psychology
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
nervous system
network of nerve cells and fibres which transmit nerve impulses between body parts
2
New cards
Brain (CNS)
controls movement thoughts, automatic responses to world around you
3
New cards
Spine (CNS)
runs from the base of the brain to the lower middle section of the spine, the brain stem connects this to the brain, enables communication to the rest of the body
4
New cards
Central nervous system
Complex of nerve tissues that control activities in the body
5
New cards
Phepherial nervous system
nervous system outside of brain and spinal cord - comprised of various nerve endings and the ganglia, communicates to body via nerves. Makes up somatic NS and Automatic NS
6
New cards
ganglia
a collection of neuron bodies found in the voluntary and autonomic branches of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
7
New cards
Somatic Nervous system (SNS)
responsible for voluntary movement of skeletal muscles, has nerves that communicates sensory information to the CNS through sensory and motor neurons
8
New cards
Sensory (afferent)
It informs the central nervous system about stimuli impinging on us from the outside or within us, transmits pulses from phepherial organs to CNS
9
New cards
Motor (efferent)
the part of the nervous system that controls voluntary movement, may include skeletal muscles and neural connections with muscle tissues, transmits impulses from CNS to phepherial organs to cause an action
10
New cards
Automatic (NS)
controls bodily functions that are not consciously directed like non skeletal muscles like internal organs and glands - heart rate, breathing,
11
New cards
Sympathetic
Arouses in danger (stressed) where dominates fight, flight, freeze - heart rate speeds up, bladder gets loose
12
New cards
Parasympathetic
Automatic day to day functions like heart rate, maintains internal environment (homostasis) slows heart rate down,
13
New cards
Dendrites
receives input from other neurons and carry signals to the body - receives communication from other cells
14
New cards
Cell body
contains genetic information and maintains neuron structure
15
New cards
myelin sheath
makes electrical impulses transmit quick, also acts as an insulating layer
16
New cards
axon
cable that snakes away from the main part of the cell it is where electrical impulses from the neuron travel away to be received by other neurons.
17
New cards
axon terminals
Terminal release transmitter substances into gap called synaptic cleft between terminals and the dendrites in the next neuron
18
New cards
Name 3 types of neurons
Sensory, Motor and interneurons
19
New cards
Sensory neuron
carries signals from other parts of your body into the Central system
20
New cards
Motor neuron
carries signals from CNS to outer parts like muscles, skins and glands
21
New cards
Interneuron
connects various neurons within the brain and spinal cord
22
New cards
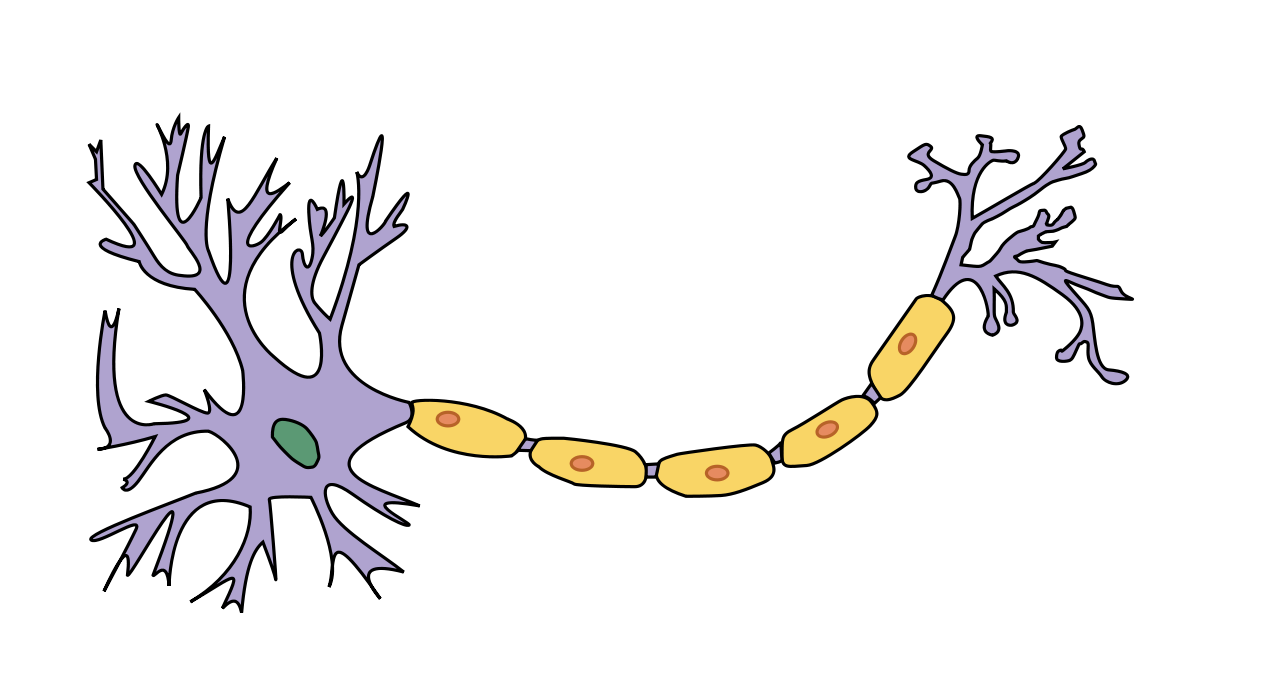
label !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
DO NOT INCLUDE SCHWANN CELL,
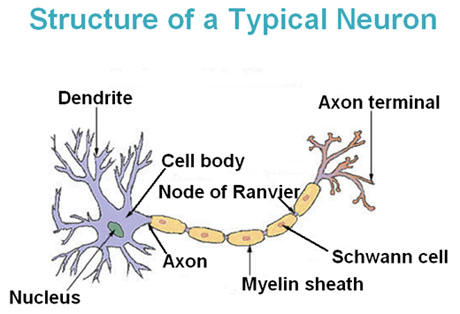
23
New cards
what is a neural transmission
Neurotransmission is the process by which signalling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron, and bind to and react with the receptors on the dendrites of another neuron a short distance away
24
New cards
8 ethical guidelines in psychological research
* Protection from harm - physical and psychological
* Informed consent
* Withdrawal rights
* Deception
* Confidentiality
* Privacy
* Voluntary participation
* Debriefing
* Informed consent
* Withdrawal rights
* Deception
* Confidentiality
* Privacy
* Voluntary participation
* Debriefing
25
New cards
composition of hind brain
medulla, cerebellum
26
New cards
hindbrain
controls automatic bodily functions and motor functions, reptile brains
27
New cards
medulla
is located in the brainstem in the brain stem in front of the cerebellum
It's a continuation of the spine, controls breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, blood temp and respiration
It's a continuation of the spine, controls breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, blood temp and respiration
28
New cards
cerebellum
located at the back of the head below the temporal and accipitral lobe above the brain stem, it coordinates voluntary movement and controls speech production, learning skills and walking
29
New cards
composition of mid brain
reticular formation
30
New cards
Mid brain
controls fine motor skills, regulating bodily temp, controls when you sleep,
it is responsible for receiving and processing sensory information from our sense and then sends it to other brain regions that deal with hearing seeing tasting and touching
it is responsible for receiving and processing sensory information from our sense and then sends it to other brain regions that deal with hearing seeing tasting and touching
31
New cards
reticular formation
network of neurons that connects forebrain with hind brain. Controls arousal and sleep/wake cycle, it filters information so we attend only to inputs relevant to us
32
New cards
forebrain composition
hypothalamus, thalamus
33
New cards
forebrain
receiving and processing sensory information, thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language, and controlling motor function.
34
New cards
hypothalamus
located at the base of the brain. It controls basic survival actions, sleep, regulated body temperature, realises hormones
35
New cards
thalamus
located above the brain stem and between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, communication centre of the brain, receives information from the ears, eyes, skin and other sensory organs, it regulates the overall activity in the cerebral cortex
36
New cards
what are the 4 lobes/ apart of the cerebrum
occipital, parietal, frontal, temperal
37
New cards
role of cerebal cortex
outer layer of the forebrain is called cerebral cortex
Responsible for; receiving info from environment, higher order thinking process ( problem solving). Memory, learning and emotion regulation
\
Responsible for; receiving info from environment, higher order thinking process ( problem solving). Memory, learning and emotion regulation
\
38
New cards
left hemisphere
> verbal functions (speaking, reading, writing)
>mathematical skills
>analytical \n >sensory and motor info of the right side of the body
>mathematical skills
>analytical \n >sensory and motor info of the right side of the body
39
New cards
right hemisphere
>controls non-verbal tasks (drawing, puzzle)
>spatial activities (maps, reading faces, recognizing faces)
>perception of others emotion
>sensory and motor info of the Left side of the body
>spatial activities (maps, reading faces, recognizing faces)
>perception of others emotion
>sensory and motor info of the Left side of the body
40
New cards
Corpus callosum:
transfers info registered in one hemisphere to the opposite hemisphere for processing
41
New cards
42
New cards
43
New cards
44
New cards
45
New cards
46
New cards
47
New cards
48
New cards
49
New cards