qcaa chem
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Why is KHP used as a standard solution rather than NaOH in a titration
KHP does not absorb water from the air; therefore, an accurate concentration can be determined for KHP.
NaOH easily abosrbs water and ionises
difference between alpha glucose and beta glucose, specific wording
α-glucose has its OH group attached on the opposite side of the carbon ring (trans) to the CH2OH group, while β-glucose has its OH group attached on the same side of the ring (cis) as the CH2OH group.
Explain, at an atomic level, why no colour change occurs once the chromate dichromate solution has established equilirbium
yellow chromate ions and orange dichromate ions are re-formed at the same rate at which they are broken down, so the colour remains constant because the [CrO4 2–] and [Cr2O7 2–] remain constant.
why esterifciation and transesterifcation are optimal processes
In esterification, free fatty acids (long chain carboxylic acids) react with an alcohol to produce esters (triglycerides) and water. In transesterification, esters (triglycerides) react with an alcohol to produce fatty acid alkyl esters (FAAEs) (biodiesel) and glycerol. A two-step process maximises the conversion of FFAs to biodiesel (FAAE).
Explain how the biodegradability of polylatic acid is related to its structure
Polylactic acid contains an ester linkage. Microorganisms produce enzymes that can hydrolyse the ester linkage to decompose PLA into CO2 and water.
When calculating Ka
make sure u convert it into a form where its raised to a whole integer
e.g.
10-7.9= 1.26 × 10^-8
Explain the relationship between the pH range of colour change for phenol red and its pKa value
identifies that colour change occurs when the [HIn] = [In– ] [1 mark]
• explains that when [HIn] = [In– ], the Ka of phenol red equals [H+], and therefore pH equals the pKa [1 mark]
• identifies that the pH range of colour change is pKa ±1 [1 mark]
• explains that the pH range of colour change occurs either side of pKa because colour change is detected when the [HIn] : [In– ] ratio changes [1 mark]
what does enzymes use to break starch down into glucose
hydrolysis to break glycosidic bonds
Difference between amylose and amylopectin
amylose has 1,4 glycosidic bonds, while amylopectin has 1,4 and 1,6 glycosdic bonds
amylose has a helix shape, while amylopectin has a spherical shape
Comparison of alpha helix and beta pleated sheets in secondary structure of proteins
a-helix structure and ẞ-pleated sheets both form H-bonds between two peptide bonds on polypeptide chains
Difference: a-helix structure contains only intra-chain H-bonds while B-pleated sheets contain inter-chain (2 polypeptide chains) or intra-chain H bonds
Geometric isomers vs structural isomers
Both keep the same molecular formula
structural isomers change the overall structure, different bonding arrangements with different atoms
geometric isomers have the same bonding of atoms but the atoms are arranged differently in space
Soap and its cleaning related to its structure
Soap contains a non-polar, hydrophobic group and a polar, hydrophilic group.
The ionic salt is attracted to the polar water, allowing the soap to dissolve in water while the non-polar fatty acid chain is attracted to non-polar oils allowing the soap to dissolve in the oils.
Thus, soap can form a bridge between polar water and non-polar oils that water can't dissolve by itself
why cellulose is harder to convert to glucose than starch
Cellulose is a linear polymer. The β-glucose monomers in cellulose can pack closely together. This increases hydrogen bonding between adjacent chains, which reduces interactions with water (solvents) and makes hydrolysis of cellulose more difficult than starch
if an amino acid
In chromatogrophy, the solvent is the what phase
mobile phase
Chromatogrophy rules
“Compounds move with the phase they’re more similar to in polarity.”
When you take an aliquot, what is the significance for the c=n/v
the concentration stays the same, so that means the moles and volume change by the same proportion
e.g. if you go from 500ml to a 25ml aliquot, you divided the volume by 20, therefore you also divided the moles by 20.
so to find the amount of moles present in the original solution multiply the moles in the 25ml aliquot by 20
Three common acid + base reactions
Acid + Base
Acid + carbonate
Acid + Metal
salt + water
salt + water + carbox dioxide gas
salt + Hydrogen gas
the pH and pKa equation for indicators
pH = pKa + log (In-/ HIn)
Therefore when the pH < pKa, there exists more Hln and the indicator is in its acidic form
When pH >pKa, there exists more In-, meaning the indicator is in its basic form.
how to differentiate between physical and chemical change
Does the substance change its chemical identity?
Yes → Chemical (a new substance is formed)
No → Physical (same substance, maybe just different form or state)
can it be easily reversed
Do tert alcohols or primary alcohols have higiher boiling point
Primary alcohols have higher boiling point becuase their OH group is more easily accesible to form hydrogen bonds and keep strong intermolecular forces
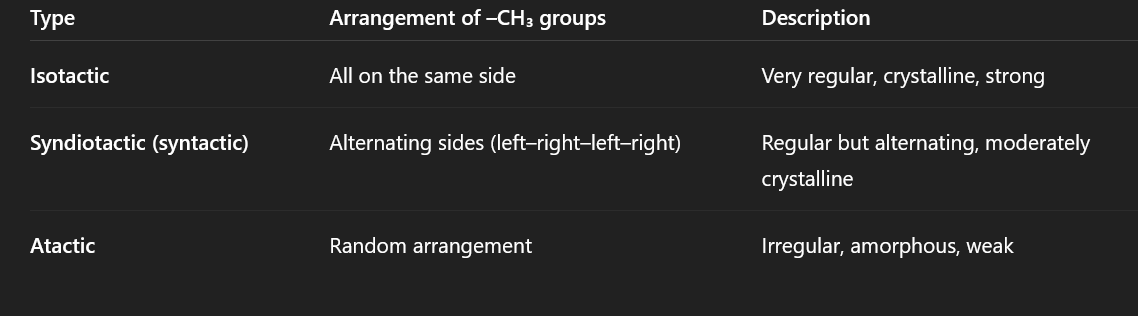
tactility for polypropene
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography involves using x-ray to determine the structure of molecules in a crystal form
What is diffraction
Waves bending when encountering matter (crystal atoms)
electron density map
So the more electrons an atom has (i.e. the higher its atomic number), the more strongly it scatters X-rays.
For example:
Hydrogen (Z = 1) → 1 electron → almost invisible.
Carbon (Z = 6) → 6 electrons → clearly visible.
Oxygen (Z = 8) → even stronger signal.
Bromine water test
add Bromine water to test if its an alkene or alkane
an alkene will react and decolourise while the alkane will stay orange/brown solution colour
Elimination reaction of Alcohol into alkene
What’s removed: H₂O
Reagent: Concentrated acid (H₂SO₄ or H₃PO₄)
Conditions: Heat (~170 °C)
Type: Acid-catalysed elimination
Elimination reaction of haloalkane into alkene
What’s removed: HX (a hydrogen + halogen)
Reagent: Ethanolic KOH (base)
Conditions: Heat under reflux
Type: Base-induced elimination
Alkane into a Haloalkane requires what conditions
UV light, heat energy, X2 (halogen)
Conditions for esterification
H2SO4, heat in reflux
Conditions for haloalkane into alcohol
dilute NaOH
because if it was concentrated NaOH in ethanolic solvent, it would cause an elimination reaction and form an alkene
conditions to make polyalkene
catalyst, heat
alkene into alcohol conditions
concentrated acid (H3PO4), steam
Difference between glycogen and amylopectin
both include 1,4 - glycosidic and 1,6 - glycosodic bonds made from alpha glucosoe monomers
but glycogen is more branched and compact and found in animals
while amylopectin is not as frequently branched and found in plants
Primary Structure of Protein
the specific sequence of amino acids
Secondary Structure of protein
the localised folding of chains due to hydrogen bonding
alpha helicase, and beta pleated sheets
Tertiary structure of protein
The overall 3D shape of proteins, caused by interactions between the R-groups
can be caused due to hydrogen bonds, hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonding, disulfide bridges (covalent bonds between SH)
Quaternary structure
Lactose
A disaccharide that consists of one glucose and one galactose molecule together
Maltose
disaccharide of two alpha glucose
sucrose
one alpha glucose and one fructose
Main goal of green chemistry
reduce waste, save energy (temperature, pressure), use renewable resources, make safer chemicals, use less hazardous reagents
difference between LDPE (low density polyethylene) and HDPE (high density polyethylene)
LDPE has highly branched chains, meaning it can’t pack closely and has weak london dispersion forces
HDPE is a very linear chain with minimal branching, allowing it to pack closer and have strong dispersion forces.
Biodiesel production from FFA-rich oils (the usual “two-step” process)
We start with waste oils or fats that contain a lot of free fatty acids (FFAs) and triglycerides.
FFAs can’t directly undergo transesterification efficiently — they form soap instead.
So, we first convert those FFAs into esters (not triglycerides!) through esterification.
Then, we perform transesterification on the triglycerides already present in the oil.
During transesterification

saponification