Body Fluids
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Hemocytometer Formula
(Avg # of cells counted x dilution factor) / (# of LARGE squares counted x 0.1)
(Avg # of cells counted x dilution factor) / (# of SMALL squares counted x 0.04 x 0.1)
Cells counted on hemocytometer
Synovial fluid viscosity
Hyalunronidase breaks down hyalunronate
String test used to determine viscosity
CSF order of draw
#1 chemistry and immunology
#2 microbiology
#3 hematology
#4 other testing
Traumatic tap vs hemorrhage
Traumatic tap
greatest amount of blood in tube 1, least in last tube
after centrifugation, colorless supernatent
Hemorrhage
consistent amount of blood in all tubes
after centrifugation, xanthochromic supernatent
has erythrophagocytosis
CSF Index
assess permeability of blood-brain barrier
CSF/serum albumin index = albuminCSF/albuminSERUM
Chylous vs pseudochylous effusion
Chylous effusions
obstructions in lymphatic fluid drainage
more triglycerides, chylomicrons and lymphocytes
Pseudochylous effusion
chronic inflammatory conditions
high cholesterol levels
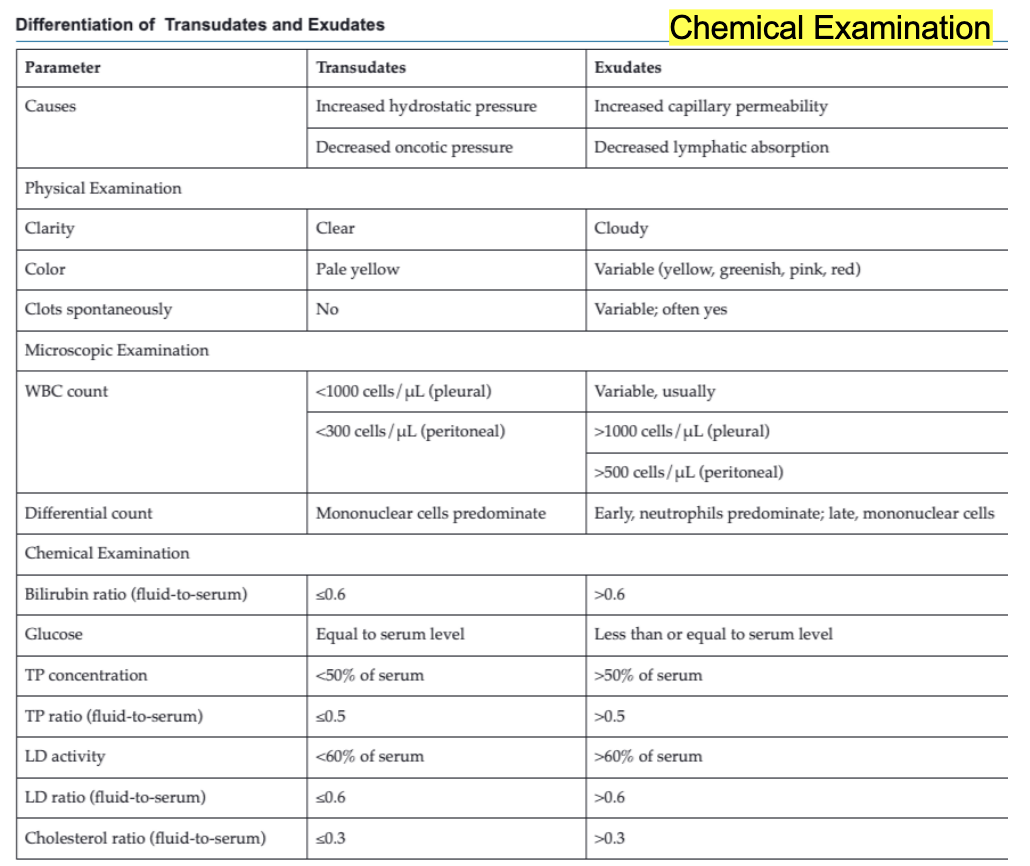
Transudates vs exudates
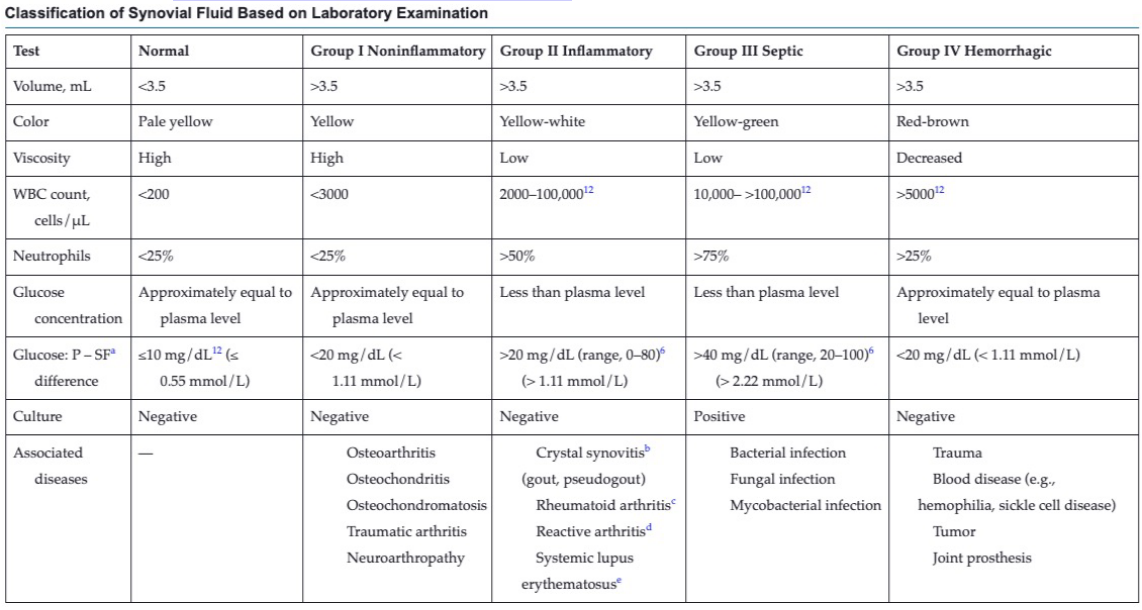
Joint disorder classification
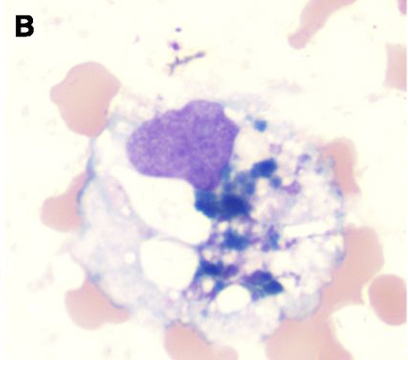
Signet rings vs LE cell
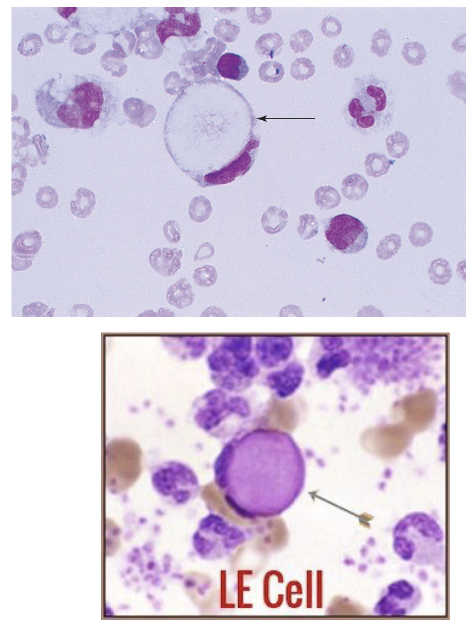
Macrophage with large vacuole, large pink blob in vacuole indicates lupus erythematosus (LE)
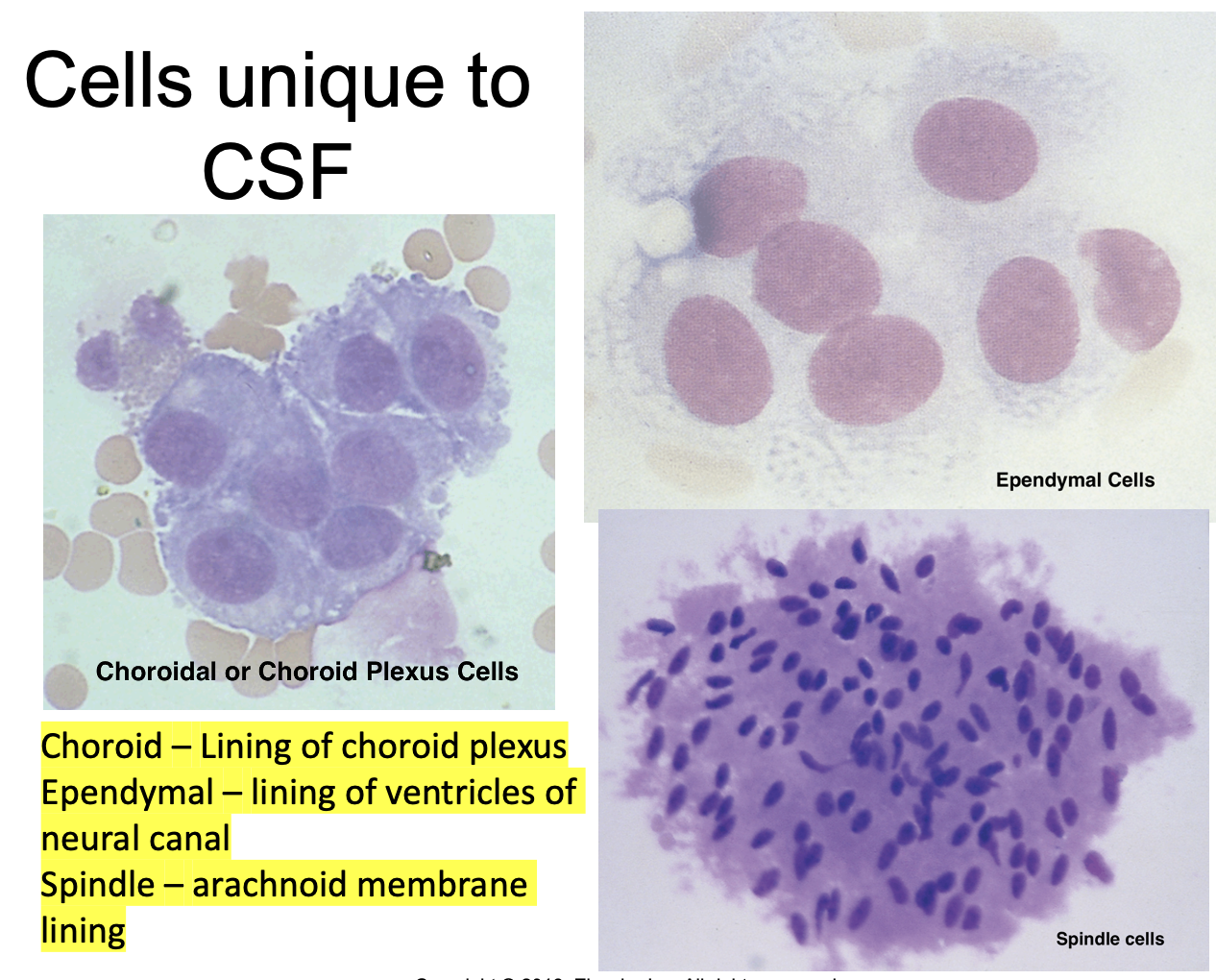
CSF Lining Cells
Mesothelial cells in serous fluid (pericardial, peritoneal, pleural)
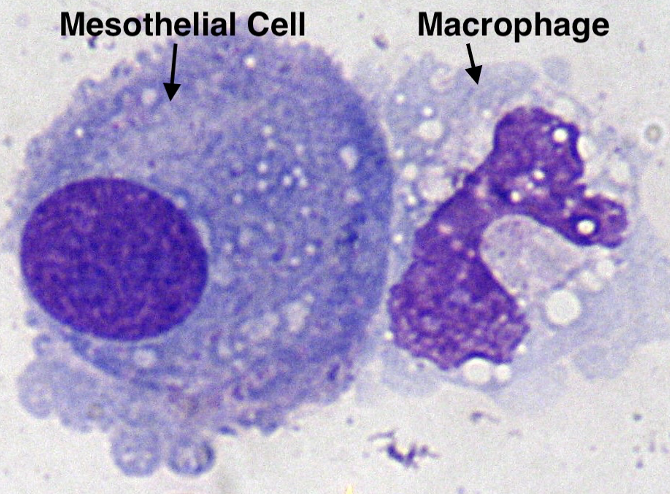
Synoviocytes
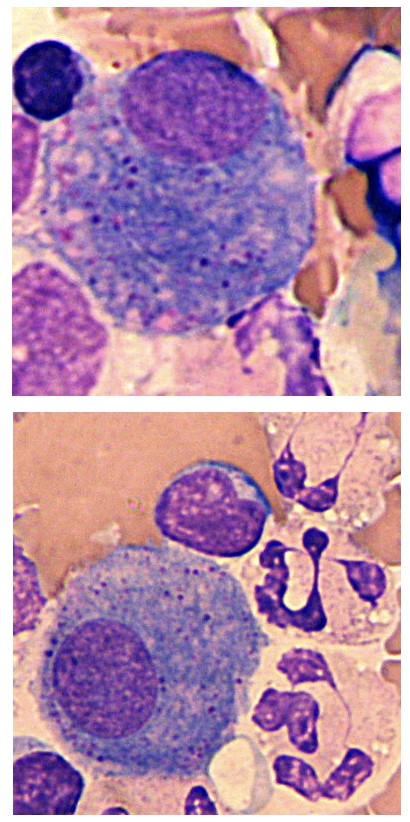
Hemosiderin granules
Degraded hemoglobin
Hematoidin crystal
Further degeneration of hemoglobin
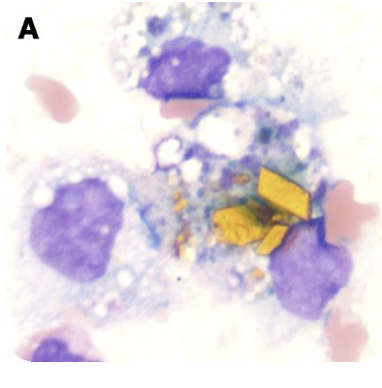
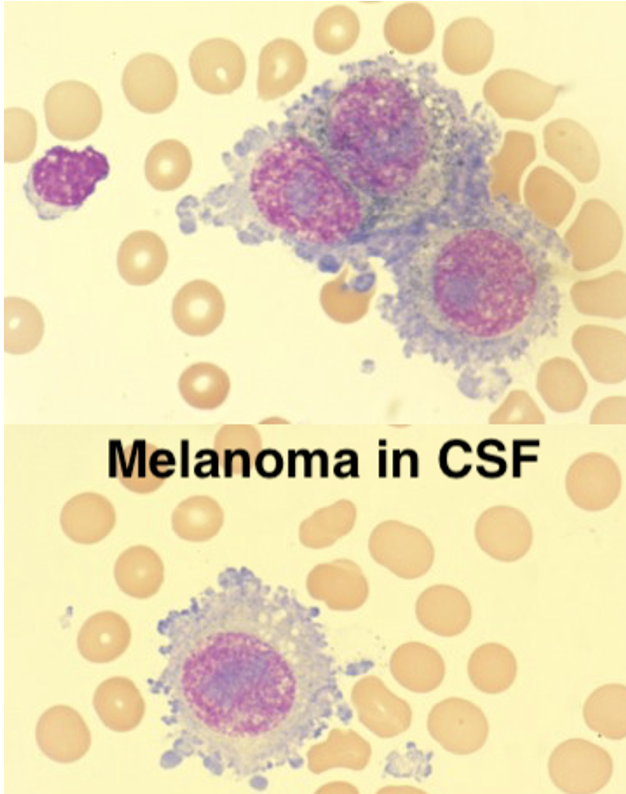
Malignant cells in CSF
Microorganisms in CSF
Cryptococcus neoformans - caused by breathing fungal spores
Naegleria fowleri - amoeba that thrives in warm freshwater lakes, rivers, hot springs
Effusion
accumulation of fluid in a body cavity indicating an abnormal or pathological process
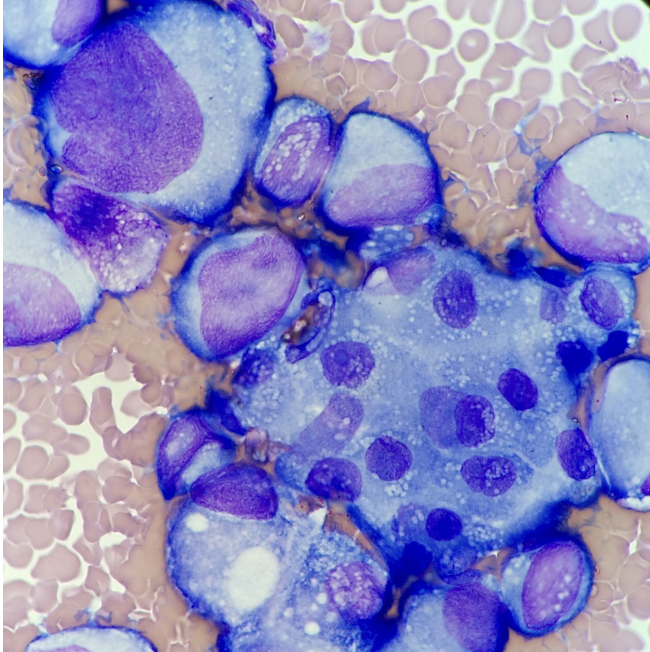
Malignant cells in serous fluid
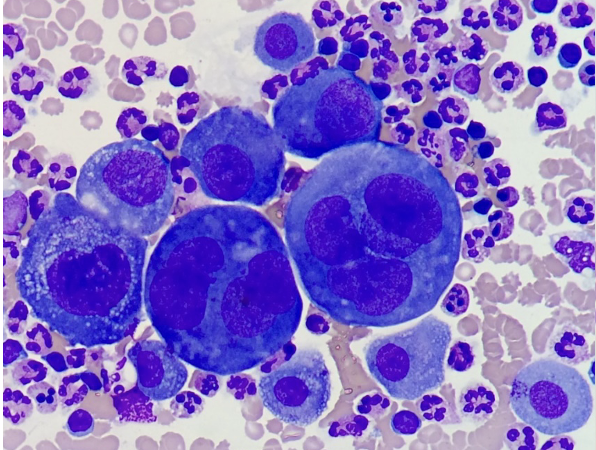
MSU vs CPPD
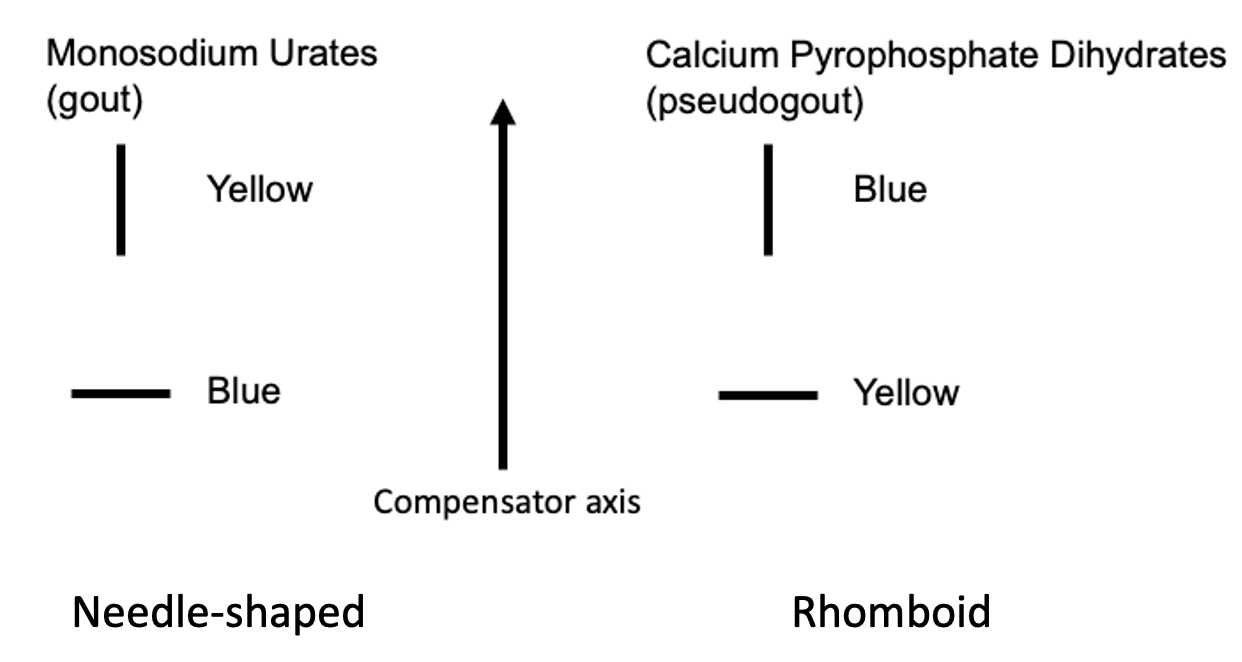
Corticosteroid crystals
Can resemble MSU or CPPD
Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL)
not naturally occurring fluid, not sterile site —> common to see bacteria
Amniotic fluid vs normal urine
Amniotic fluid
has glucose
significant protein
creatinine like plasma
no urea
Normal urine
no glucose or protein
high creatinine and urea
Amniotic fluid physical examination
normal amniotic fluid is colorless or pale yellow
yellow or amber = bilirubin
greenish = meconium
pale pink or red = blood or hemoglobin
dark red/brown = fetal death
Neural tube defects
high concentration of alpha fetoprotein and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) indicates neural tube defects
Probability of respiratory distress syndrome
fetal lung maturity tests
L/S ratio
phosphatidylglycerol
foam stability index
lamellar body counts
Lecithin/Sphingomyelin (L/S) Ratio
surfactants allow alveoli in lungs to stay open during respiration
week 33 — both produced equally
week 34-36 — lecithin increase and sphingomyelin constant
L/S ratio >2 = maturity of fetal lungs
hemolysis and meconium-contaminated specimen should not be used
Phosphatidyl glyverol (PG)
phospholipid that enhances the spread of surfactants across the alveolar surface
Foam Stability Index (FSI)
A stable foam is produced by surfactants when shaken vigorously with ethanol
Lamellar Body Counts
Can use automated hematology counter’s platelet channel to measure lamellar bodies
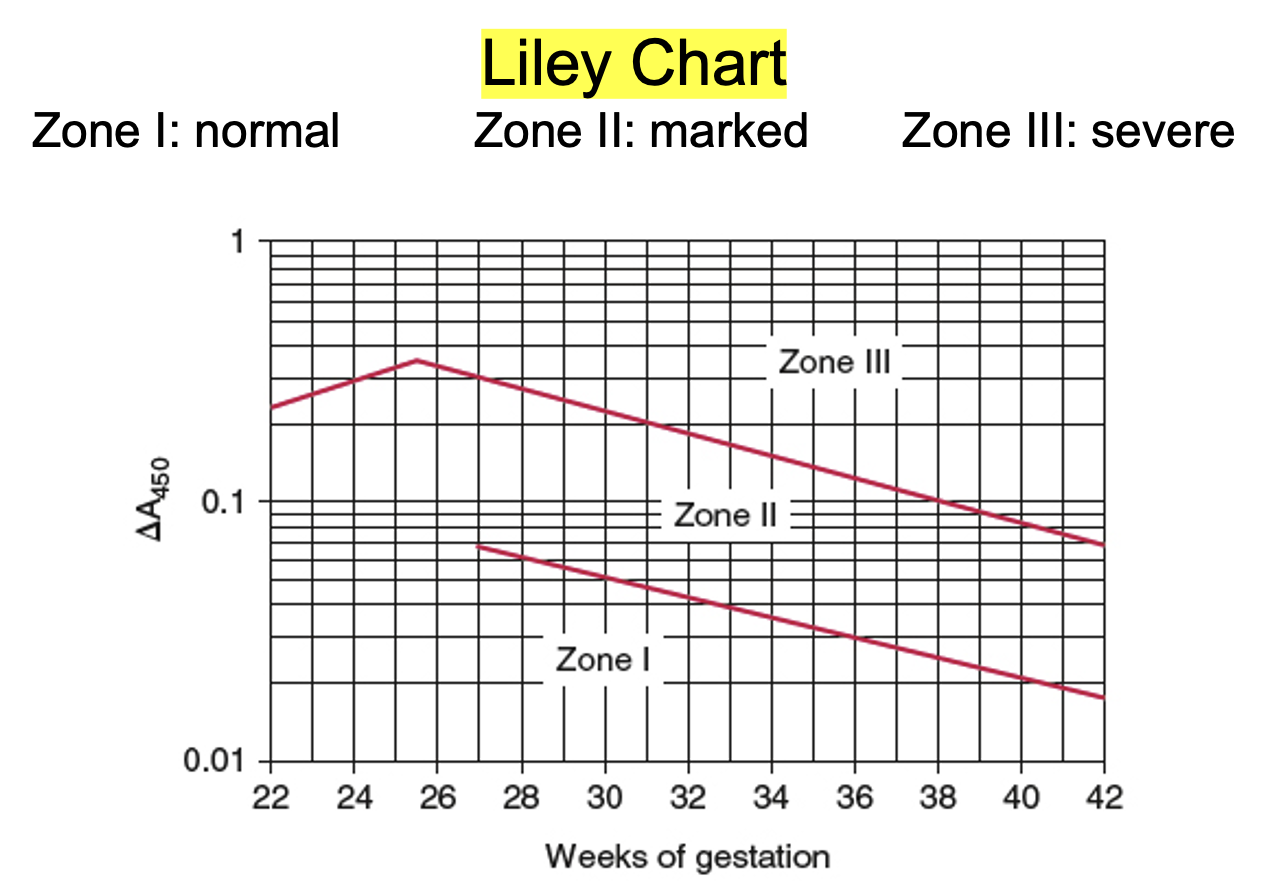
Amniotic Fluid Bilirubin (∆A450)
Amniotic fluid with a bilirubin peak at 450 nm
Hemolyzed and meconium-contaminated speciment not acceptable
Liley Chart
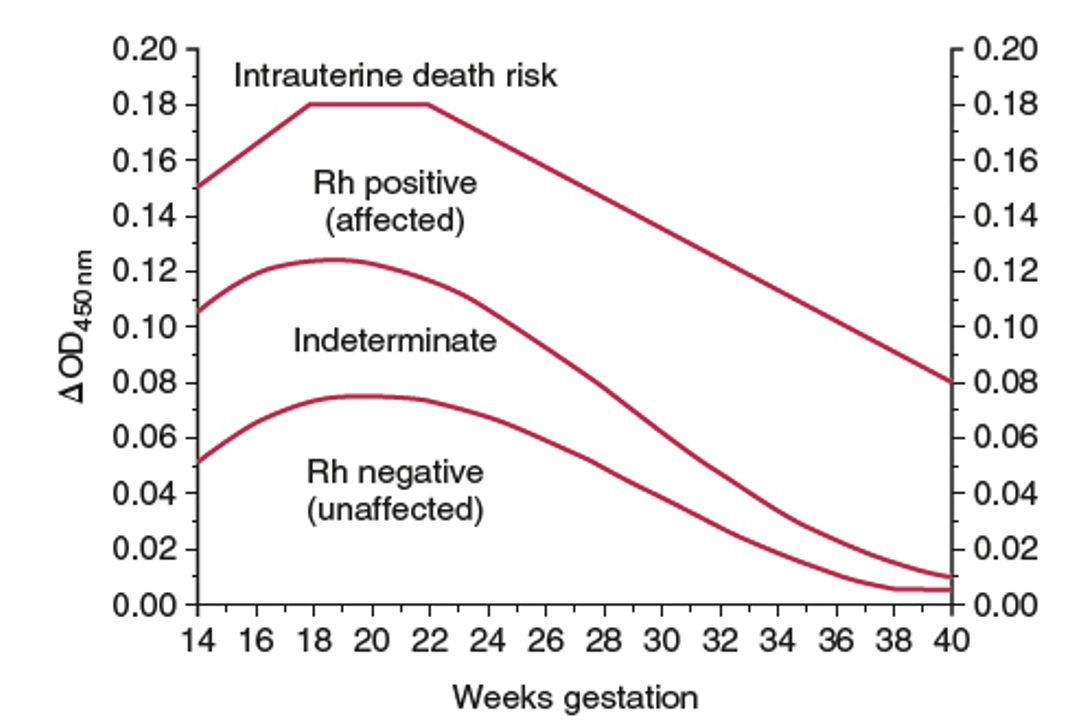
Queenan Chart
Premature delivery in vaginal fluid analysis
Fetal fibronectin (fFN)
Placental alpha-macroglobulin-1 (PAMG-1)
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1)
Sweat Analysis
cystic fibrosis diagnosed with sweat chloride test
Secretory vs Osmotic
Secretory — increased solute secretions by intestine draws water into intestine
Osmotic — ingestion of unabsorbed solutes draws water into intestine
calculated fecal osmolality = 2 x (Na + K)
>20mOsm/kg = osmotic
Fecal fat
increased meat fibers point to maldigestion
Occult blood
Guaiac-based
Immunochemical-based
Prophyrin-based
Semen analysis
agglutination caused by IgG and IgA
abnormalities
fructose = malfunction of seminal vesicles
alpha-glucosidase = epididymis
citric acid, zinc, acid phosphatase = prostate
Fecal fat 2 slide test
Slide 1 — qualitative orange-red staining of neutral fats
Slide 2 — acidified and heated before staining to detect total fats
Maldigestion = increased neutral fats on 1st slide
Malabsorption = normal amount of fat on 1st slide with increased total fat on 2nd slide
Fecal carbohydrate testing
Undigested carbohydrates in stool tested using Clinitest based on copper reduction principle