EXAM 4
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Bacterial Infection of skin: Acne
Propionibacterium acne
Opportunistic Pathogen - When immune system is weakend
Bacterial Infection of skin: Dermatitis “Hot Tub Rash”
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is naturally antibiotic resistant because it lives in the soil and is always exposed. True pathogen, hospital-associated.
Found in soil
Gram-negative rod (test)
Non-lactose fermenting on MacConkey agar (turns pale pink),
Green pigment is found on general media
Knowing that is microbe has oxidase +, oxidases enzymes/o2 to be used. Smells like a fruity, corn, nike ordor
Skin Bacteria: Staphylococus aureus
Apart of normal flora
Gram positive cocci
Majority cause of skin infection
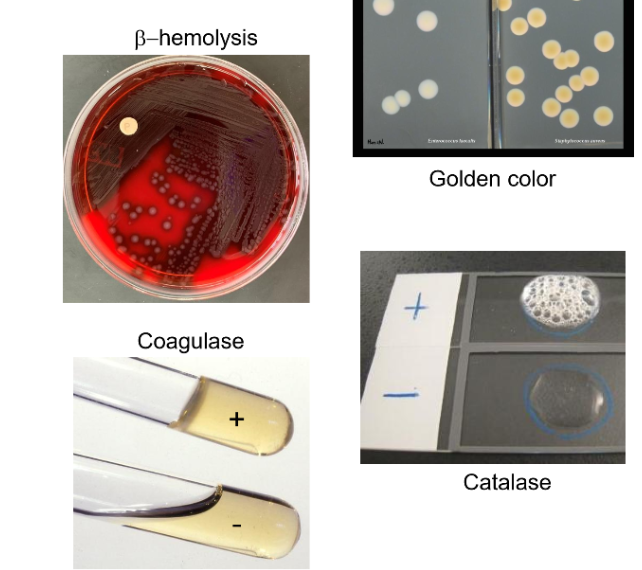
How to identify Staphylococcus aureus (s. aureus)
Golden colonies
Beta Hemolysis on blood agar plate
Catalase + (turns more solid less liquid)
Coagulase + (Bubbles)
Staph aureus Virulence Factors
Has a capsule making it easy to invade into cells
Coagulation - allows bacteria to clot blood covering itself in a fibrin shield evading the immune response
Protein A - Prevents antibodies from binding to IgG antibody, preventing phagocytosis
Releases toxemias: Exfoliative toxin + TSST-1 (toxic shock syndrome)
Strain of Staphylococcus Aureus: MRSA
MRSA: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a strain that is resistant to many antibiotics, leading to more difficult treatment options for infections.
MRSA Strains: Hospital-Associated (HA-MRSA)
mecA gene present
Resistant to all antibiotics EXCEPT vancomycin
Treated with Vancomycin
MRSA Strains: Community-Associated (CA-MRSA)
mecA gene present
Resistant to methicillin, sensitive to many others
HAS PVL GENE
Staff Aureus toxemias that affect skin: What is toxemia?
A toxin enters bloodstream (-emia: in the blood prefix)
Bacteria is not present at the site of symptoms
Bacteria are NOT in the blood, a TOXIN is
Staff Aureus toxemias that affect skin: Scalded Skin Syndrom (SSS)
Exfoliative toxin released causes this
Bacteria colonize in intestine, toxin enters the bloodstream, and skin peels off in sheets
More found in children under 2
Staff Aureus toxemias that affect skin: Toxic Shock Syndrom (TSS)
TSST-1 caused this
Toxin enters the bloodstream, and extreme fever, vomiting, and rash
More common in adults
What is Group A Strep skin infection?
Defined by carbohydrates expressed on surface of bacteria
Gram positive cocci
Diagnosis of Group A Strep skin infection?
Catalase negative
Beta-hemolysis (transparent hemolysis on blood plate)
Group A typing
Group A Strep (GAS) Virulence Factors skin infection?
Capsules
M protein - fuzzy layer of capsule that inhibits phagocytosis mimicing human molecules, creating self-reactive antibodies
SPE A and SLO toxemias released
Group A Strep (GAS) Necrotizing Fasciitis skin infection
Group A Strep cells are producing toxins that kill cells in said area. Group A Strep is more common to cause necrotizing fasciitis rather than staph.
SPE A is a SUPER ANTIGEN - Toxin causes an OVER REACTION for immune response, leading to rapid tissue destruction
Group A Strep (GAS): Toxic Shock Syndrome skin infection
Toxemia is associated with SPE A super antigen (staph = TSST-1)
Less common
Similar wound infection/menstral product infection
Treatment for Group A Strep skin infection
Antibiotic treatment is a MUST
M proteins will attack our own cells, causing rheumatic fever
Viral infections of the skin: Diseases/Microbes
Measles (Rubeola) - exanthems
Rubella (German Measles) - exanthems
Roseola - exanthems
Chickenpox/shingles (Varicella) - exanthems
Fifth disease - exanthems
Cold sores and skin herpes
Hand, foot, and mouth disease
Warts
What are exanthems?
Group of viral diseases that are characterized by a rash. The virus is actually causing a respiratory disease but we will be reacting from a rash
Vaccines must be live attenuated (weakened virus injected)
Viral infections of the skin: Measles (Rubeola) EXANTHEM
Caused by measles virus
Macular ((colored and flat (versus papular which is colored and popped up)) rash, fever, cough
Koplik spots - Red patches with white centers + diagnostic indicator
Most contagious human virus
Mnemonic: “Ruby has Koplik spots”
MMR Vaccine: Live attenuated because it is exanthem and covers measles, mumps, and rubella.
Severe outcomes of measles (Rubeola)
Pneumonia
Immune amnseisa - kills immune cells to cause secondary infection
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) - virus replicates in brain after years of infection and is ALWAYS FATAL (brain goes hard)
Viral infections of the skin: Rubella (German Measles) EXANTHEM
Caused by rubella virus
Macular rash, fever, respiratory symptoms
Congenital rubella syndrome: a serious condition resulting from maternal infection during pregnancy, leading to birth defects. Mother is infected in first trimester of pregnancy
Mnemonic: Bella is German and pregnant
Viral infections of the skin: Roseola EXANTHEM
Caused by human herpesvirus
A common and mild disease, only lasting for a few days
Mnuemonic: Rosie is no big deal
Viral infections of the skin: Chickenpox (Varicella) + Shingles (Zoster) EXANTHEM
Cause by varicella-zoster virus (VSV), another herpesvirus via respiratory route
Primary disease: Chickenpox (varicella), rash with vesicles
Virus goes latent in nerve cells, becoming shingles
Live-attenuated vaccine
Secondary Disease of Chickenpox + Shingles: Shingles
Virus is reactivated in the nerve
Vesicles erupt in path of nerve
Adults >50
Shingles-specific, subunit vaccine
Viral infections of the skin: Fifth Disease EXANTHEM
Caused by parvovirus B19
“Slapped cheek” rash
Viral infections of the skin: Cold sores and cutaneous herpes
Cold sores (sores near mouth) caused by HSV-1 (Herpes Simplex Virus)
Vesicular rash
Herpesviruses transmits via direct contact
Virus goes latent in nerve ganglion on face
Viral infections of the skin: Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
Caused by coxsackievirus 16
Vesicular rash spread via direct contact
Respiratory + Enterovirus (infects gut)
Viral infections of the skin: Warts
Caused by Human Papillomavirus
Rough papules
Transmits via direct contact
Fungal Infections and skin
Fungal diseases are called “mycoses”
Fungal Infections and skin: Ringworm (Tinea)
Common fungal infection by dermatophytes because they love moisture
Fungal Infections and skin: Candidiasis
Caused by Candida albicans > Normal flora on our skin/Opportunistic infections
Happens after antibiotic use and is common in immunocompromised individuals
Parasitic infections and skin
Parasites: Leishmaniasis and Hookworm
Insects: Scabies and Lice
Parasitic infections and skin: Leishmaniasis (Parasite)
Caused by Leishmania species
Protozoan parasite, spread by sand fly (vector)
“Volcanic” ulcers form
Parasitic infections and skin: Hookworm (Parasite)
Caused by helminths, it can be found in the South US
Hook enters skin after stepping barefoot on contaminated soil
Parasitic infections and skin: Scabies (Insect)
Caused by mites
Burrows under skin to lay eggs, causing an itchy maculopapular rash
Parasitic infections and skin: Lice (Insect)
Head lice is caused by pediculus humanic capitis (cap = on head)
Common in children causing itchy scalp because of blood taken
Treated with insecticides
Diseases of the eyes
Conjunctivitis (Pink eye)
Ophthalmia Neonatorum
Trachoma
Keratitis
Ocular Hispoplasmosis
Diseases of the eye: Conjunctivitis (-itis, infection of the conjunctiva)
Source can be viral or bacterial; viral is clear discharge, bacterial is purulent (includes yellow pus because of dead white cells) discharge
Very easy to spread
Diseases of the eye: Ophthalmia Neonatorum (newborn conjunctivitis)
Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis can be transferred from mother to baby (the mother had STIs and baby was given STIs during birth)
Treatment: Antibiotic eye drops/ointment
Diseases of the eye: Trachoma
Caused by chlamydia trachomatis
Causes chronic inflammation and scarring of the eyelid/conjunctiva, creating bumps on the cornea, leading to blindness due to damaged cornea/eyelid. Results in blindness
Treatment: Antibiotics because it is bacterial infection; lashes may grow inward
Bacteria of Trachoma: Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis is an obligate intracellular bacterium: very small, cannot be seen under a microscope, gets inside of a cell, and replicates within the cell. Leads to lysis of the cell.
Antibiotics need to inhibit the cell replication to block translation
Diseases of the eye: Keratitis
Caused by: Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1)
Virus infects cornea
Essentially reactivated herpes after being latent
Leads to blindness due to damage of the cornea, antiviral is used
Fungal infection of the eye: Ocular Histoplasmosis
Caused by a fungus in contaminated soil (from bat/bird droppings)
Initially infects our lungs after inhalation, then passes to eyes
Plaques build up within our blood vessels within our retina, leading ot blindness
Treatment: No antifungals, only injections to halt the disease course of blood vessel buildup. Lasting blindness/eye damage may occur
Disease of the ears: Otitis externa (swimmer’s ear) (Otitis meaning ear infection, second word being location of ear infection)
Infection of the outer ear
Symptoms: Red, itchy ear canal with discharge
Cause: Bacterial, fungal, or viral from
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (found in hot tub rash)
Aspergillus sp.
Disease of the ears: Otitis Media
Infection of the middle ear and eustachian tubes (connected to respiratory system)
Symptoms: Pain, discharge, and pressure in ear
Caused by: Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus Influenzae (due to respiratory connection)
Disease of ear: Otitis Interna/Labyrinthitis
Infection of the inner ear
Caused: Viral infection
Symptoms: Vertigo, dizziness, vomiting
Disease of wounds: Burn Wounds
Bacteria: Pseudomonas Aeruginosa (gram-neg rod)
Disease of wounds: Surgical site infections (SSIs)
Cause: Patient’s normal flora (staph a + escherichia coli) cause opportunistic infection after surgery
Symptoms: Fever, pus, redness at surgery site
Disease of wounds: Gas Gangrene
Cause: Clostridium perfringens (philanges), strict anaerobe creating gas bubbles within muscle tissue. Inhibiting blood flow to our muscle, resulting to tissue death
Gangrene - tissue death due to lack of blood flow
Can occur after childbirth or in diabetes
Anatomy of the Cardiovascular system
Closed sterile system
Function of the lymphatic system
Permeable, carries white blood cells
Supports the cardiovasular system and overlaps
Disease of the cardio/lymph systems
If infections reac the cardio/lymph system, they are considered systemic
Signs and symptoms are often non-specific (Non-specific means they do not clearly indicate a specific disease and may vary among patients.)
General diseases of the cardiovascular and lymphatic system
Bacteremia
Lymphangitis
Septicemia (sepsis)
Severe sepsis
Septic shock
Endocarditis
General diseases of the cardiovascular and lymphatic system: Bacteremia
Presence of bacteria in the blood
Any bacteria could cause disease given the right conditions
Viremia, fungemia, and parasitemia
General diseases of the cardiovascular and lymphatic system: Lymphangitis
Inflammation of lymph vessels
Can occur after bacteremia
General diseases of the cardiovascular and lymphatic system: Septicemia
Uncontrolled growth of microbes in the blood
Sepsis is the body’s inflammatory response to septicemia
Symptoms are present
Fever, chills, increased heart rate, shortness
General diseases of the cardiovascular and lymphatic system: Severe Sepsis
Blood pressure drops (hypotension) following inflammatory response
Must be treated with fluids
General diseases of the cardiovascular and lymphatic system: Septic Shock
Severe sepsis but fluids no longer support the patient
Organ failure, lower mortality rate
General diseases of the cardiovascular and lymphatic system: Endocarditis
Infection causes inflammation of heart lining (endocardium)
Abnormal heart architecture puts you at risk for
Rheumatic fever
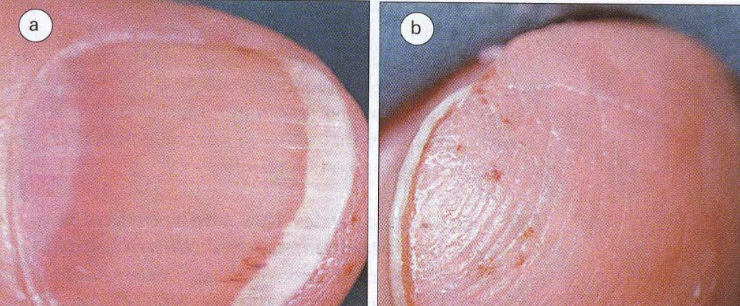
Symptoms include
Splinter
Hemorrhages under fingernails
Night sweats
Heart murmur
Diagnosis of sepsis and endocarditis
Blood culture is necessary because few organisms are present
Treatment must happen quickly because then it will become too broad for antibiotic treatment
Bacterial diseases: Causes of sepsis/endocarditis
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Viridians streptococci
Enterococcus sp.
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus agalactiae
Endotoxic shock
Gram-negative
Gram-positive
Bacterial diseases that cause sepsis/endocarditis: Staphylococcus aureus
Causes both sepsis and endocarditis
Gram-positive cocci
Diagnosis of S. aureus
Culture is beta-hemolytic on blood agar
Catalase positive
Coagulase positive
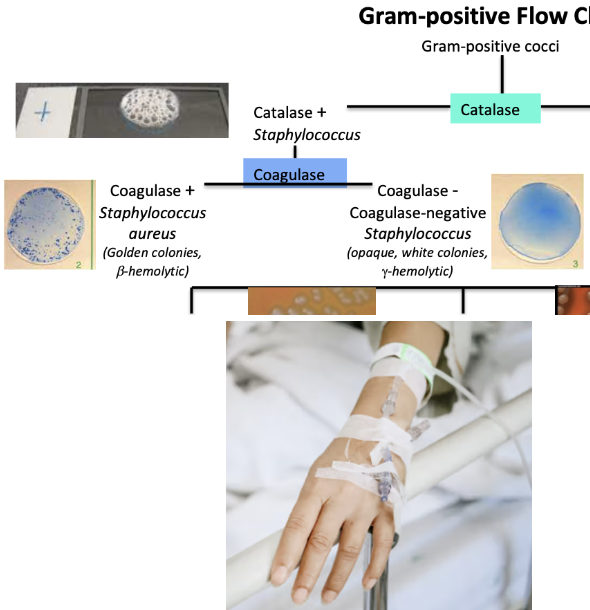
Bacterial diseases that cause sepsis/endocarditis: Staphylococcus epidermidis
Causes sepsis
Gram-positive cocci
Causes biofilms
May come from indwelling medical devices (medical devices inserted in the body)
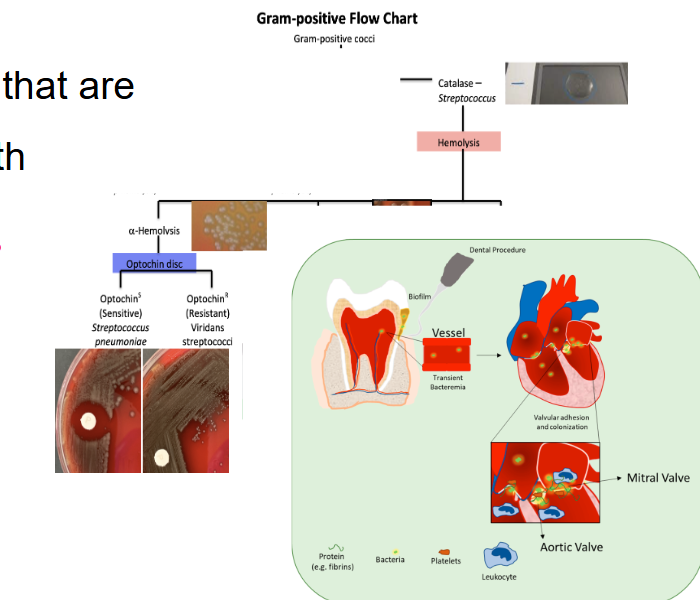
Bacterial diseases that cause sepsis/endocarditis: Viridans Streptococci
Causes endocarditis
Gram-Positive cocci
May come from dental procedures
A group of streptococci that are normal flora in the mouth
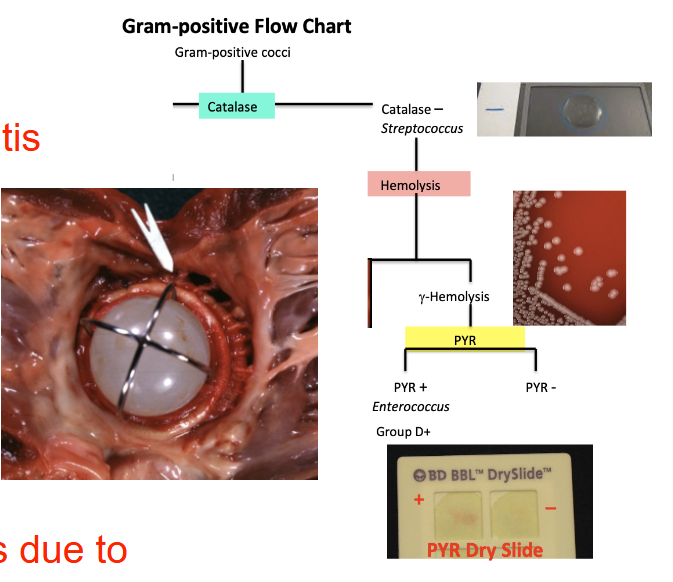
Bacterial diseases that cause sepsis/endocarditis: Enterococcus sp.
Causes both sepsis and endocarditis
Gram-positive cocci
Leading cause of endocarditis due to prosthetic heart valves
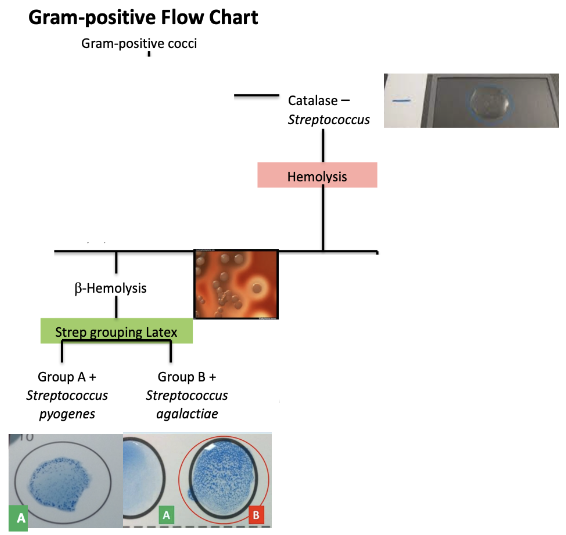
Bacterial diseases that cause sepsis/endocarditis: Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Strep)
Causes sepsis
Gram-Positive cocci
Group A Strep sequelae (complications/diseases arising after untreated group a strep)
Rheumatic Fever
Occurrece are pharyngitis (strep throat)
The immune system makes antibodies to M protein
Predisposes patient to endocarditis (Heart infection of inflammation of heart lining)
Lemierre’s Syndrome
Occurs after pharyngitis
An abscess may burst, and infection can cause clots in the jugular
Can be fatal
Bacterial diseases that cause sepsis/endocarditis: Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Strep)
Sepsis of newborns
Gram-positive cocci
Passes through vaginal canal
Bacterial diseases that cause sepsis/endocarditis: Endotoxic shock
Subtype of septic shock
As bacteria die, a endotoxin is released and causes symptoms of fatigue, confusion, loss of apetite
Endotoxins may be gram-negative or gram-positive bacteria characterized by a severe systemic inflammatory response that leads to organ dysfunction.
Gram-Negative Endotoxic Shock
Endotoxin is in the LPS
Antibiotics that lyse the bacterial cells will release more endotoxin
Must use antibiotics carefully to avoid worsening the shock
Gram-Positive Endotoxic Shock
Less common
Endotoxin is lipoteichoic acid (LTA)
Bacterial Diseases: Zoonotic diseases
Plague
Brucellosis
Tularemia
Lyme Disease
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Bacterial Diseases: Plague
The bacteria is yersinia pestis
Spread from rodents by fleas
Can result in sepsis
Bacterial Diseases: Brucellosis
The bacteria is Brucella sp.
Can lead to sepsis
Comes from unpasteurized dairy, handling infected animals, exposure to contaminated meat
No person-to-person spread, only animal to person
Bacterial Diseases: Tularemia
The bacteria is Francisella tularensis
Spreads by vectors of infected animals and inhalation of aerosols
Common in vets and landscapers
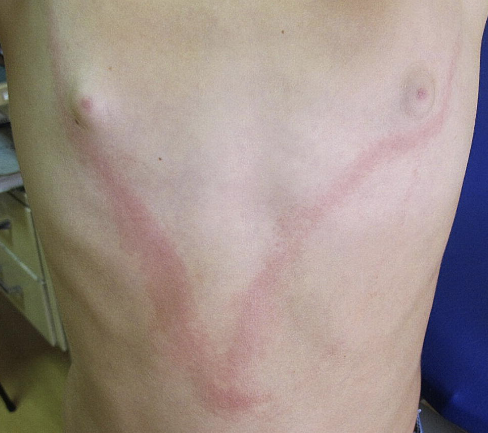
Bacterial Diseases: Lyme disease
The bacteria is Borrelia Burgdorferi
Vector: Deer ticks, because deer ticks feed on mice and bite deer
Present across the U.S.
Looks like a bullseye rash for diagnosis
Bacterial Diseases: Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
The bacteria is Rickettsia Rickettsii
Vector: Wood ticks and dog ticks
Rash on hands and feet
Reservoir: mammals
Diseases of Cardio and Lymph: Viral Diseases
Infectious Mononucleosis
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
Hemorrhagic Fever
Acute retrioviral syndrome and AIDS
Viral Diseases of Cardio and Lymph: Infectious mononucleosis (mono)
Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesvirus) EBV
Seen in young adults/teens
Diagnosis of mono
EBV infects B cells - look for atypical B cells in peripheral blood smear
Monospot test is used
Viral Diseases of Cardio and Lymph: Infectious mononucleosis (mono) EBV → Burkitt Lymphoma
Cancer of B cells, causing swelling in lymph nodes
Viral Diseases of Cardio and Lymph: Hemorrhagic Fever
Bloody fever
Causes damage to blood vessels and initiates leaks
Caused by several viruses
Ebola virus
Yellow virus - vector is mosquitos
Dengue virus - vector is mosquitos
Changes to climate impact spread of vector-based diseases
Viral Diseases of Cardio and Lymph: Acute retroviral syndrome and AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus HIV
Retrovirus (RT)
Primary disease: Acute retroviral syndrome
Virus infects CD4 T Cells
A virus inserts itself into genome and become persistent
Persistence becomes AIDS
Secondary disease: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS
Lack of immune response leads to overwhelming infections, which leads to death
Prevention and treatment for AIDS
Prevention
STD Screening
PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis)
Treatment
Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
If treated properly, no virus is present
Fungal Side Story of AIDS
ARC: AIDS-related complex
Patients with AIDS suffer from infections that do not affect healthy people
Most are fungal infections
Cryptococcus
Candidiasis
Pneumocystis
Histoplasmosis
Parasitic Diseases
Toxoplasmosis
Malaria
Trypanosomiasis
Parasitic Diseases: Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasma Gondii protozoa
Comes from cat feces
Dangerous for fetuses
Parasitic Diseases: Malaria
Plasmodium sp. protozoa
Vector: Mosquitoes
Diagnosis
Parasites in peripheral blood smear
Treatment
Anti-Malarial drugs
Parasitic Diseases: Trypanosomiasis
Trypanosoma Cruzi protoza
Vector: Tsetse fly
Symptoms
Sleepiness
Anatomy of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF)
Should be sterile
Meninges
Layers of lining around the spinal cord and brain
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Helps prevent infection
Prevents uptake of drugs and antibiotics
CNS is immunologically privileged meaning it reduced an immune response
Bacterial Diseases of the nervous system
CNS
Meningitis
Neonatal meningitis
Toxemias
Tetanus
Botulism
PNS
Hansen Disease (Leoprosy)
Bacterial Diseases of the nervous system: Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges
Bacterial is the most serious but can occur from many microbes
Symptoms
Headache
Stiff or painful neck
Brudzinski’s Sign:
Raising neck up will cause knees to flex.