International Economics Final
1/526
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
527 Terms
What is the name given to a tax on imported goods?
tariff
A Chinese student pays tuition at a U.S. university. The Chinese government classifies this transaction as:
a service import
The difference between the total value of a country’s exports and the total value of its imports is defined at the country’s:
Trade balance.
If country X has a GDP of $1 trillion, exports $200 billion to country Y, and imports $300 billion from country Y, then its bilateral trade balance with country Y is:
-$100 billion
“Value-added” in the context of international trade refers to:
the difference between the value of exports and the value of imported inputs used in producing exports.
What does a country’s GDP measure
the value of all final goods produced in a year
The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act
was passed as a reaction to the Great Depression in the United States
Most countries saw a significant drop in international trade between 2008 and 2009. What was the cause of that temporary reduction?
the Global Financial Crisis
What is the immediate effect of increasing tariffs on a country’s economy?
It reduces the volume of imports
More than half of migration is:
from non OECD countries to OECD countries.
The key reason for horizontal FDI is:
to avoid or minimize taxes or tariffs
David Ricardo’s model explains trade based on:
technology
A country’s factors of production includes
labor, capital and and natural resources
The Ricardian model focuses on how differences in _________ influence international trade patterns.
comparative costs
What is the Marginal Product of Labor
extra output obtained by using one more unit of labor
A nation will gain from trade if it
consumes outside its PPF and produces along its PPF
According to the principle of comparative advantage, specialization and trade increase a nation's total output because:
resources are directed to their highest productivity
Assume that two countries (Home and Foreign) each produce two goods (corn and wheat) under constant cost production. Home produces 0.5 ton of corn or 1 ton of wheat with a day of labor. Without trade (in autarky), Home's daily production is 20 tons of wheat and 10 tons of corn. How large is Home's labor force?
40 workers
International trade equilibrium occurs where
the total world import demand curve intersects with the total world export supply curve
with other things unchanged, a rise in the average price of imports or a fall in the average price of exports will
worsen terms of trade
Assume that Germany and China can produce beer and cloth. If the MPLc/MPLb for Germany is 2/5 and the MPLc/MPLb for China is 1, then Germany and China have a comparative advantage in:
beer and cloth, respectively
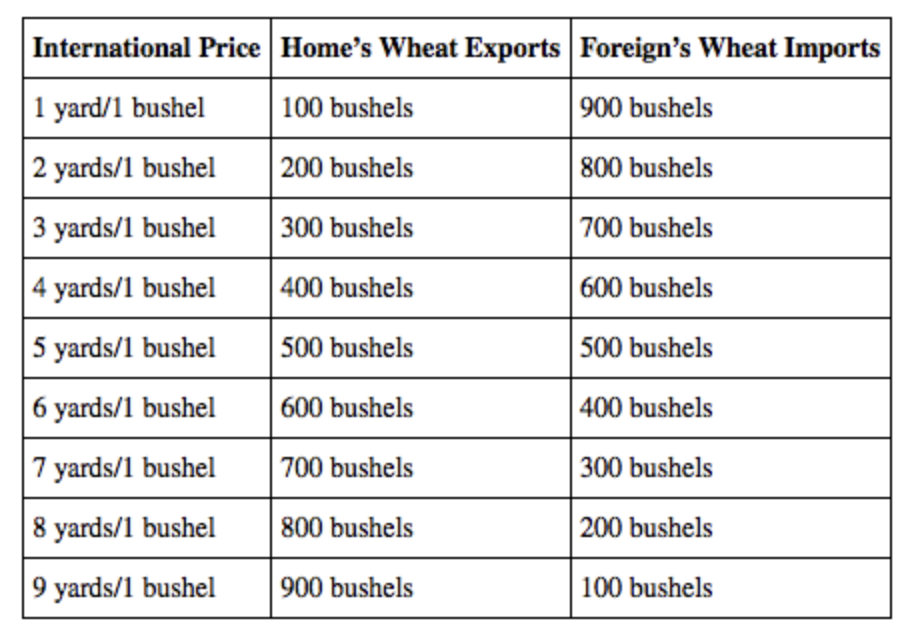
Home has a comparative advantage in wheat, and Foreign has a comparative advantage in cloth. Once trade occurs, Home produces 1,000 bushels of wheat, and Foreign produces 1,000 yards of cloth. The following table shows the amount of wheat that Home is willing to supply and Foreign is willing to buy at various international prices. In equilibrium, how many bushels of wheat will Foreign import?
500 bushels
In the United States, one worker can produce 10 tons of steel per day or 20 tons of chemicals per day. In the United Kingdom, one worker can produce 5 tons of steel per day or 15 tons of chemicals per day. International trade will occur between the United States and the United Kingdom so long as 1 ton of steel trades for:
at least 2 tons of chemicals, but no more than 3 tons of chemicals
Which of the following statements describes what the Ricardian model predicts as a nation improves its technology and productivity?
its standard of living will rise
In competitive labor markets, the wage equals
the marginal product of labor times the price of output
A nation will export the product in which it has a comparative advantage, which results from the good being relatively ____ than in the importing nation.
less expensive
Based on the Ricardian assumption of complete mobility of labor between industries, it must be true that for two industries labeled A and B, PA x MPLA ____ PB x MPLB .
=
Assume the MPLt = 5 tennis rackets and MPLb = 4 baseball bats. If the economy has 100 workers, then the economy can produce
a maximum of 500 tennis rackets
The marginal rate of substitution is measured as the ____ and has a ____ slope.
the slope of an indifference curve; negative
Under the condition of autarky, which attainable combination gives the nation the MOST utility?
point A
The optimal production bundle of goods A and B under conditions of autarky will occur where MPLA/MPLB =____ .
MU(B)/MU(A)
The international relative price and total quantity of a traded good or service is determined by:
the intersection of the total world import demand curve with the total world export supply curve.
Home has a comparative advantage in wheat, and Foreign has a comparative advantage in cloth. Once trade occurs, Home produces 1,000 bushels of wheat, and Foreign produces 1,000 yards of cloth. The following table shows the amount of wheat that Home is willing to supply and Foreign is willing to buy at various international prices. What is the international price of wheat?
5 yards/ bushel
The Ricardian model (with constant opportunity costs) predicts that a nation will
specialize completely
In the Ricardian model, wages are equal across industries because
workers are freely mobile between industries
If export prices increase, what can we expect the wages in the export sector to do according to the Ricardian model?
increase
Assume that two countries (Home and Foreign) each produce two goods (corn and wheat) under constant cost production. Home produces 0.5 ton of corn or 1 ton of wheat with a day of labor. Without trade (in autarky), Home's daily production is 20 tons of wheat and 10 tons of corn. Suppose that Home completely specializes, and it consumes 20 tons of wheat after it begins trading with Foreign. Home trades with Foreign at a 1-to-1 ratio of corn for wheat. How many tons of corn does Home consume when it trades with Foreign?
20 tons of corn
In the United States, one worker can produce 10 tons of steel per day or 20 tons of chemicals per day. In the United Kingdom, one worker can produce 5 tons of steel per day or 15 tons of chemicals per day. The United Kingdom will gain the most from trade (and trade will be feasible) if 1 ton of steel trades for:
2 tons of chemicals
Suppose that the introduction of computers increases the productivity of workers in the developed world. What you would expect wages to do according to the Ricardian model of trade?
rise mainly in the developed countries
Using the data in the table, what will happen to the U.S. labor force after trade occurs with China according to the Ricardian model?
U.S. labor will move from apparel to agriculture, where its marginal productivity is higher. U.S. jobs in apparel will be exported to China, wheat exports will create additional jobs in agriculture, and the value of output produced by U.S. labor will increase.
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Mercantilism is still influential today as, for example, when a country imposes a tariff on another country's exports of a product to protect the first country's domestic production of that good.
B) When two countries have different opportunity costs of production of two different goods, each of the countries is able to achieve higher levels of societal utility by specializing and trading.
C) Ricardo advocated for government intervention to promote a trade surplus.
D) A distinction between Smith's and Ricardo's approach to trade is that the former focused on absolute advantage whereas the latter emphasized comparative advantage.
Ricardo advocated for government intervention to promote a trade surplus
In the Specific Factors model, the production possibilities frontier is bowed out from the origin because
of diminishing marginal returns to labor
In the two-sector specific-factors model, as more labor is added to a sector, we will see:
the marginal product of labor decrease
In an economy in which labor is mobile and homogeneous, the wages between industries will be:
equal
Consider the following information for a hypothetical economy: if the price per bicycle is $20 and the wage per worker is $60, then what is the marginal product of labor?
3 bicycles
If the price per bushel of wheat is $3 and the marginal product of labor is 4 bushels per hour, then what is the hourly wage?
$12
A microeconomic analysis shows that in a competitive economy in which labor is homogeneous and mobile, the ratio of the prices of the products in equilibrium is inversely proportional to:
the ratio of the marginal products of labor
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, the slope of the production possibilities curve equals:
the ratio of the marginal products of labor utilized in the two sectors
If a nation begins to trade, it will be able to sell (export) the product for which its own relative price is:
lower than in other nations
Unlike in the Ricardian model, free trade in the specific-factors model:
does not require specialization in the production of only one good (or one sector).
Consider the information provided about the price of agricultural and manufactured goods in two countries (Home and Foreign). Under the condition of no trade, what is the relative price of manufactured goods?
1.66 of the agricultural good in home
Which term describes a situation in which a nation engages in no trade and produces everything it consumes?
autarky
As a nation opens up to free trade:
the relative price rises in the export sector and falls in the import sector
As a nation increases its production of exports, demand for all factors of production used in the exporting sector will:
rise
If the wage rate in the agriculture sector is lower than in the manufacturing sector, then labor will migrate to the manufacturing sector. This will cause:
both the wage and the marginal product of labor in the manufacturing sector to decrease.
As a general rule, when there are specific factors, owners of factors specific to the importing industry are ______________, whereas the mobile factor owners (such as labor) in that industry are ______________.
harmed; either benefited or harmed, depending on consumption paterns
As a general rule, the return to (or rental price of) a specific factor used in a product tends to:
rise disproportionally when the product is exported.
In the specific-factors model, suppose that a country exports the manufacturing output. Will landowners be better or worse off following the opening of trade with other countries?
they will be worse off
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model, an increase in the price of manufactured goods will cause a(n):
increase in the real rental of capital
What is the total payment to owners of capital in the manufacturing sector?
$500
Suppose that the wage is $20 per hour in a two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) Specific Factors model. Currently, the prices of manufactured and agricultural outputs are $5 and $1, respectively; the marginal product of labor in the manufactured sector is 6 units per hour; and the marginal product of labor in the agricultural sector is 10 units per hour. What does the specific factors model predict will happen to the distribution of labor between the two sectors?
The manufacturing sector will demand more labor, and the agricultural sector will demand less labor at the current wage.
Refer to the graph below of two countries, "Home" and "Foreign," showing their production possibilities, indifference curves, and an international ratio of prices with trade equilibrium in a specific factors model framework. The asterisks shown for Foreign's axis labels are to distinguish them from Home's axis labels. With trade between these two countries, Home will export ____ to Foreign. Foreign will export ____ to Home.
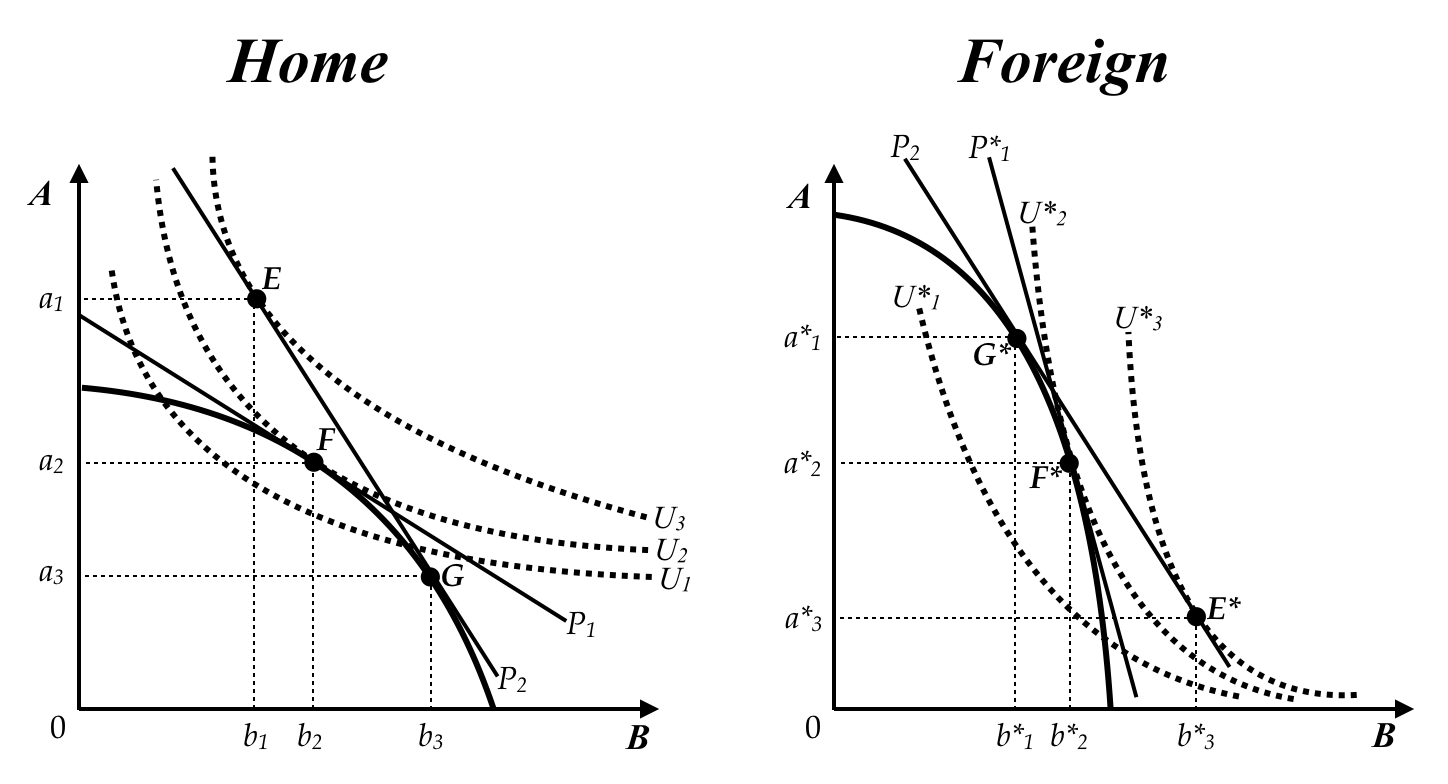
b3 minus b1; a*1 minus a*3
Which factor loses from trade in the short run in the specific factors model?
one that is specific to the importing industry
The specific factors model concludes that if there is an increase in the relative price (and an expansion) of one industry, the factor specific to that industry
will experience an increase in its marginal product.
Suppose that the home country in the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific factors model has a comparative advantage in agricultural output. Will workers be better or worse off following the opening of trade with other countries?
Workers may be better off or worse off because the real wage in terms of the agricultural good will fall and the real wage in terms of the manufactured good will rise.
Suppose that a country has a comparative advantage in agricultural products. When trade occurs, according to the specific factors model, the nominal and real returns on land will
both rise
Which of the following statements is true in the Specific Factors model where labor is able to move freely between sectors?
wages in each sector must be the same
Because of the “law of diminishing marginal returns” to a factor, as more labor is employed, its marginal product:
falls
As relative prices in various industries change due to trade, the marginal product of fixed resources used in the expanding industry __________, and the marginal product of fixed resources used in the contracting industry __________.
rises; falls
If the relative price of one product rises and labor is mobile, then in the short run
labor will move to the sector where the output price increase happened
Suppose that the home country in the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific-factors model exports its manufactured output. What will happen to the relative price of manufactured output when trade occurs?
it will rise
A change in the relative price of one good versus another will cause a change in marginal product and the allocation of labor resources. When the price of good A increases relative to the price of good B and labor is mobile, the equilibrium real wage in industry A will:
rise in terms of good B
Countries with the highest ratios of trade to GDP, calculated as (imports + exports)/2, tend to have:
the highest gains from trade
If a nation begins to trade, it will wish to buy (import) the product for which its own relative price is:
higher than that in other nations
In the two-sector (manufacturing and agriculture) specific factors model, suppose that the home country exports the manufacturing output. Why does the return to capital change after trade occurs?
there is more labor used per unit of capital in the manufacturing sector
The Heckscher–Ohlin theorem explains patterns of trade between countries using:
abundance or scarcity of factors of production
The Heckscher–Ohlin model assumes that:
consumer tastes and technologies are the same in the two countries.
The labor/capital ratio in the capital-intensive industry is _____ the labor/capital ratio in the labor-intensive industry.
less than
The PPF of a country will be skewed toward the good that:
uses its abundant factor intensively
Most trading nations do not completely specialize. Incomplete specialization is mainly due to:
increasing opportunity costs
Indonesia is relatively abundant in labor, whereas Belgium is relatively abundant in capital. In both countries, shirt production is relatively more labor-intensive than computer production. According to the Heckscher–Ohlin model, Indonesia will have a(n) ________ advantage in the production of __________.
comparative; shirts
Refer to the table below showing US capital/labor ratios for specific industries. Which industry is the most capital intensive?
chemicals and allied products
What are the post-trade quantities of shoes and computers produced by the country shown in this graph?
150 shoes; 300 computers
Which statement about the Heckscher–Ohlin model is correct?
It offers an explanation of the effects of trade on factor abundance.
It offers an explanation of the effects of trade on the returns to capital and labor.
It does not offer an explanation of the patterns of trade.
It does not offer an explanation of the gains from trade.
It offers and explanation of the effects of trade on the returns to capital and labor
Suppose Country A has 700 workers and 26,000 units of capital, and Country B has 18,000 workers and 700 units of capital. Technology is identical in both countries. Assume that wine is the capital-intensive good and cloth is the labor-intensive good. Which of the following statements is correct if the nations start trading with each other?
Rental rates of capital in Country A will increase
The table below represents autarky and free-trade production, consumption, and factor use for a country. Did the capital–labor ratio used in the production of good X rise, fall, or remain unchanged as Suburbia moved from autarky to free trade?
it rose
Suppose that, with trade, the price of shoes (which are labor-intensive) increases by 10%. Then which of the following can you say for sure about real returns to labor and capital in the country in the long run?
Real Rental rates will fall
The Leontief paradox found that
U.S exports were labor intensive
Compared with the rest of the world in 2017, the United States was most relatively abundant in:
R&D scientists
A problem with measuring the factor shares to determine scarcity or abundance is that:
the quantity of a factor may not be as important as its productivity
A country’s effective factor endowment is defined as its:
actual factor endowment times factor productivity
After accounting for differing _________ as well as _________, evidence for many countries is broadly consistent with the Heckscher–Ohlin model.
factor productivities; factor endowments
The Heckscher-Ohlin model predicts that the factor of production used more intensively in the production of exports will experience:
increased demand and an increase in its relative price
Suppose the following are true: (1) France and Italy only trade with each other, (2) each produces wine and bread, (3) The production of bread is relatively capital intensive while the production of wine is relatively labor intensive, and (4) France is relatively abundant in capital while Italy is relatively abundant in labor. According to the HO model, free trade between France and Italy should result in
increased returns to capital in France and increased wages in Italy.
With trade, this country will ____ computers.
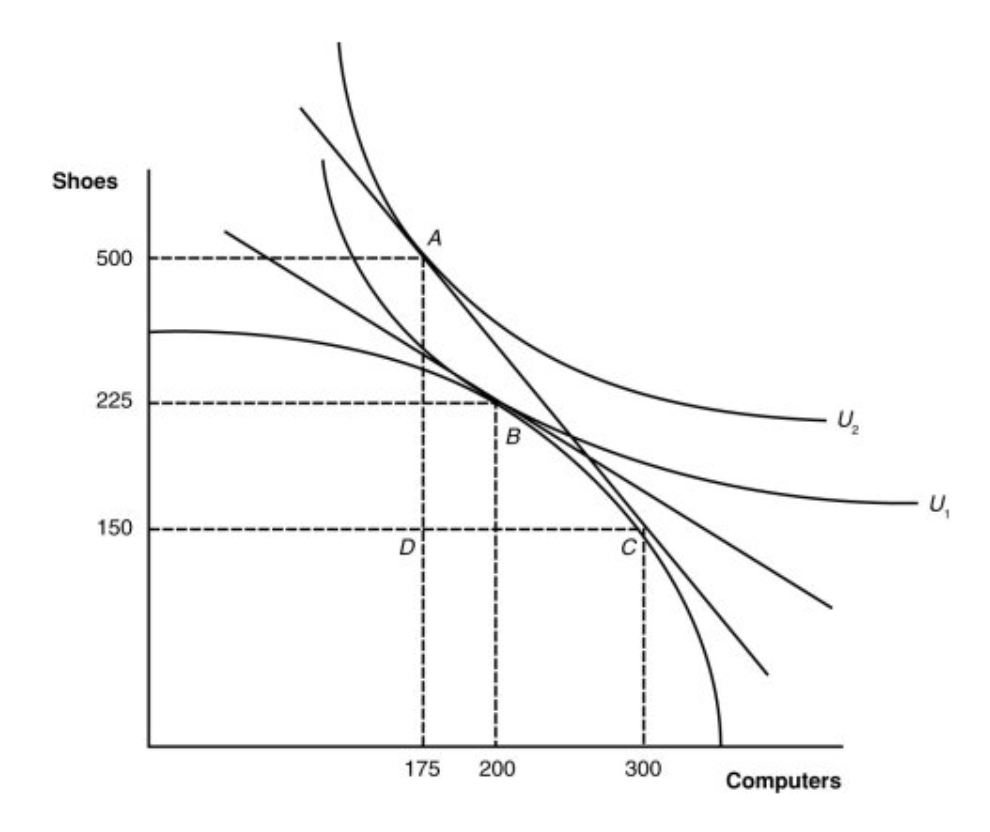
export 125
The graphs below show the production possibilities frontiers, indifference curves, and pre-trade and post-trade ratios of prices for two countries: Home and Foreign. Product B is capital intensive while Product A is labor intensive in a Heckscher-Ohlin framework. What does the new international ratio of prices with trade tell you about the terms of trade?
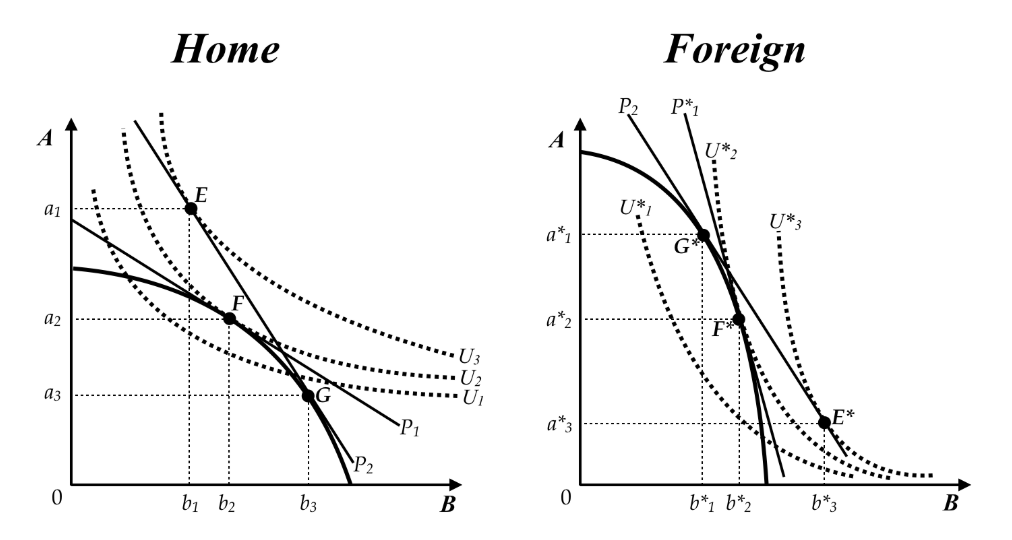
The relative price of B is now higher for Home’s producers than under autarky
In a capital-abundant country, free trade will cause a(n) __________ in the rental of capital and a(n) ____________ in the marginal product of capital.
increase; increase
The Heckscher-Ohlin model assumes that there are two countries, each of which produces two goods (say manufactures and agriculture) using labor and capital. Which of the following is an additional assumption of the Heckscher-Ohlin model?
The ratio of the quantity of labor to the quantity of capital is different for each nation, resulting in different relative endowments of capital and labor.
Refer to the table below showing US capital/labor ratios for specific industries. Which industry is the most labor intensive?
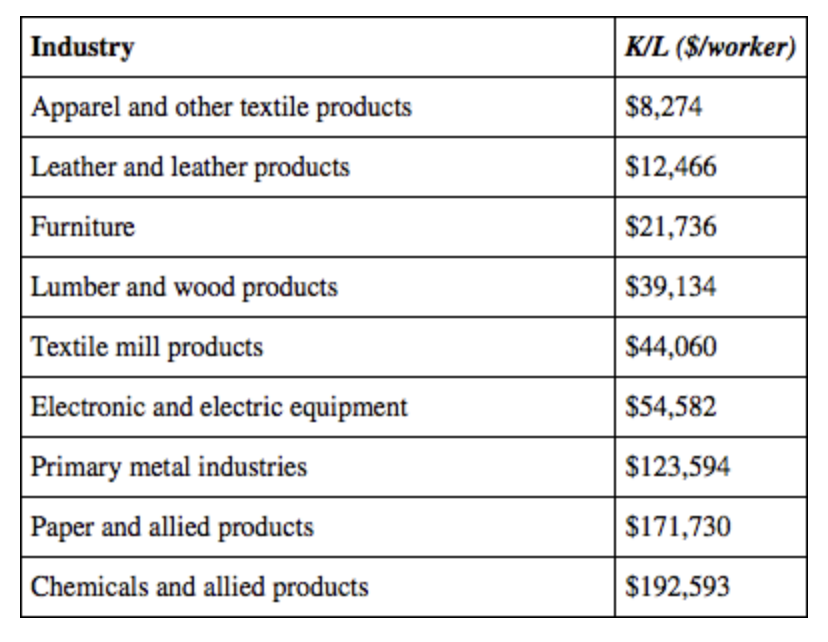
Apparel and other textile products
The graphs below show the production possibilities frontiers, indifference curves, and pre-trade and post-trade ratios of prices for two countries: Home and Foreign. Product B is capital intensive while Product A is labor intensive. In the Heckscher-Ohlin model of international trade, what does the trading pattern tell you about these countries' factor endowments?
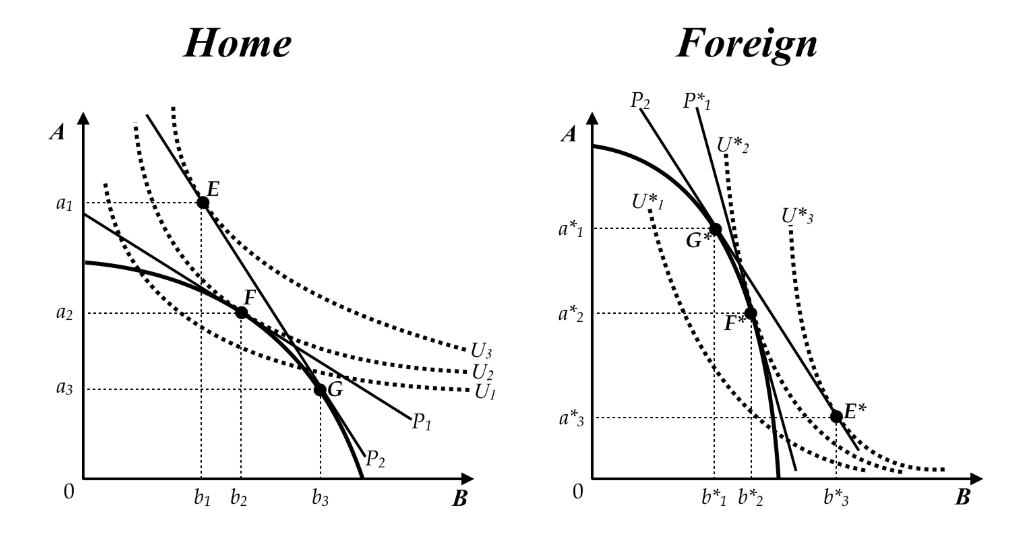
Foreign is more labor-abundant than home