C341 Organic Chemistry Exam 3
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What are the reagents for Markovnikov hydrohalogenation of alkenes?
HX (X = Cl, Br, I)
What are the reagents for anti-Markovnikov hydrohalogenation of alkenes?
HX, ROOR (X = Cl, Br, I)
What are the reagents for acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes? Does it form carbocations?
dilute H2SO4, H2O, and yes
What is the regioselectivity of acid-catalyzed hydration?
markovnikov
What are the reagents for oxymercuration reduction? [2 steps]
(1.) Hg(OAc)2, H2O
(2). NaBH4
What is the regioselectivity of oxymercuration reduction? Do carbocations form?
markovnikov and no.
What is the stereoselectivity of Oxymerucation reduction? [syn or anti?]
anti-addition
What is the mechanism for oxymercuration reduction?
1. Nucleophilic attack
1b. Mercurnium OAc bridge formation
2. Nucleophilic attack
3. Loss of leaving group (HgOAc + leaves via free-radical replace with NaBH3)
What is the stereoselectivity of Hydroboration Oxidation? [syn or anti?]
syn-addition
What are the reagents for Hydroboration Oxidation?
(1.) BH3•L (L could be THF, Et2O, SMe, etc) (Borane Complex)
(2.) H2O2, MOH (M = alkali metal)
What is the regioselectivity of Hydroboration Oxidation? (mark or anti-mark?)
anti-Markovnikov
What is the mechanism for Hydroboration-Oxidation?
1. Proton Transfer
2. Nuc attack
3. Rearrangement
--REPEAT ABOVE 2 TIMES--
4. Nuc attack
5. Loss of Leaving Group
6. Proton Transfer
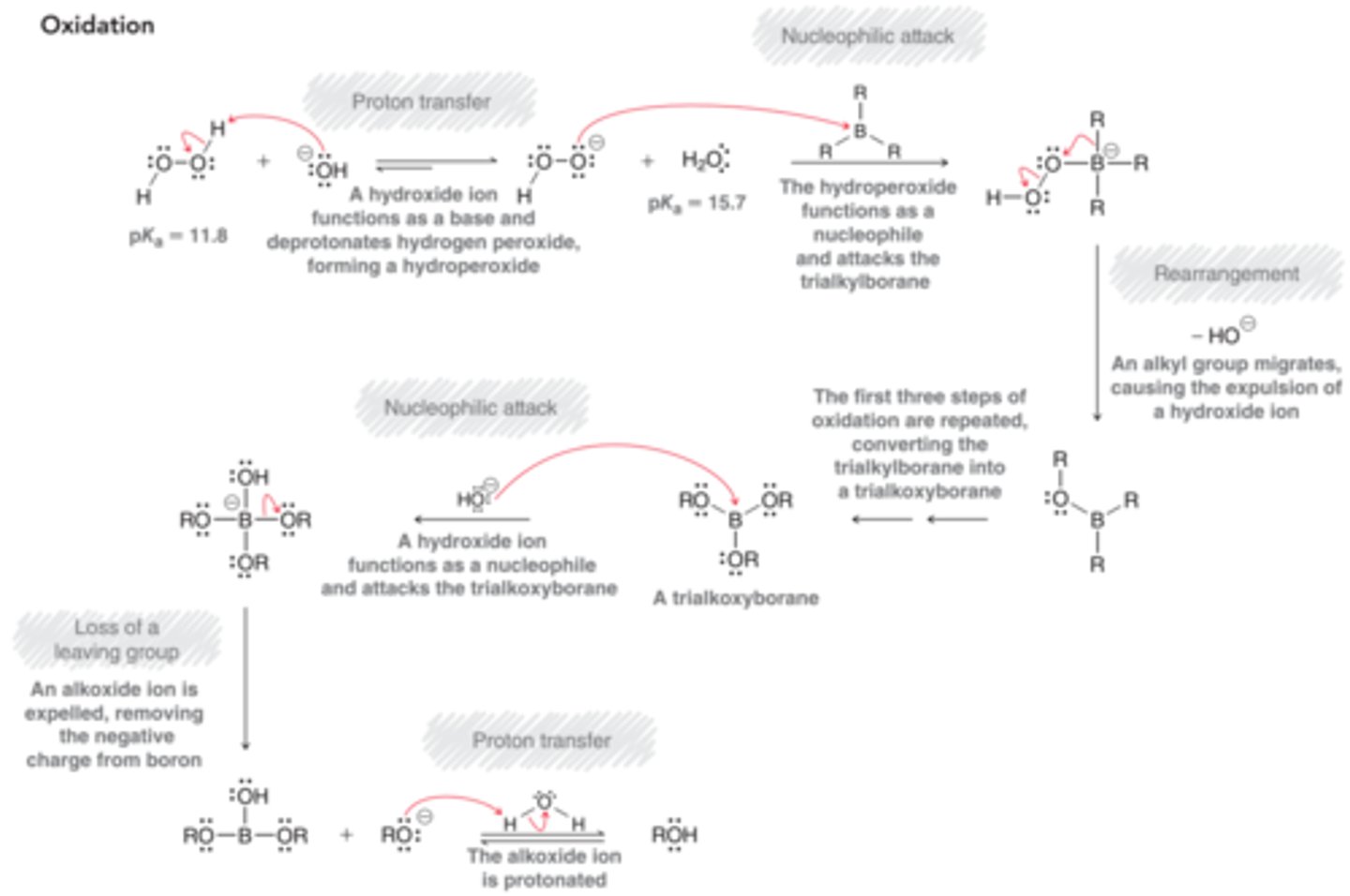
Reagents for Catalytic Hydrogenation?
H2, Metal Catalyst
(M or M/C where M = Pt, Pd, or Pt/C, Pd/C, Ni, Rh/C..etc) OR Wilkinson's Catalyst = (PPh)3RhCl
Stereoselectivity of Catalytic Hydrogenation? [syn or anti?]
syn-addition
What is the product for Cat. Hydrogenation for alkene and alkynes?
alkane
What is the product for alkene hydrohalogenation?
alkyl halide, (more subst. side bearing the halogen)
What is the product for peroxide induced alkene hydrohalogenation?
alkyl halide, (less subst. side bearing the halogen)
What is the product for acid-cat. hydration and oxymerucration reduction?
alcohol, with more subst. side bearing OH
What is the product for hydroboration oxidation of alkenes?
alcohol, with less subst. side bearing OH
Reagents for Halogenation?
X2 (X = Cl, Br ONLY)
Stereoselectivity for halogenation?[syn or anti?]
anti
What is the halogenation intermediate?
chloronium bridge or
bromonium bridge
what happens in the halogenation mechanism?
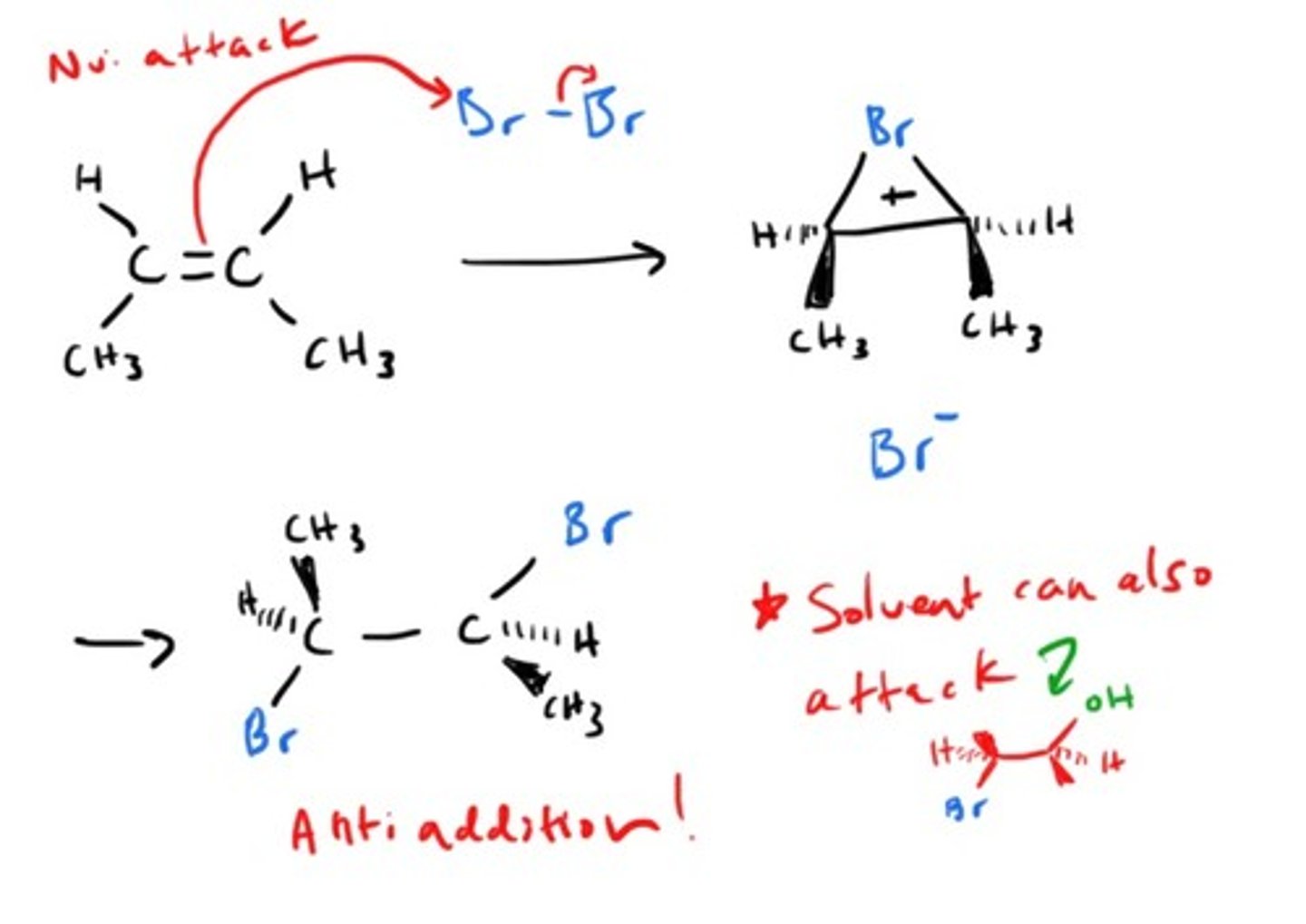
Products of halogenation starting with an trans-alkene? (meso or racemic?)
meso dihalide
Products of halogenation starting with a cis-alkene?(meso or racemic?)
racemic dihalide
Halohydrin formation reagents?
X2, H2O
In halohydrin formation, which side of the alkene gets the halogen and what side gets the alcohol?
more subst. OH
less subst. Br
mixture if tetra-substituted alkene
what is the stereoselectivity of a halohydrin formation? (syn or anti?)
anti-addition
What reagent causes an alkene to form an epoxide?
RCO3H
If four different groups are on an alkene, what is the stereospecificity of epoxide formation? (meso or racemic?)
Racemic
What are the reagents for anti-dihydroxylation?
(1.) RCO3H or mCPBA
(2.) Acidic-Conditions (H3O+)
Mechanism for anti-dihydroxylation?
In the first part of the process, a peroxy acid(RCO3H) reacts with the alkene to form an epoxide. The epoxide is then protonated(in this case by acid) to produce an intermediate that is very similar to a bromonium or mercurinium ion. This intermediate can then be attacked through back-side attack by water(SN2). In the final step, the oxonium ion is deprotonated to yield a trans diol. H2O is used instead of OH to deprotonate because we are considering this reaction under acidic conditions, so hydroxide ions are not present in sufficient quantity to participate in reaction
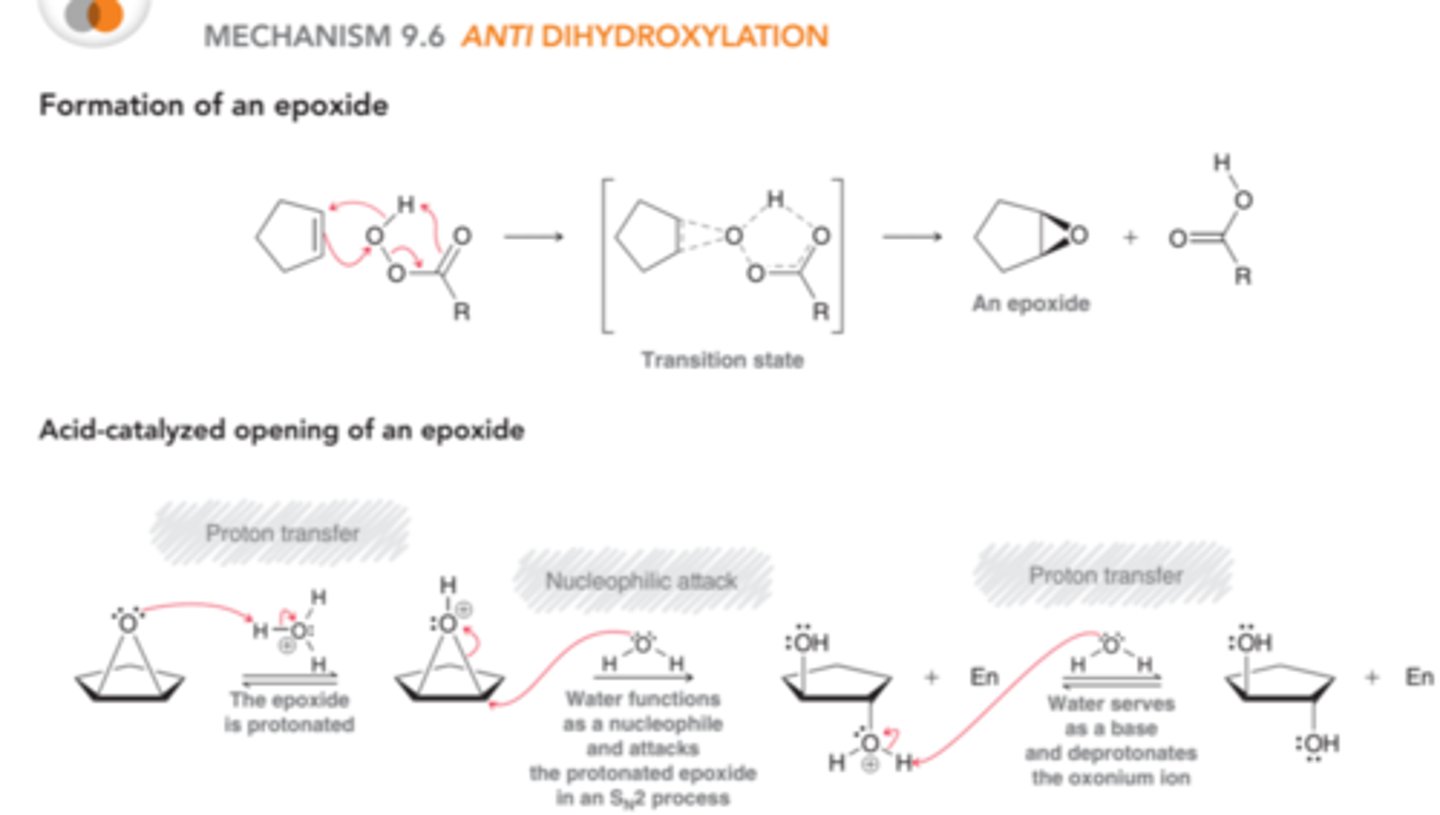
What is the product for anti-dihydroxylation?
trans-diol
What are the reagents for Syn-dihydroxylation? 4 possible answers
OsO4, NMO
OsO4, Tert-butyl peroxide
Na2SO3/H2O or NaHSO3/H2O
KMnO4, cold, NaOH, H2O
What is the product for Syn-dihydroxylation?
cis-diol
What are the reagents for Oxidative Cleavage for alkenes and alkynes?
(1.) O3
(2.) DMS or some other Mild Reducing agents such as DCM, H2O/Zn
What is the mechanism for Ozonolysis? [HARD]
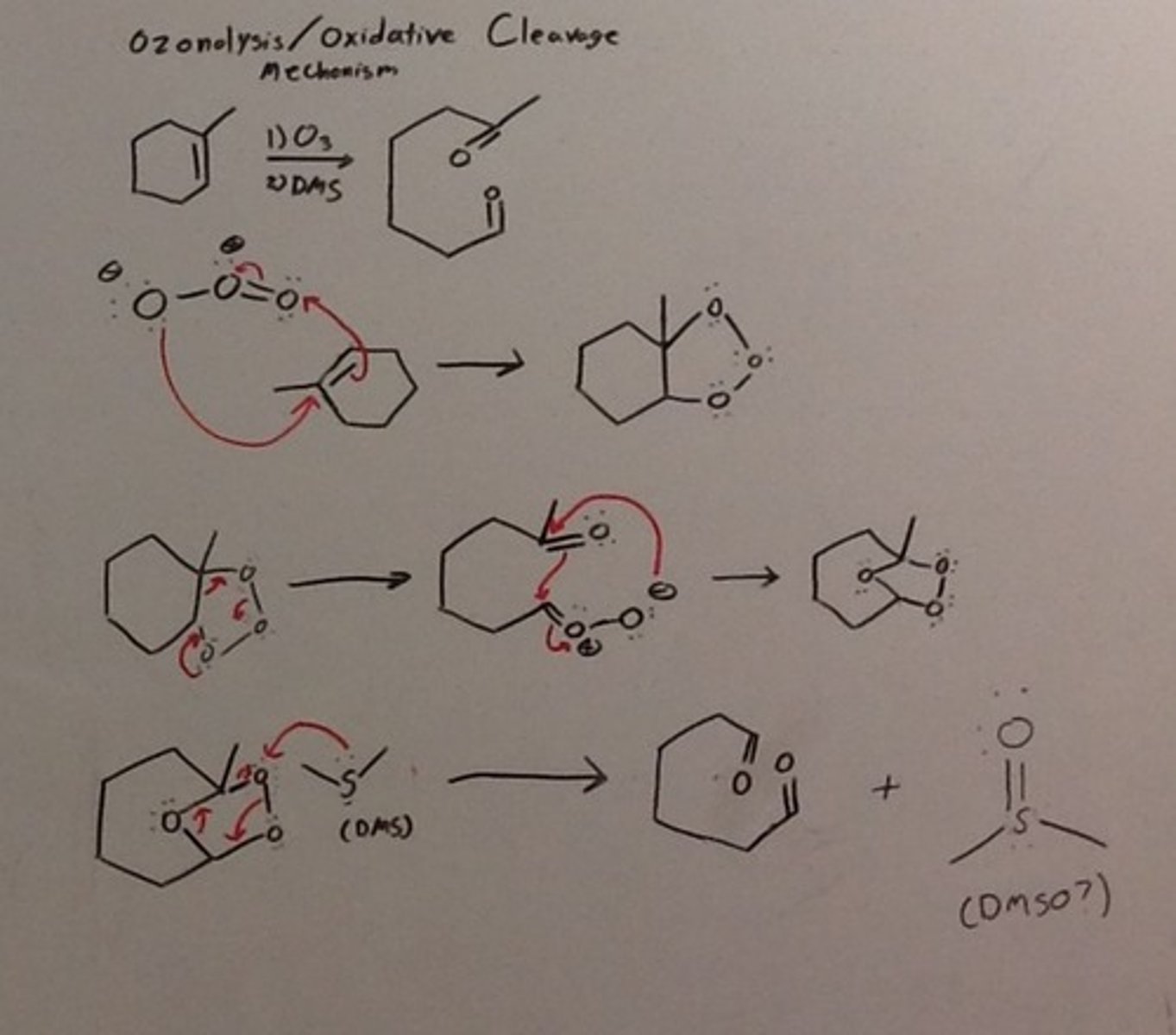
What are the reagents for alkyne hydrohalogenation to an alkene halide?
1 eq. HX where X = Cl or Br
What is a geminal dihalide?
one carbon atom bears two halogens
What is a vicinal dihalide?
a compound bearing the halogens on adjacent carbons
What bases can deprotonate alkynes?
conjugate bases of pKa > 25 compounds:
M-NH2
M-H
ButylLithium
etc.
What are the reagents to transform an alkyne to a cis-alkene?
(1.) H2
(2.) Lindlars Catalyst, Poisoned Cat., P-2 (Ni2B Complex)
What are the reagents to transform an alkyne to a trans-alkene?
Na, NH3 (l)
What is the mechanism for dissolving metal reduction?
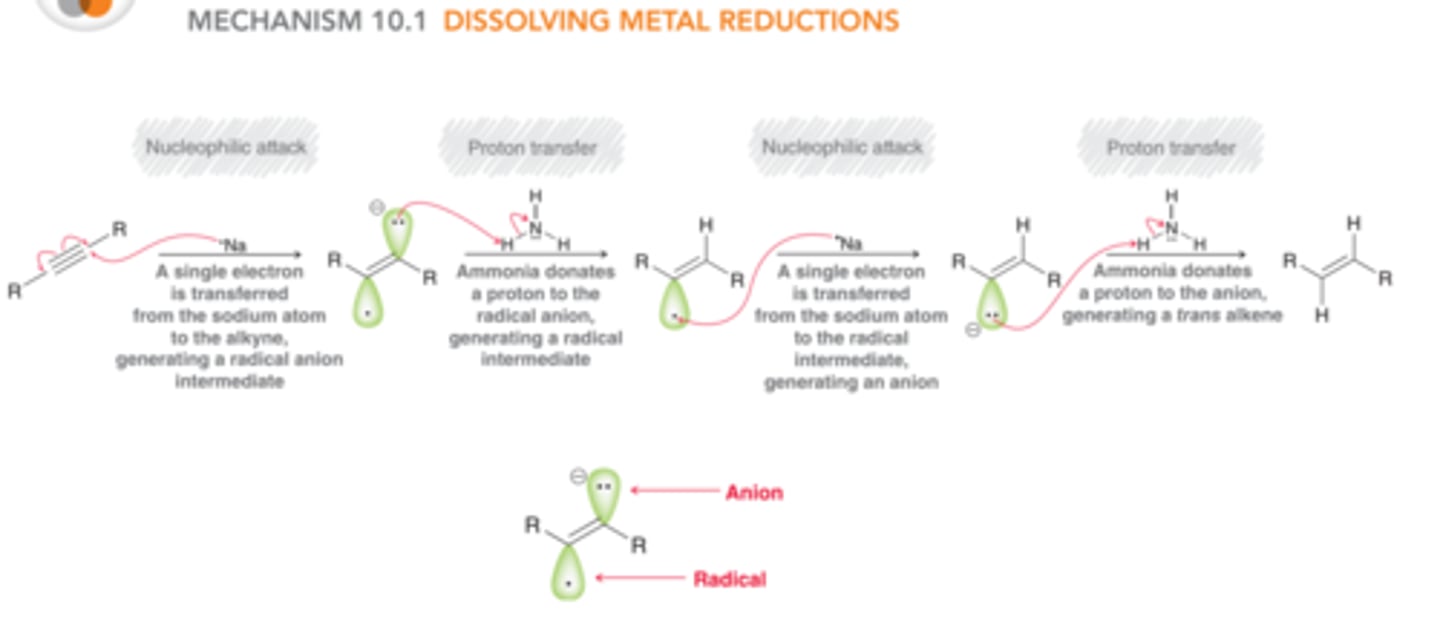
What are the reagents to transform an alkyne to a alkyl geminal dihalide?
xs. HX
What is the mechanism for hydrohalogenation of alkynes?
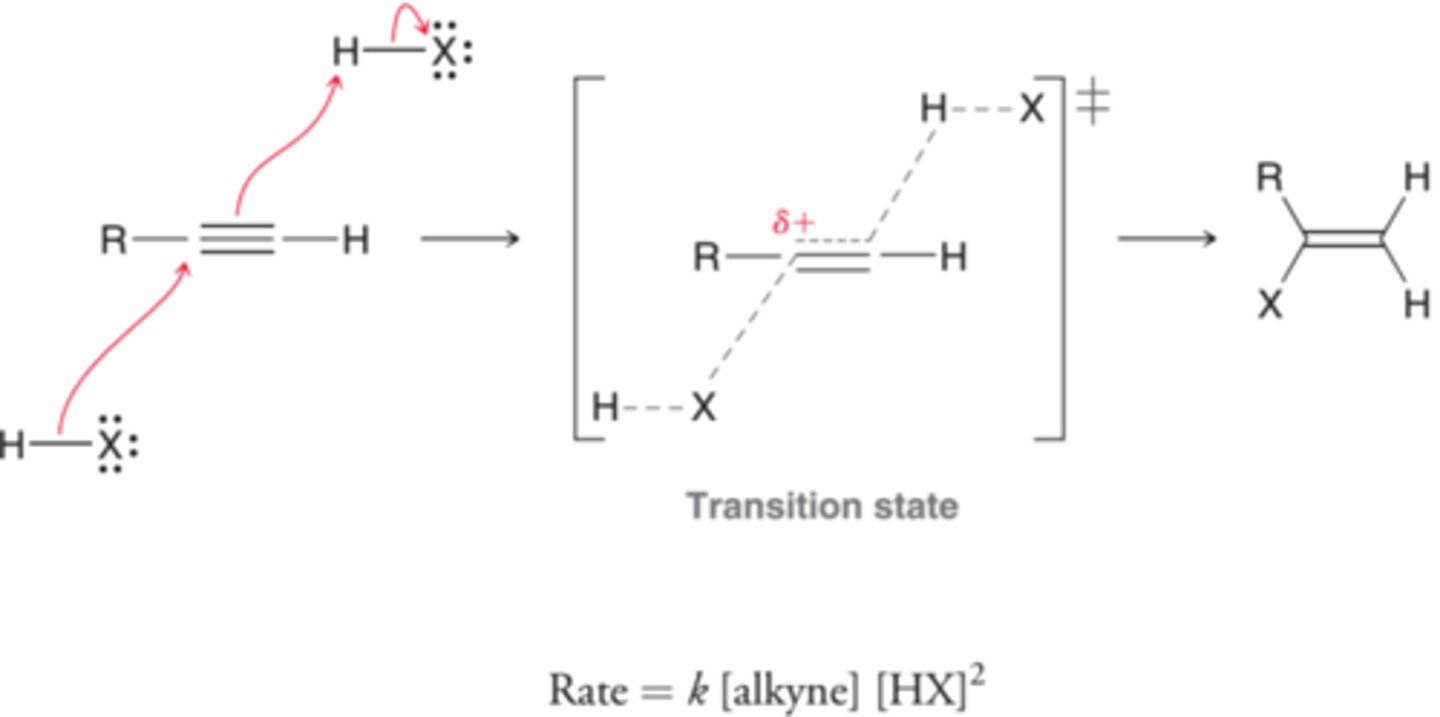
What are products for anti-mark. addition of HBr and ROOR of alkynes?
mixture of E/Z isomer alkenes
What reagents are used to transform a geminal dihalide to an alkyne?
(1.) xs NaNH2/NH3
(2.) H2O
What reagents are used in the hydration of alkynes?
H2SO4, H2O, HgSO4
What product is formed in the hydration of alkynes?
Ketone
What is the mechanism for Hydration of Alkynes?
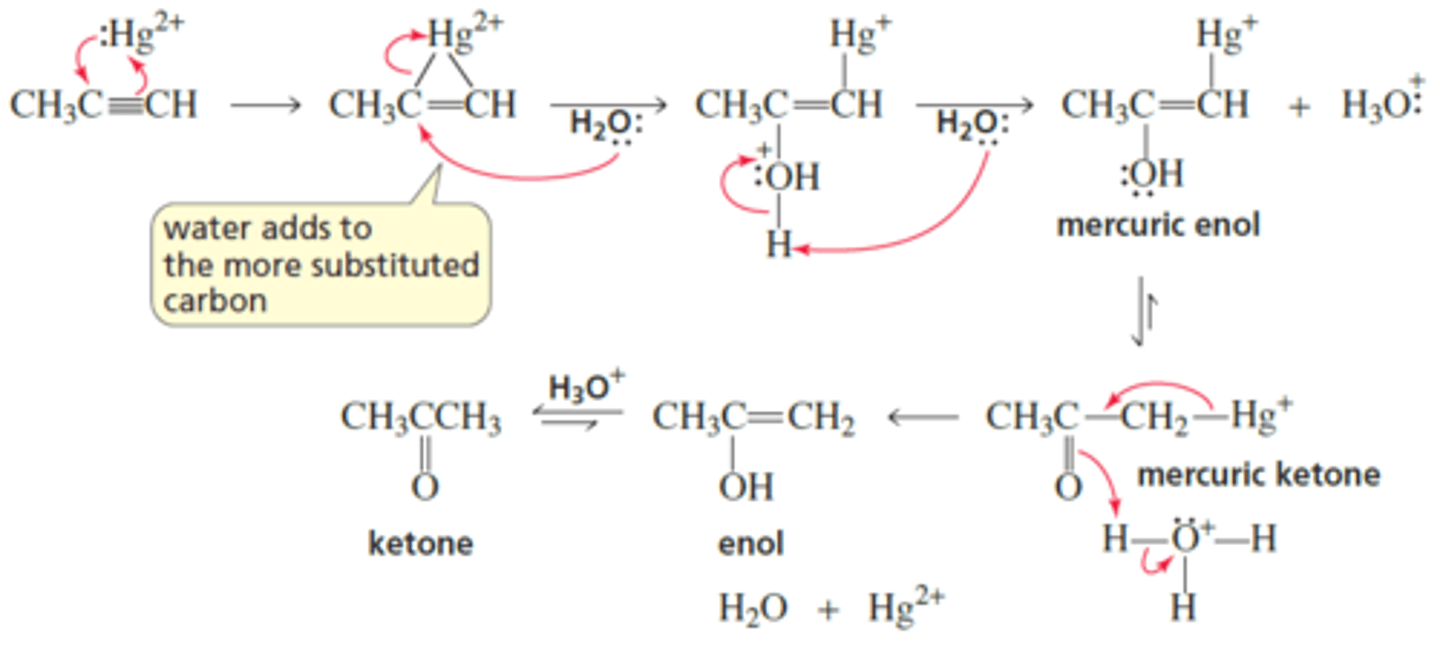
What are the preferred reagents in the anti-markovnikov addition of alkynes?
(1) R2BH (R = BULKY COMPLEX)
ex: 9-BBN or Disiamylborane
(2) H2O2, NaOH
What is the product for the hydroboration oxidation of a terminal alkyne?
aldehyde
What are the reagents for the halogenation of alkynes?
X2, CCl4
X = Cl, Br
What are the products of 1 eq. Halogenation of Alkynes?
Mixture of trans alkene halide, or cis alkene halide
What is the product of xs. Halogenation of Alkynes?
tetra halogenated alkyl halide
What are the products for internal alkynes in ozonolysis?
2 carboxy acids
What are the products for terminal alkynes in ozonolysis?
1 carboxy acid, CO2 (g)
How do you add carbon chains to alkynes?
1) react with NaNH2
2) react with alkyl halide
What is the trend in radical stability?
benzylic > allylic > 3 > 2 > 1 > CH3
What are the three steps in radical mechanisms?
Initiation, Propagation, Termination
What are common radical initiators? (THINK WEAK BOND)
Dihalides, alkyl peroxides, acyl peroxides
What are the only useful halogens in free radical reactions?
Chlorine, Bromine.
What conditions cause free radical reactions?
heat, light and radical initiators
What are the reagents in allylic halogenation?
NBS, heat and light
or Br2 heat and light (creates by-products)
What is the HBr and ROOR mechanism? [FREE RADICAL]
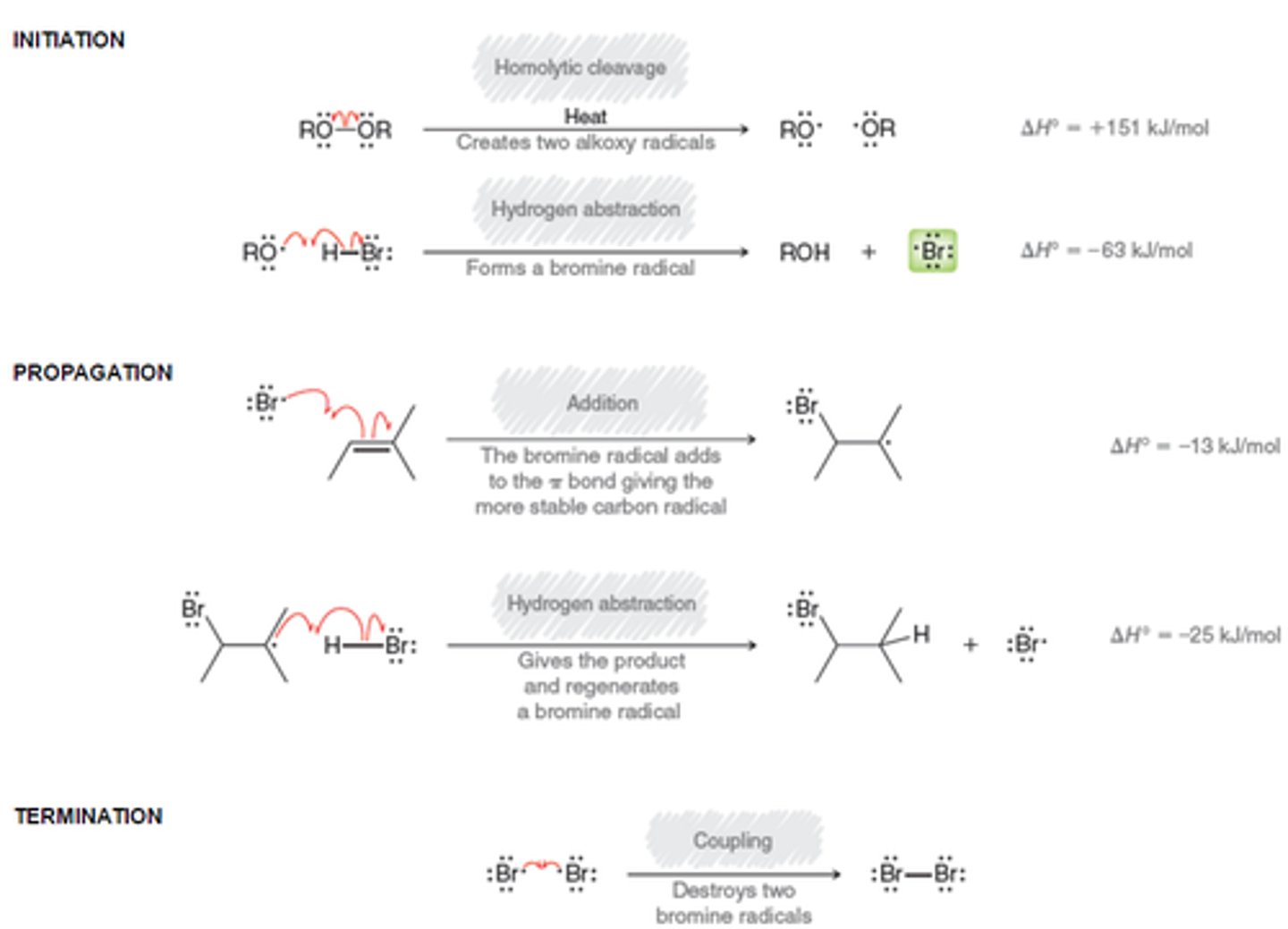
Concepts of Green Chemistry?
1. prevent waste
2. use less hazardous substances
3. use safer solvents
4. maximize atom economy.
5. use catalysts rather than stoichiometric reagents
6. energy efficiency
7. renewable feedstocks
What two questions do you ask to help you retro-synthetically?
1. is the carbon skeleton changing?
2. are functional groups altered?