Chemistry - 3.2.4: Properties of Period 3 Elements and their Oxides
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Reaction of Na with water
2Na (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2NaOH (aq) + H2 (g)
Reaction of Mg with cold water
Mg (s) + 2H2O (l) → Mg(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
How can you test whether a substance is ionic / contains ions? (2)
Heat until molten
It conducts electricity
What oxide does Na form?
Na2O
What oxide does Mg form?
MgO
What oxide does Al form?
Al2O3
What oxide does Si form?
SiO2
What oxide does P form?
P4O10
What oxide does S form?
SO2 and SO3
What period 3 elements react with cold water?
Na, Mg and Cl
Reaction of Mg with steam
Mg (s) + H2O (g) → MgO (s) + H2(g)
Reaction of Na with oxygen
2Na (s) + 0.5O2 (g) → Na2O (s)
Reaction of Mg with oxygen
Mg(s) + 0.5O2 (g) → MgO (s)
Reaction of Al with oxygen
4Al (s) + 3O2 (g) → 2Al2O3 (s)
What happens when Na reacts with oxygen?
It burns with a yellow flame to form a white powder of Na2O
What happens when Mg reacts with oxygen? (2)
It burns with a white flame to form a white powder of MgO
What happens when Al reacts with oxygen?
It burns brightly to produce a white powder of Al2O3
Reaction of Si with oxygen
Si (s) + O2 (g) → SiO2 (s)
Reaction of P with oxygen
4P (s) + 5O2 (g)→ P4O10 (s)
Reaction of S with oxygen
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
What happens when S reacts with oxygen?
It burns with a blue flame and produces fumes to form colourless SO2 gas (and some SO3)
Why can a thin layer of aluminium oxide protect aluminium from corrosion in (moist) air? (2)
It is inert
It is insoluble in water
How does electronegativity link to the type of bonding in the period 3 oxides?
If big difference in electronegativity → Ionic bonding
If small difference in electronegativity → Covalent bonding
Red phosphorus vs white phosphorus
Red phosphorus must be heated before it will react with oxygen - white phosphorus spontaneously ignites in air and the white smoke of phosphorous pentoxide is given off
Allotrope
The same element with different arrangements of atoms
2 allotropes of phosphorus
Red and white phosphorus
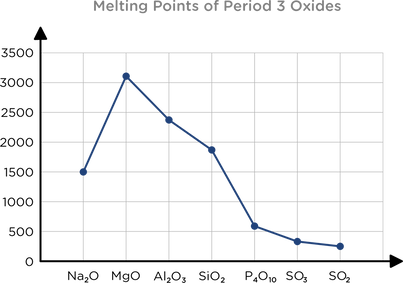
Trend in melting points of period 3 oxides
Increases from Na to Mg: greater charge, stronger ES FoA
Decreases Mg to Al: Al has some covalent character
Decreases Al to Si: Si has covalent bonds, weaker than ionic
Decreases Si to P: P has Van der Waal forces to break
Decreases to S: All have Van der Waal forces - melting point decreases as the number of electrons decreases
Why does Al2O3 have some covalent character?
The Al3+ ion is small but has a large positive charge (high charge density), so can distort the electron cloud of O2-
Is Na2O3 an acid or base? Give its reaction with water and the pH of the resultant solution.
Base, pH of ~14
Na2O (s) + H2O (l) → 2Na+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq)
Is MgO an acid or base? Give its reaction with water and the pH of the resultant solution.
Base, pH of ~9
MgO (s) + H2O (l) → Mg(OH)2 (s) ⇌ Mg2+ (aq) + O2- (aq)
What period 3 oxides are insoluble in water?
Al2O3 and SiO2
What period 3 oxides do not react with water?
Al2O3 and SiO2
Is P4O10 an acid or base? Give its reaction with water and the pH of the resultant solution.
Acid, pH of ~1
P4O10 (s) + 6H2O (l) → 4H3PO4 (aq)
H3PO4 (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + H2PO4- (aq)
Is SO2 an acid or base? Give its reaction with water and the pH of the resultant solution.
Acid, pH of ~2-3
SO2 (s) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq)
H2SO3 (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + HSO3- (aq)
Is SO3 an acid or base? Give its reaction with water and the pH of the resultant solution.
Acid, pH of ~0-1
SO3 (s) + H2O (l) → H2SO4 (aq) → H+ (aq) + HSO4- (aq)
Order the period 3 oxides according to their pH of the solution formed after reacting with water (descending)
Na2O (14)
MgO (9)
Al2O3 / SiO2 (7)
SO2 (2-3)
P4O10 (1-2)
SO3 (0-1)
Why does Na2O have that pH?
O2- ion is a very strong base so readily reacts with water to form OH- ions
Why does MgO have that pH?
It forms O2- ions but is less soluble in water than Na2O
Why does Al2O3 have that pH?
It has some covalent character, so the bonding is too strong for the ions to separate
Why does SiO2 have that pH?
It is a giant macromolecule so water does not affect it
Why does P4O10 have that pH?
It is a covalent molecule so can react with water to form acid solutions
Why does SO2 have that pH?
It is a covalent molecule so can react with water to form acid solutions
Why does SO3 have that pH?
It is a covalent molecule so can react with water to form acid solutions
Why is Al2O3 described as amphoteric?
It reacts with both acids and alkalis
What forms when Na2O3 reacts in an acid-base reaction?
A sodium salt and water
What forms when MgO reacts in an acid-base reaction?
A magnesium salt and water
What forms when Al2O3 reacts in an acid-base reaction?
When acting as a base: an aluminium salt and water
When acting as an acid: an aluminate salt [MAl(OH)4] and water
What forms when SiO2 reacts in an acid-base reaction?
A silicate salt [M2(SiO3)] and water
What forms when P4O10 reacts in an acid-base reaction?
In 3 stages, it forms MH2PO4 and water, M2HPO4 and water. then M3PO4 and water (assuming M has +1 charge)
What forms when SO2 reacts in an acid-base reaction?
In 2 stages, first MHSO3 and water, then M2SO3 and water (assuming M has +1 charge)
How can you determine the melting point of a sample? (3)
Put sample in melting point apparatus
Heat it slowly to establish the melting point range
If the melting point is close to the data book value / melts sharply, the sample is pure. If it has a lower melting point / melts over a broad range of temperatures, the sample is impure.
How can you distinguish between two different solid period 3 oxides? [e.g. Na and P oxides] (3)
React each sample with water
Add litmus paper
Litmus: turns blue with alkali solution and turns red with acidic solution
Why does Na2O form an alkaline solution when it reacts with water? (2)
Na2O contains O2- ions
These O2- ions react with water to form OH- ions
Give 2 equations that show the amphoteric nature of Al2O3
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2Al3+ + 6Cl- + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 6H+ → 2Al3+ + 3H2O
Why can’t Al2O3 / SiO2 dissolve in water?
Strong covalent bonds - water cannot supply enough energy to break lattice
Reaction of SiO2 with NaOH
2NaOH + SiO2 → Na2SiO3 + H2O