Blood plasma and plasma proteins
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What clotting factors are removed to make serum.
2,5,8
In serum formation blood is allowed to clot and then clot is retracted (TIF)
True
What leads to clot having high serotonin content.
Breakdown of platelets during clotting
Plasma protein concentration
6.4 to 8.3 g/ DL
What is the original classification of protein plasma. By whom was it done?
Howe (1922) it was based on precipitation of salts
What are the fractions of plasma proteins
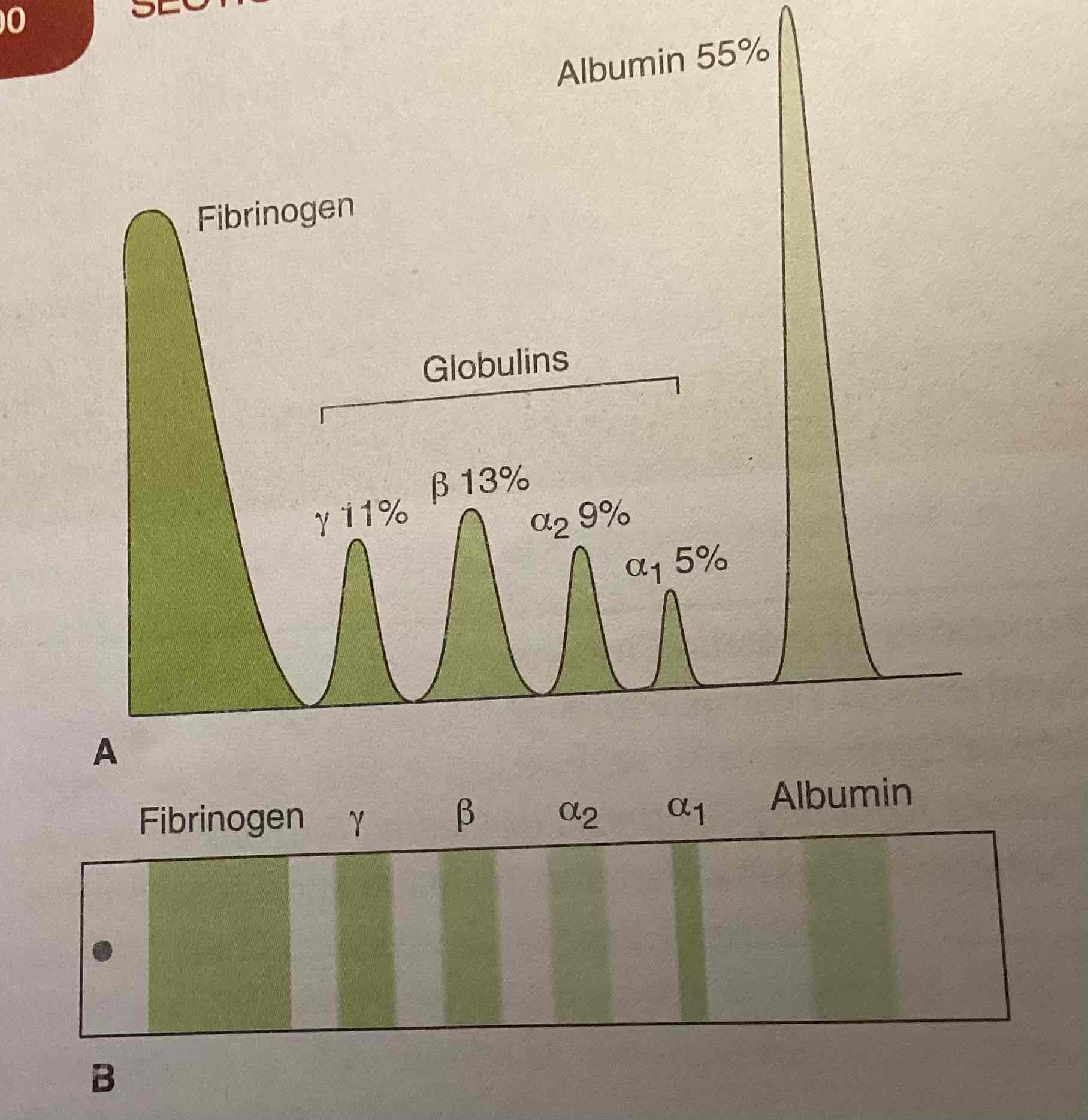
I. Albumin 2. Globulin (alpha 1, alpha2, beta, gamma 3 fibrinogen
Electrophoretic protein patterns (only to see)
Basis of paper electrophoresis proteins are identified
Molecular weight I shape of plasma protein
Fibrinogen has highest molecule or weight (500,000), the least is of albumin (69,000)

The plasma exert a ________ pressure of ____ mm Hg.
,
Oncotic, 25
What is isoelecthic point?
The ph value of the protein when it has achieved electric neutrality ie : positive and negative ion is same.
What is electrophoretic mobility?
The ability of a palein to act as an anion in alkaline solution and cation in acidic solution.
What method ultilises the property of proteins to be precipitated by various salts.
Method of separation of proteins
What solution is used to precipitate plasma protein fractions
Ammonium sulphate
Which protein is precipitated in full saturation
Albumin
Globulin is precipitated in what concentration? Condo are the further sections of globulin.
Half saturation. Englobin → 1/3 sat, rest → pseudogloubin
Fibrinogen precipitation is in what sat?
1/5
What makes protein molecules soluble in water?
Polar residues → NH 2 and COOH
What is the nature of proteins? ( acidic / amphoteric/ alkaline) and why.
Amphotericpresence of NH 2 and COOH
What mall plasma proteins excellent buffers?
Their amphoteric nature
Features of albumin. (4)
Abumin→69000, prealbumin→60,000 2. Plasma levels→ 48g/ DL 3. Synthesis occurs in liver 4 halflife is 10 days.
Globulin features (3)
Plasma levels → 2.3g/dl
Molecular weight → 90,000 to 150,000
Types → Alpha 1, alpha 2, beta 1, beta 2, gamma
Glycoproteins consist of?
Carbohydrate and proteins
Lipoproteins consist of?
Globulin and lipid
types of lipoprotein
High density, low density, very low density, chylomicron, transferrin, haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin, fetuin, immunoglobin, angiotensinogen, Haemagglutinins.
What are high density lipoproteins
Alpha lipoprotein, 50% protein and large amount of fat and cholesterol
What ore low density lipoproteins
Beta, large amountf glycosides
What are very low density lipoproteins
Beta, high amounts of triglycerides and cholesterol
What ore ihylomicions
% Triglycerides
Transferrin
90,000 molecular weight, alpha 2 beta protein, iron binding property useful for transport and storage, binds to two atoms of ferric. iron
Cerutoplasmin
Binds with copper, transport and storage
Ferris
Growth promoting protein in newborns
Haemagglutinins
Took against RBC antigen
Fibrinogen features
0.3 g / DL , 500,000, six nogreptide chain ( alpha 2, beta 2 gamma 2) joined by disulphide bonds., clotting factor
Prothrombin
40 mg / DL, 68,000, liven synthesis promoted by vitamin k