DDS LEC - Solid Dosage Forms: Tablets Part II
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Quality Standards & Compendial Requirements
Tests performed in intermediate and finished products before and after the manufacturing process in order to comply with the specifications
Routinely run to monitor the process from powder to granules up to its compression
Monitored every step so if there’s a problem in terms of the granulation, it can be addressed immediately
Also performed during product development
Used for Process Validation
Compendial Standards
Pharmaceutical standards in a compendium
Process Validation
A small-scale test run of the procedures and processes, making sure that before the upscale or the manufacturing scale production, the process meets the specifications
In Process Quality Control Tests ((IPQC Tests)
Tests done for intermediate testing
Finished Product Quality Control Tests (FPQC Tests)
Tests done for finished product testing
Particle Size Distribution
Can also be called Grain-size Distribution
Represents the relative proportions of different particle or grain sizes in a sample
Can be performed using a sieve with various sieve numbers, microscope methods, or using a RO-TAP Mechanical Sieve Shaker
Ideal Tablet
Composed of:
80% Good
20% Fine Granules
Bulk Density
Ratio of the mass to the volume of the untapped powder sample
It describes the packing of particles or granules
Dictates how much space is needed for the powder or granules to be safely stored
Tapped Density
Ratio of the mass of the powder to the volume occupied after it has been tapped for a definite number
Method I
Commonly used method
Method using Graduated cylinder in Bulk and Tap Density Tester
Method II
Method using Volumeter
Method III
Method using Vessel
Moisture Content
Presence of water in a product
2-3% moisture content before starting compression when the tablet undergoes wet granulation
Directly measure the moisture content of a sample by using the Loss On Drying (LOD) technique
If there is excessive moisture, granules will stick to the dye cavity
Will not result in a 1 solid tablet because of sticking
If done manually, done in a drying oven with a balance to determine the initial and final weight of the sample and using a simple mathematical calculation to determine the moisture content
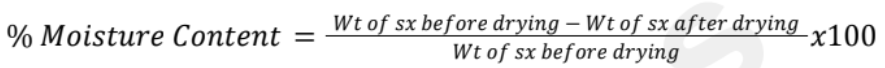
Tablet Hardness
Determines the quality of tablet in terms of rigidity and resistance to chipping or breakage during transport and storage
Stokes-Monsanto Tablet Hardness Tester
If not available, use Rule of Thumb
Stokes-Monsanto Tablet Hardness Tester
Spring gauge and screw mechanism
Place the tablet upright
Screw clockwise
Continue screwing until a crack forms
Not the reading - Tablet Hardness
Uncoated, Oral Tablet Acceptable Hardness Range
4-10 kg
Sublingual, Chewable Acceptable Hardness Range
2-3 kg
Buccal Tablets Acceptable Hardness Range
10 kg
Sustained Release Acceptable Hardness Range
10-20 kg
Rule of Thumb
Used if Stokes-Monsanto Tablet Hardness Tester is not available
Place the tablet in between the 2nd and 3rd finger
Let it fall to the floor and the tablet should not break
Tablet Weight
Establish how many granules are placed in the die cavity and it should be uniform
Quantity of fill in the die of the tablet press
USP Weight Variation Test - determination of dosage form uniformity
Minimum of 10 tabs are weighed individually, and the average is calculated
The tablets are assayed to determine homogeneity of drug distribution
Maximum % Weight Variation Allowed for <130 mg
± 10%
Maximum % Weight Variation Allowed for 130 mg to 324 mg
± 7.5%
Maximum % Weight Variation Allowed for >324 mg
± 5%
Tablet Thickness
Non-official test for tablets
In-house specification sample (within the manufacturing company): ± 5%
Can give an idea in terms of the disintegration and dissolution profile
Tablet Friability Test
Tests the durability of tablets during packaging processes
Makes use of a tumbling apparatus where tablets are exposed to rolling and repeated shocks from free fall within the transparent synthetic polymer with polished internal surface drum
Condition: 100 revolutions
Speed: 25 ± 1 revolution per minute (4 minutes)
Criteria: Weight loss should not be more than 1%
Rotates clockwise and drops the tablets and will continuously repeat
Twice
In case of cracked, cleaved, or broken tablets present, repeat the test _____.
% Weight Loss Formula

Disintegration Test
Measures the ability of a tablet to break apart into smaller particles or granules to allow the active drug to be absorbed into the body
1 tab is placed per cylinder, then a disk is placed in top of the tablet to prevent the tablet from floating
Condition:
Volume: 900 mL distilled water (or whatever is specified)
Temperature: 37 ± 2°C - body temp
Sample: 6 tablets
Time:
Uncoated or Plain Tablets: 30 mins
Delayed-Release Tablets: 60 mins
Criteria:
All tablets should have disintegrated completely
If 1 or 2 tablets fail, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets (repeat test twice)
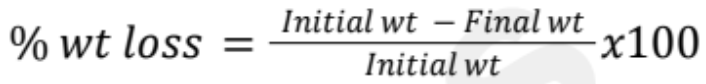
Time for Uncoated or Plain Tablets in Disintegration Test
30 minutes
Time for Delayed-Release Tablets in Disintegration Test
60 minutes
Dissolution Test
Process by which solid substances enters in a solvent to yield a solution
From powders, after disintegration, the drug is slowly dissolved or when it is present in the solution, it can be concluded that it is now ready for absorption
Type of Apparatus:
Apparatus I - Rotating Basket
Apparatus II - Rotating Paddle
Apparatus III - Reciprocating Cylinder
Apparatus IV - Flow-Through Cell
Apparatus V - Paddle Over Disk
Apparatus VI - Rotating Cylinder
Apparatus VII - Reciprocating Holder
Importance:
Guides formulation and product development
Product monitoring
Ensures consistent bioequivalence characteristics from batch to batch
In-Vitro
Establishes the amount of drug released
In-Vivo
Establishes the amount of drug absorbed
Quadrant 1
High Solubility
High Permeability
Fast to dissolve, Fast to be absorbed by the body for its therapeutic effect
Quadrant 2
Low Solubility
High Permeability
Slow to dissolve, Fast to be absorbed by the body for its therapeutic effect
Quadrant 3
High Solubility
Low Permeability
Fast to dissolve, Slow to be absorbed by the body for its therapeutic effect
Quadrant 4
Low Solubility
Low Permeability
Show to dissolve, Slow to be absorbed by the body for its therapeutic effect