1.2.9 Indirect taxes and subsidies (copy)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
ad valorem tax
tax levied as a percentage of the value of the good e.g. VAT 20% of an item
specific tax
tax levied on volume or weight e.g. sugar tax
who taxation affects
it is levied on suppliers
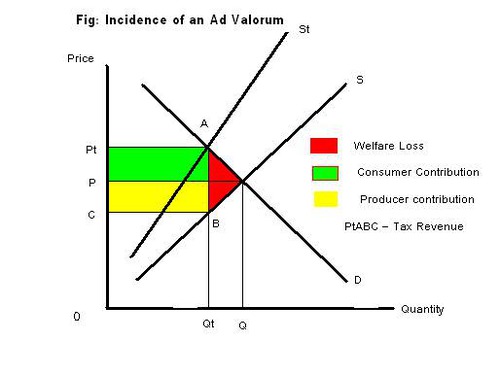
ad valorem tax diagram
specific tax diagram
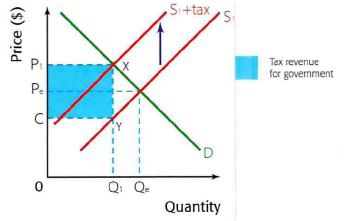
impact of the introduction of a tax
causes supply curve to shift upwards from s to s1 because it leads to an increase in the cost of production, this will cause a rise in price from p to p1 and a fall in output from q to q1
the size of the tax is shown by...
...the vertical difference between supply curves
if the demand curve (PED) is perfectly elastic or supply curve (PES) is perfectly inelastic
the supplier will pay all the tax
the demand curve (PED) is perfectly inelastic or supply curve (PES) is perfectly elastic
all the tax will be passed on to the consumer
benefit to gov: ceteris paribus, the more inelastic the demand curve
the higher revenue of tax because quantity demanded falls less than the increase in price
impact of indirect tax on consumers
-higher price -lower choice -lower quality -people seek alternatives -regressive - low income households hit hardest
impact of indirect tax on firms
-increase in the cost of production -lower output -reduced profits -> lower producer surplus -potential job losses -potential bankruptcy
impact of indirect tax on governments
-increase in inflation -reduced consumer confidence -reduction in damage to environment/health -price protests -increased tax revenues
subsidy
a form of government support - financial or otherwise - to encourage supply of a good/service
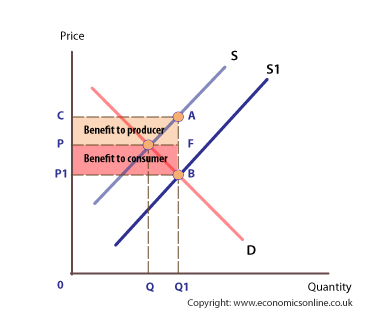
subsidy diagram
inelastic market demand subsidy
fall in price will have a smaller increase in demand
elastic market demand subsidy
fall in price will have a larger increase in demand
main issue with subsidies
the opportunity cost
why subsidies are greatly supported
increases both consumer and producer surplus and the cost of subsidies get spread across many taxpayers so a limited cost for the government
impact of subsidy on consumers
-lower price -more choice -better quality -greater consumption of merit goods
impact of subsidy on firms
-reduced production costs -increased competitiveness -increased output -greater revenue and profits -protection of jobs -prevent bankruptcy -more investment in capital
impact of subsidy on governments
-opportunity cost of subsidy -greater consumption of merit goods -greater tax revenues from increased consumption -downwards pressure on inflation -lower unemployment rate -greater dependency could make firms dependent and inefficient