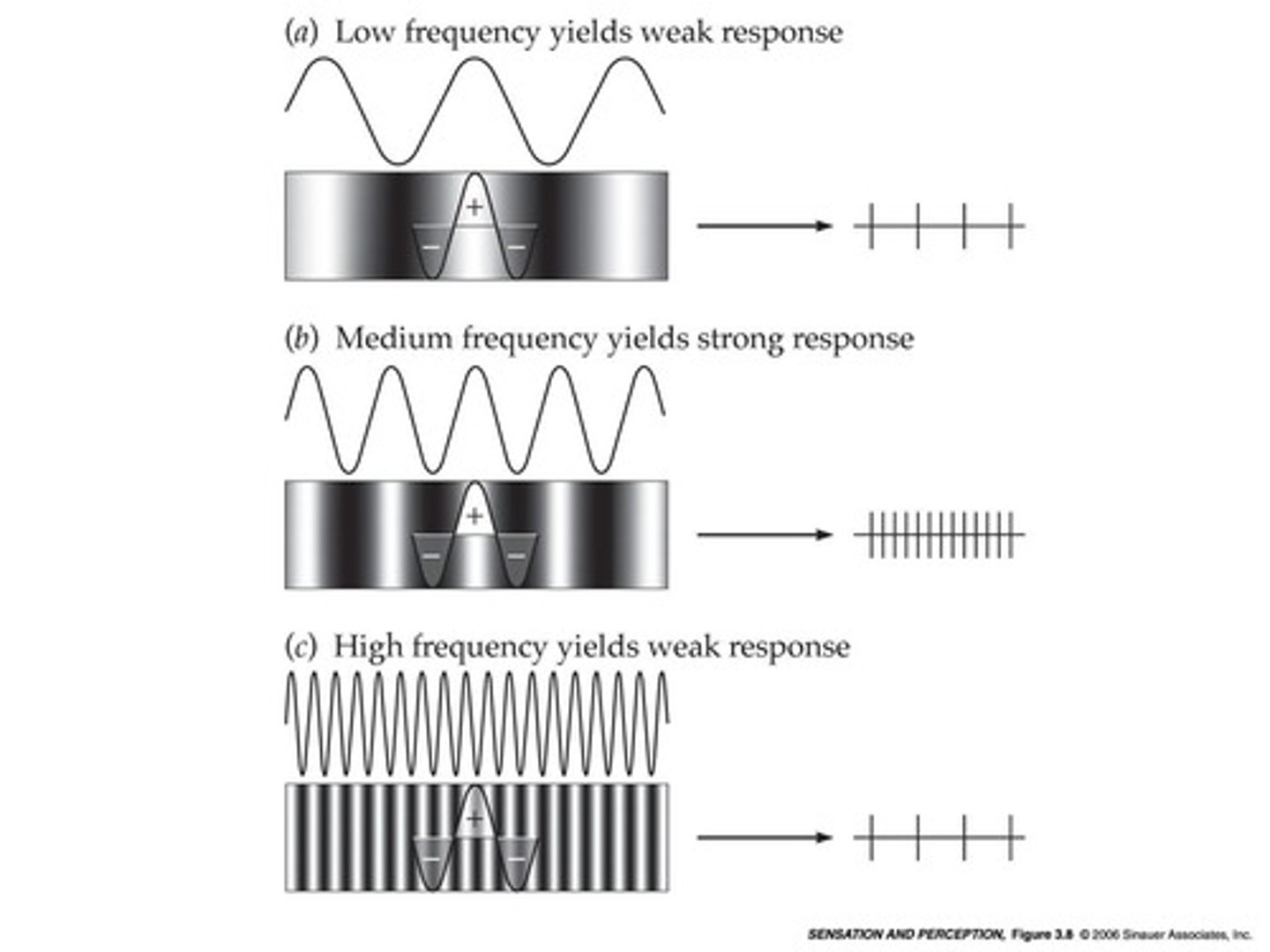
What is a low pass filter in spatial vision?
A low pass filter allows low spatial frequencies to pass while filtering out high spatial frequencies.
What is a high pass filter in spatial vision?
A high pass filter allows high spatial frequencies to pass while filtering out low spatial frequencies.
What is a band pass filter?
A band pass filter allows frequencies between two cutoffs to pass, filtering out both lower and higher frequencies.
What is the Nyquist frequency?
The Nyquist frequency is the minimum sampling rate required to accurately capture a signal without aliasing.
What is the role of the primary visual cortex (V1)?
The primary visual cortex processes visual information, featuring topographical mapping and selective responsiveness to orientations.
What are the three types of cortical cells in V1?
Simple cells, complex cells, and hypercomplex cells, each with different responsiveness to stimuli.
What is selective adaptation in spatial vision?
Selective adaptation refers to the phenomenon where prolonged exposure to a stimulus reduces sensitivity to that stimulus.
What is interocular transfer?
Interocular transfer is the phenomenon where adaptation in one eye affects perception in the other eye.
What is the function of the LGN (Lateral Geniculate Nucleus)?
The LGN serves as a relay station for visual information, receiving input from the reticular activating system and sending it to the visual cortex.
What are parvocellular layers in the LGN?
Parvocellular layers are color-sensitive layers with small receptive fields, responsible for fine detail and low temporal resolution.
What are magnocellular layers in the LGN?
Magnocellular layers are not color-sensitive, have large receptive fields, and are very sensitive to temporal changes and movement.
What is the significance of cortical magnification?
Cortical magnification refers to the disproportionate representation of the central visual field in the primary visual cortex.
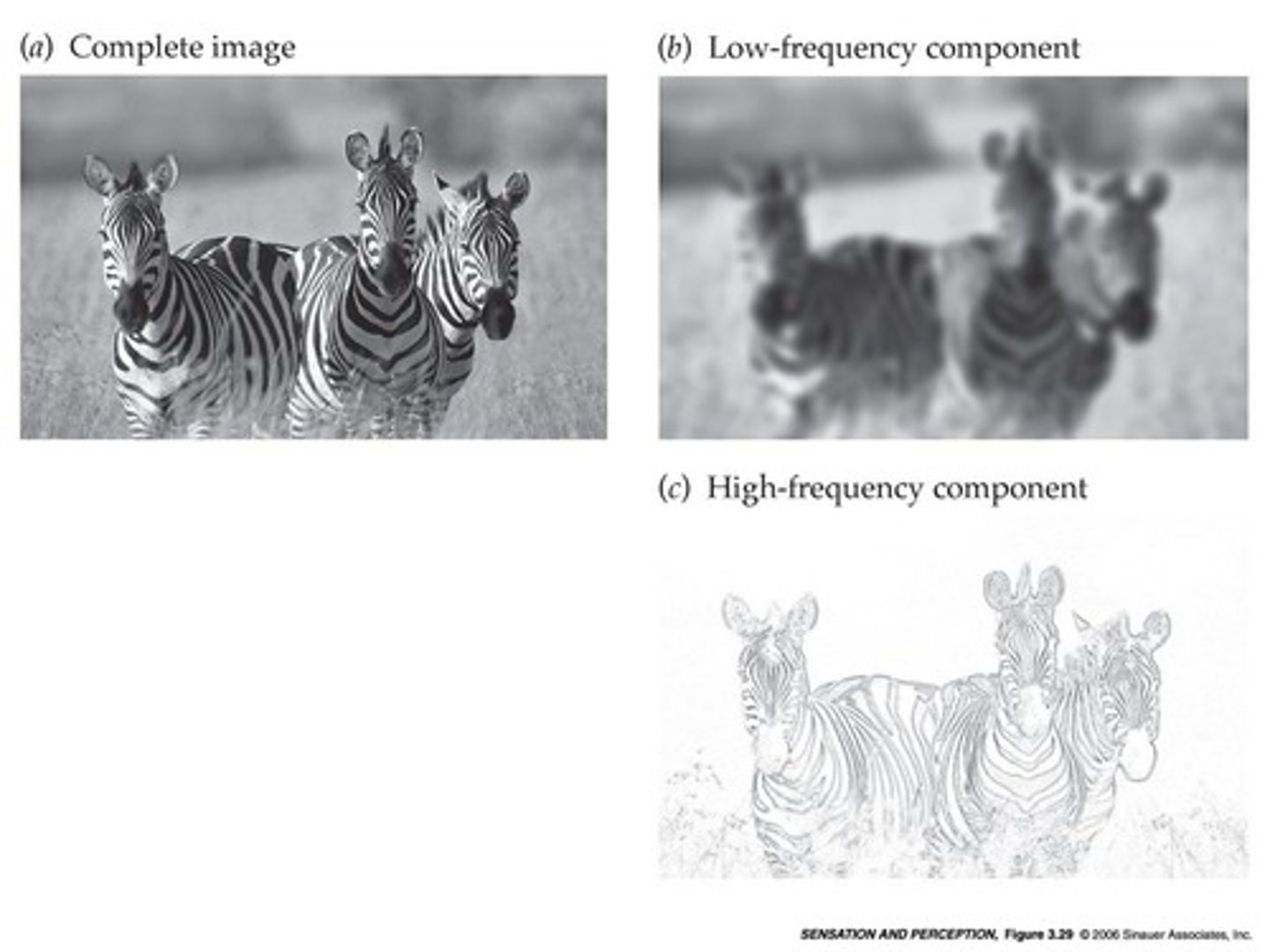
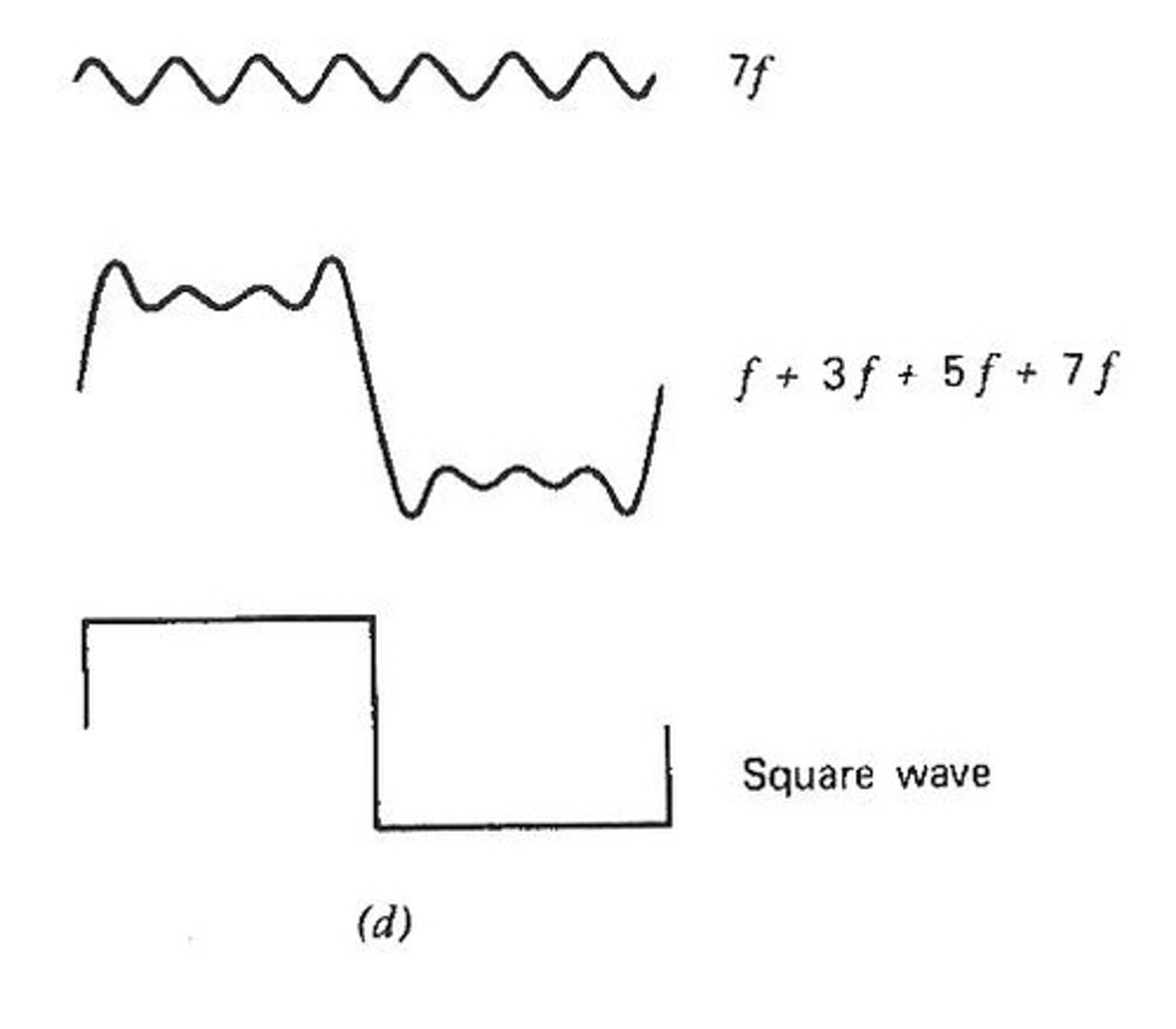
What is the role of Fourier analysis in visual perception?
Fourier analysis breaks down complex images into their simplest components, allowing the visual system to evaluate each spatial frequency separately.
What is end stopping in hypercomplex cells?
End stopping is a process where hypercomplex cells increase firing rates with bar length until a certain point, then decrease as the bar length exceeds their receptive field.
What is the concept of population coding in visual perception?
Population coding refers to the idea that many neurons respond to a stimulus in various orientations, and the brain interprets this collective response to perceive the stimulus.
What is the function of simple cells in V1?
Simple cells have a straightforward relationship between their on/off regions and the preferred stimulus orientation.
What is the function of complex cells in V1?
Complex cells respond to their preferred stimulus orientation and motion regardless of its position in the receptive field.
What is the function of hypercomplex cells in V1?
Hypercomplex cells are selective for orientation, motion, and length of stimuli.
What is the significance of the hypercolumn in the striate cortex?
A hypercolumn is a 1-mm block of striate cortex containing all necessary machinery to process visual information for a specific part of the visual field.
What is the role of the reticular activating system in visual processing?
The reticular activating system controls arousal and may influence the amount of visual stimulation reaching the cortex.