topic 5 - separate chemistry 1
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
state what most metals are known as
transition metals
state the properties of transition metals
high melting/boiling point
high density
they form coloured compounds
catalysts of metals and their compounds
state what the oxidation of iron causes
corrosion
state the definition of corrosion
the gradual destruction of metal
due to chemical reactions between metals, oxygen and water
explain how the exclusion of oxygen can prevent iron rusting
rusting is the reaction of oxygen, water and metal together
to form iron oxide
without oxygen, this reaction cannot take place
explain how the exclusion of water can prevent iron rusting
rusting is the reaction of oxygen, water and metal together
to form iron oxide
without water, this reaction cannot take place
explain how sacrificial protection can prevent iron rusting
when iron is galvanised with a metal of a higher reactivity
the iron is protected from water and oxygen by a physical barrier
although reactions will take place with the galvanised metal, oxygen and water
the iron will remain unreacted
state what electroplating is
process where
the surface of one metal
is coated with the layer
of a different metal
explain how electroplating can be used to improve the appearance of metal objects
electroplating allows a metal object to be coated in a layer of another metal
this coating could improve the appearance of the metal object
e.g. silver plating cutlery and jewellery
explain how electroplating can be used to improve the resistance to corrosion of metal objects
electroplating allows a metal object to be coated in a layer of another metal
this coating is usually a metal with higher reactivity than the metal object
this mean the metal coating will react with oxygen and water and corrode
meaning the metal object is physically protected from the oxygen and water
state what a metal alloy is
where metals are physically mixed together
but not chemically combined
explain why converting metal into alloys increases the strength of the product
alloys often have properties that differ to the pure metal
alloys contain atoms of different sizes that disrupt the regular arrangement of atoms
this makes it harder for the layers of metal atoms to slide over each other
making the alloy harder than the pure metal
thus making it stronger
explain why iron is alloyed with other metals to produce alloy steels
cast iron from a furnace is 96% iron
with carbon, phosphorus, silicon and sulfur impurities
cast iron is too brittle for many common uses
so it is alloyed to make steel by removing some of the impurities
where it can then be used for actions such as construction, transport and manufacturing
explain how the uses of aluminium as foil is related to its properties
used in domestic food wrapping/storing food
as it has a low reactivity
and is very malleable
state what the magnalium alloy is made of
magnesium
aluminium
explain how the uses of magnalium in aircraft parts is related to its properties
magnalium is low density
and corrosion resistant
meaning it is a safe material to use in aircrafts
explain how the use of copper in electrical wirings is related to its properties
copper is corrosion resistant
and an electrical conductor
making it a safe material to use in the wirings
state what brass is made of
copper
zinc
explain how the use of brass in pins for electrical plugs is related to its properties
brass is stronger than copper
and is also an electrical conductor
making it a good material to use in the pins
state what jewellery gold is made of
gold
copper
explain how the use of jewellery gold in in jewellery is related to its properties
the gold alloy allows the jewellery to stay strong
whilst still remaining shiny
and corrosion resistant
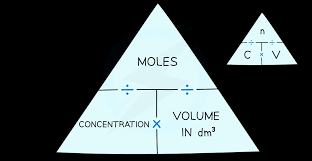
state the equation to find concentration in mol/dm³
concentration (mol/dm³) = no. of moles (mol) / volume (dm³)
state the equation to convert concentration in mol/dm³ to g/dm³
g/dm³ = mol/dm³ x Mr
state the equation to convert concentration in g/dm³ to mol/dm³
mol/dm³ = g/dm³ / Mr
state the method of how to carry out an acid-alkali titration
use pipette and pipette filler to place 25cm³ of NaOH solution into the conical flask
place the conical flask on a white tile so the tip of the burette is inside the flask
add a few drops of suitable indicator to the conical flask
perform a rough titration by taking an initial burette reading, while swirling the flask
quickly close the tap when a sharp colour change occurs and record the final volume at eye level
repeat the titration with a fresh flask of NaOH solution
at the rough end volume, add the solution from the burette one drop at a time until the indicator just changes colour
record the volume to the nearest 0.5cm³
repeat until 2 concordant results are achieved
explain how to use titration results to carry out simple calculations
write out the balanced reaction of the neutralisation reaction
calculate the moles of the known solution given the volume and concentration
use the equation to deduce the moles of the unknown solution
use the moles and the volume of the unknown solution to calculate the concentration
state the equation to find percentage yield
% yield = (actual yield / theoretical yield) x 100
state what actual yield is
the yield of a reaction
that is usually less than the calculated theoretical yield
state what causes the actual yield of a reaction to be less than the theoretical yield
incomplete reactions
practical losses during the experiment
competing, unwanted reaction
state what atom economy is
studies the amount of reactants that get turned into useful products
it’s used to analyse the efficiency of reactions
state the equation to find atom economy
atom economy = (Mr of desired products / Mr of all reactants) x 100
explain why a particular pathway in a reaction is chosen to produce a specified product using atom economy
reactions that have low atom economies use up a lot of resources
and produce excess waste material
which needs to be disposed of
making it an expensive procedure
these reactions are unsustainable as they aren’t economically attractive
explain why a particular pathway in a reaction is chosen to produce a specified product using yield
high yield rates are desirable attributes of chemical reactions
as they produce less waste products
therefore improving the efficiency of the reaction
making the reaction more economically-attractive
explain why a particular pathway in a reaction is chosen to produce a specified product using equilibrium position
in reversible reactions, the position of equilibrium may need to be changed in favour of the products by altering reaction conditions
explain why a particular pathway in a reaction is chosen to produce a specified product using usefulness of by-products
if by-products can be sold or reused that would improve the atom economy of a reaction, making it a more economical pathway
alternative methods of production could also be considered that may produce a more useful by-product
state what the molar volume of any gas at room temperature and pressure is
the volume occupied by one mole of molecules of any gas
at room temperature and pressure
state the molar volume of any gas at room temperature and pressure
24 dm³
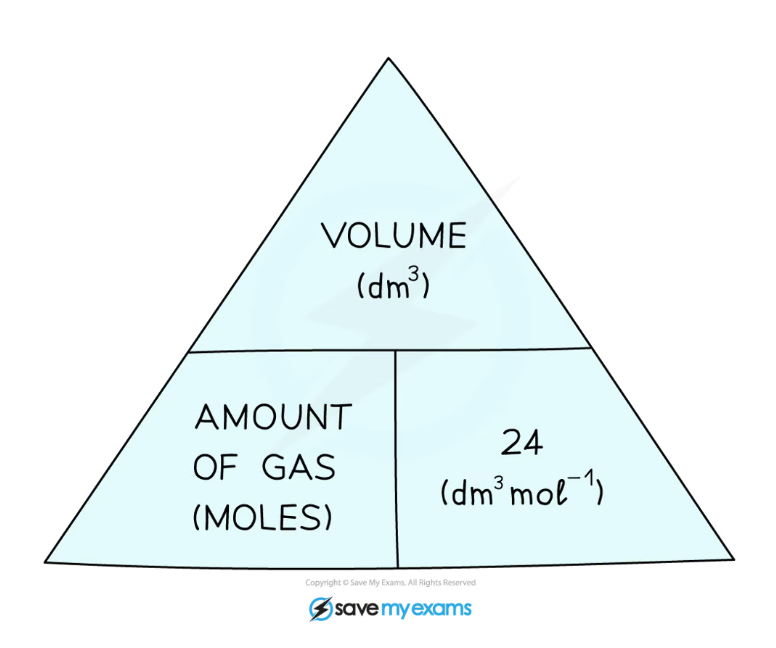
state the molar volume equation
vol (dm³) = mol x molar volume (dm³/mol)
state Avogadro’s Law
at room temperature (20°C) and pressure (1 atmosphere)
one mole of any gas
has a volume of 24dm³
state what type of reaction the Haber process is
reversible reaction
between nitrogen and hydrogen
to form ammonia
predict how the rate of attainment of equilibrium is affected by changes in temperature
higher temperature
means the particles have more kinetic energy
predict how the rate of attainment of equilibrium is affected by changes in pressure
higher pressure
means the frequency of successful collisions between particles
will increase
predict how the rate of attainment of equilibrium is affected by changes in concentration
higher concentration
means more particles per given volume
increasing the frequency of successful collisions between particles
predict how the rate of attainment of equilibrium is affected by the presence of a catalyst
lowers activation energy
allowing a reaction to reach equilibrium faster
explain how conditions in industrial reactions are related to the availability and cost of raw materials and energy supplies
if the cost of extraction of raw materials is too high or they are unavailable, then the process is no longer economically viable
many industrial processes require huge amounts of heat and pressure which is very expensive to maintain
production energy costs are also a factor to be considered carefully and alongside the raw materials issue
explain how conditions in industrial reactions are related to the control of temperature is used to produce an acceptable yield in an acceptable time
a higher temperature would favour the reverse reaction as it is endothermic so a higher yield of reactants would be made
a lower temperature would favour the forward reaction as it is exothermic so a higher yield of products will be made
however, at a lower temperature, the rate of reaction is very slow
so a COMPROMISE TEMPERATURE between having a lower yield of products but them being made quicker must be found
explain how conditions in industrial reactions are related to the control of pressure is used to produce an acceptable yield in an acceptable time
lower pressure would favour the reverse reaction as the system will try to increase the pressure by creating more molecules so a higher yield of reactants will be made
higher pressure would favour the forward reaction as it will try to decrease the pressure by creating fewer molecules so a higher yield of products will be made
however high pressures can be dangerous and very expensive equipment is needed
so a COMPROMISE PRESSURE must be found between a lower yield of products that are made safely and economically
explain how conditions in industrial reactions are related to the control of a catalyst is used to produce an acceptable yield in an acceptable time
presence of a catalyst DOESN’T affect the position of equilibrium
but it DOES increase the rate at which the equilibrium is reached
because the catalyst increases the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions by the same amount
thus, the concentration of reactants and products is the same at equilibrium as it would be without the catalyst
so the use of a catalyst allows for an acceptable yield to be achieved at a lower temperature by lowering the activation energy required
describe the Haber Process
hydrogen and nitrogen react
to form ammonia
in a reversible reaction:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
describe the formation of ammonia in the Haber Process
formation of ammonia is exothermic
formation of nitrogen and hydrogen is endothermic
predict the ideal conditions for the Haber Process
as the formation of ammonia is exothermic
Le Chatelier’s Principle would predict that:
reaction will produce a higher yield at a lower temperature
and using a higher pressure would increase the yield
as there are fewer moles of gas on the right than on the left of the equation
state the ideal conditions of the Haber Process
temperature - 450ºC
pressure - 150 atmospheres
catalyst presence - yes
state what fertilisers contain to promote plant growth
nitrogen
phosphorus
potassium
state the reaction of ammonia to produce a fertiliser
ammonia + nitric acid → ammonium nitrate
NH3 (aq) + HNO3 (aq) → NH4NO3 (aq)
describe the method of the laboratory preparation of ammonium sulfate
add ammonia solution and a few drops of methyl orange to a conical flask using a pipette
add dilute sulfuric acid to the burette using a measuring cylinder and note the starting volume
add the sulfuric acid to the conical flask slowing until the methyl orange changes colour
calculate the volume of acid added and repeat the titration without indicator
transfer the solution to an evaporating basin and heat to partially evaporate water
remove the evaporating basin from heat and allow filtrate
after a few days ammonium sulfate crystals will appear
filter to remove any remaining water
this is a SMALL SCALE OPERATION
describe the industrial preparation of ammonium sulfate
LARGE SCALE OPERATION
ammonia is prepared by Haber Process and sulfuric acid by the Contact Process
most common industrial process involves filling a large reactor chamber with ammonia gas
sulfuric acid is sprayed into the chamber from above and ammonium sulfate powder is produced
compare the laboratory preparation and industrial production of ammonium sulfate (EQUIPMENT)
LAB:
simple equipment needed
prepared using a titration apparatus
INDUSTRIAL:
hugely expensive and complex
compare the laboratory preparation and industrial production of ammonium sulfate (REACTANT CONCENTRATION)
LAB:
low concentrations
less heat given off
INDUSTRIAL:
high concentrations
exothermic reaction
compare the laboratory preparation and industrial production of ammonium sulfate (SEPARATION OF PRODUCT)
LAB:
crystallisation is used which is a slow process
INDUSTRIAL:
heat produced is used to evaporate water from the reaction mixture
this makes a very concentrated ammonium nitrate product
state what a chemical cell does
produces a voltage
until one of the reactants is used up
describe the reaction inside a fuel cell
hydrogen and oxygen are used
to produce a voltage
and water is the only product
state the strengths of fuel cells
do not produce any pollution
produces more energy per kilogram than petrol or diesel
no power is lost in transmission
no batteries to dispose of - better for the environment
quieter - less noise pollution
state the weakness of fuel cells
materials used in producing fuel cells are expensive
high pressure tanks are needed to store sufficient hydrogen and oxygen - dangerous and difficult to handle
become less efficient in low temperature
hydrogen is expensive to produce and store