the living world - biomes and ecosystems
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Define biome.
A global ecosystem of plants and animals.
Define biodiversity.
The amount and variety of species within an ecosystem.
Define ecosystem.
A community where living organisms interact with each other and their non-living environment.
What is interdependence?
The process of biotic components relying on one another (for survival).
What do most food chains/webs consist of?
A producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, and tertiary consumer (apex predator).
What are decomposers?
An organism that decomposes organic material - e.g. fungi and bacteria.
Why are decomposers important in food chains?
They return nutrients to the soil and release energy to be recycled.
The source of energy in a food chain is //.
Energy from the Sun.
What’s the difference between biotic and abiotic factors?
Biotic - Living (e.g. plants or animals)
Abiotic - Non living (e.g. sunlight or soil)
What is biomass?
Organic material from recently living organisms.
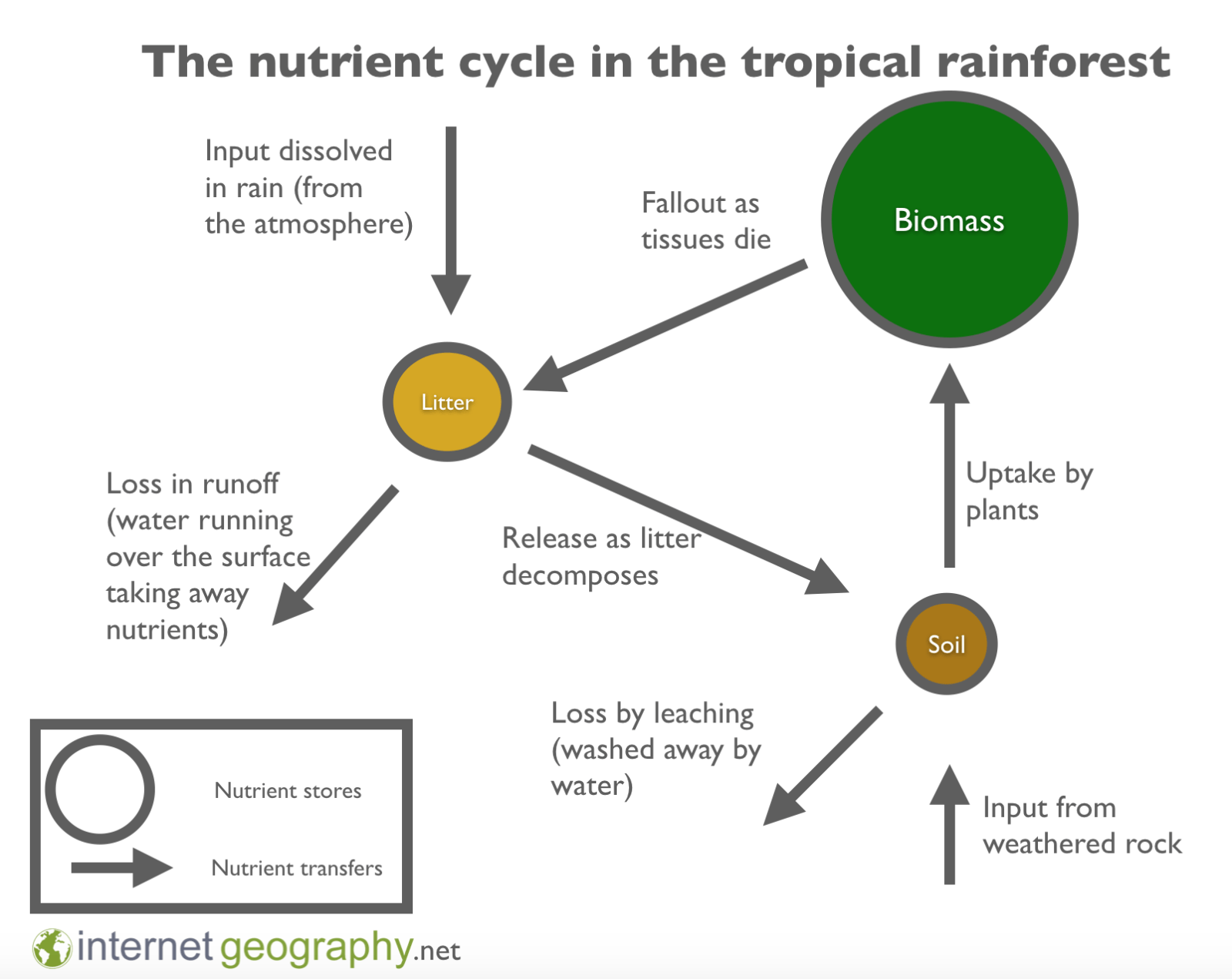
What is the nutrient cycle and what does it consist of?
The continuous process where nutrients move between organisms and the non-living environment. Consists of biomass, litter (what sits on the soil), and soil.
What does the nutrient cycle in a TRF look like?
High amounts of nutrients in the biomass, but little in the litter and soil, due to fast decomposition in hot and wet conditions - plants rapidly absorb nutrients.
What are some examples of natural ecosystem disruption? (4 points)
Wildfires (caused by high temperatures or lightning).
Invasive species.
Flood or droughts.
Disease.
What are some examples of human ecosystem disruption? (4 points)
Hunting of animals.
Deforestation.
Clearance of land via fire.
Introduction of pesticides/fertilisers/herbicides.
How is energy lost?
Excretion and respiration.
High // and high // can cause rapid plant growth, leading to more biodiversity.
Temperatures and rainfall.
Where in the world is an example of ecosystem restoration?
Yellowstone Park USA:
Rewilding of wolves to help ecosystem balance.
National Park: protected by the state for the enjoyment of the general public/the preservation of wildlife.
Where in the world is an example of high biodiversity?
Epping Forest, England:
Four seasons
High interdependence between species