Species Interactions and Their Types
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Species interactions
Interactions that occur between two different populations that live in the same area.
Intraspecific interactions
Interactions that occur between individuals of the same species.
Interspecific interactions
Interactions that occur between individuals of different species.
Competition
An interaction between two or more species in which both organisms rely and compete for the same resource(s) and are harmed to some extent.
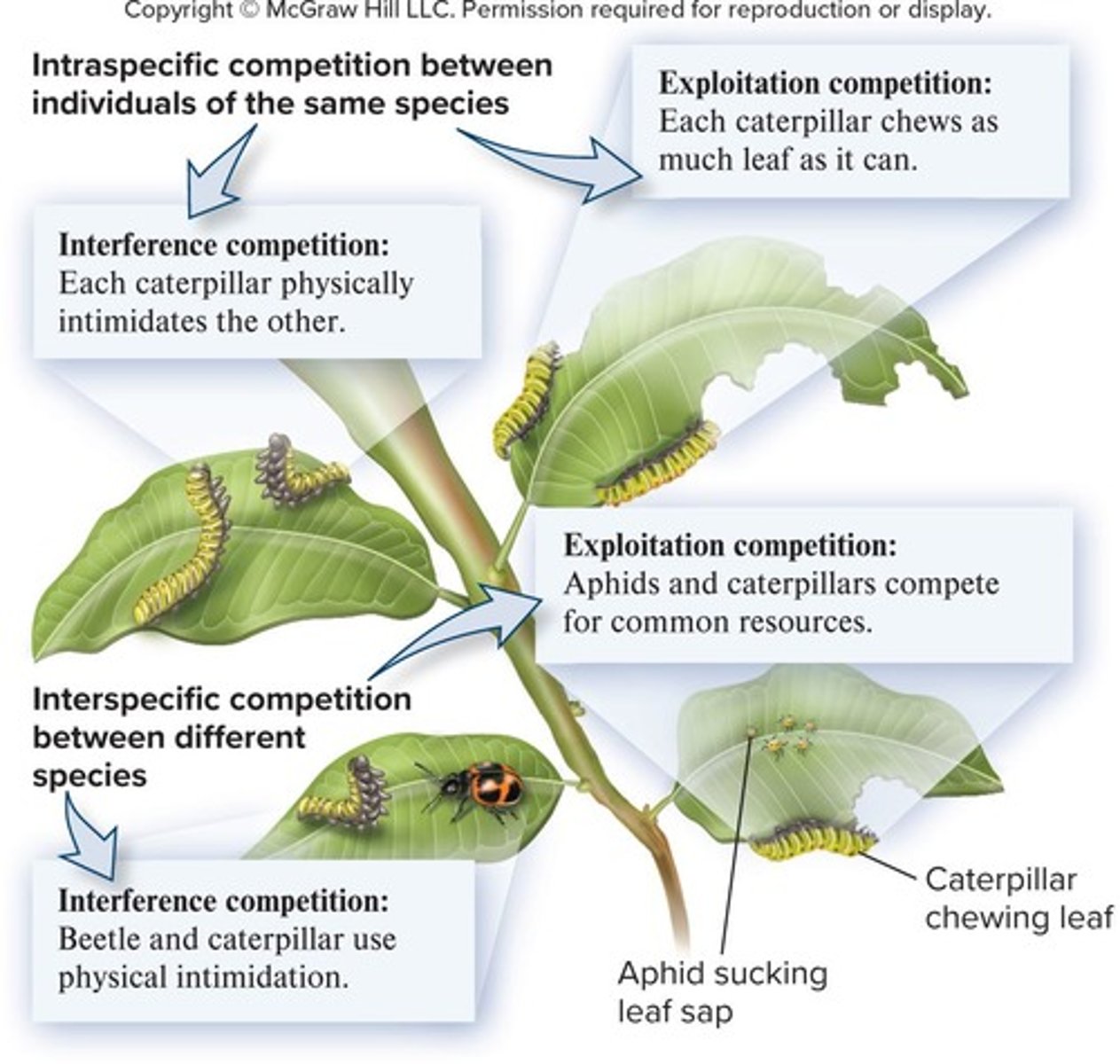
Intraspecific competition
Competition among individuals of the same species, for example, multiple bidders on eBay driving the cost of an item higher.
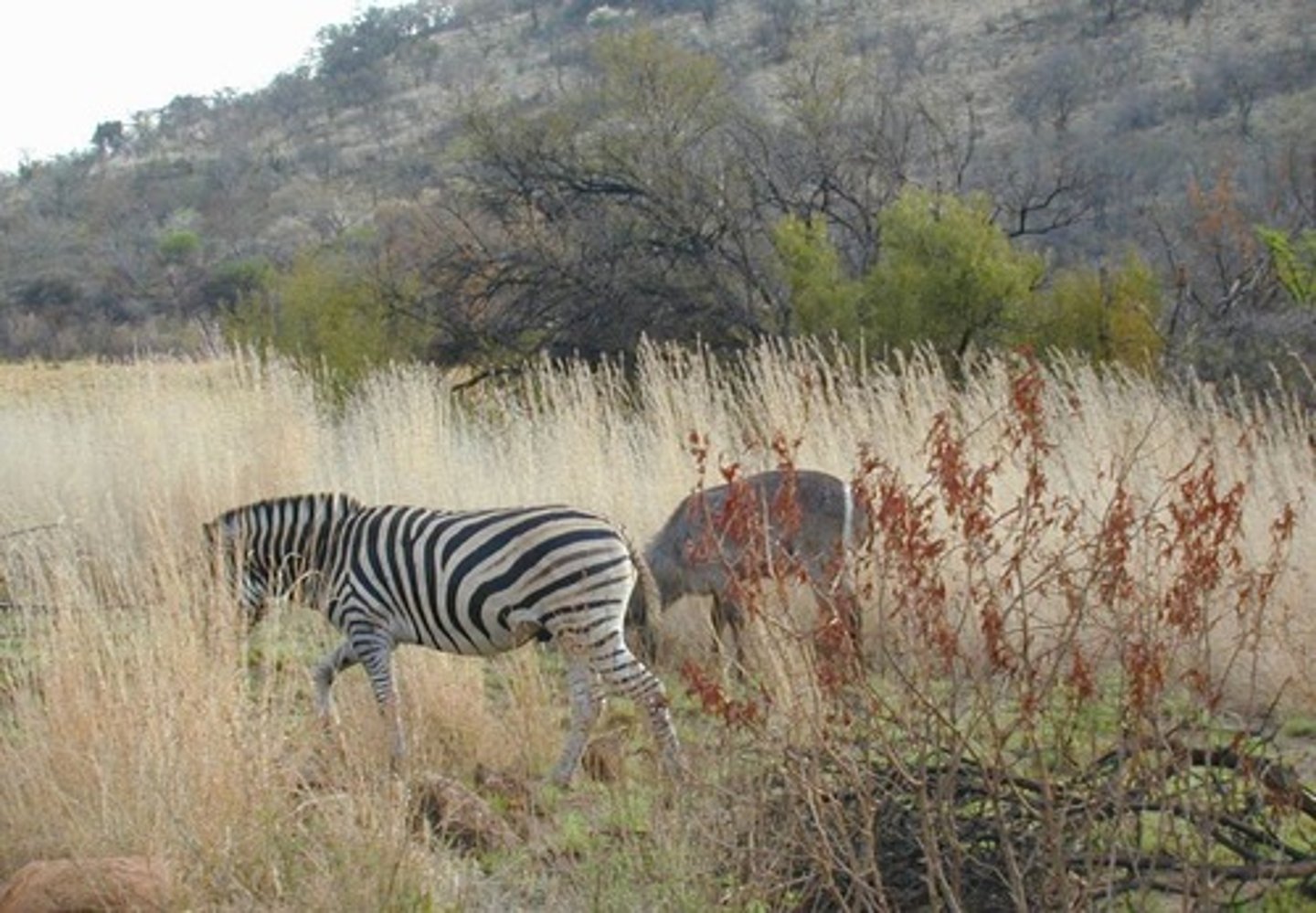
Interspecific competition
Competition between individuals of different species, for example, zebras and gazelles grazing on the same grassland.

Exploitation competition
Individuals compete indirectly through the consumption of a common limited resource, with each obtaining as much as it can.
Interference competition
Individuals interact directly with one another by physical force or intimidation.
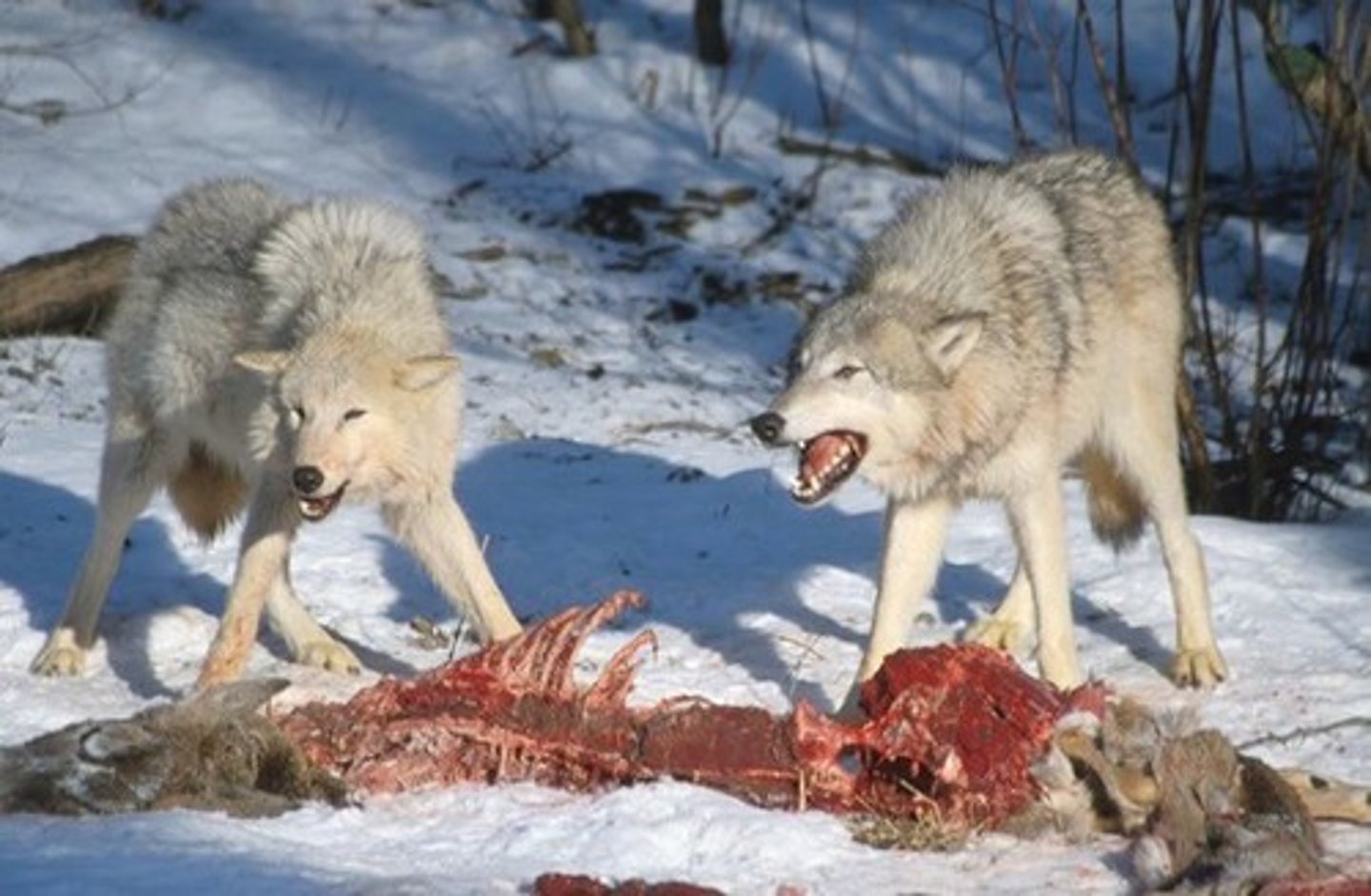
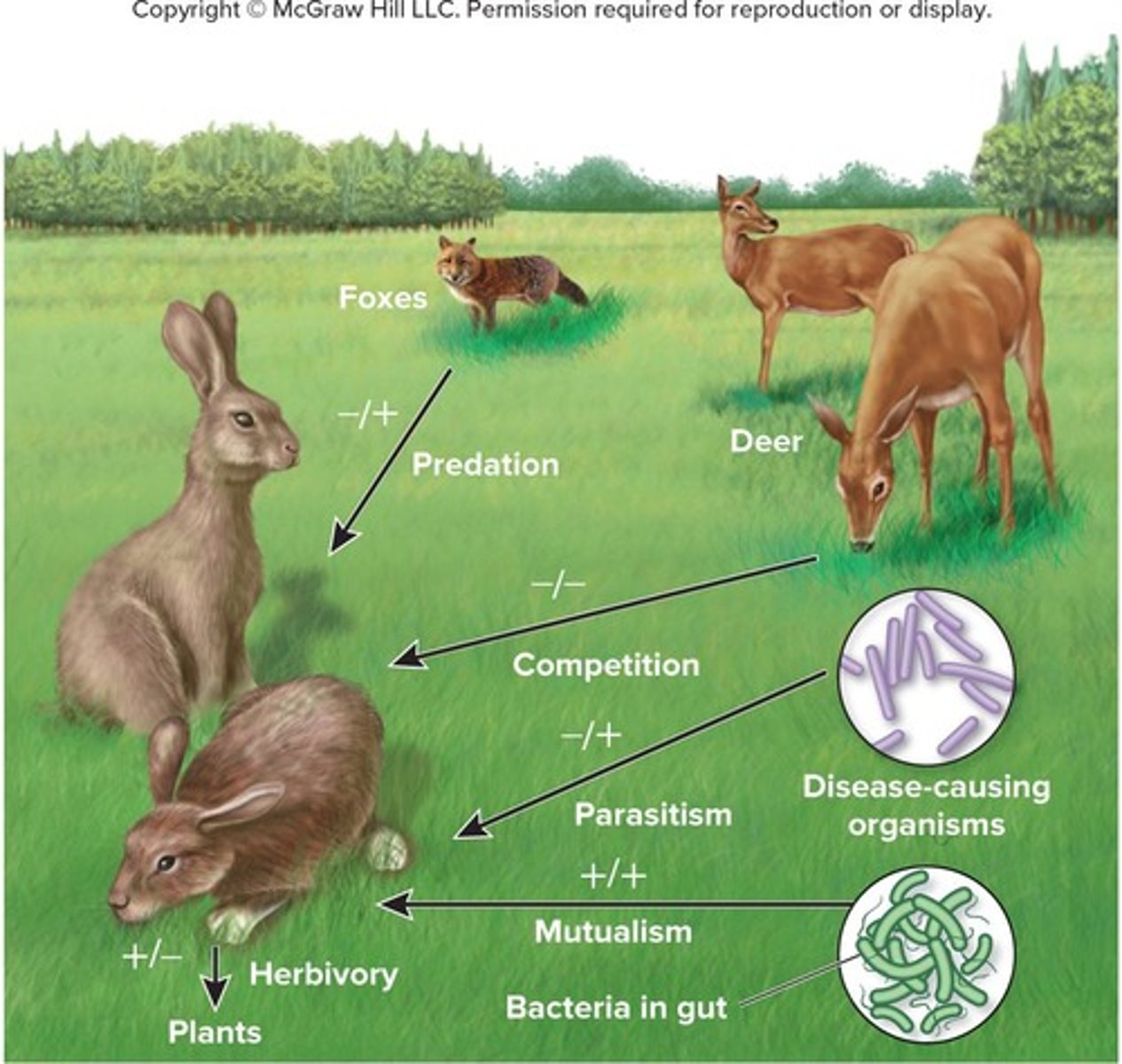
Predation
An interaction where the action of the predator results in the death of its prey.

Herbivory
An interaction where herbivores feed on plants, having a positive effect for herbivores and a negative effect for plants.
Parasitism
An interaction where one species benefits at the expense of another, often harming the host.

Mutualism
An interaction where both species benefit from the relationship.
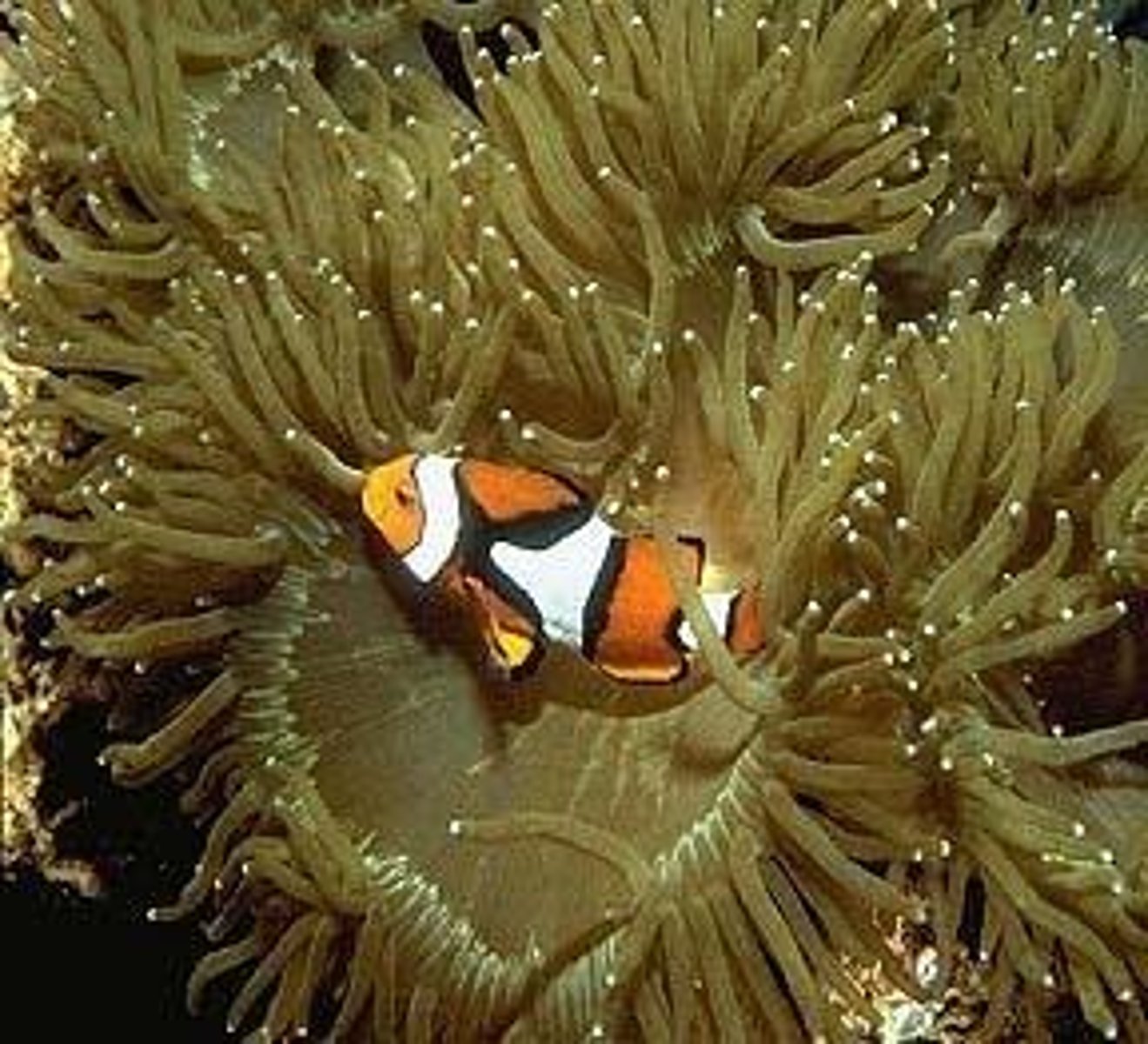

Commensalism
An interaction where one species benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed.

Amensalism
An interaction where one species is harmed while the other is unaffected.
Limiting factors
Factors that can limit population growth such as resources and space.
Survival of the fittest
A concept that describes the process of natural selection where individuals better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce.
Resources
Elements such as territory, prey, or food that are competed for by species.
Positive effect
An interaction that benefits one species.
Negative effect
An interaction that harms one species.
Neutral effect
An interaction that neither benefits nor harms either species.
Predation
Influences the fitness of both predators and prey.
Survival and Reproduction
Individuals must both feed and avoid being eaten to survive and reproduce.
Adaptation
Organisms have adapted to improve ability to survive and reproduce and will be passed on to its offspring.
Predator Traits
Predators exhibit traits such as sharp teeth, claws, and venom, that enhance their ability to catch food.
Prey Avoidance Strategies
Certain organisms have evolved strategies to avoid being the prey, including chemical defense, camouflage, displays of intimidation, mimicry, and armor and weaponry.
Mechanical Defenses
Plant examples include mechanical defenses such as thorns and spines, and various chemicals.
Herbivory
Herbivory is the consumption of plant material by animals (herbivores are animals that eat plants).
Herbivore Adaptations
To maximize nutrient intake, many herbivores have evolved adaptations that allow them to determine which plants contain fewer defensive compounds and more high-quality nutrients.
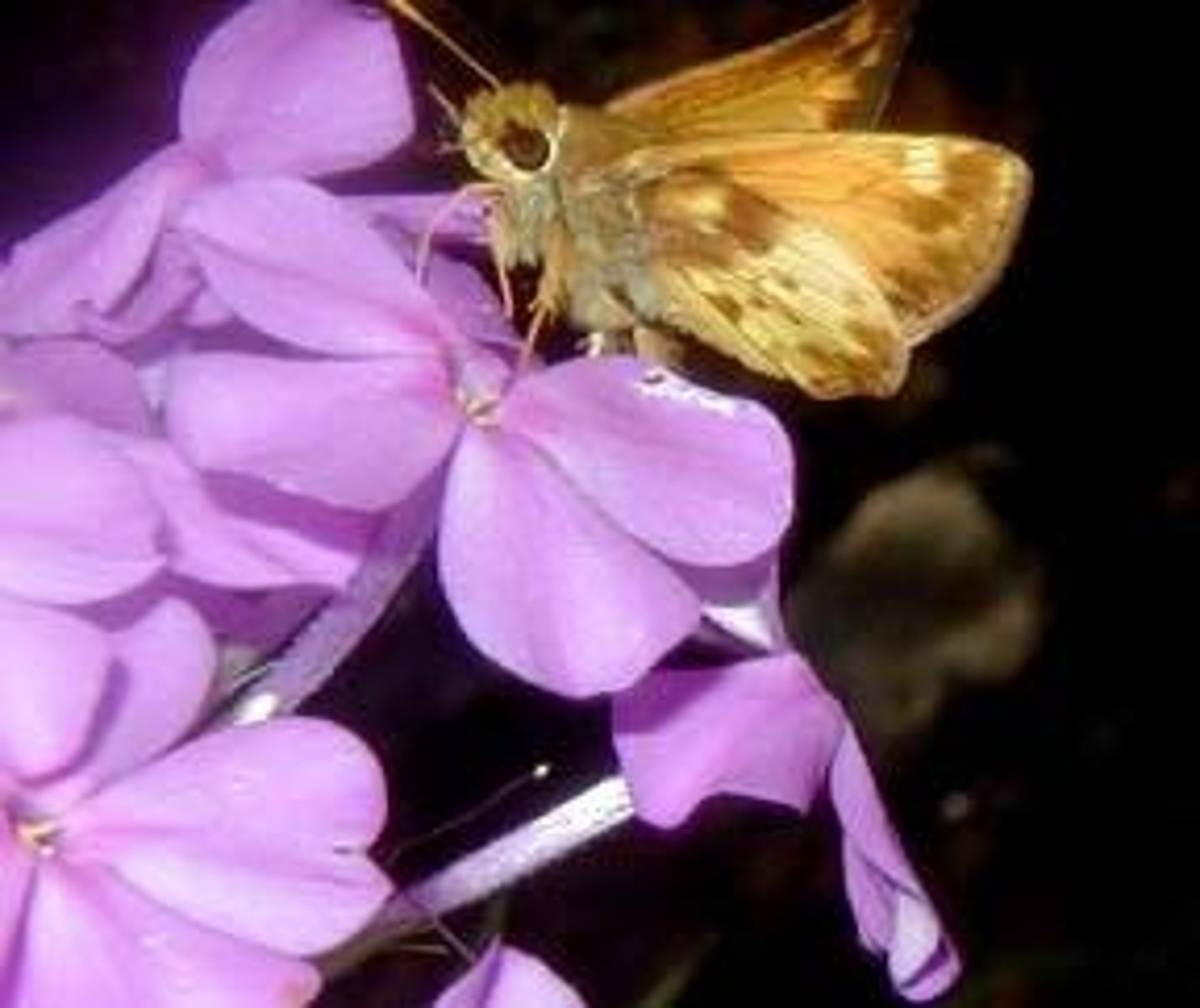
Chemical Sensors
Some insects, such as butterflies, have chemical sensors on their feet that allow them to taste the plant before they consume any part of it.
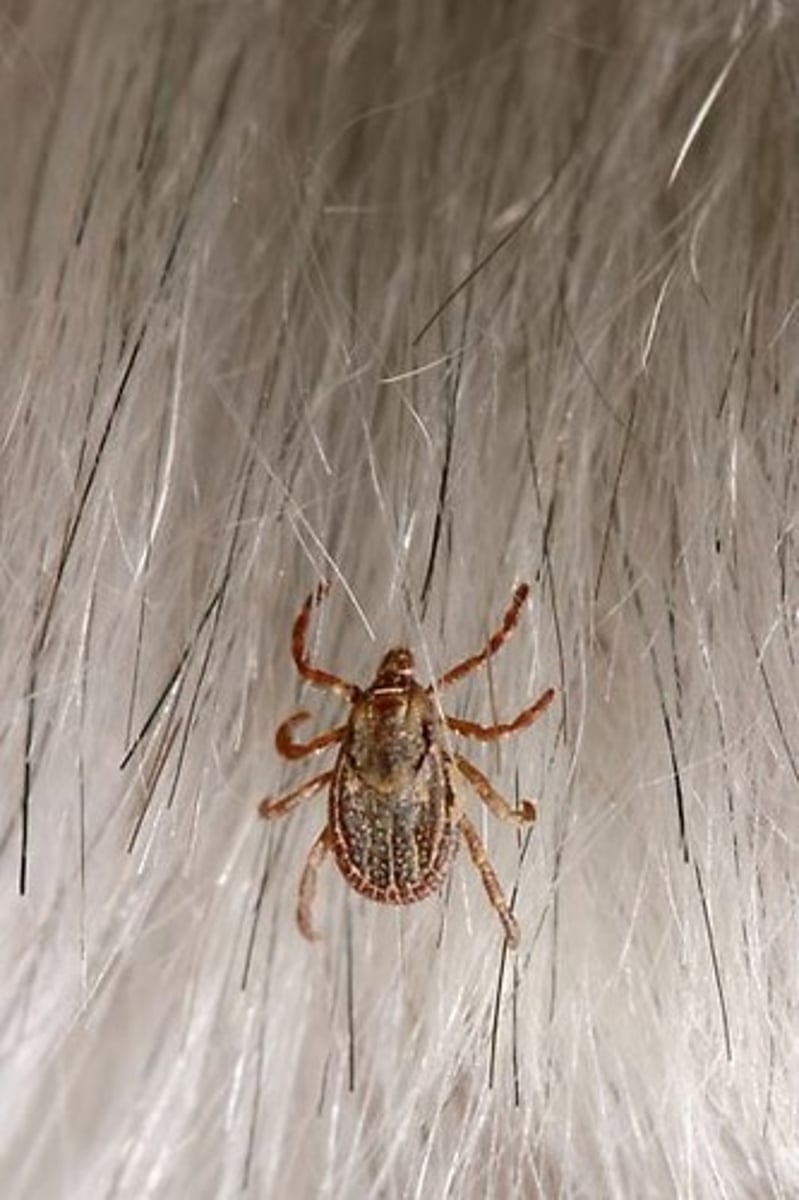
Parasitism
Involves an organism (called the parasite) that lives in, on, or with another organism (called the host) that directly or indirectly harms the host.
Parasite-Host Relationship
The parasite feeds off the host and benefits at the host's expense (host is harmed, but not lethal).
Duration of Parasitism
Many parasites inhabit their host for long periods of time, but do not normally kill it outright.
Examples of Parasitism
Example: a flea or tick on a dog.
Mutualism
Both species receive a benefit from the other.
Example of Mutualism
Example: bacteria in our intestines.
Commensalism
One species benefits and the other is unaffected (does not benefit nor harm).
Example of Commensalism
Example: barnacles on a whale.

Amensalism
One species is harmed and the other is unaffected (does not benefit nor harm).
Example of Amensalism
Example: humans causing animals to be harmed due to pollution, fires, etc., and elephants stepping on ants or leveling brush.