B Lymphocyte Development
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Where do B cells reside?
secondary lymph tissue like lymph nodes and spleen within the germinal centers
What are the primary lymph tissues
bone marrow and thymus
What are the secondary lymph tissues
Lymph nodes and spleen
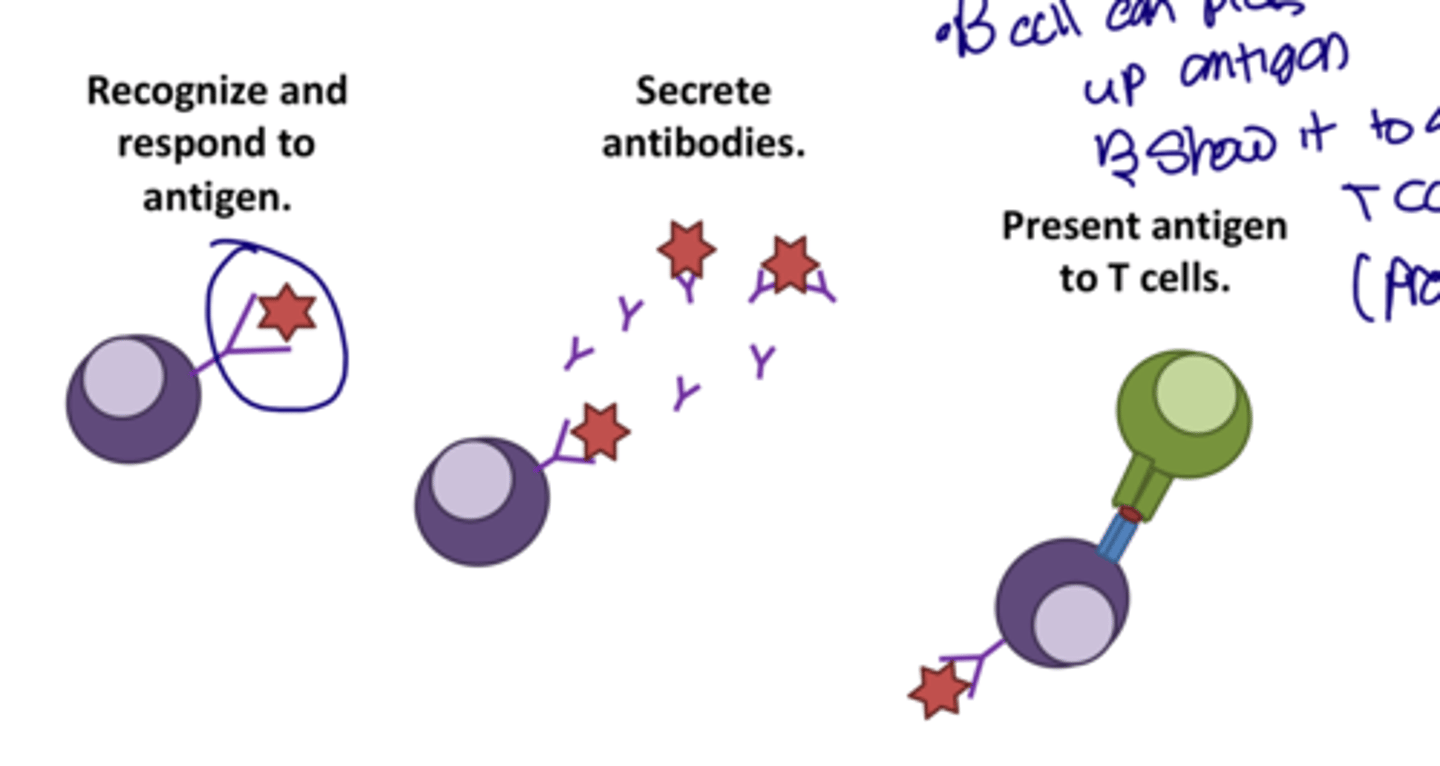
How do B cells bind to antigens
B cells bind to free antigens floating around, they differ from T cells in which they are not MCH presentation restricted.
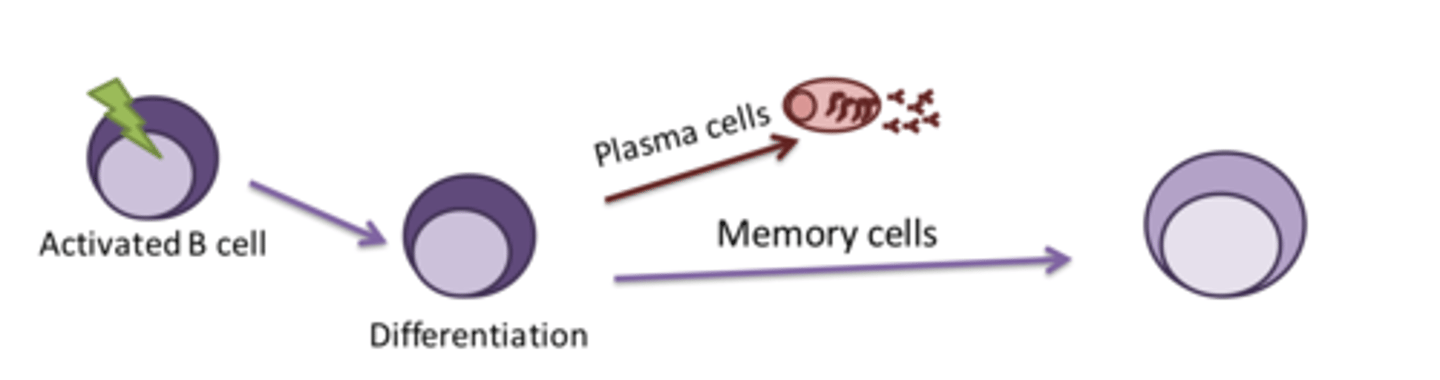
What occours when a mature B cell is activated
It is signalled to proliferate and then become a plasma cell which has the sole job to make anitbodies
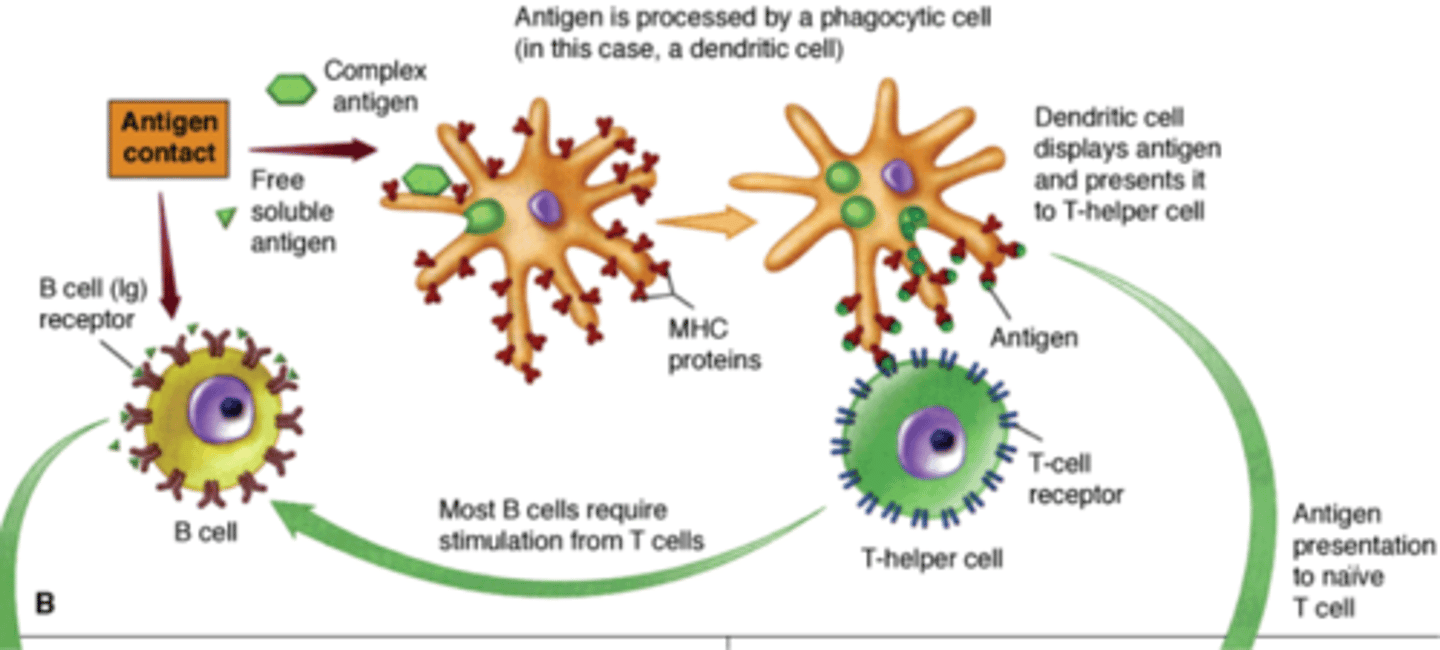
How are mature T cells activated?
They are activated when the MHC presents the antigen in a readable/ processed form that the T cell can understand and then act
How can a B cell interact with a T cell
It can carry the Antigen to the T cell and present it in replace of the MCH
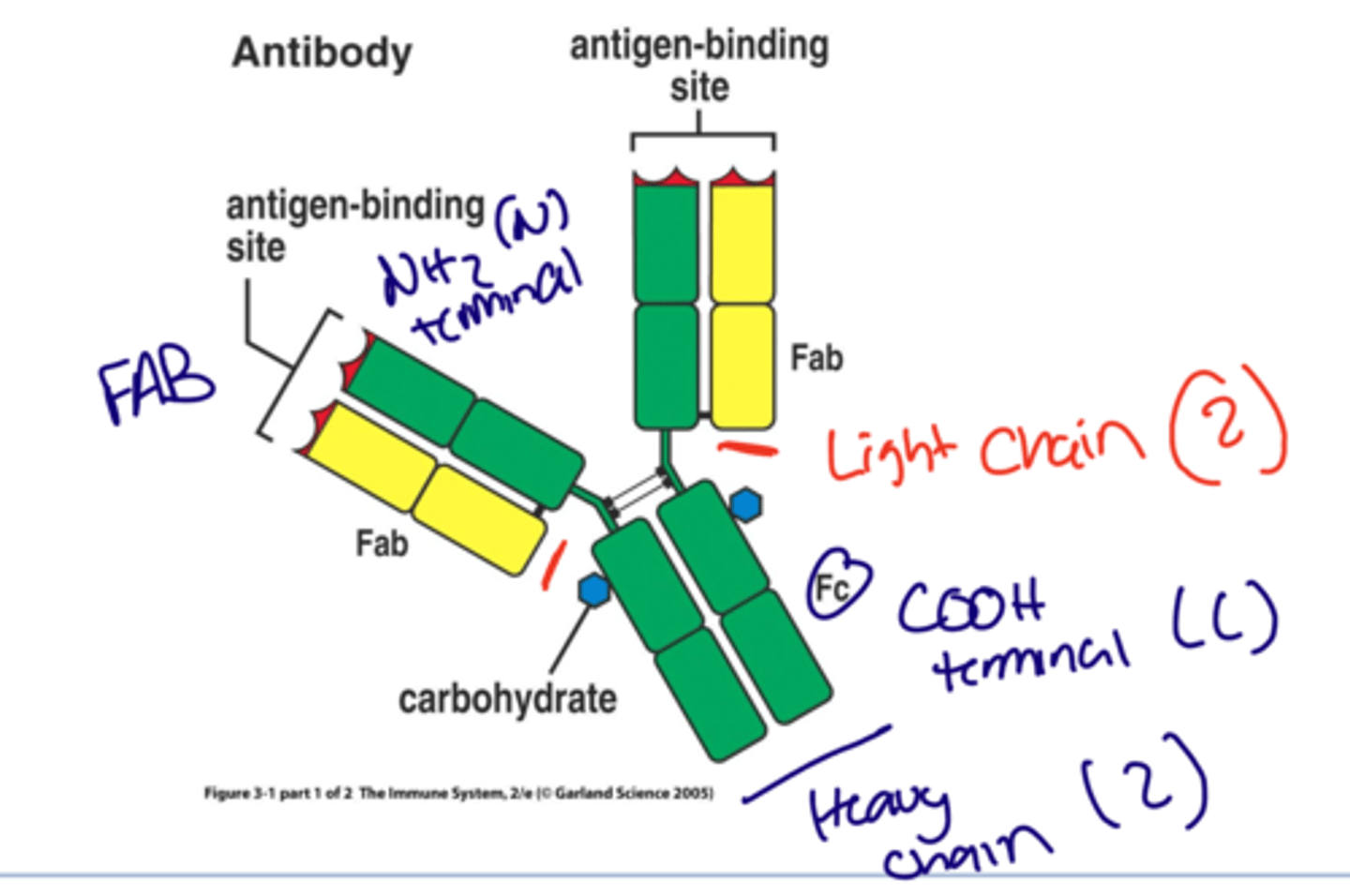
Describe the Antibody general structure
There are 4 chains total, two Heavy chains and two light chains attached to the ends of the Heavy chains on the outer side.
The top Half including the light and heavy chain is called Fab
The bottom half only containing heavy hain is called Fc
FC = C terminus
FAB = N terminus
What are the 5 different isotypes of antibodies?
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, IgD
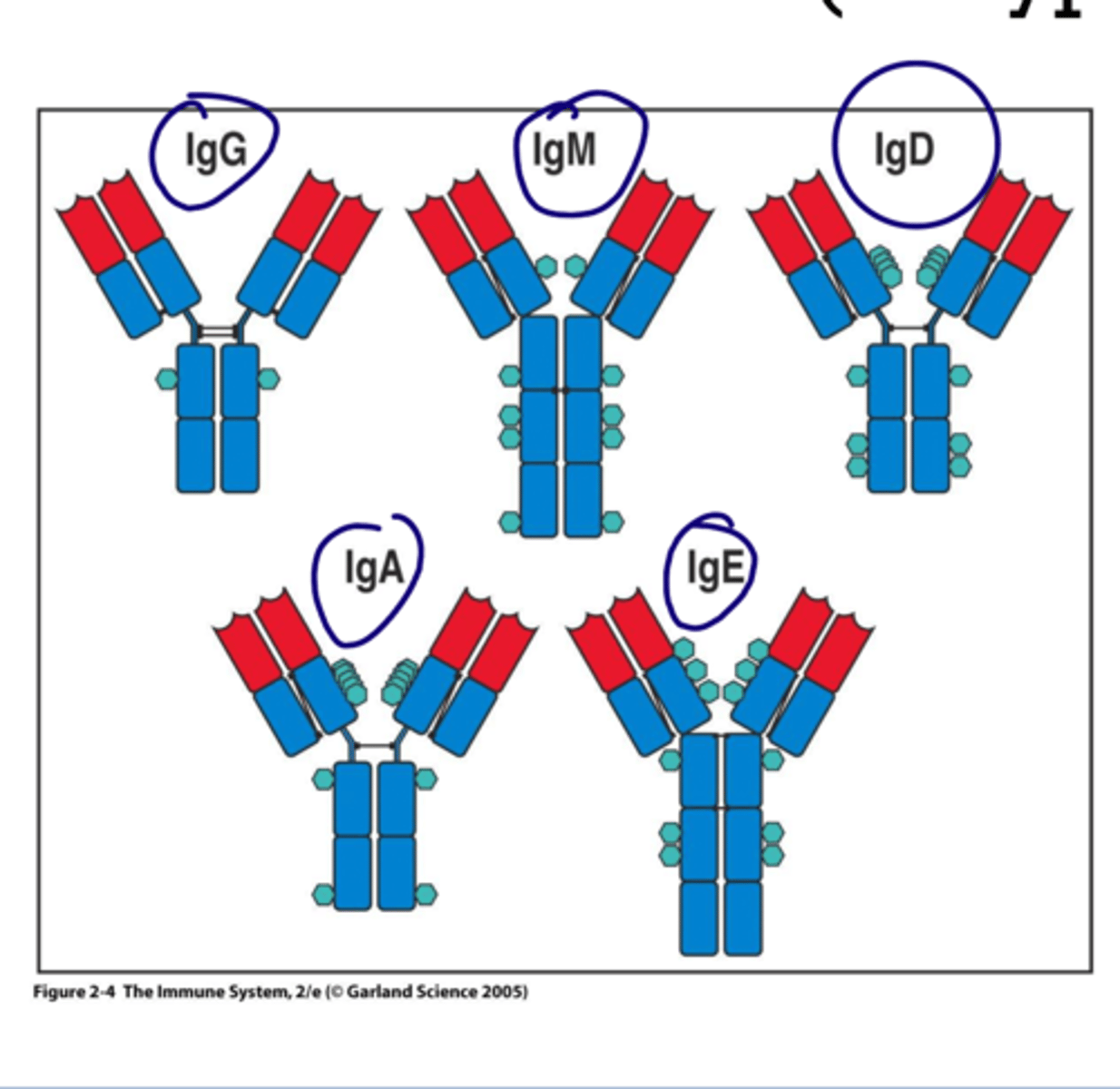
What portion of the antibody determines the Isotype?
The FC determines the antibody class/isotype
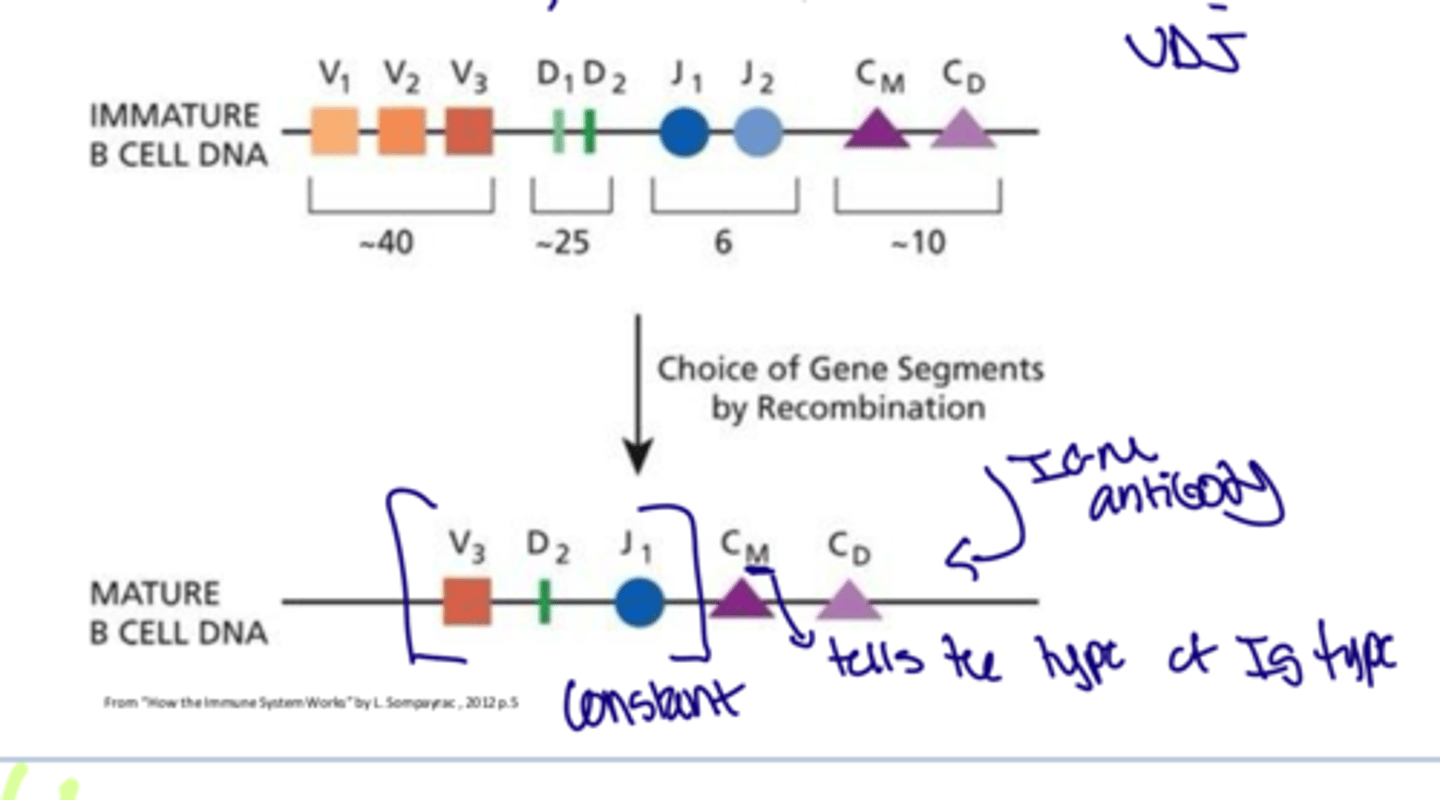
What is the arrangement for the heavy chain
VDJ
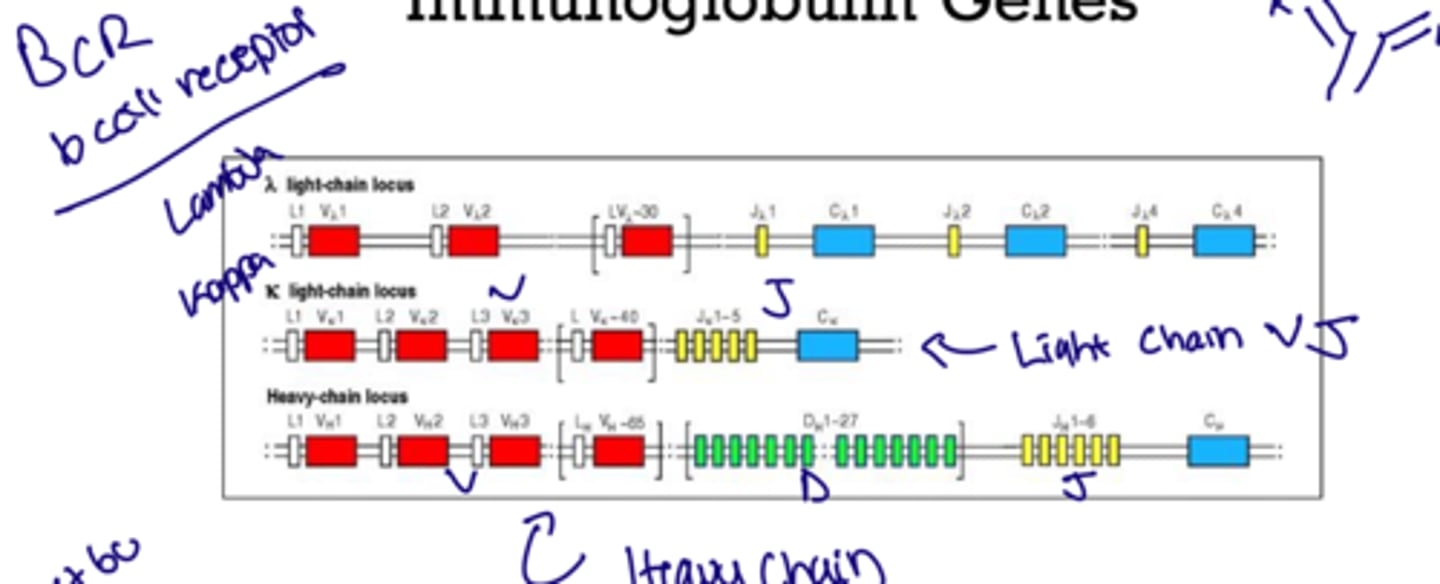
What is the arrangement for light chain
VJ
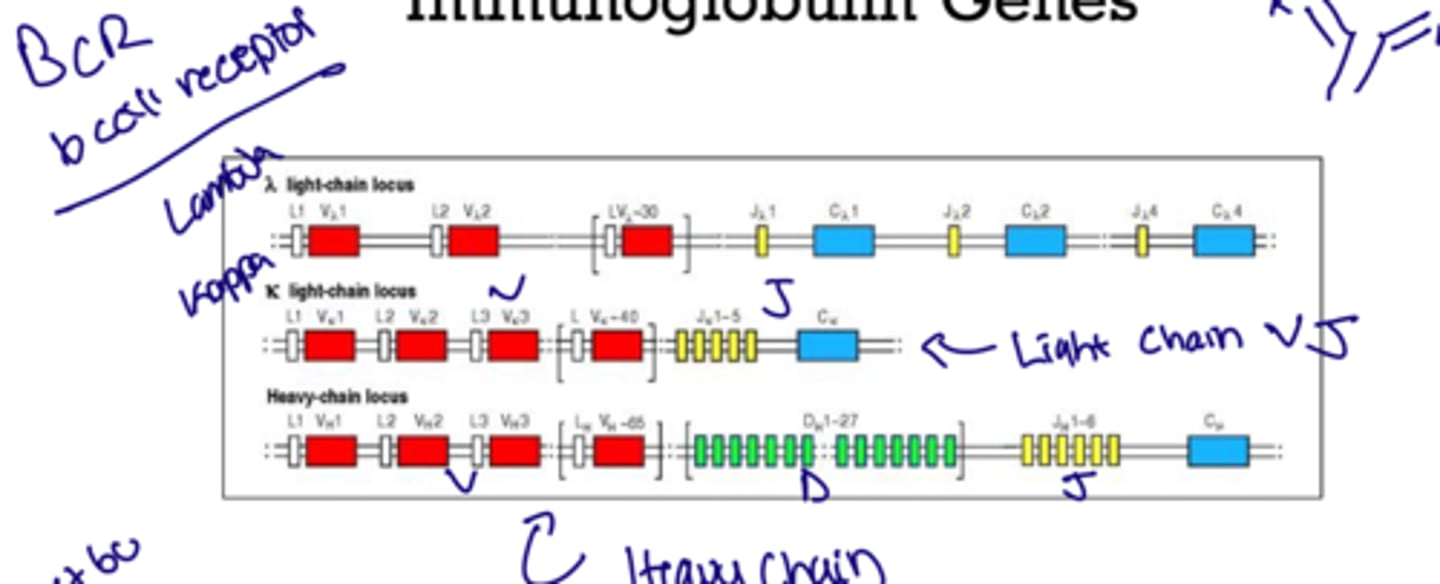
What are the loci chain types
Lambda or Kappa which work better when bound to a mimicked pair so lambda to lamba or kappa to kappa
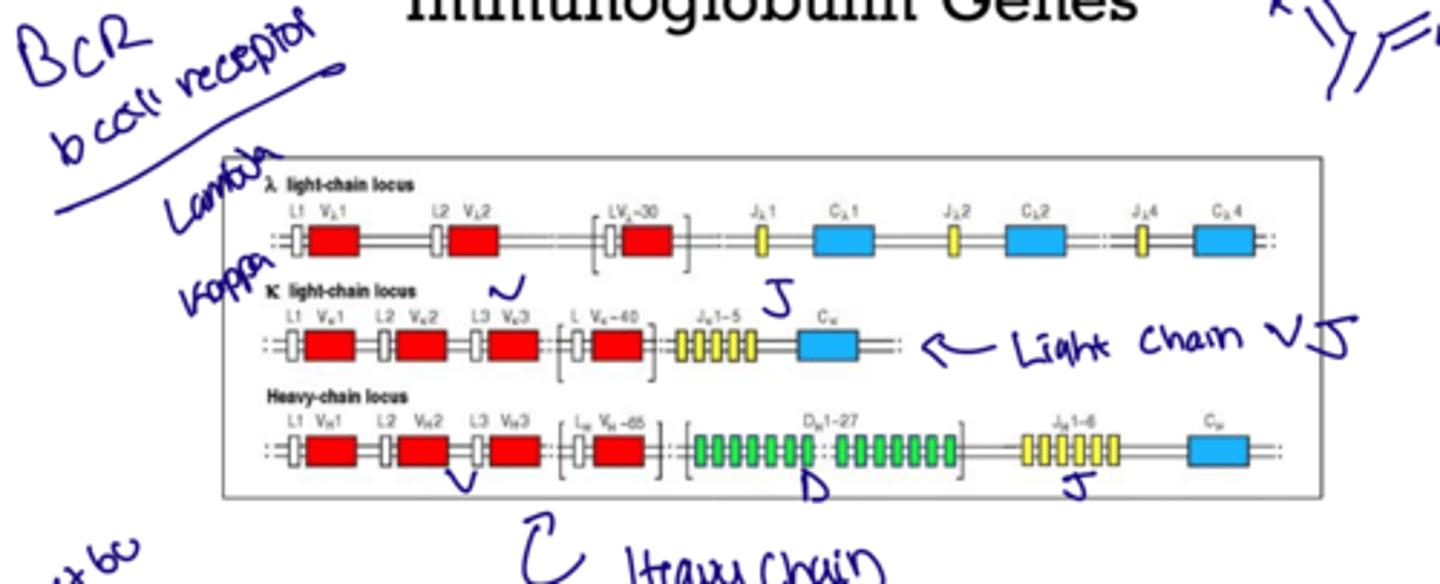
What protein mediates the gene rearrangement?
Rag-1 and Rag-2
How to tell the type of antibody?
Pay attention to the type of C right after the VDJ/ VJ arrangement
Omenn syndrome
RAG protein has partial enzymatic activity from missense mutations, causes rapid fatal immunodeficiency
Lack or complete elimination of circulating T or B cells
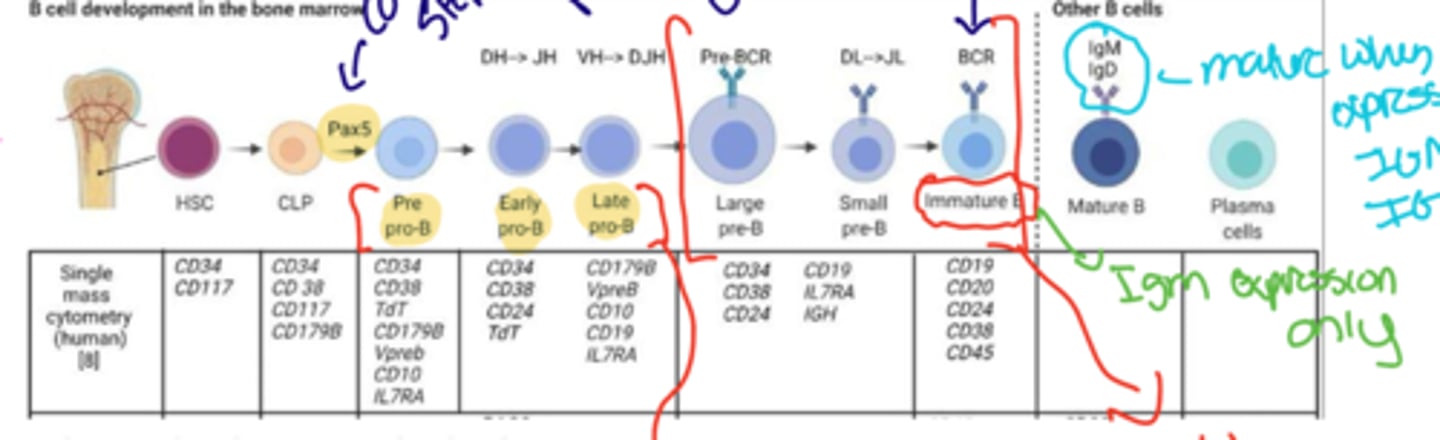
Explain the development of a B cell from the stem cell progenitor
- Stem cell begins in the bone marrow
- Travels to a GC
- interacts w/ Pax 5 which is the defining step
-becomes a Pre pro B cell
-goes through early and late stages for reassembly of VDJ
-builds the Heavy chain in reassembly
-Picks up Cd 19 to enter the B cell commitment phase
-Starts building Light chain
-Develops BCR and becomes a immmature B cell
-During this time it is only displaying IGM and then matures to get the IGD cell after leaving
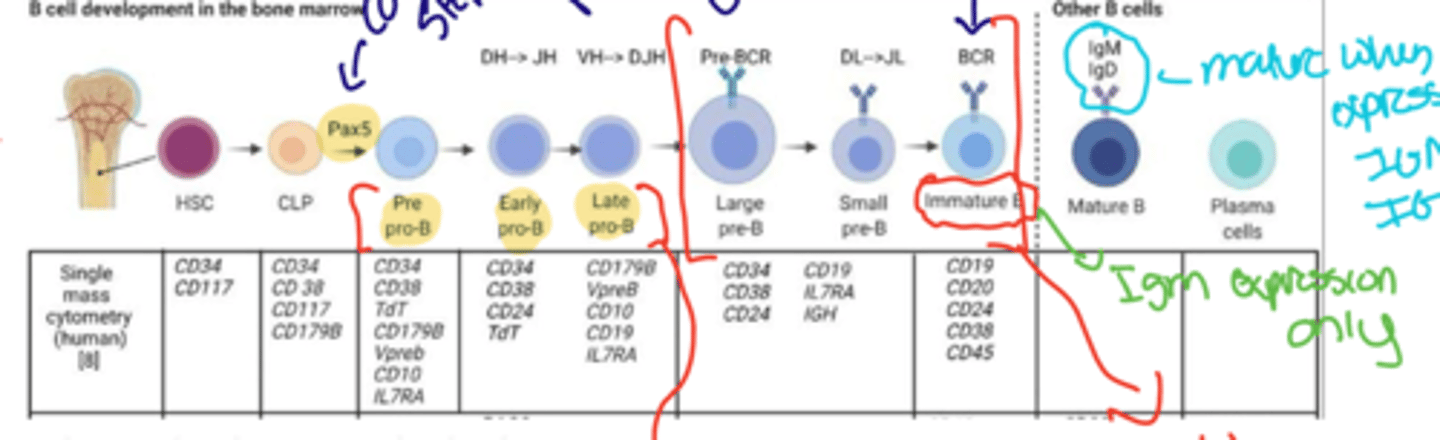
When does a B cell become mature
When it leaves the bone marrow. It is now naïve until it encounters antigen.
- it contains the IGM and IGD
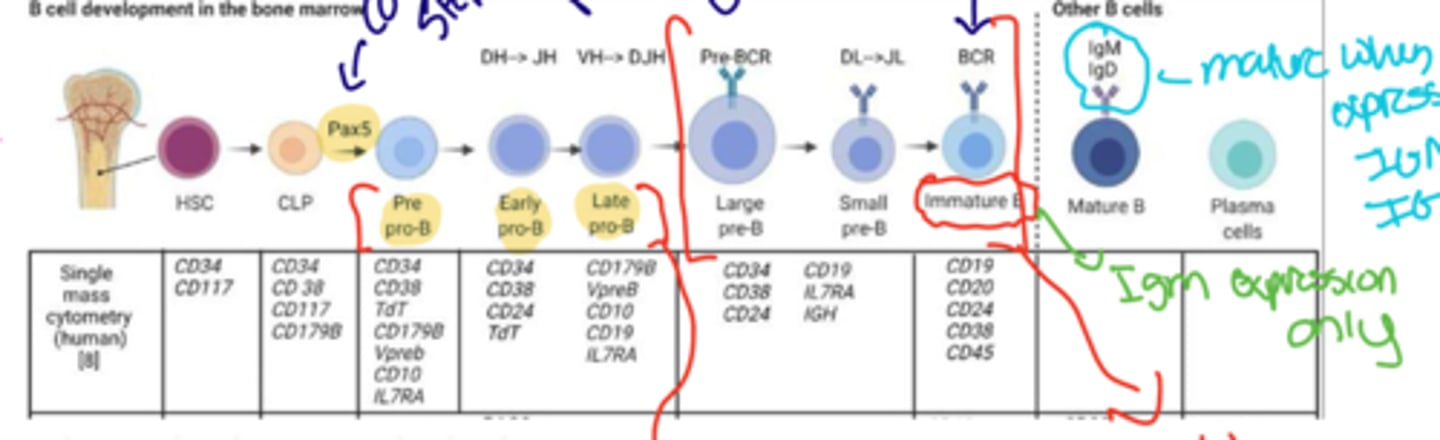
Diagram for B cell development
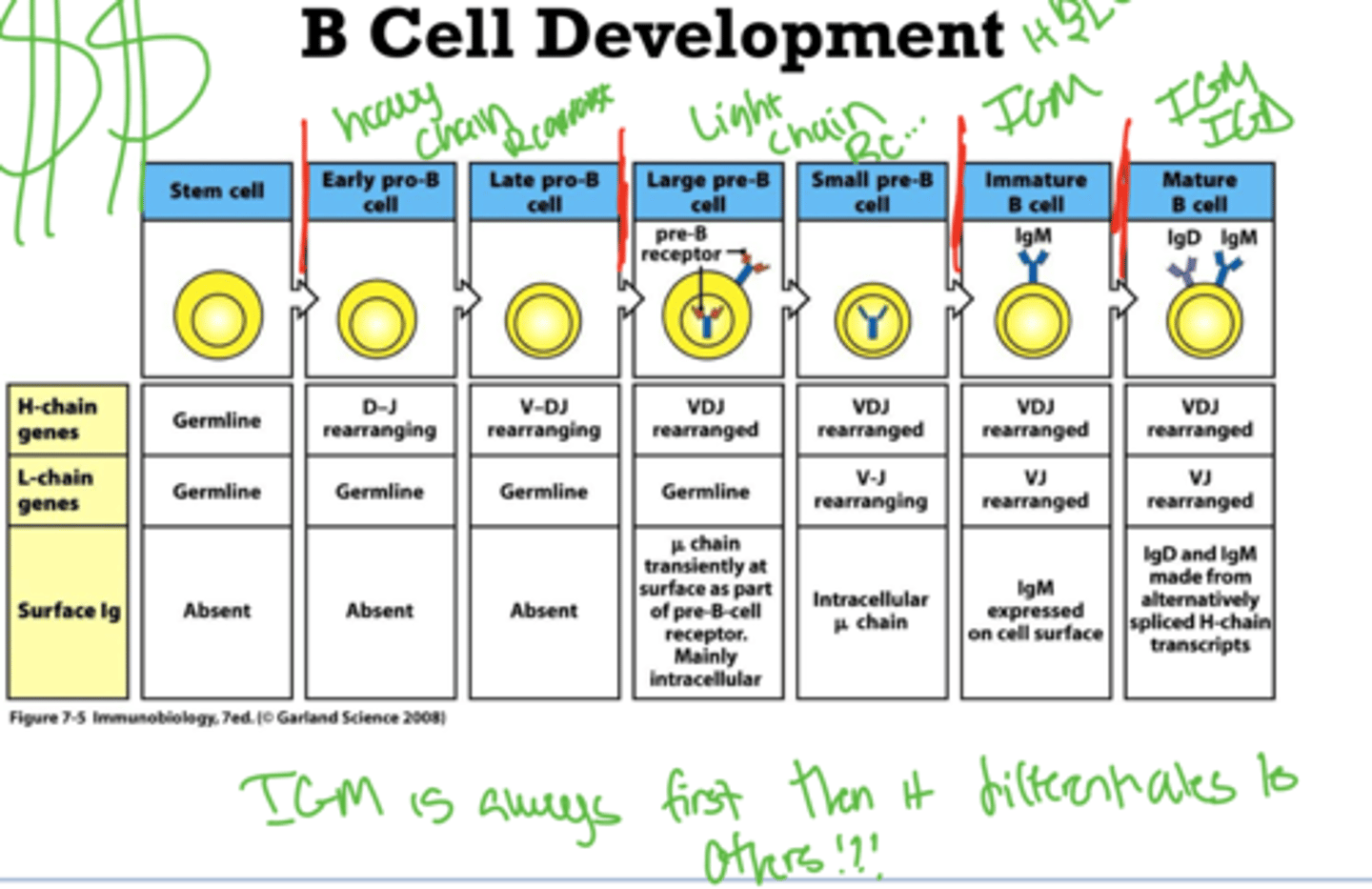
How does the B cell go from Pro to Pre B cell
Creates functional Heavy chain then uses surrogate light chain to see if binding is possible, if it is it proceeds, if not it dies
What chain is made in pro
Heavy chain
What chain is made in pre
Light chain
Light chain B cell development check points
Heavy chain forms in the pre then goes through first checkpoint w/ surrogate
light chain forms in pro then goes through second checkpoint where it tries to attach to the formed heavy chain, if it doesnt work death
Negative selection and B cells
After positive selection occurs, Immature B-Cells that bind to self-antigen are eliminated from the immune repertoire
Bone Marrow
What is negative selcetion develop
Develops central tolerance
Anergic B cell
incapable of future activation
Receptor editing
Immature B cells that fail negative selection they have the ability to self edit to fix itself instead of apoptosis. this slavages B cells but it only has 1 try
Why do Immature B cells exit the bone marrow before maturing?
They exit to go to the secondary lymph tissues where they will pick up the IGD in the periphery then leave to become mature
What is B cell peripheral tolerance
It is the same thing as central tolerance just in the secondary/peripheral lymp tissues
What is necessary for the B cell receptor complex to work
Ig alpha and beta are necessary to mediate the signalling, if it is not there the B cell wont work
What CDs are located on the B receptor complex
CD 19, 20, 21, 81
Which CD5 is located in the Fetal B cells
CD5 + is located in fetus
Which CD5 is located in adult B cells
CD5 - alongside the CD 19,20,21,81
Cd 19 function
signaling chain of the complex
CD 21 function
recognizes the CD3 fragments deposited on pathogens
CD 81 function
signaling complex w CD19 and surface molecules
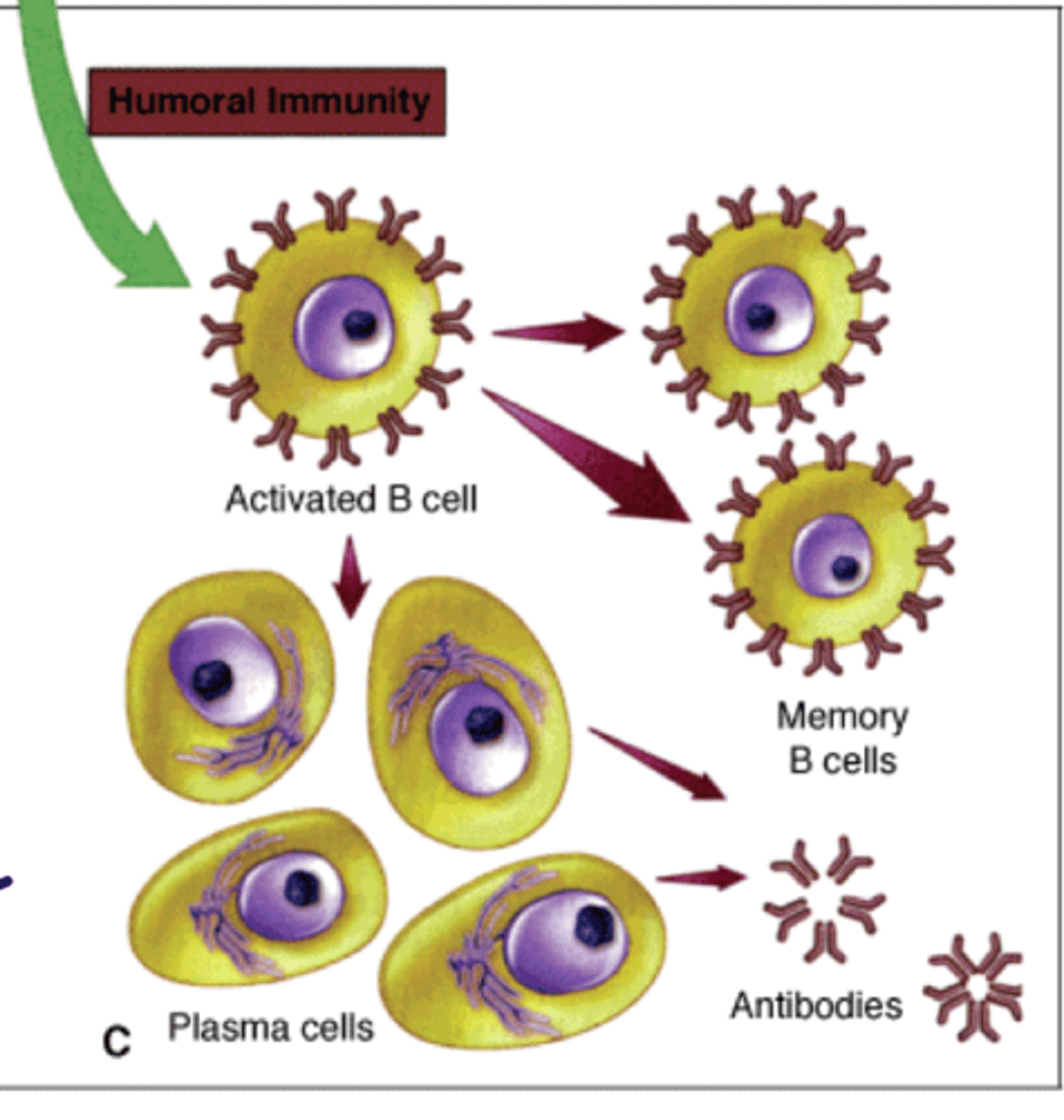
What occours when B cells differenciate into Plasma Cells
no more IgM and no longer responds to antigens
- no longer express MHC 2
Begin expressing CD 27
What CD do plasma cells express
CD 27
What are the two cells that are created from B cell differentiation?
Plasma cells and the memory cells, this happens when cd27 comes into play