Cardiovascular System: Heart Anatomy, Function, and Clinical Connections
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
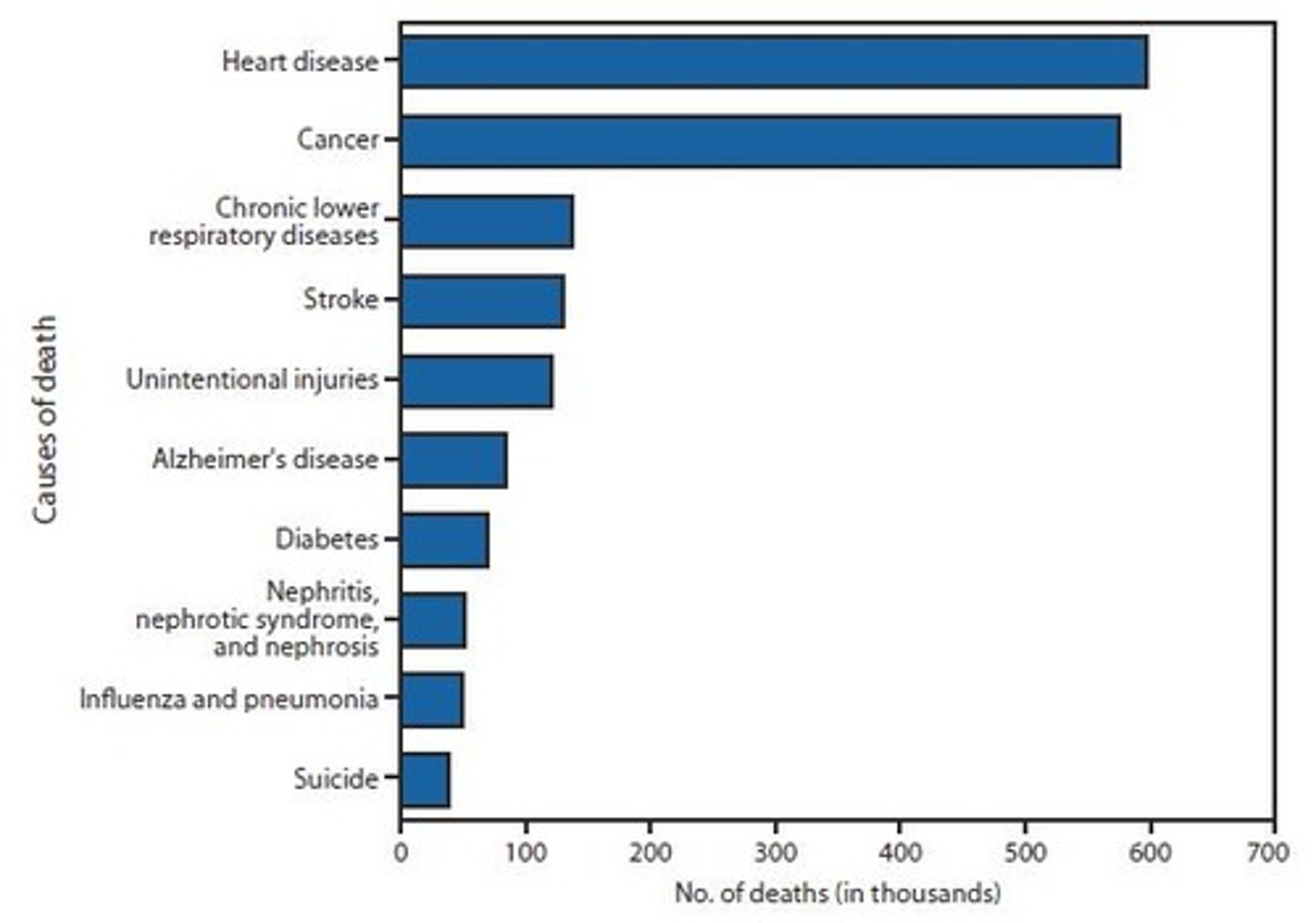
What is the #1 cause of death worldwide?
Heart disease
What is 'Holiday Heart Syndrome'?
Arrhythmias caused by binge drinking during the holidays.
What are common cardiac conditions encountered by nurses?
Myocardial infarction (MI), Congestive heart failure (CHF), Arrhythmias, Valve disorders.
What does the term 'cardiovascular' refer to?
Cardio = heart, vascular = vessels.
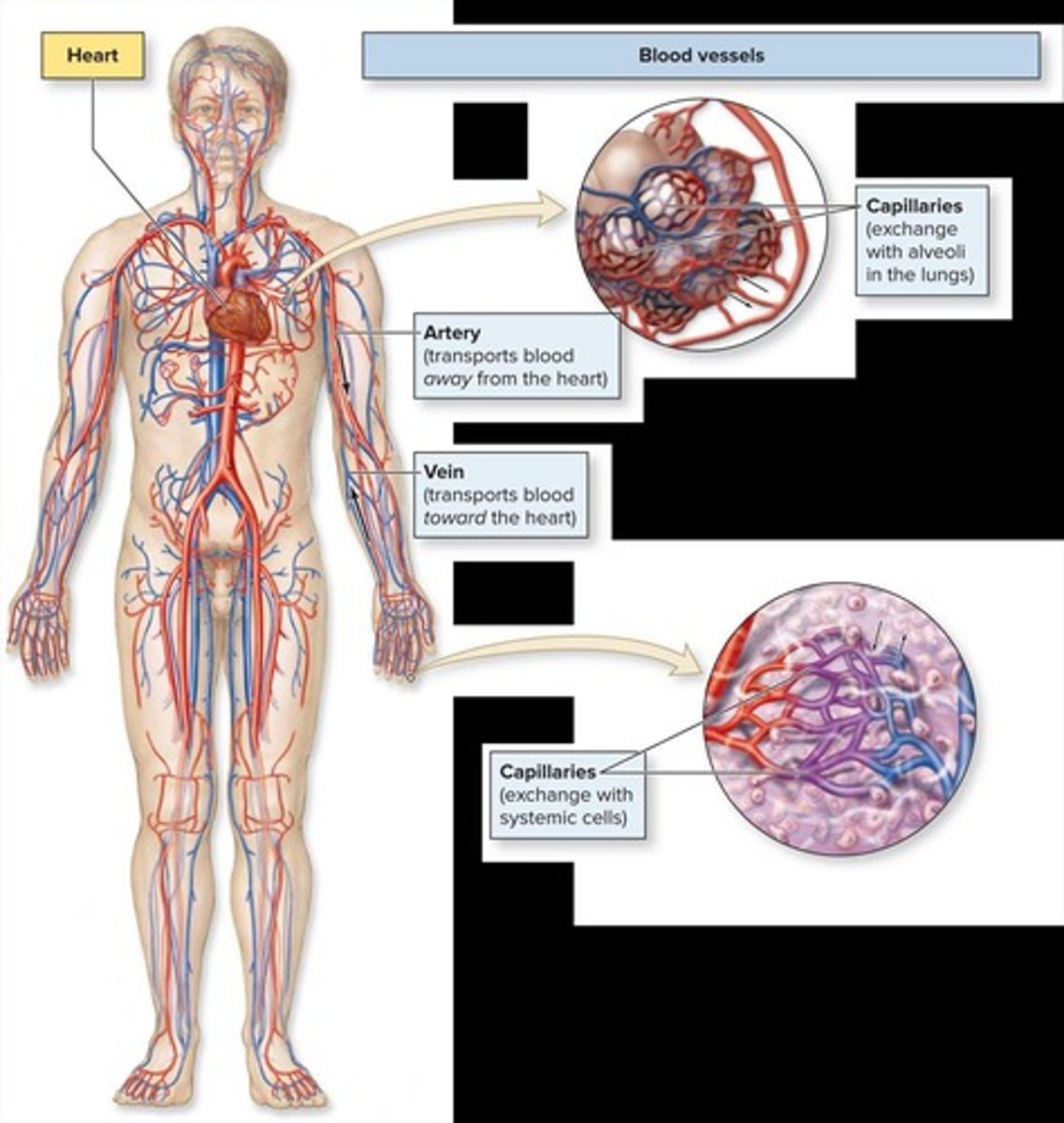
What are the general functions of the cardiovascular system?
Deliver O₂ & nutrients, remove CO₂ & waste, distribute hormones & immune cells, maintain blood pressure & perfusion.
What is perfusion?
Blood flow per tissue mass (mL/min/g).
What can cause failure to perfuse?
Pump failure, vessel blockage, low pressure.
What are the three types of blood vessels?
Arteries, veins, capillaries.
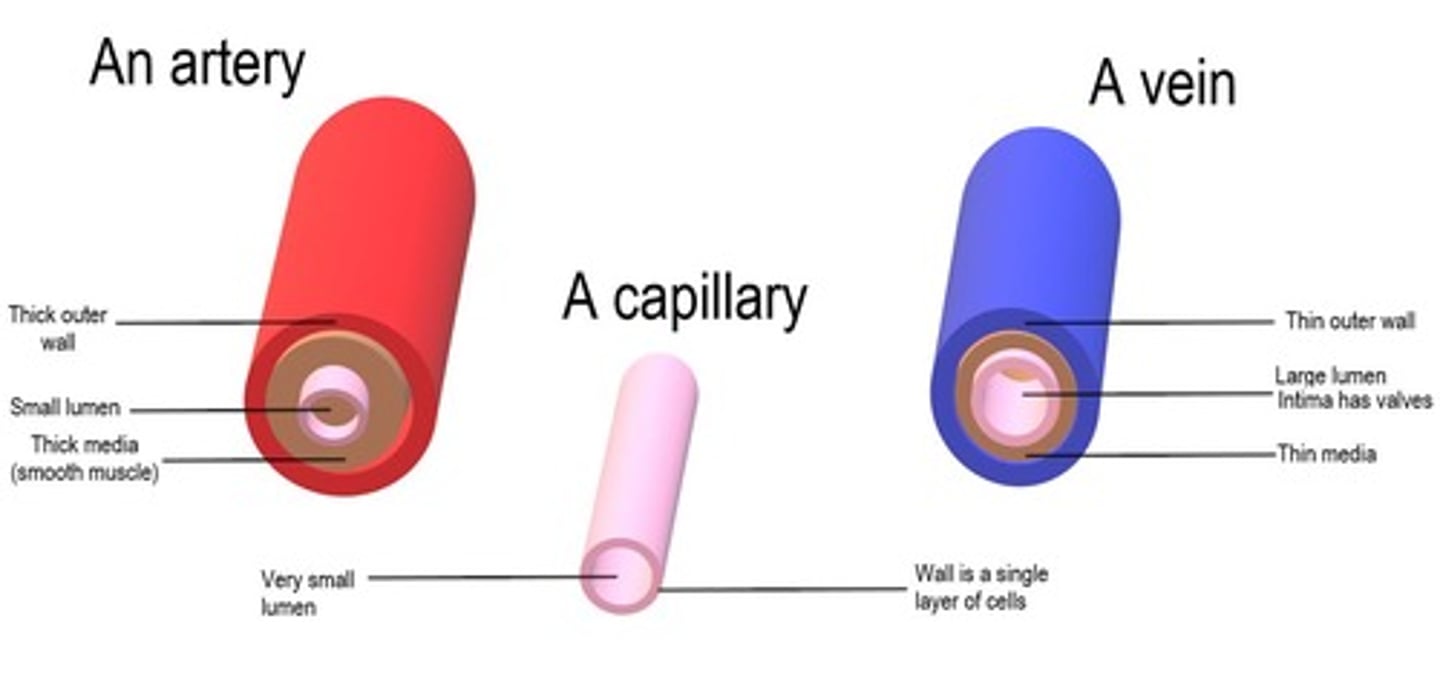
What is the function of arteries?
Carry blood away from the heart.
What is the function of veins?
Carry blood toward the heart.
What is the role of capillaries?
Site of O₂/CO₂ and nutrient/waste exchange.
What are the four chambers of the heart?
Right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle.
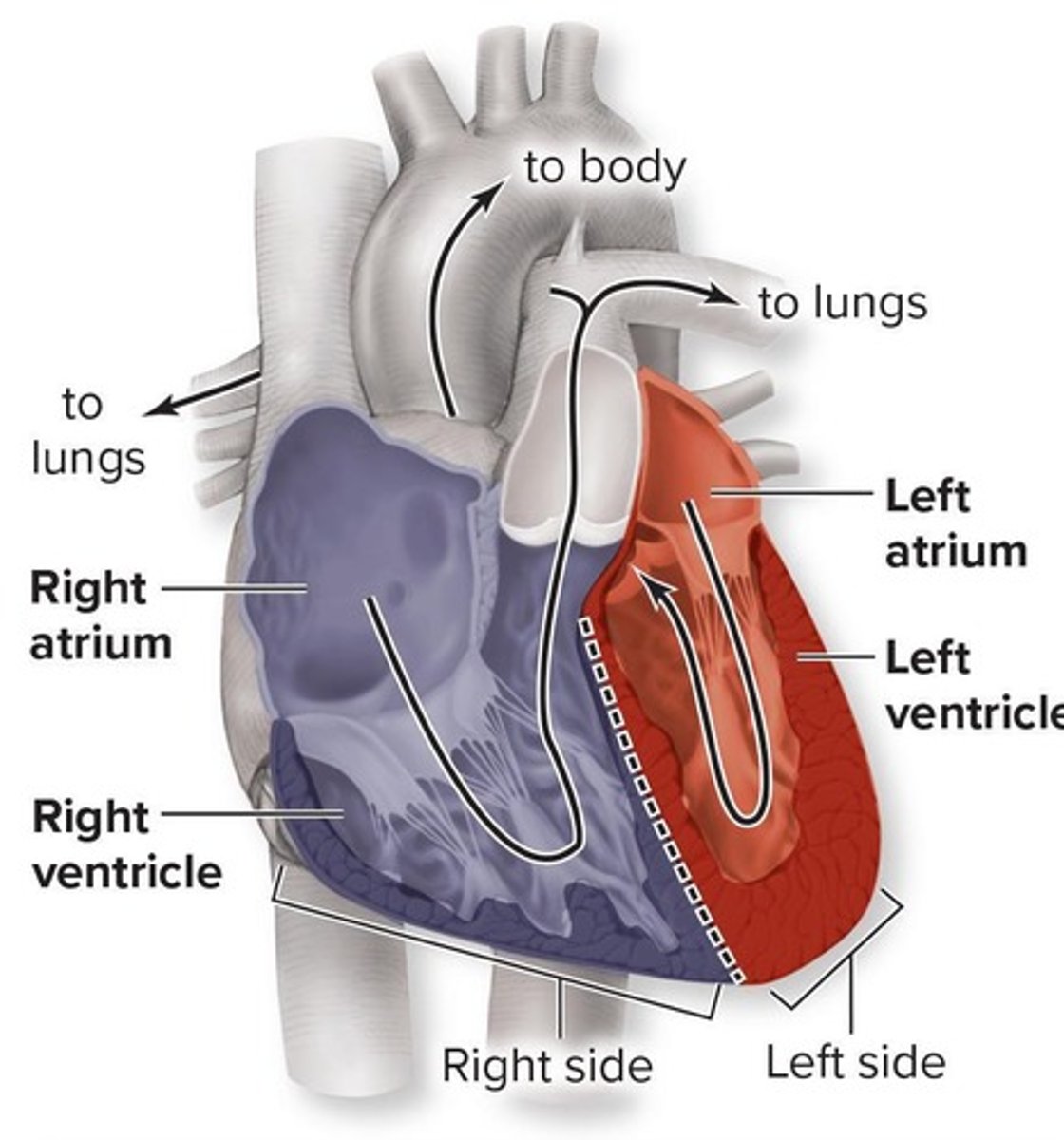
What is the function of the right atrium?
Receives deoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cava.
What is the function of the left ventricle?
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta.
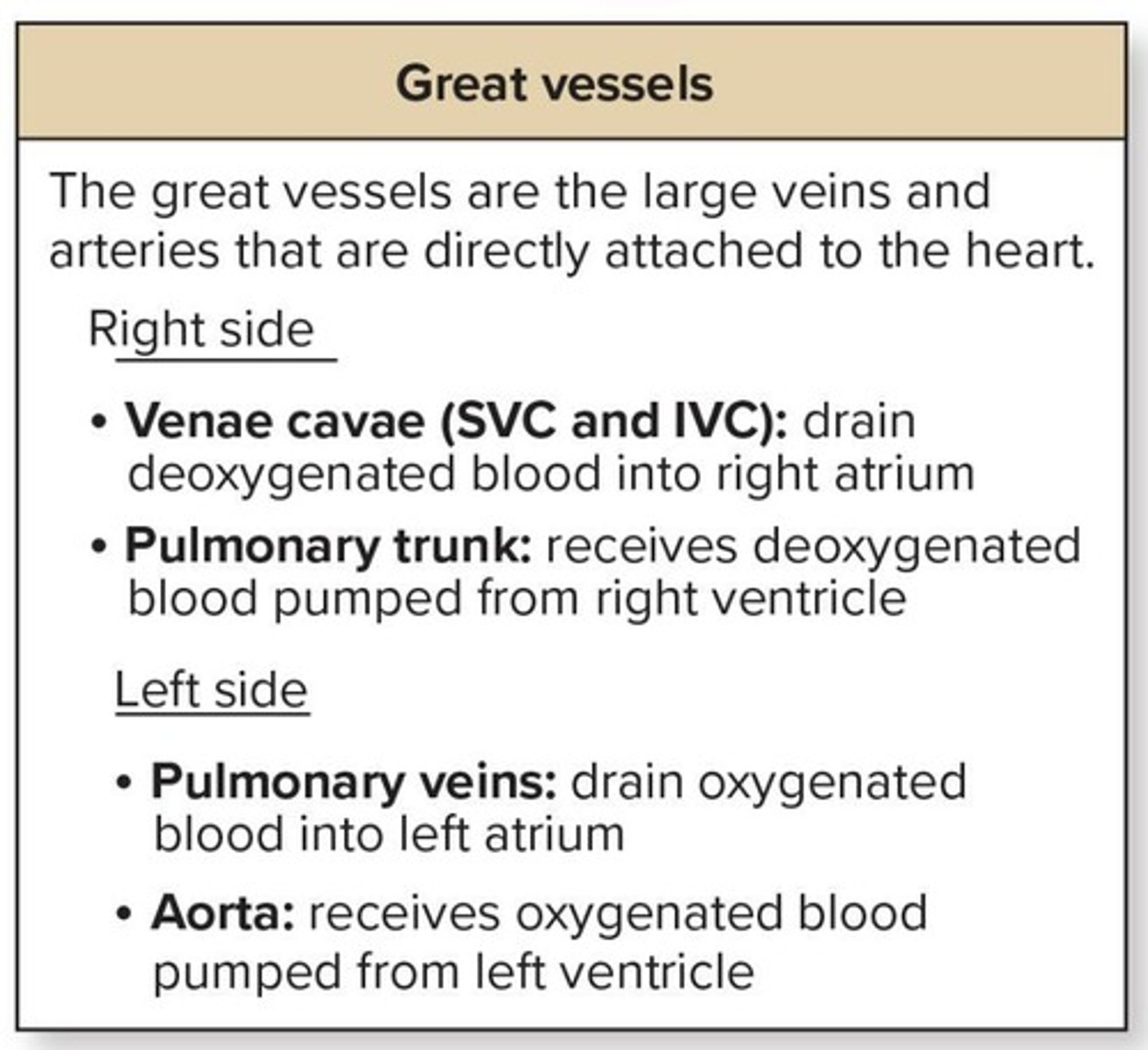
What are the great vessels of the heart?
Superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary veins, aorta.
What are the two types of heart valves?
Atrioventricular (AV) valves and semilunar valves.

What is the function of the tricuspid valve?
Separates the right atrium from the right ventricle.
What is the function of the mitral valve?
Separates the left atrium from the left ventricle.
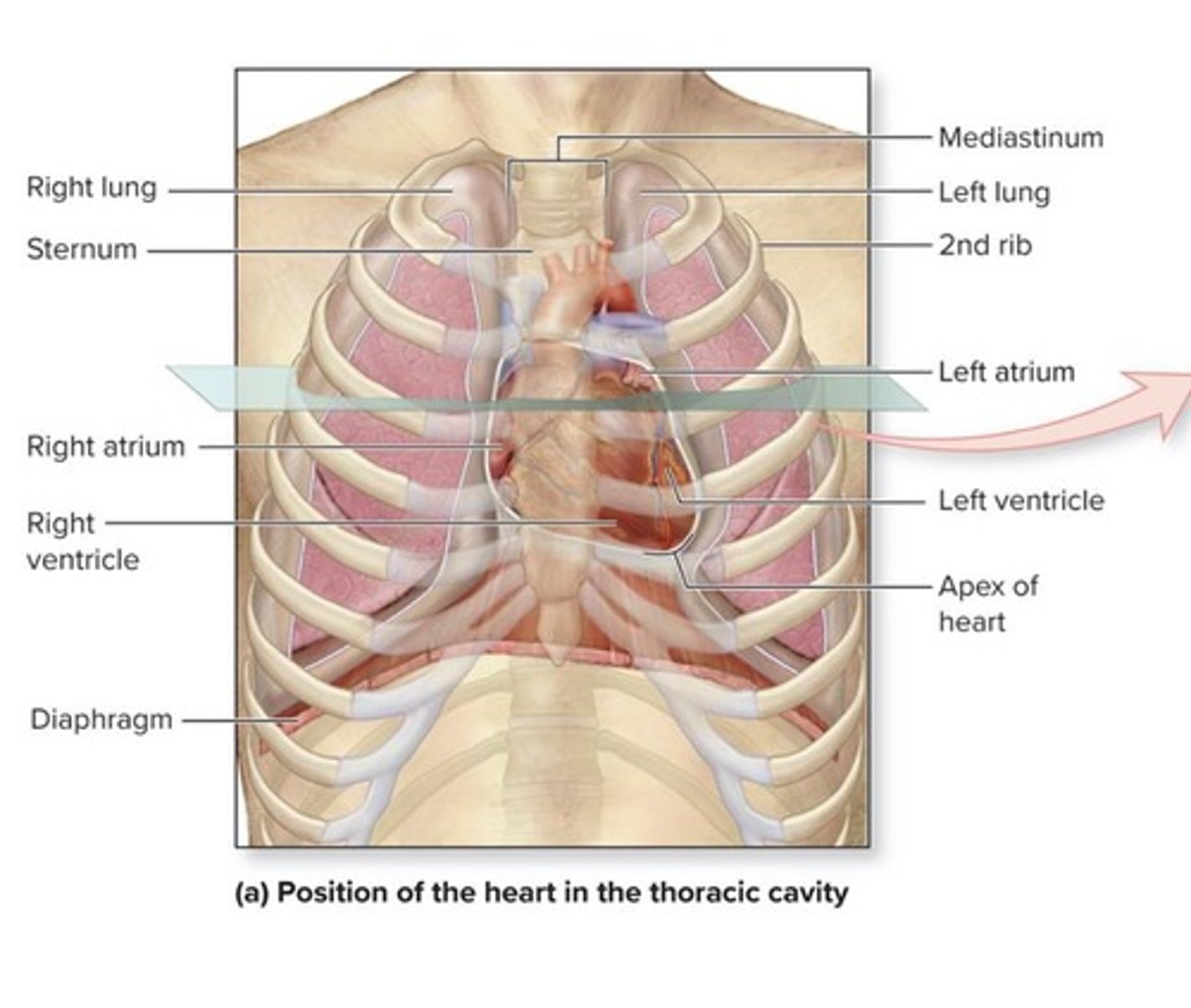
Where is the heart located?
In the mediastinum, thoracic cavity, protected by the sternum and ribs.
What are the three layers of the heart wall?
Epicardium, myocardium, endocardium.
What is cardiomegaly?
Enlargement of the heart.
What can cause cardiomegaly?
Long-standing hypertension, coronary artery disease, valve disease.
What is the structure of cardiac muscle?
Striated, branched, short cells with 1-2 central nuclei.
What is the role of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
Provide mechanical and electrical linkage for synchronous contraction.
What fuels does cardiac muscle rely on?
Fatty acids, glucose, lactate, amino acids.
What happens to cardiac muscle during ischemia?
Damage can occur within minutes.