Unit 5 Learning/Behavioral Psychology
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
classical conditioning
- learning by association
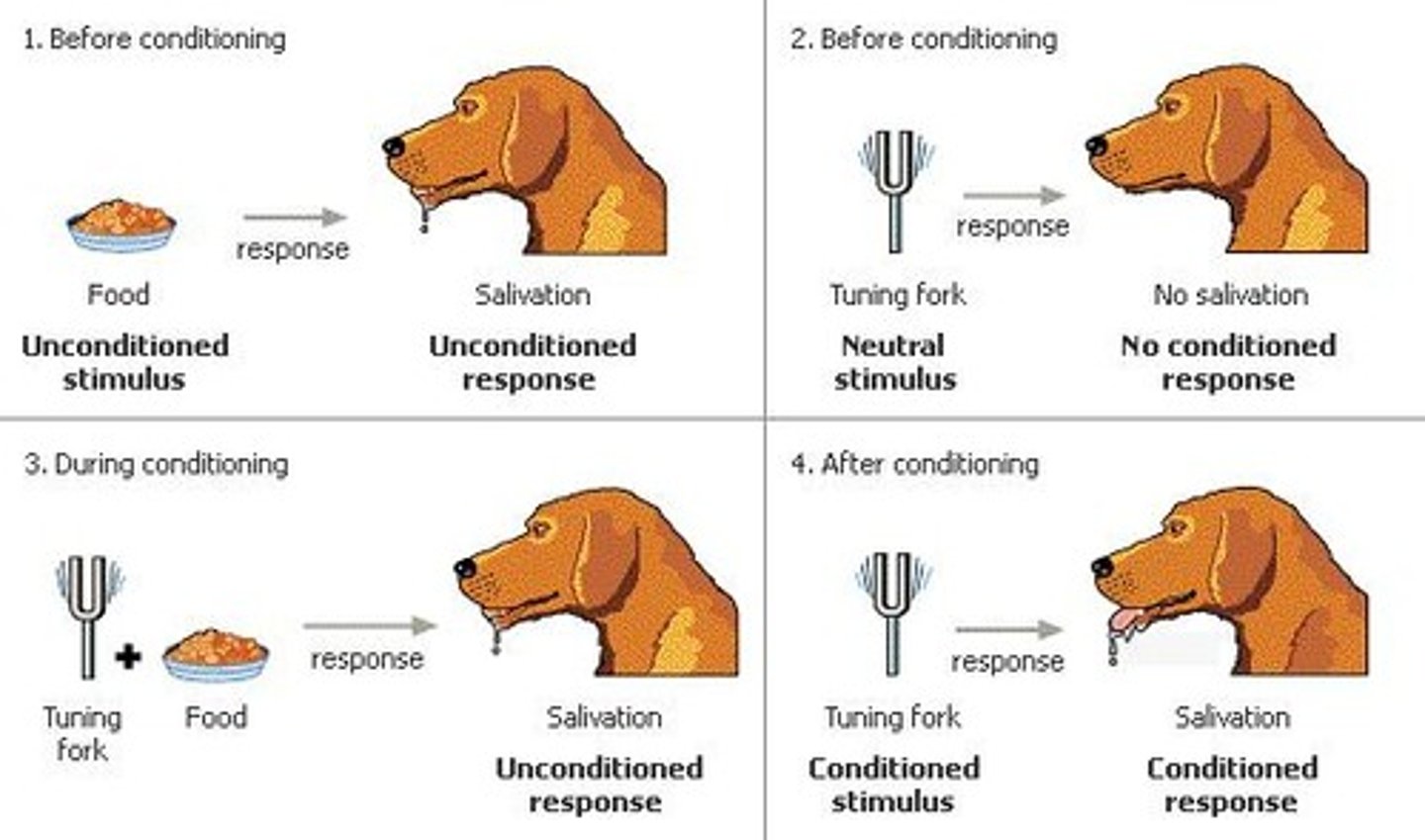
Pavlovs Dog experiment
conditioned dogs to droll to the ringing of a bell
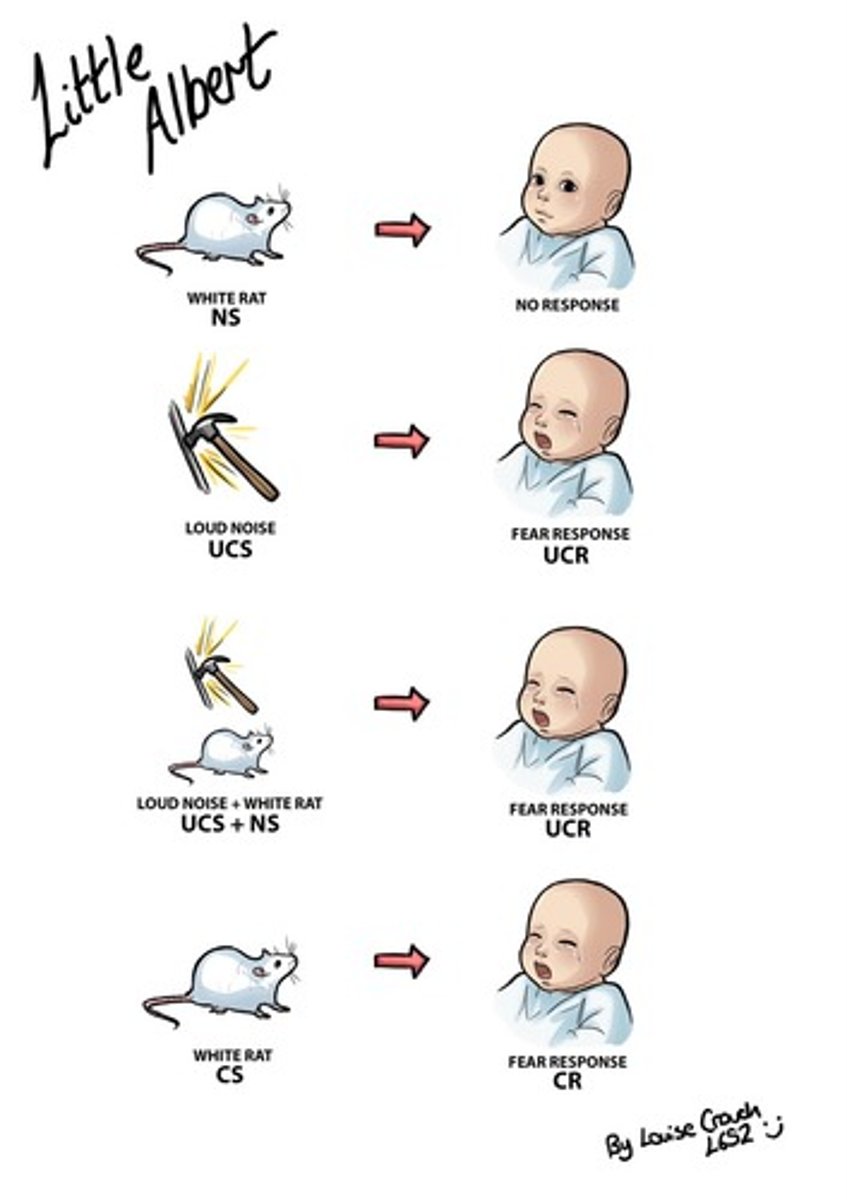
Watsons Little Albert Experiment
conditioned the baby to fear white rat when loud noise is played
NS
- something that when its by its self it inflicts no response at first
- sound, noise, pain, etc
UCS
- stimulus that is associated with NS to cause an UCR
- not trained or learned
UCR
- an unconditioned reaction to the UCS
- not trained or learned
CS
- always the same as the NS
- it is trained/learned
CR
- Should always be similar to the UCR
- is trained/ learned from the CS
Acquisition
- the pairing of a UCS with a NS
- best when NS comes before UCS
Taste aversion
- a learned association between food and a neg experience that leads you too avoid it in the future
ex: your sick, which causes you to throw up, but you think its because of the greasy fries you at
Generalization
- when stimuli similar to the CS also causes the CR without training
ex: Albert the baby was scared of all furry animals not just rats
Discrimination
- when only the CS cause the CR
Extinction
- repeated exposure of the CS w/o the UCS makes the CS a NS again
ex: after awhile of hearing a bell, you stop thinking of food
Spontaneous Recovery
- After extinction and w/o additional conditioning, the CR suddenly reappears temporarily
Operant Conditioning
Learning by consequences
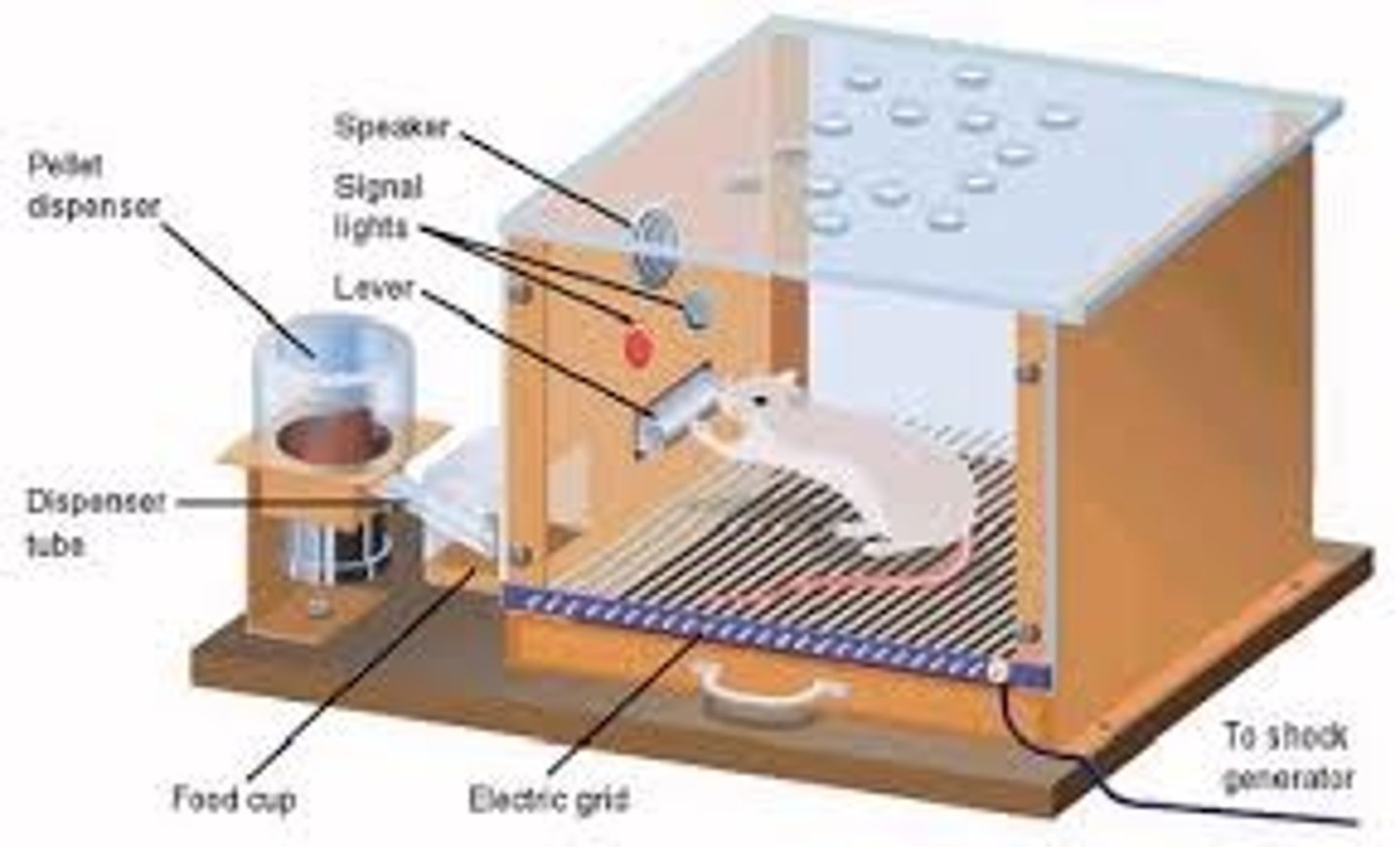
Skinner box
- chamber designed to teach rats how to push a lever
Positive Reinforcement
- rewarding consequence that increases the chances a behavior will be repeated
ex: money, treats/food, praise, clapping

Negative reinforcement
- the removal of a negative consequence that increases the chance the behavior will be repeated
ex: beeping to buckle your seat belt, nagging
keywords: avoid or escape
Positive Punishment
- adds a negative consequence to decrease a bad behavior
ex: getting a ticket, bad grade, spank, yelled at
Negative Punishment
- removes a pleasant stimulus to decrease a behavior
ex: time out, screen time, grounding, loss of dessert
Escape
- removes if after the negative stimulus has already started
ex: buckling to make the beeping stop
Avoidance
- removes negative stimulus before the stimulus has started
ex: buckling up before starting the car
Learned helplessness
- a state that occurs after a person has experienced a stressful/traumatic situation repeatedly
ex: dogs got shocked and had no way of escaping, when they were put in the same situation but had an escape, they just sat their
Superstitious Behaviors
- learned because it happened to be followed by a reinforcer, even though this behavior was not the cause of the reinforcer
ex: you wore Christmas socks during fb game and they won, so you where those socks every game
Primary reinforcer
- anything biologically necessary
ex: food, water, sleep
Secondary reinforcer
- anything else
ex: stickers, money, praise
Shaping
- rewarding each step towards a behavior
ex: teaching a dog to roll over (sit, lay down, roll over)
Chaining
- rewarding only after the full set of behaviors has been complete
ex: dog rolls over he gets treat
Instinctive Drift
- tendency of animals to revert to their natural behaviors
- can interfere with learned behaviors
Continuous Reinforcement
- reinforcement after every behavior
- best method for learning a new behavior
- over justification can occur
Partial Reinforcement
- reinforcement that does not occur after each behavior
- best method to prevent extinction
Over justification Effect
- when people are given outside motivation to perform a task, their intrinsic motivation declines
ex: you like to read on your own but when your mom tells you to read you don't want to
Fixed ratio
- reinforcement after a SET of behaviors
ex: free drink after you by 10 drinks, test every three units
Fixed Interval
- reinforcement after a SET amount of time
ex: studying for a weekly test, getting paid every 2 weeks
*scalped shaped line on graph
Variable ratio
- reinforcement after a random number of behaviors
ex: slot machine/gambling, # of shots taken to score a goal
- addictive
Variable Interval
- reinforcement after a random amount of time
ex: winning a video game level, fishing, be real app
Latent Learning
- learning in the absence of reward
Insight learning
- occurs when one suddenly realizes how to solve a problem (light bulb moment)
Cognitive map
- visualizing something in your brain
ex: imagining me and karah walking to math class in your head
observational learning
- learning by imitation
Model
- person who demonstrates what to do
ex: teacher, of YouTube video tutorial
Vicarious Learning
- when we learn by watching someone else's reinforcement or punishment and adjusting your behavior
ex: brother gets yelled at for messy room, so I make sure my room is clean
Bandura's Bobo Doll Experiment
- lady hit the doll, the kids copied her. when the kids were punished, they did it less.
- kids learn and imitate