ap human geography: unit 5
1/32
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
mediterranean climate
humid winters, dry summers
heavy rain and unexpected high winds
hot or cold temperatures
many diverse soil types
types of agriculture: meditteranean agriculture
dry/arid climate
little precipitation
always hot, sunny
very little vegetation
type of agriculture: pastoral nomadism
tropical climate
generally high temperatures
wet/dry seasons
soil easily eroded because of rainfall
type of agriculture: shifting cultivation and plantation
mediterranean agriculture
olives, grapes, figs, almonds, walnuts, grasses/shrubs
pastoral nomadism
herding animals (cattle, reindeer, camels, etc) type of animal depends on climate
practiced in arid or semi-arid regions, Northern Africa, Mongolia, Central Asia, and Middle East
transhumance - moving herds to new places based on seasons
shifting cultivation
subsistent extensive farming
when soil loses fertility, farmers move to another field
a type of shifting cultivation is when farmers clear the land by burning vegetation (slash and burn agriculture)
leads to deforestation
practiced in southeast asia, central and south america, and africa
plantation agriculture
large commercial farming of one particular cash crop
takes place in LDCs where as produce is sold are located in MDCs
labor-intensive, but low labor cost
cotton, tobacco, tea, and coffee
market gardening
fruits and vegetables are grown near an urban market so local farmers can access
driven by perishability and demand for fresh items
intensive and utilizes green houses and fertilizers
mixed crop/livestock system
crops and livestock raised for profit
specific crops are fed to livestock for quality meat
mostly occurs in east NA and EUrope
ranching
raising of domesticated animals for the production of meat and other byproducts
uses large areas of land
practiced in western united states, south america, and australia
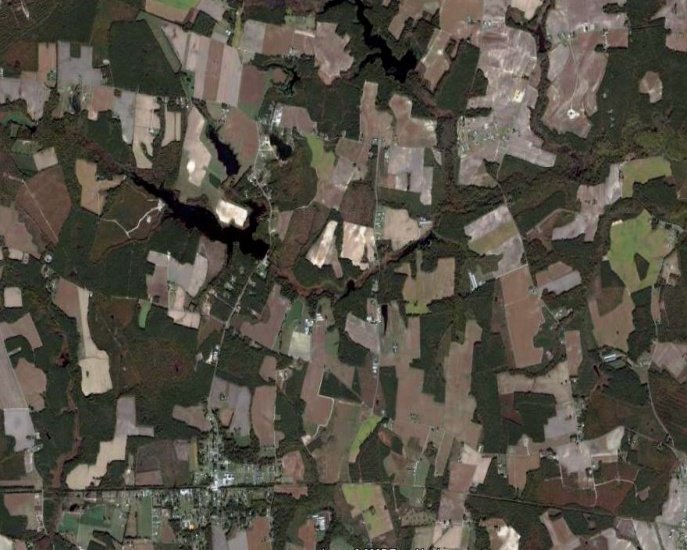

metes and bounds
irregular shapes that reflected the location of physical features and traditional patterns of use
metes for smaller areas, bounds for larger areas
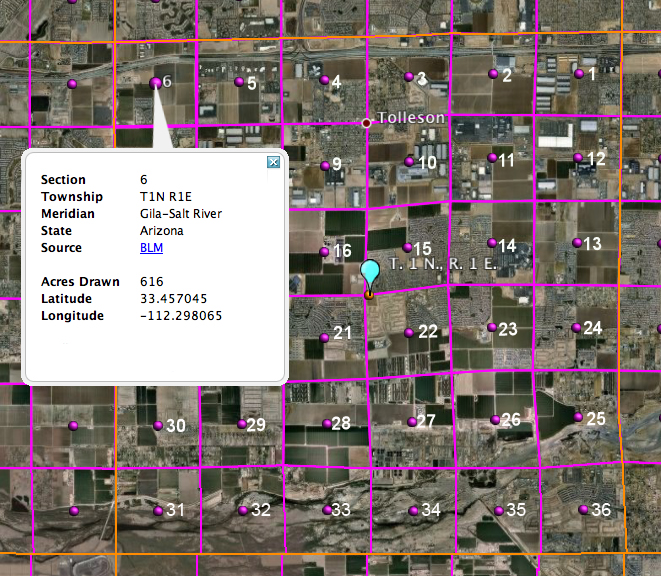
township and range system
rectangular land division
western usa was divided this way
range is the measurement of east to west
township is the measurement of distance north to south
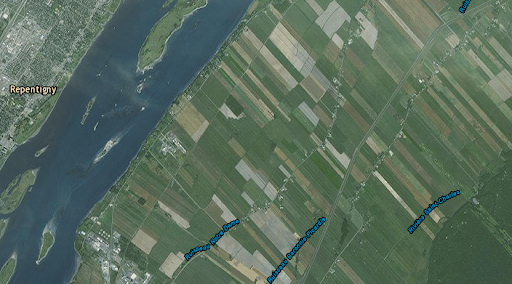
long-lot system
farms were long, thin sections of land
ran against a river so many farmers could benefit from the water
ex. louisiana and quebec
first neolithic agricultural revolution
origin of farming
marked by domestication of plants and animals
mostly subsistence farming
occurred in five hearths: southwest asia, east asia, south asia, africa, and the americas
fertile crescent
southwest asia
columbian exchange
global movement of plants and animals between afro-eurasia and the americas
europeans brought plants, animals, and diseases like bananas, cattle, pigs, goats, smallpox, malaria, measles
americas gave plants and animals like turkeys, potatoes, corn, maize. chocolate
second agricultural revolution
influenced by the advances of the industrial revolution
started in 1700s in Britain, and diffused globally to other MDCs
green revolution
goal: increase food production and reduce poverty and hunger especially in LDcs
began in mexico and eventialy spread to asia. andlatin america
third agricultural revolution
born out of science, research, and tech
continues today
expanded mechanization of farming, devloped new global agricultural susytems, and used scientific and informstion tyechnologies to further previous advances
bid-rent theory
closer land is to an urban center, the more valuable it is
economies of scale
increase in efficiency to lower the per-unit production cost, resulting in greater profits
commodity chain
a process used by corporations to gather resources, transform them into goods, and then transport them to consumers
ex. agriculture as a whole is a commodity chain and directly relates to agribusiness
vertical integration
ownership of other businesses involved in the steps of producing a particular good
carrying capacity
the number of people that USA farmers can support giving the available resources
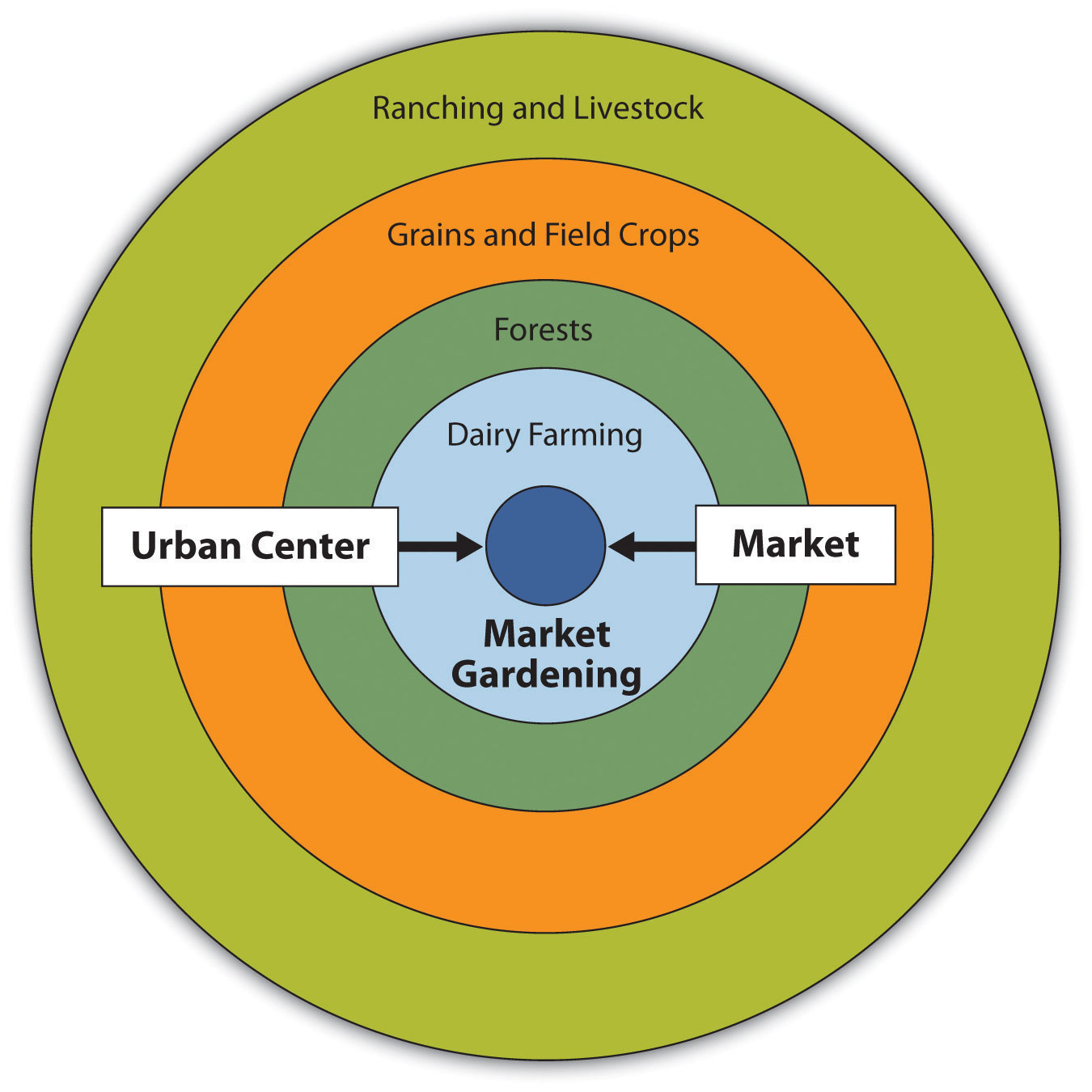
von thunen model
1st: dairyfarming/horticulture next to market because of perishability
2nd: forests/lumber because they are hard and heavy to carry to the market
3rd: crops like wheat and corn. did not perish as quickly. corn can be used to feed livestock in second n fourth ring
4th: grazing for livestock because of lower transportation costs, farmers can just walk them to the market
fair trade movement
promotes higher incomes for producers and more sustainable farming practices
subsidies
government providing financial support to farmers
desertification
fertile land becomes infertile, possibly caused by alteration of natural vegetation in arid areas
value-added crops
consumers are more wiling to pay for because of special qualities or because they are difficult to acquire
organically grown meats, free-range chicken. and eggs, rare plants
food insecurity
when lack to access to adequate food because of limited money or other resources
food desert
a neighborhood where residents have little to no access to healthy, affordable food
gender-specific obstacles
discriminatory practices that prevent female farmers from reaching their potential productivity
crop gap
resulted because of gender inequality, with a gap of 20 to 30 percent between male and female farmers