Cardia and nervous
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:53 PM on 7/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
1
New cards
3 types of cardiovascular vessels
Arteries, veins, and capillaries
2
New cards
The heart lies within the middle mediastinum with
Pericardial sac
3
New cards
A heart is the size of
A mans loosely clenched fist
4
New cards
Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the lungs and sends it from
The right ventricle to the lungs (pulmonary circulation )
5
New cards
Left atrium recieved oxygenated blood from the lungs and suds it it from the
left ventricle to The body ( systemic circulation )
6
New cards
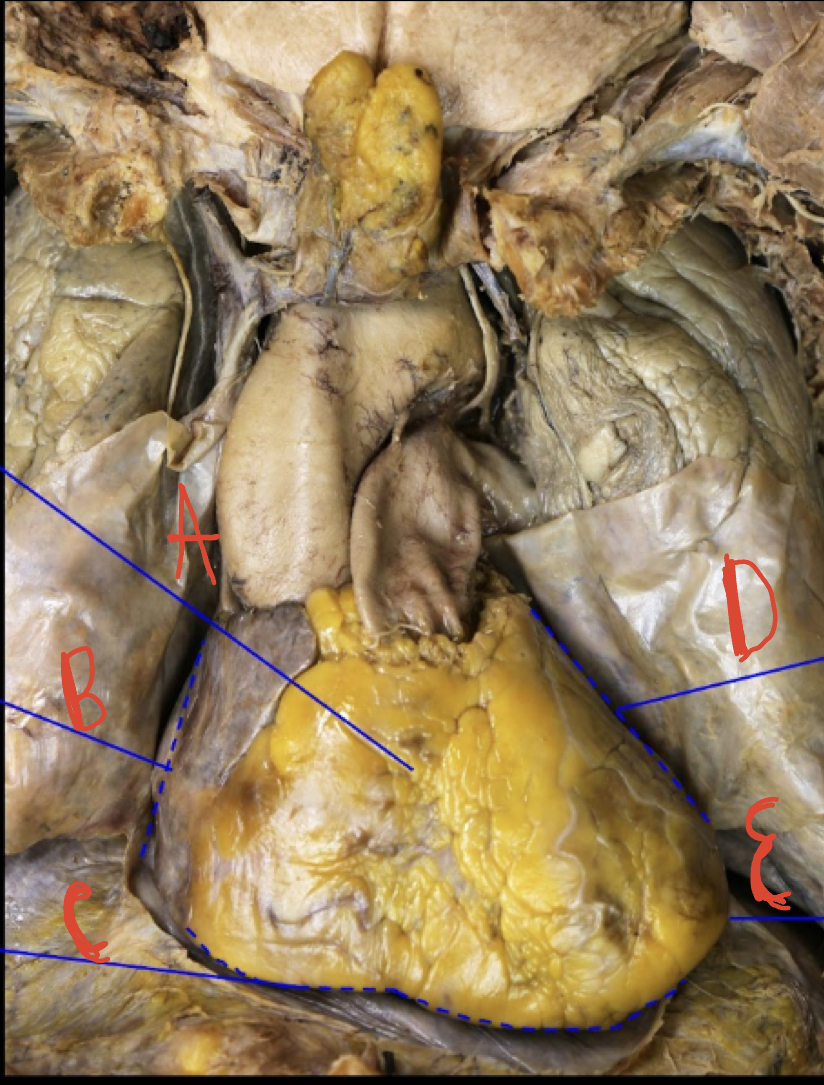
Anterior view of the heart
A: sternocostal surface, B: Right border, C: Diaphragmatic surface, D: Left border, E: Apex
7
New cards
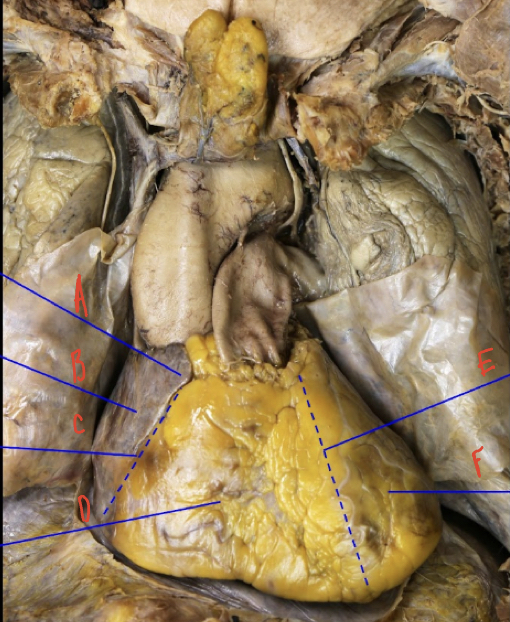
Anterior view of the heart
A: Right Auricle
B: right Atrium
C: Coronary sulcus
D: Right Ventricle
E: Anterior interventricular sulcus
F: L ventricle
B: right Atrium
C: Coronary sulcus
D: Right Ventricle
E: Anterior interventricular sulcus
F: L ventricle
8
New cards
Superior and inferior vena cava carry
Deoxygenated blood to the right atrium
9
New cards
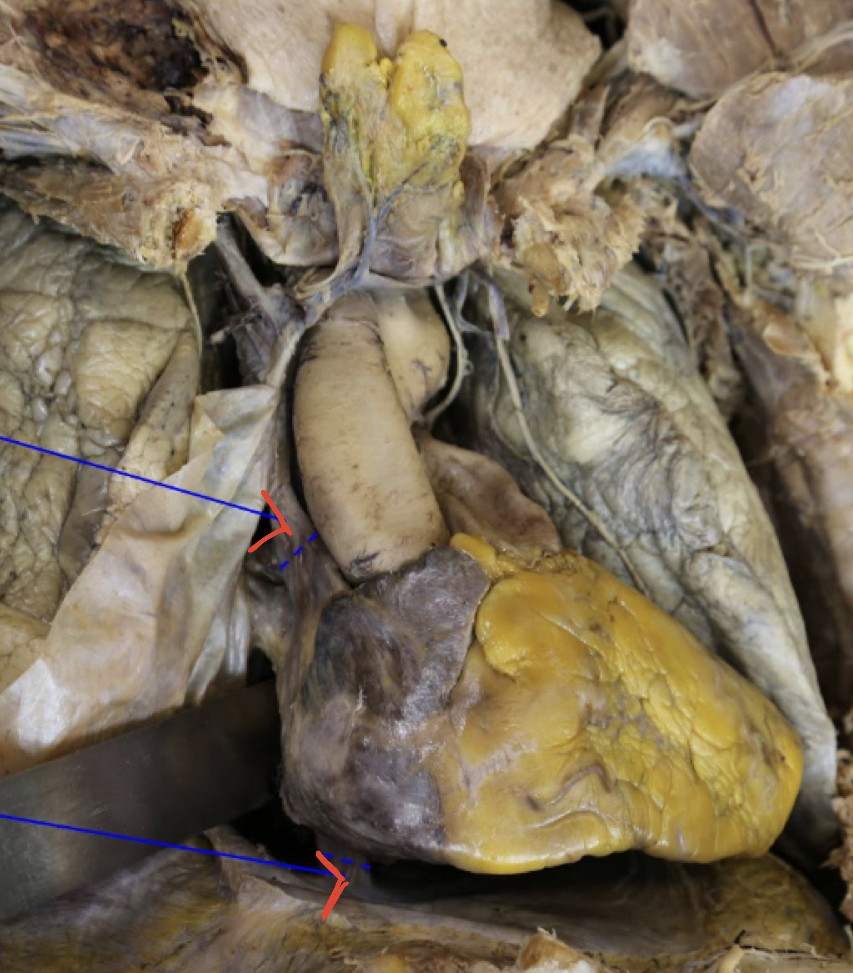
Superior vena cava
Inferior vena cava
Inferior vena cava
10
New cards
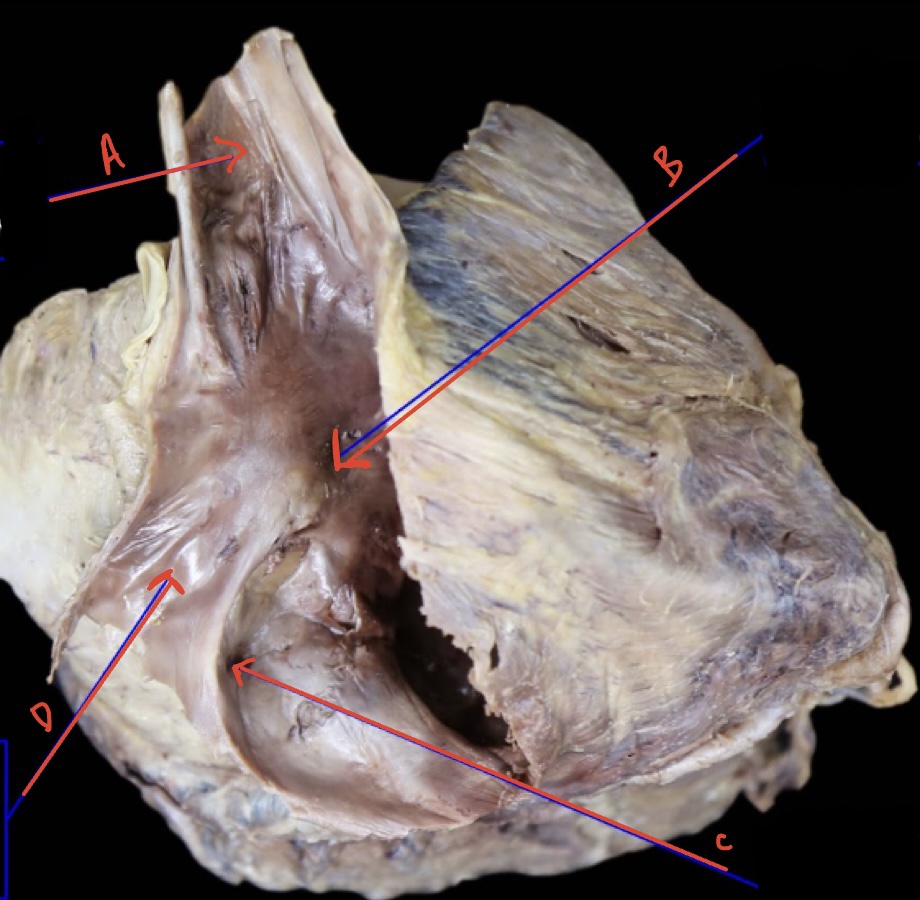
Right atrium internal anterolateral
A : Opening of superior vena cava
B: Fossa oval is
C: opening of coronary sinus
D: Inferior vena cava reflected
B: Fossa oval is
C: opening of coronary sinus
D: Inferior vena cava reflected
11
New cards
The right ventricle muscular wall is _____ than the left ventricle
Thinner
12
New cards
The right ventricle is characterized by the
Thick muscular elevation called the trabeculae Carneae
13
New cards
Three papillary muscles
Anterior, posterior and septal
14
New cards
Septomarginal trabecula is a
Feature of the right ventricle containing a part of the right bundle branch and extends from the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle
15
New cards
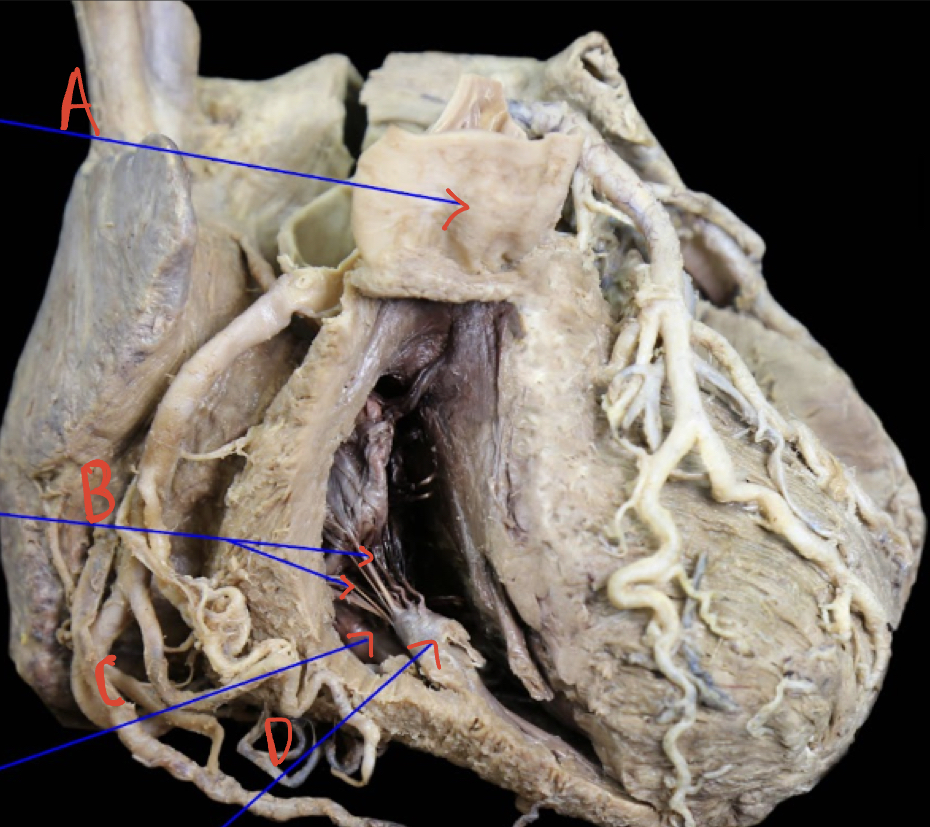
Right ventricle internal anterior
A: Pulmonary trunk
B: chordae tendineae
C: Trabeculae carneae
D: Papillary muscle
B: chordae tendineae
C: Trabeculae carneae
D: Papillary muscle
16
New cards
The left atrium is smooth walled exceot for
Pectinate muscles in the auricle
17
New cards
4 pulmonary veins 2 ___ __and 2__ ___ that
Left
Right
Bring oxygenated blood from the lungs enter the atrium
Right
Bring oxygenated blood from the lungs enter the atrium
18
New cards
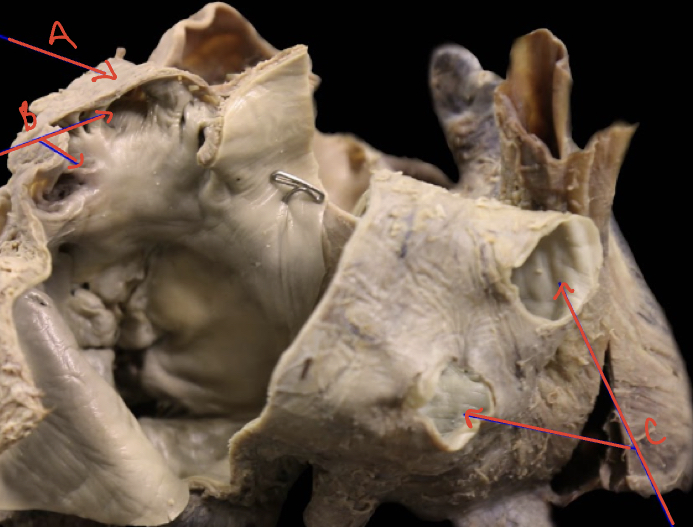
Left atrium internal posterior
A ) left auricle
B) pectinate muscle
C) opening of pulmonary vessels
B) pectinate muscle
C) opening of pulmonary vessels
19
New cards
The left ventricle is __ __x__ _______ than the right ventricle
2x thicker
20
New cards
_____ __papillary muscles,__ __ __and__ __________. Which one is thicker
2
Anterior and Posterior
Anterior is thicker
Anterior and Posterior
Anterior is thicker
21
New cards
___ _______ mitral valve
Double leaflet
22
New cards
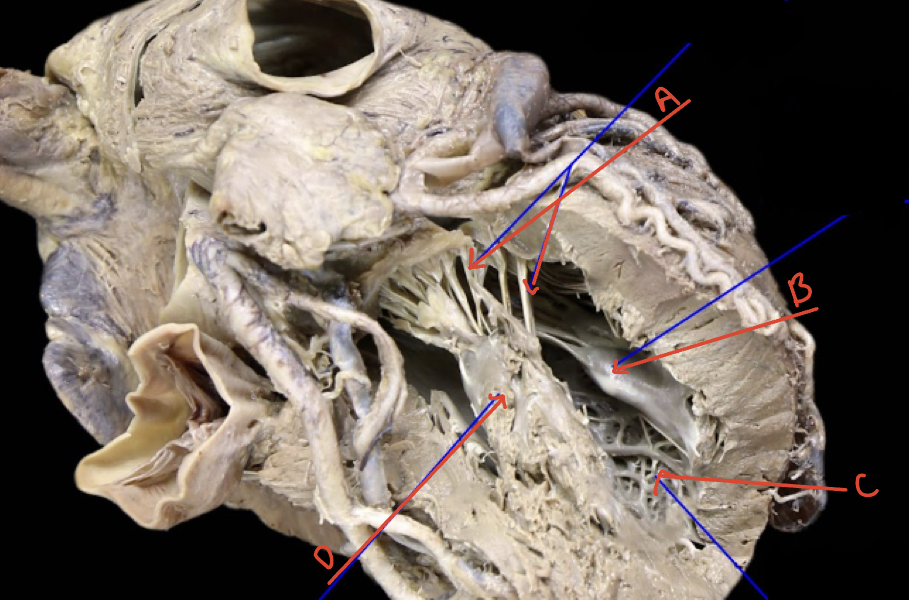
Left ventricle internal left superolateral
A: Chordae Tendineae
B: Posterior papillary muscle
C: Trabeculae Carneae
D: Anterior papillary muscle
B: Posterior papillary muscle
C: Trabeculae Carneae
D: Anterior papillary muscle
23
New cards
Pulmonary (__________) and aortic (___________) valves
Left and right
24
New cards
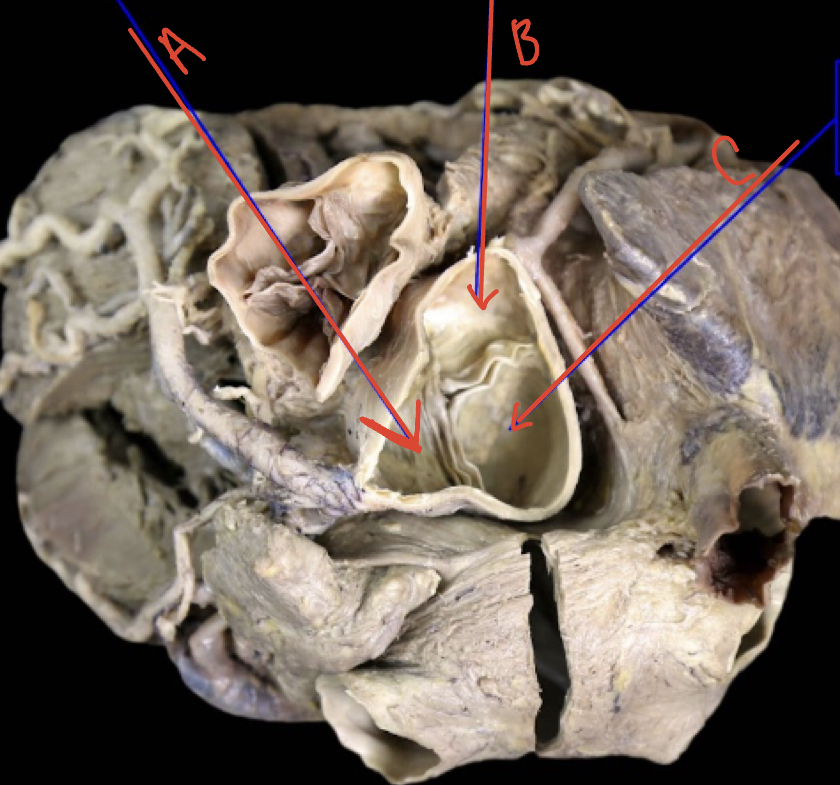
Heart superior
A) left semilunar (coronary) cusp
B) Right semilunar (coronary) cusp
C) Posterior semilunar (Non coronary) cusp
B) Right semilunar (coronary) cusp
C) Posterior semilunar (Non coronary) cusp
25
New cards
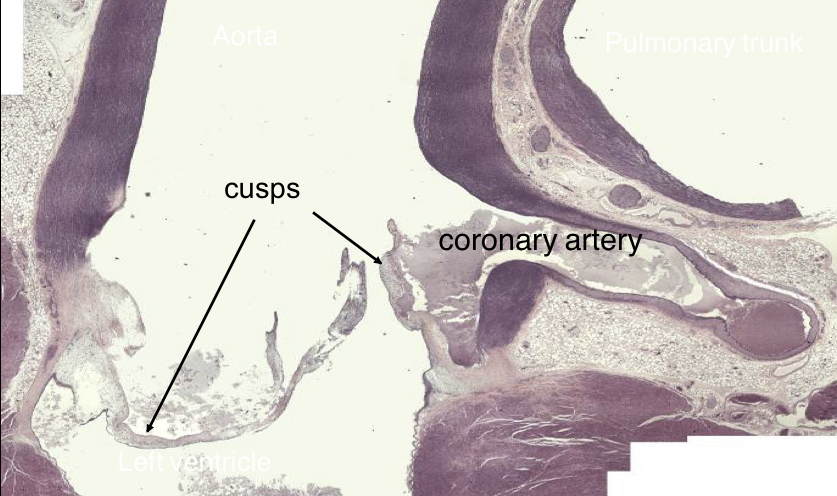
Aortic valve
26
New cards
Striated muscle, branched muscle fibers, central nuclei, joined by intercalated disks, acts to spread depolarization through intercalated disks
Myocardial muscle
27
New cards
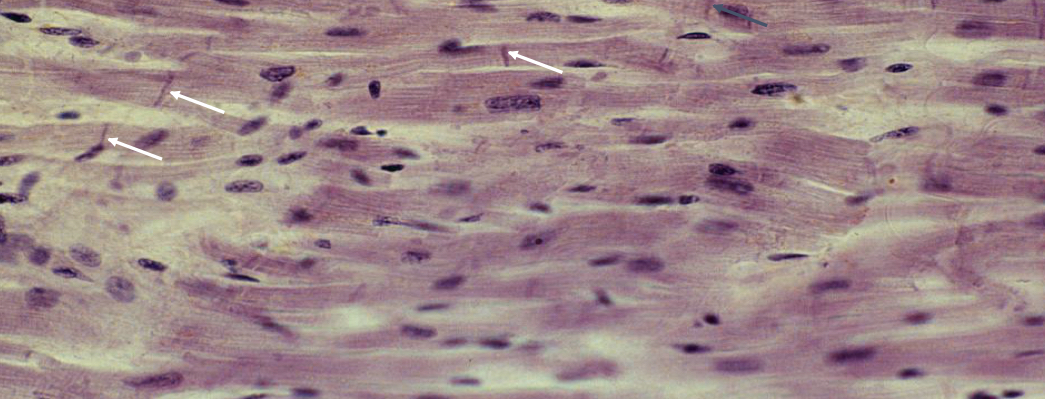
What is the picture showing? What are the arrows pointing at?
Myocardial muscle
Arrows show intercalated disks
Arrows show intercalated disks
28
New cards
3 layers of blood vessels
Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia
29
New cards
Tunica intima
Innermost, endothelium and variable amount of CT
30
New cards
Tunica Media
Middle layer, mostly smooth muscle
31
New cards
Tunica adventitia
Outermost CT
32
New cards
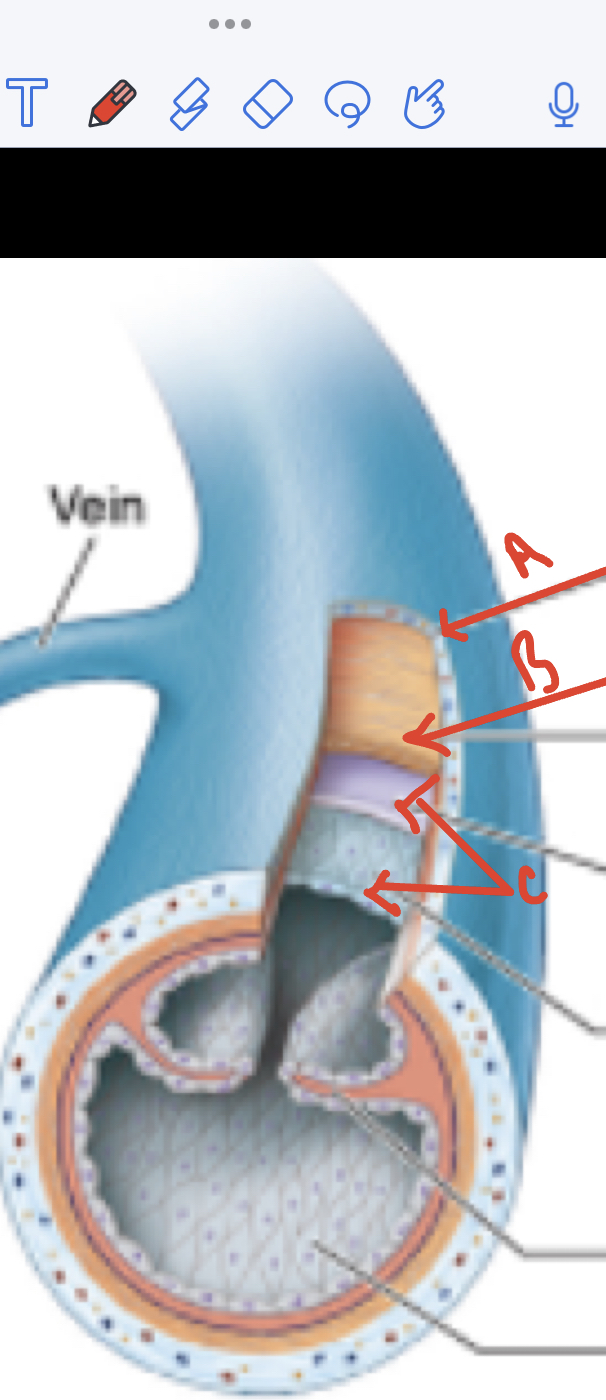
A) Adventitia
B) Media
C) Intima
B) Media
C) Intima
33
New cards
Arteries nearest the heart
Layers of the elastic tissue in the tunica media allows the vessels the expand in systole and elastically contrary during diastole to move the blood in muscular arteries
Layers of the elastic tissue in the tunica media allows the vessels the expand in systole and elastically contrary during diastole to move the blood in muscular arteries
Large elastic arteries aka conducting arteries
34
New cards
Thick muscular walls
Vasoconstrict due to the sympathetic nervous system or circulating hormones such as angiotensin II
Vasoconstrict due to the sympathetic nervous system or circulating hormones such as angiotensin II
Muscular arteries aka distributing arteries
35
New cards
Small lumen and relatively thick smooth muscle wall and regulate the filling of capillary beds
Arterioles
36
New cards
Inferior vena cava is an example, thin walled, thin muscular tunic (tunica media), and thick prominent CT tunuc (tunica adventitia) with longitudinal smooth muscle bundles
Large veins
37
New cards
Relatively thin walled, thin muscular tunic (tunica media), thick prominent CT tunic ( tunica adventitia), have valves to prevent backflow of blood, and skeletal muscle contractions and valves help blood move towards the house
Medium veins
38
New cards
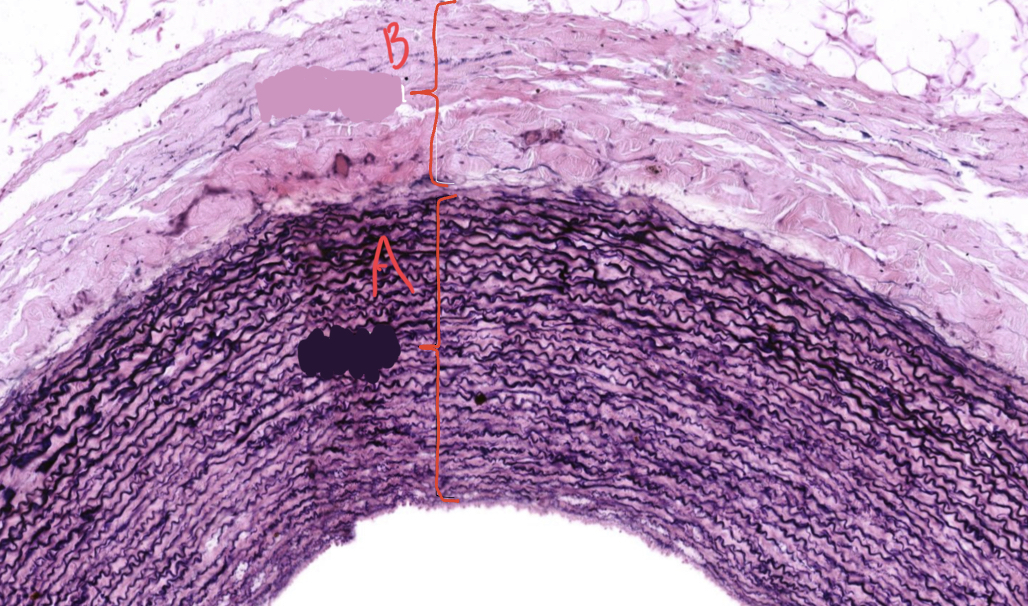
This is an image of ? What is A and B
Elastic artery
A:tunica media
B: Tunica adventitia
A:tunica media
B: Tunica adventitia
39
New cards
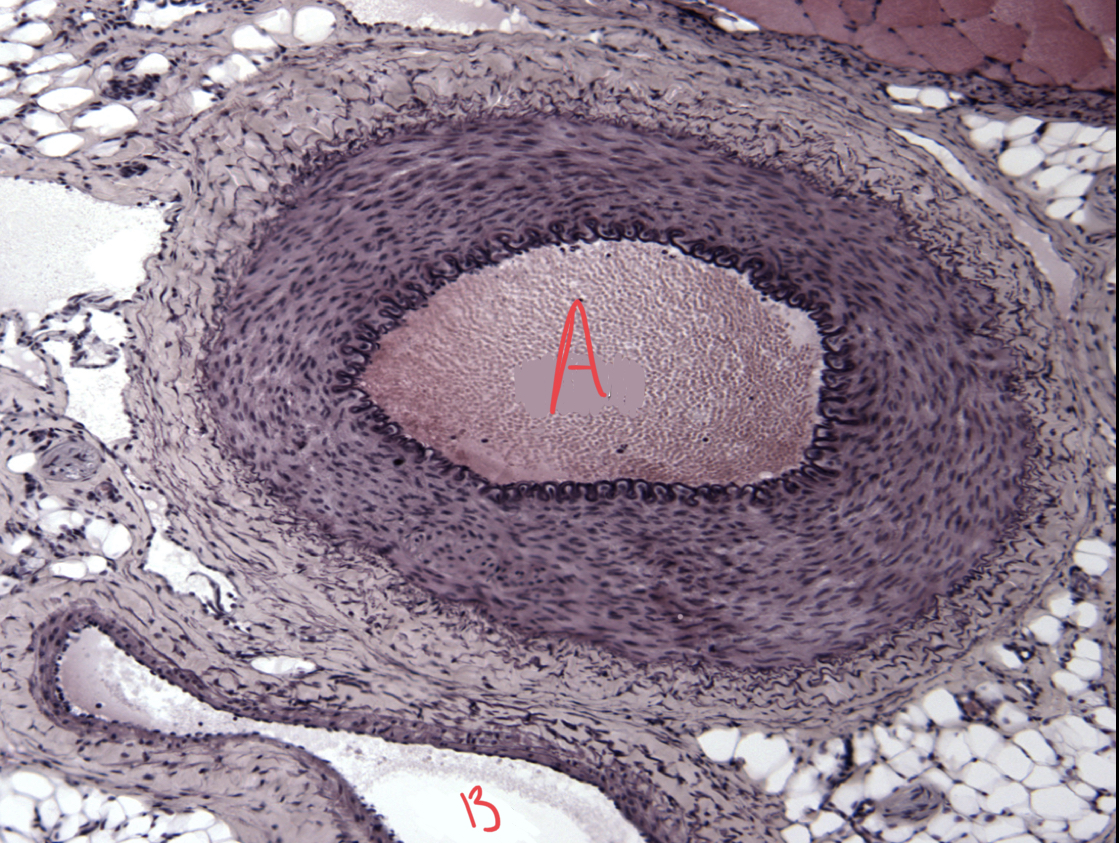
A: artery
B: vein
B: vein
40
New cards
Artery vs Vein? Round like a hose.
Artery
41
New cards
Artery vs Vein? Flat /collapsed/ low pressure
Vein
42
New cards
In limbs arteries are surrounded by ____ __veins which helps__ ____
Veins which helps warm venous blood returning to the heart
43
New cards
Capillaries exchange vessels
Allows exchange between blood and interstitial fluid , exchange of O2 and CO2, exchange of nutrients and waste products
44
New cards
Simple thin walled vessels made up of only endothelial cells and their basal lamina
Capillaries
45
New cards
3 types of capillaries
Continuous, fenestrated, and sinusoidal
46
New cards
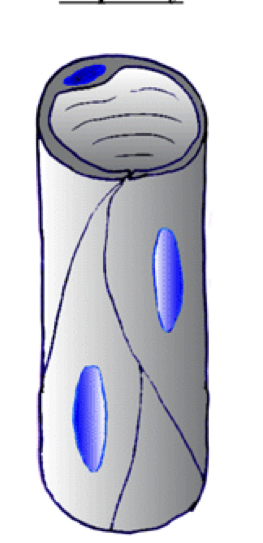
Capillary type and location found
Continuous capillary, can tell because endothelial goes all the way around
found in fat, muscle, and nervous system
found in fat, muscle, and nervous system
47
New cards
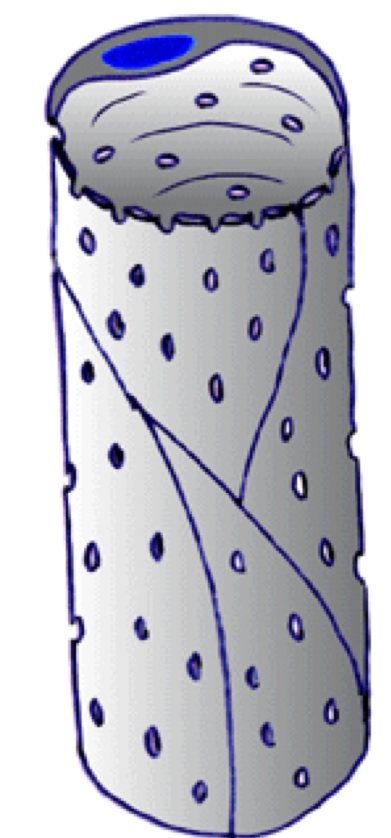
Capillary type and location found
fenestrated ; can tell due to coarse openings
Found in intestinal villi, endocrine glands, kidney glomeruli
Found in intestinal villi, endocrine glands, kidney glomeruli
48
New cards
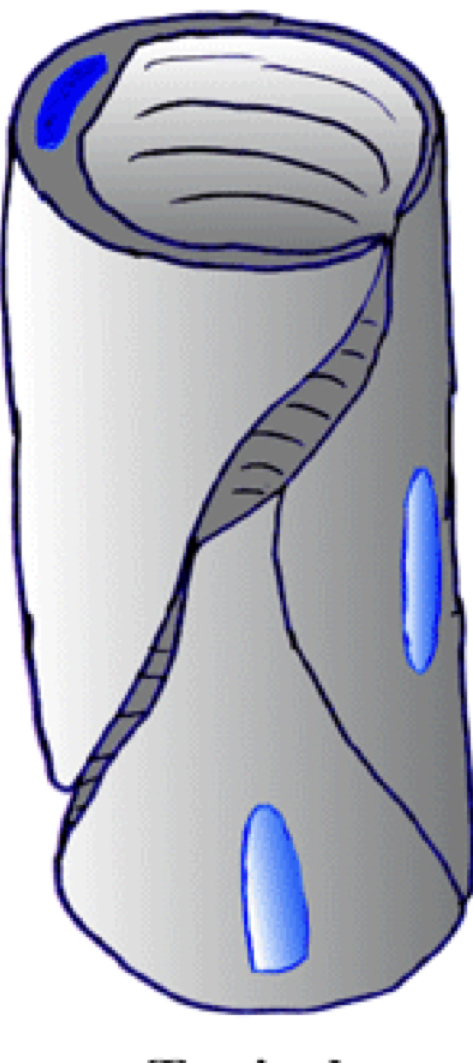
Capillary type and location found
Sinusoidal, blood moves slowly and macrofages sit outside
Found in liver bone marrow and spleen
Found in liver bone marrow and spleen
49
New cards
Build up of plaque in the arteries
Involves the tunica intima
Causes strokes
Associated with hyperlipidemia
Involves the tunica intima
Causes strokes
Associated with hyperlipidemia
Vascular disease/ atherosclerosis
50
New cards
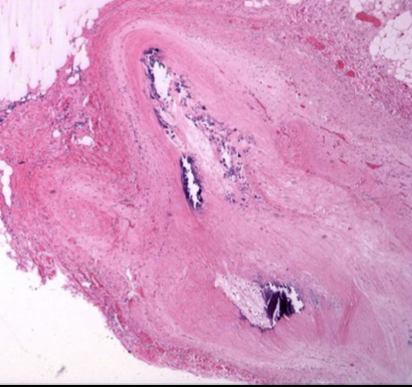
Coronary artery plaque
51
New cards
Lymphatic system
Very important in in immune system
Lymph is filtered by lymph nodes
Lymph is filtered by lymph nodes
52
New cards
Melanoma is commonly spread through
Lymphatic system to the Lymph nodes
53
New cards
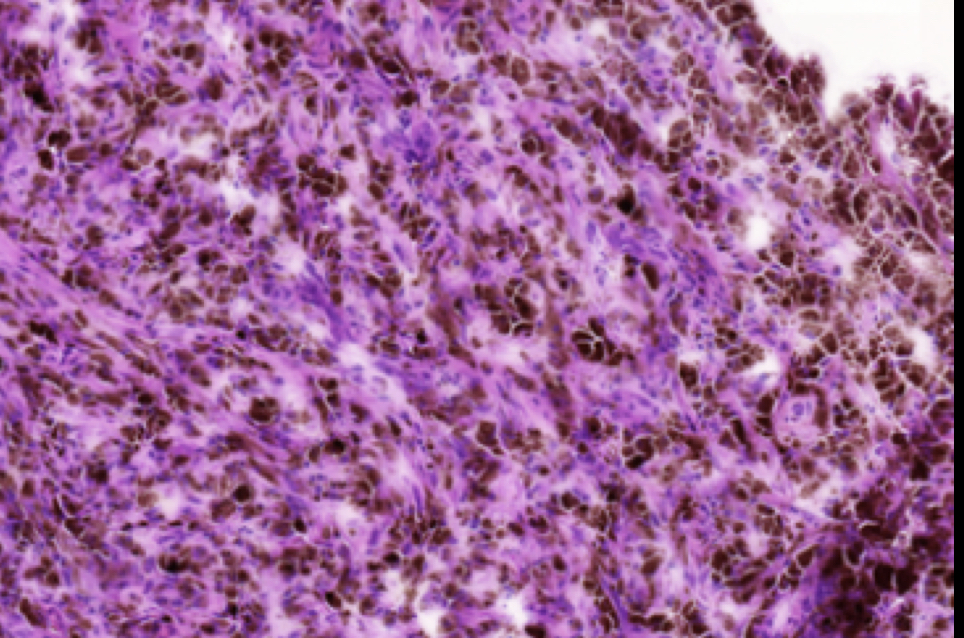
Lymph node filled with malignancy melanoma
54
New cards
Edema is a
Accumulation of fluid in the CT compartment
55
New cards
Lymphedema
In breast cancer patients lymph nodes are removed from the axilla to prevent the spread of cancer. due to this lymphatic drainage from the upper limbs is impaired resulting in lymphedema
56
New cards
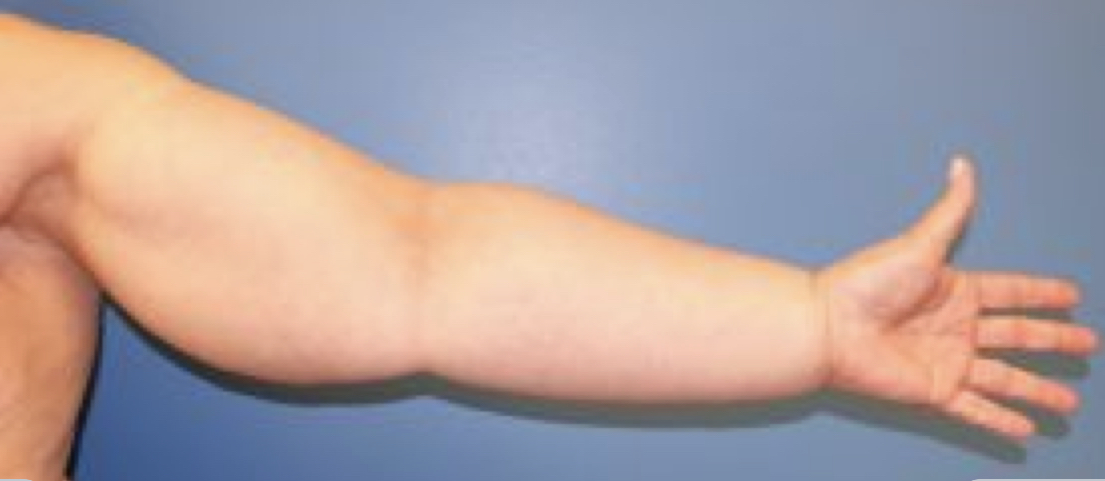
Lymphedema
57
New cards
Spinal Cord, Brain, and myelination via oligodendroglia
CNS
58
New cards
Peripheral Nerves, sensory ganglia, and Myelinization is by Schwann cells
PNS
59
New cards
Sympathetic, parasympathetic, enteric (gut nervous system) and myelinization is by Schwann cells
ANS
60
New cards
How many neurons are estimated in the human nervous system
86 B
61
New cards
How many different types of neurons are in the nervous system
Thousands
62
New cards
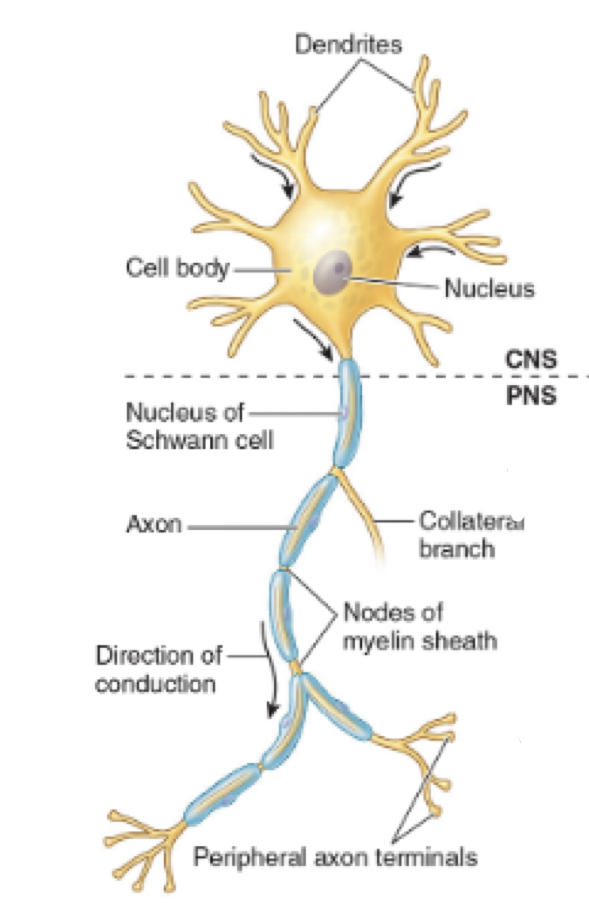
What type of neuron is this?
Multipolar Motor Neurons
* dendrites
* One neuron
* Motor neurons
* dendrites
* One neuron
* Motor neurons
63
New cards
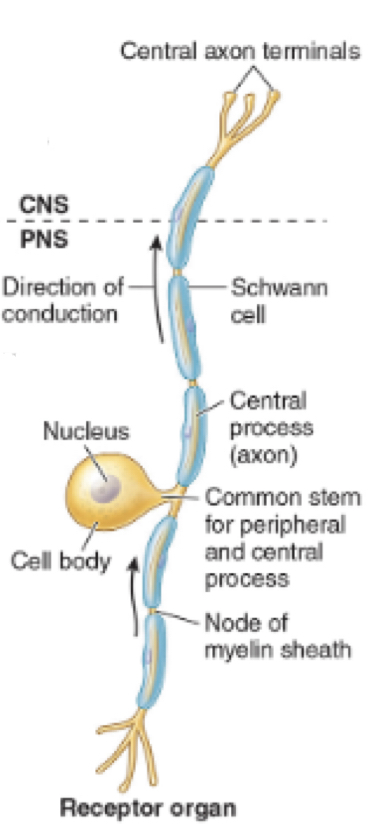
What type of neuron is this?
Pseudounipolar sensory neuron
Spinal ganglia
Ans → CNS
Spinal ganglia
Ans → CNS
64
New cards
Glial cells supportive roles in the nervous system
* support
* Insulate
* Nourish
* Insulate
* Nourish
65
New cards
Five types of glial cells in the CNS
* Astrocytes
* Oligodendroglia
* Ependymal
* Choroid plexus
* Microglia
* Oligodendroglia
* Ependymal
* Choroid plexus
* Microglia
66
New cards
2 types of glia cells in PNS and ANS
Schwann cells - mylinating cells
Satellite cells
Satellite cells
67
New cards
The spinal cord has central __________ and on the outside ascending and descending mylienated axons
Grey matter
68
New cards
Surrounding the cord are meninges three layers of CT?
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
69
New cards
Posterior horn is
Sensory
70
New cards
Anterior horn is
Motor
71
New cards
Posterior roots and root lets carry info to the
Spinal cord
72
New cards
Anterior rootlets and roots carry motor axons to the
Periphery
73
New cards
Primary sensory, pseudounipolar neurons are in the
Spinal ganglia
74
New cards
Lower motor neurons the axons of which synapse on muscle fibers are in the
Anterior horns
75
New cards
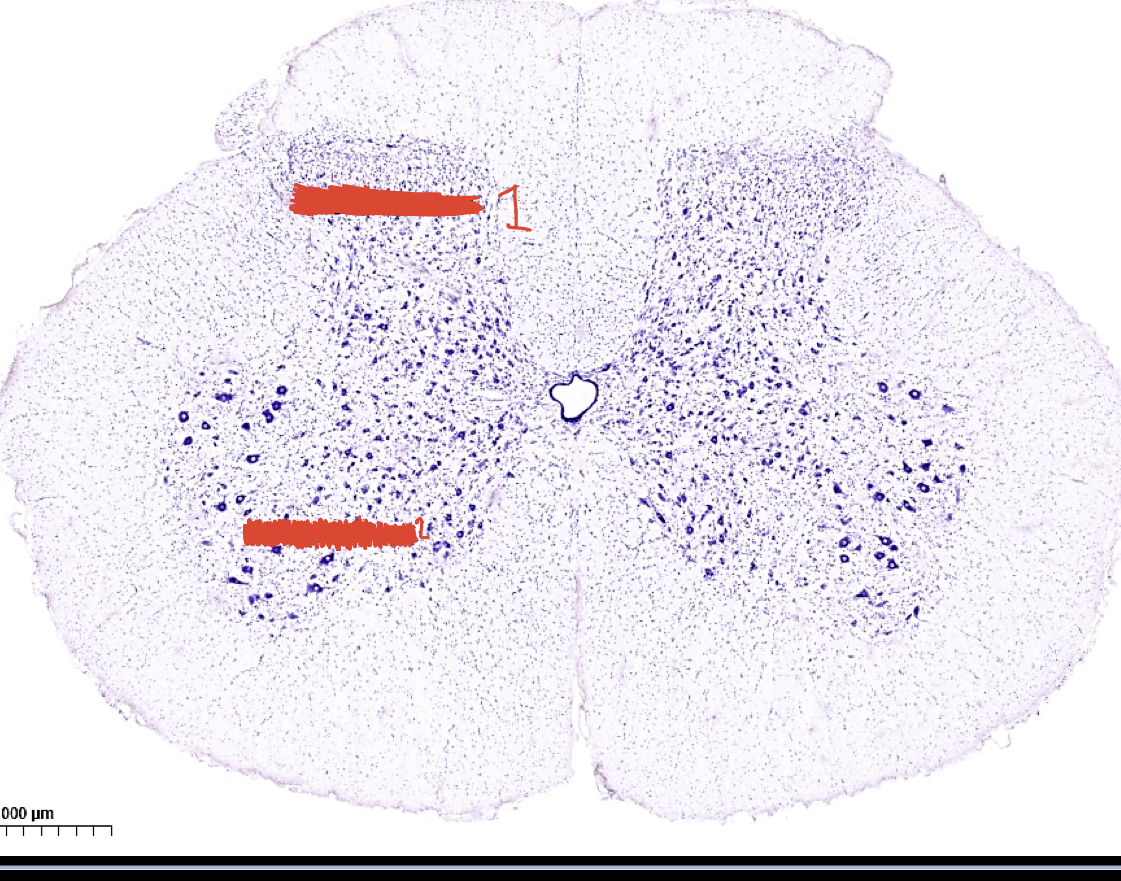
1 posterior horn
2 anterior horn
2 anterior horn
76
New cards
Cerebral cortex is organized in lobes where there is
Functional localization
77
New cards
Subcortical nuclei include the
Basal ganglia and the thalamus
78
New cards
Brainstem has nuclei involved with the cranial nerves and regions involved in
Respiration and cardiovascular regulation
79
New cards
The cerebellum is involved in
Coordination of planning and executing movements
80
New cards
Why are there folds in the brain
Due to the expanding size in evolution
81
New cards
Brain folds
Gyri
82
New cards
Valleys of the brain
Solsi
83
New cards
Most of the cortex in the human brain has 6 layers and is called the
Neocortex
84
New cards
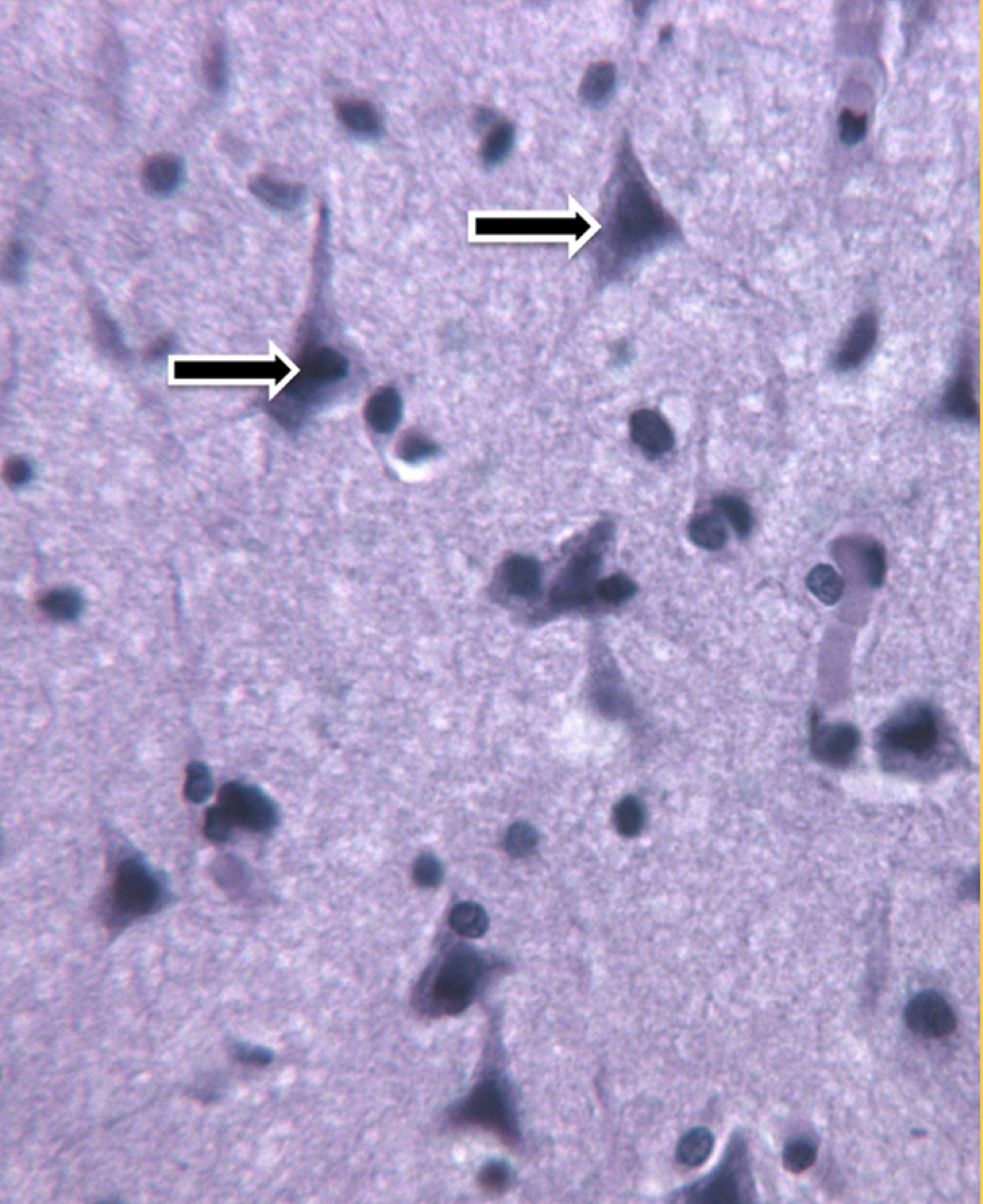
Neocortex and arrows are pyramidal neurons
85
New cards
Damage to specific areas in the brain from a stoke causes
Specific deficits
86
New cards
How is the human body organized
Segmentally organized
87
New cards
Why is segmental organization not as apparent in limbs
complex development
88
New cards
What becomes evident during the somite period of embryonic development
The segmental nature of the human body and nervous system
89
New cards
By 28-30 days of gestation when the embryo is approximately 4.5 mm in length the human embryo has how many somites
30-35
90
New cards
Medial portions of somites become sclerotomes which gives rise to
VERTABRAE
91
New cards
Lateral portions of somites become
Dermatomyotomes
92
New cards
Cels that migrate posteriorly give rise to
Epaxial, deep back muscles, and overlying dermis
93
New cards
Anteriorly migrating cells give rise to
hypoxia muscles of the trunk, limbs, and overlying dermis
94
New cards
Flexor muscles of the limbs lead to
Triceps
95
New cards
Extensor muscle of the limbs become
Biceps
96
New cards
Anterior and posterior rots unite with the intervertebral foramen to form
Spinal nerves
97
New cards
Why are spinal nerves referred to mixed nerves
Because they have both sensory and motor neurons
98
New cards
Just past the point of union the spinal nerve branches into
Posterior ramus and anterior ramus
99
New cards
Posterior rami go to
Deep back muscle and skin over them
100
New cards
Anterior rami go to
Anterior body