Forensic Biology Exam 3
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
How is DNA different from other types of evidence?
can be used to ID specific suspects
What is a DNA profile?
IDs someone based on genetic code
Who are the only people that share the same DNA?
identical twins
What can DNA be used to determine?
kinship
What is the Innocence Project?
use DNA to exonerate falsely accused suspects
What are some limitations of the Innocent Project?
limited taxpayer funding
privacy concerns
When was DNA profiling/fingerprinting first used to ID a murder suspect?
1986
What method is used now instead of gel electrophoresis?
Short tandem repeat analysis
What are limiting factors of DNA profling?
cost
time
backlogs
degradation of DNA
What improvements have been made in DNA profiling?
better tech and lab protocols
gov legislation
CODIS
rapid test DNA kits
What is gel electrophoresis?
developed by Alec Jeffreys, scientists manually load DNA fragments into gel to receive DNA profile of bands sorted by size
What are short tandem repeats?
introduced in 1991, the FBI acknowledges 13 core markers
What is an STR profile?
unique to the individual, determined by commercial kits and analyzers
True or False: Most DNA is coding
False
What are the pairs of nucleotides
DNA
adenine-thymine
cytosine-guanine
RNA
adenine-uracil
How many chromosomes are found in human body cells?
46
True or False: Humans genes are arranged randomly?
False, all humans have the same genes arranged in the same order
Where is DNA evidence recovered from?
white blood cells, skin cells, semen, saliva, hair, fingerprints
How should DNA evidence be stored?
dry, cool areas out of direct sunlight
What is a serologist?
specialize in analysis of bodily fluids and conduct tests to determine if source is human
What is CODIS?
the Combined DNA Index System, repository of DNA evidence of unknown ID
What are some types of DNA profiling analyses?
STR analysis: nuclear DNA and Y chromosome
mtDNA analysis
familial searching
forensic genealogy and SNPs
genetic genealogy and SNP profiling
DNA phenotyping
What are more advances in DNA profiling?
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Snapshot
Data mining
Modeling and machine learning algorithms
Converting SNP loci to bar codes
What is rape or sexual battery?
Having sexual relations:
against consent
while person is unconscious
while person is under the influence
if person is feeble-minded or insane
if person is under the age of consent
What is a minimal fact interview?
Intended to be brief and non-intrusive, establishing basic facts of the assault. Should not be used a test for victim credibility.
What is a victim-centered response?
focuses on actions and choices of offender, not action or inaction of victim
What is a trauma-informed response?
seeks to reduce trauma to victim by responding in compassionate, sensitive, nonjudgmental manner
What do the type and sequence of sexual acts help determine?
motivation
What may verbal activity of the rapist reveal?
information or motivation, specific words and tone matter
What may the verbal activity of the victim reveal?
motivation or gratification of rapist determined by what the victim was forced to say
What might cause a sudden change in attitude of the rapist?
sexual dysfunction, completion, sudden interruptions, lack of fear from victim
What might theft during the rape indicate?
evidentiary: items with DNA - experience with crime
valuables: little income
personal: keepsakes/trophies
Delayed reporting can lead to what?
loss of recollection of details and evidence
Transgender victims of sexual assault
½ expected to experience but only 9% are reported
POC, homeless, incarcerated face higher rate
Important to address victim by preferred name
Why are deaf victims reluctant to reach out?
no interpreter or teletypewriter at agency
belief that event will not be accurately conveyed
Why don’t women report sexual assault?
lack of belief in ability of police
worries about unsympathetic treatment and discomforting procedures
embarrassment
self-blame
fear of reprisal
apprehension of being further victimized
How many reported cases are false?
2-8%
How should physical evidence be preserved by victim?
responding officer should ensure evidence is secure and advise victim to not alter the crime scene
What is included in a sexual battery examination kit?
vials for blood and semen
specimen envelope for hair
smear slides for vagina, etc
vaginal, cervical, saliva, buccal, and extra swabs
underwear specimen bag
genoprobe
What other information might the victim supply?
details about condom and wrapper - color, shape, texture, odor, taste, lubrication
sexual and hygienic habits
What purpose do photos of injuries serve?
corroborate victim’s account of attacks
help develop suspect’s modus operandi
What might electronic evidence capture?
events of assault and pre- and post-assault behavior of victim and perp
What might social media evidence reveal?
chronology or circumstances surrounding assault
What might cell-phone evidence reveal?
GPS and usage data might reveal location of suspect, victim, witnesses, assault
What needs to be determined about drug or alcohol facilitated assaults?
prescription and OTC meds used by victim
voluntary recreational substances
victim’s experience with drugs and alcohol to determine tolerance and expected levels of intoxication
black outs and missing periods of time
amount consumed
sensory experiences after consumption
What are the most commonly used drugs in sexual assaults?
GHB
valium
ambien
temazepam
flexeril
xanax
benadryl
What are the effects of GHB?
central nervous system depressant
can be felt within 10-20 min of ingestion
coma can occur 30-40 min after ingestion
traceable in blood for 4-8 hrs and in urine for 12-15 hours
What is evidence that forced sodomy occurred in a male murder victim?
evidence of strangulation with a belt, strap, or ligature
What are autoerotic deaths?
sexual asphyxia that occurs as results of masochistic activities of the deceased, often male
What is a psychological autopsy?
an analytical statement prepared by a mental health professional based on the deceased’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior
What is the purpose of a psychological autopsy?
to form a logical understanding of death from:
tangible physical evidence
documented life events
intangible, emotional factors
What is the most common cause of death in children?
physical abuse perpetrated by parents
What is battered-child syndrome?
clinical term often used to describe physically abused children
What are the types of burn injuries?
immersion in hot water for punishment
scalding by hot liquids
contact “inflicted” - can’t be concealed
spill/splash injuries from falling hot liquids
What percent of child abuse cases include burn injuries?
6-20%
What are characteristics of 1st degree burns?
redness
usually heal by themselves
What are characteristics of 2nd degree burns?
partial skin damage
blisters containing clear fluid
pink underlying tissue
often heal by themselves
What are characteristics of 3rd degree burns?
full skin destroyed
deep red tissue underlying blister
bloody blister fluid
possible muscle and bone damage
requires professional treatment
What are characteristics of 4th degree burns?
penetrate deep tissue to fat, muscle, and bone
requires immediate professional treatment
What is SIDS?
sudden infant death syndrome, often a crib death possibly caused by laying on the stomach and re-inhaling carbon dioxide but is likely spontaneous apnea
What does SIDS show in an autopsy?
congestion and edema of lungs with minor evidence of respiratory tract inflammation
What is the difference between coup and contrecoup injuries?
In coup injuries, the head is stationary and is struck by a moving object. It causes both dermal and subdermal hematomae. In contrecoup injuries, the moving head hits a stationary object, causing only subdural hematoma.
What is Shaken Baby Syndrome?
severe intentional application of violent force or shaking that results in intracranial injuries to the child
What is the mechanism of injury in SBS?
combo of physical factors like the proportionately large size of the adult relative to the child
What are some outward sign of SBS?
pale/blue skin, lethargic eyes
What is Munchausen Syndrome by Proxy?
a parent/caretaker suffering from Munchausens attempts to elicit medical attentions for themself by injuring or inducing illness in the child
What is Munchausen Syndrome?
psychological disorder in which the patient fabricates symptoms of disease/injury to undergo medical tests, hospitalization, or treatment
What are the 2 main categories of child molestation?
situational
preferential
What are the types of situational child molestors?
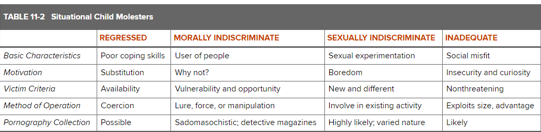
What are the types of preferential child molestors?
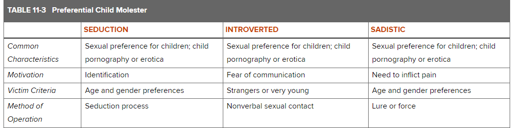
What types of reports are included in unfounded cases?
unsubstantiated suspicions
insufficient info
fictitious reports by adults and by children
What are the 2 categories of child pornography?
child pornography: sexual explicit reproduction of a child’s image
commercial
homemade
child erotica: material relating to children that serves a sexual purpose
published
unpublished
What is helpful in interviewing children?
anatomically correct dolls
establish rapport and reduce stress
reduce vocab problems
allow child to show what may be difficult/embarrassing to say
enhance quality of info
establish competency
What is the Protection of Children from Sexual Predators Act of 1998?
use of interstate facilities to transmit info about minors
transfer of obscene materials to or from minors
definition of sexual activity to include production of child porn
What is Child Abduction and Serial Murder Investigative Resource Center?
provides on-site supportive resources for law enforcement
What is child sex tourism?
tourism organized with primary purpose of facilitating a commercial-sexual relationship with a child, by-product of sex trafficking
What was the company in New York that transported clients to various South Asian countries for sexual business?
Big Apple Oriental Tours
What percent of sex tourists are American?
25%
How many children are involved in sex tourism in Thailand?
10k according to government reports but the actual number is likely up to 800k
What percent of children experience online sexual solicitation?
13%, mostly females 14-17
What are characteristics of online sexual offenders?
70% male, 43% men 18+
What types of social media sites are used for internet crimes?
ones that disappear or go into ghost mode like snapchat, instagram, facebook, and yikyak
What is an Amber alert?
voluntary partnership between law enforcement, state transportation officials, and broadcasters to activate an urgent news bulletin in most serious child abduction cases
What is included in an Amber alert?
description of missing child, suspected abductor, and any vehicles involved
What is sex offender registration?
Created in 1994, required states to create sex offender registries within 3 years or lose funding
What information is included in the sex offender registration?
name
address
DOB
SSN
physical description
fingerprints
photograph
What are forms of notification about sex offenders?
passive allows citizens to access info at their local law enforcement agencies
active permits government agencies to disseminate info to vulnerable individuals and organizations
What is rapid response deployment?
an approach that focuses on training patrol officers in the principles and tactics of rapid deployment for responding to critical incidents